Unit 1: Scientific Foundations of Psychology (personal edit)
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychology
AP Psychology
Unit 1: Scientific Foundations of Psychology
Chapter 1
Psychology
plato
philosoper
Roots of Psychology
Scientific Foundations of Psychology
aristotle
locke
Leading Psychologists
Nature-nurture controversy
Structuralism
Wilhelm Wundt
G. Stanley Hall
Edward Titchener
Functionalism
William James
Functionalists
Mary Whiton Calkins
First female American Psychological Association
Principal Approaches to Psychology
Behavioral Approach
Behaviorists
Ivan Pavlov
Psychodynamic Approach
Psychoanalytic
Humanistic Approach
AP PSYCHOLOGY
9th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Operational definition
The specific procedure used to determine the presence of a variable
Validity
The extent to which an instrument measures or predicts what it is supposed to
Ivan Pavlov
________ trained dogs to salivate in response to the sound of a tone
classical conditioning
Freud
________ believed that early life experiences shape personality and that the unconscious is the source of desires, thoughts, and memories.
Reliability
________ is consistency or repeatability.
G Stanley Hall
Founded the American Psychological Association
Founded a psychology lab using introspection at Johns Hopkins University (and became its first president)
Descriptive Statistics
Numbers that summarize a set of research data obtained from a sample.
Locke
Believed that mind and body interact symmetrically (monism)
Knowledge comes from observation
What we know comes from experience (we are born "a blank slate”)
Participation
________ in a study should be voluntary, and not coerced or influenced as part of a grade, raise, or promotion.
Statistical significance (p)
A measure of the likelihood that the difference between groups results from a real difference between the two groups rather than from chance alone.
American Psychological Association (APA)
The ________ lists ethical principles and code of conduct for all psychologists.
Wundt
________ used trained introspection to study
the mind's structure
identify consciousness's basic elements (sensations, feelings, and images)
Nature vs. Nurture
If our behavior is determined by genes or learned through experience
standard deviation
The degree to which scores vary from the mean value for the set.
Neuropsychologists
________ explore the relationships between brain/nervous systems and behavior.
median
The middle score when the set of data is ordered by size.
mode
The ________ is the most frequently occurring score in a set of research data.
Case Study
An in-depth examination of a specific group or single person that typically includes interviews, observations, and test scores.
Meta analysis
________ provides a way of statistically combining the results of individual research studies to reach an overall conclusion.
Survey Method
Researchers use questionnaires or interviews to ask a large number of people questions about their behaviors, thoughts, and attitudes.
Clinical psychologists
________ treat people with temporary psychological crises like grief, addiction, or social issues and those with chronic psychiatric disorders.
Social psychologists
________ focus on how a persons mental life and behavior are shaped by interactions with other people.
Humanist Approach
Values feelings and believes people are naturally positive and growth-seeking.
Inferential statistics
Used to interpret data and draw conclusions
Psychoanalytic theory
Uses unconscious internal conflicts to explain mental disorders, personality, and motivation
Demand characteristics
cues that might indicate the research objectives to participants
Variability
The spread or dispersion of scores for a set of research data or distribution.
Double-Blind
A research design in which neither the experimenter nor the participants know who is in the experimental group and who is in the control group.
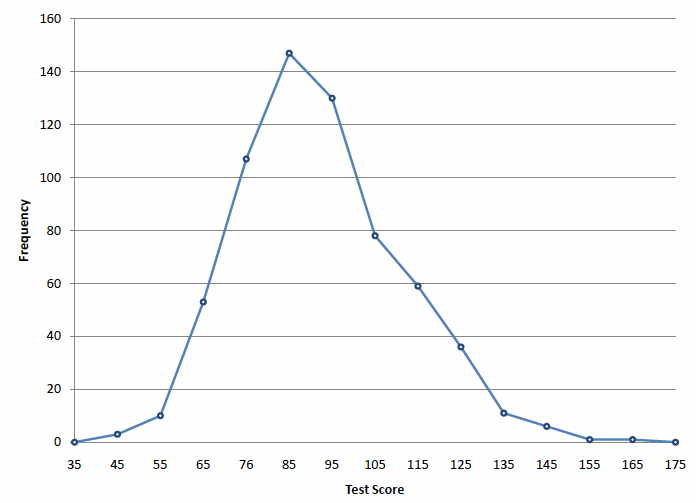
Frequency polygon
A line graph that replaces the bars with single points and connects the points with a line.
Single blind procedure
A research design in which the participants don’t know which treatment group- experimental or control- they are in.
biopsychosocial (eclectic) model
Integrates biological processes, psychological factors, and social forces to provide a more complete picture of behavior and mental processes.
Placebo effect
Cases when experimental participants change their behavior without any experimental manipulation.
Random selection
Can be achieved by putting all the names in a hat and picking out a specified number of names, by alphabetizing the roster of enrollees and choosing every fifth name, or by using a table of random numbers to choose participants.
mean
The arithmetic average of the set of scores.
Sample
a subgroup of the population
Experimental group
receives the treatment
Control group
does not receive the treatment
Between-subjects design
The participants in the experimental and control groups are different individuals
Confounding variables
a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable
Placebo
an imitation pill, injection, patch, or other treatment