chapter 19- disorders associated with the immune system
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
type 1 reactions are called
anaphylactic reactions
2
New cards
type 1 anaphylactic reactions occur minutes after a person … to a antigen is … to that antigen
sensitized, re-exposed
3
New cards
in type 1 anaphylactic reactions antigens combine with … antibodies
IgE
4
New cards
in type 1 anaphylactic reactions the IgE antibodies then attach to … and …
mast cells and basophils
5
New cards
in type 1 anaphylactic reactions, mast cells and basophils then undergo … and release …
degranulation, mediators
6
New cards
in type 1 anaphylactic reactions, what are the 3 mediators mast cells and basophils release
histamines, leukotrienes, prostaglandins
7
New cards
histamines increase … of blood capillaries
permeability
8
New cards
leukotrienes allow for prolonged … of …
contraction of smooth muscles
9
New cards
prostaglandins affect … and increase …
smooth muscles, mucus secretion
10
New cards
what are the two types of type I (anaphylactic) reactions
systemic anaphylaxis
localized anaphylaxis
localized anaphylaxis
11
New cards
systemic anaphylaxis is otherwise known to be a
anaphylactic shock
12
New cards
an anaphylactic shock/ systemic anaphylaxis reaction is the result of when an…
individual sensitized to an antigen is exposed to it again
13
New cards
what are the two potential results of systemic anaphylaxis
circulatory collapse
death
death
14
New cards
what is a systemic anaphylaxis reaction/ anaphylactic shock usually treated with
epinephrine
15
New cards
a localized anaphylaxis is usually associated with
ingested or inhaled antigens
16
New cards
localized anaphylaxis reaction symptoms are usually dependent on..
route of entry
17
New cards
give three examples of localized anaphylaxis reactions
hives
hay fever
asthma
hay fever
asthma
18
New cards
type II reactions are also refereed to as … reactions
cytotoxic
19
New cards
type II (cytotoxic) reactions undergo activation of … by the combination of … or … antibodies with an antigenic cell
complement, IgG or IgM
20
New cards
what are the two results of activation of complement by the combination of IgG and IgM antibodies with an antigenic cell
cell lysis
damage by macrophages
damage by macrophages
21
New cards
what group system is associated with type II (cytotoxic) reactions
ABO blood group system
22
New cards
antibodies from against certain …. …. on red blood cells
carbohydrate antigens
23
New cards
type O red blood cells have … antigens
no
24
New cards
type III reactions are also referred to as … reactions
immune complex reactions
25
New cards
type III (immune complex) reactions antibodies from against … …. in the serum
soluble antigens
26
New cards
in type III (immune complex) reactions antibodies form … …. that lodge in the basement membranes beneath the cells
immune complexes
27
New cards
what does the formation of immune complexes activate and cause
activate complement
cause inflammation
cause inflammation
28
New cards
what is known to be a rare side-effect of toxoid-containing vaccines
Arthur reaction
29
New cards
in what 2 places does the Arthur reaction normally occur
in glomeruli
other vessel walls
other vessel walls
30
New cards
why does an Arthur reaction occur in glomeruli and other vessel walls
complement activation in a patient with already circulating IgG to an injected antigen
31
New cards
serum sickness can occur with … and … due to an injection of … …
swelling and inflammation
foreign serum
foreign serum
32
New cards
type IV reactions are also referred to as…
delayed cell-mediated reactions
33
New cards
what is an example of a type IV (delayed cell-mediated) reaction
allergic contact dermatitis
34
New cards
what combines with proteins in the skin, which produces an immune response in an allergic contain dermatitis
haptens
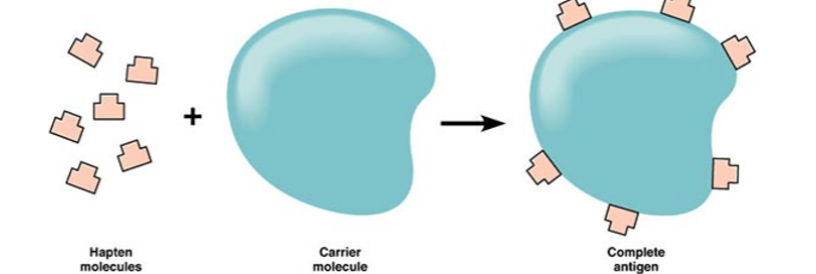
35
New cards
give 4 examples of triggers of allergic contact dermatitis reactions
poison ivy
cosmetics
metals
latex
cosmetics
metals
latex
36
New cards
which type of reaction is very rare
type III
37
New cards
which types of reactions need previous exposure to the antigen
type I and type IV
38
New cards
an autoimmune disease is when our immune systems respond to … …. causing … to organ systems
self antigens
damage
damage
39
New cards
autoimmunity is loss of
self-tolerance
40
New cards
self-tolerance is the ability to…
discriminate self from non-self