GCSE Drama Terminology
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Gel colour
(gel is the see-through plastic sheet that a white light is shone through)

Shadow
An area from which light is blocked.

Light
If it's naturalistic it may signify daylight, moonlight, lounge interior, If it's symbolic it may represent danger, eeriness, madness, etc.
Temperature
cold/warm 'warm straw coloured' or 'cold blue'
Fade/snap/crossfade
a fade up can have the effect of a rising sun in naturalism, or an intensifying danger in symbolism
Blackout - different to a snap, which means the spee
Blackout
different to a snap, which means the speed the light is cut out. A blackout marks the end of a significant moment - like an act, or the whole production.
Wash/pool/spot
where your light is focused on the stage
Lantern type
profile spot (hard edged, focused beam), Fresnel (pool of light, no hard edges, more stage coverage), flood (covers stage) strobe
Light Intensity
dim, bright
Positioning of light on stage
(including where the projection would be) flat angle, uplift, light from behind (creating silhouette)
Gobo
A metal cutout that is placed in front of the lens of a lighting instrument to create different shadowed images on stage
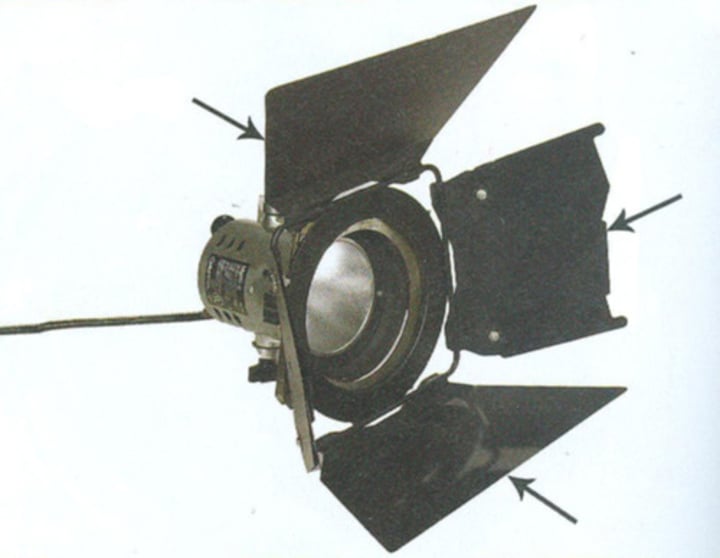
Barn Doors
Metal flaps attached to the front of a lighting instrument; used to control where the light falls on a scene

beam
ray of light

Profile spotlight
(hard edged)
a type of stage lantern that produces a sharply defined beam. These lanterns are used to focus on a particular character or part of the stage
Pitch
speaking in a high, low or natural voice.
Pace
- the speed at which someone speaks, eg the speed of response in an argument
Pause
a dramatic pause at a crucial moment could merit a comment.
Tone
this suggests your mood and your intention towards the listener, eg happy or sad.
Volume
you might be commenting on audibility but you're more likely to be discussing the effect of a loud, powerful voice or a quiet, nervous or sad voice.
accent
you may be talking about how someone has achieved a convincing accent or how the choice of accent enhanced their characterisation
emphasis
the pressure on individual words that makes them stand out. Emphasis or stress for a particular effect is significant and can change the meaning of a sentence as well as the feeling behind it.
intonation
the pressure on individual words that makes them stand out. Emphasis or stress for a particular effect is significant and can change the meaning of a sentence as well as the feeling behind it.
Intonation
the rise and fall of the voice. There's a clear movement up at the end of a sentence when we ask questions for example. Intonation also helps us to say what we mean.
speed
How fast an actor will move their body.
motion
how an actor moves, in slow motion, robotically, with fluidity.
stance
how an actor stands
Gait
the manner in which in an actor talks
gestuers
Hand movements, used to show meaning or emphasis
levels
are very important, eg if you wish to show dominance you will probably have the person in authority on a higher level
closeness
is also important as there's usually much greater intensity when the characters are close together.
Proxemics
shows how intimate characters are with each other
Posture
is the position of a person's body when standing or sitting, eg a soldier would stand upright but a drunk person would slump.
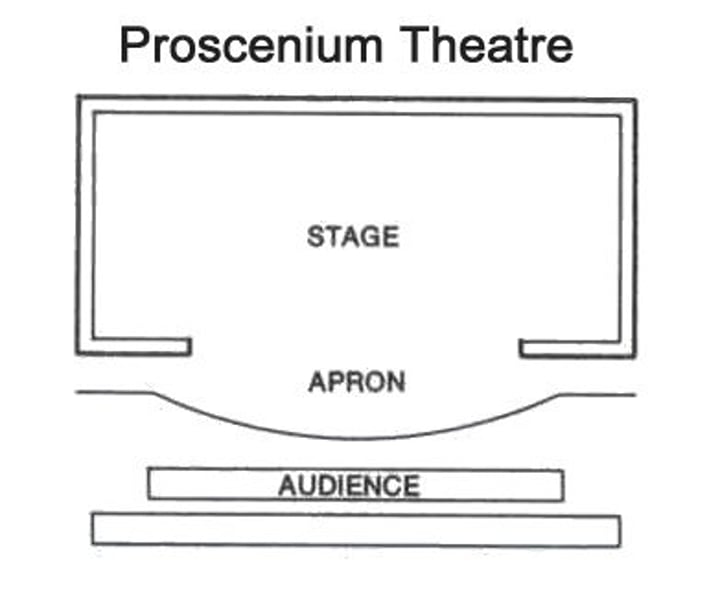
Proscenium Arch
an arch framing the opening between the stage and the auditorium in some theaters.
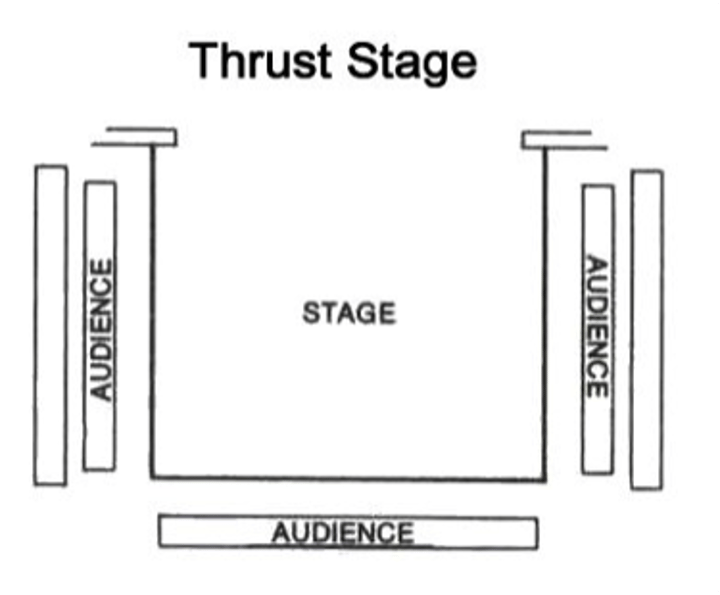
thrust stage
a theater stage that extends out into the audience's part of a theater and has seats on three sides
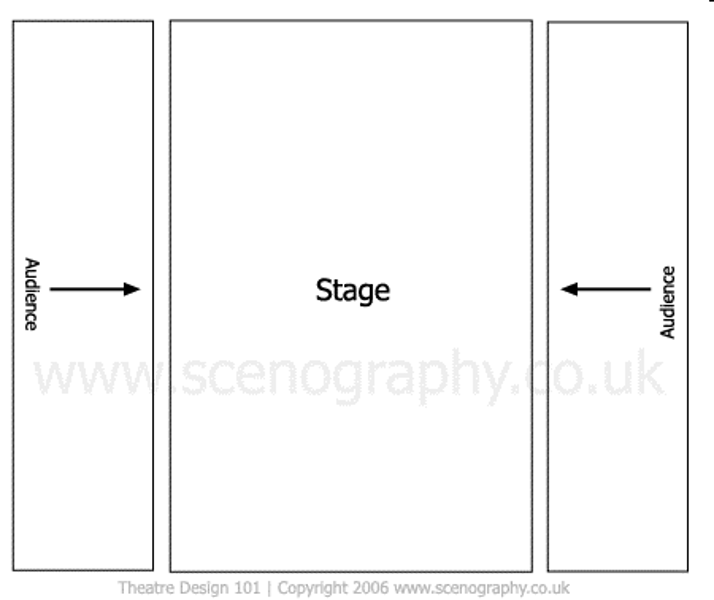
Traverse stage
Audience seated on two sides of the acting area. Seats are often raked.
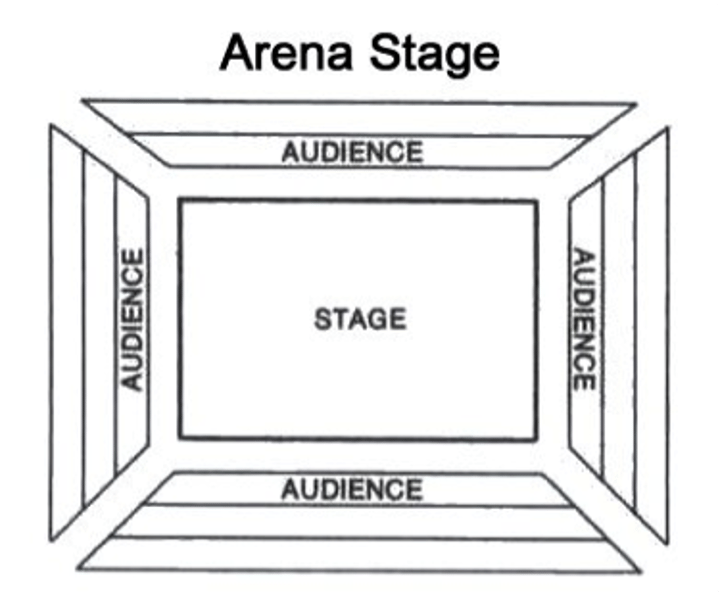
In The Round stage
A stage that is positioned at the centre of the audience - ie there is audience around the whole stage.
stage directions
Upstage Right
Upstage
Upstage Left
Stage Right
Centre Stage
Stage Left
Downstage Right
Downstage
Downstage Left
Clothing
Imagine you are looking at the character you are talking about. Look at everything about them from head to toe. Describe everything you see.
· Hair Style
· Make up (even for boys, might be bruises, dark eye make up)
· Jewelry?
· Glasses?
· Top
· Trousers
· Shoes
· Accessories
You need to fully describe what they are wearing. Think about;
· Colour
· Style
· Material
· Time period
· Reasoning
silhouette lighting
the background is evenly lit, with the figures remaining unlighted, revealing only their contours
diegetic sound
Any voice, musical passage, or sound effect presented as originating from a source within the film's world.
non-diegetic sound
sound that can be heard by the audience only, not the characters.
Cyclorama
A background curtain on a set that is stretched tight and pulled to cover the walls and curves of the studio, forming a solid background color.
The back wall of the stage which can be painted or lit
distressed clothing
torn/dirtied
Timbre
quality of sound
Texture
The feel, appearance, or consistency of a surface, substance, or fabric.
Floodlight
This is one of the simplest lanterns. It does not have a lens and cannot be focused. As a result, it provides a general wash of light. It is also normally used for lighting flat scenery.
Profile Spot
This provides a strong beam of light that can be focused on a specific area of the stage. The defined beams are perfect for long throws and can be used to cut shapes on stage and project gobos.
Follow Spot
This sits on a stand and is designed to follow performers around the stage. It is a more powerful variation of a profile spot with additional features such as an iris (to adjust focus, creating a sharp or more blurred edge).
Fresnel Spot
This is used to create a general wash of light across the stage. The Fresnel has a stepped lens that causes light to scatter, producing a softer feel. "Barn Doors" on all four sides of the lantern can be opened and closed to determine the spill of light.
Par Can
This cannot be focused and is one of the cheaper types of lantern. Often used in Rock concerts, Par Can lanterns throw a very harsh, strong beam of light, creating a dramatic effect.
Blackouts
To remove or the removal of all or almost all light on the performing area, usually done rapidly.
Bleed Through
The effect created by adjusting the intensity of the illumination directly on a theatrical scrim inversely with the intensity of the illumination behind it. This causes the scrim to go through a phase of changing transmission.
Bump
To change the intensity of a luminaire or group of luminaires instantaneously, usually for a short duration of time, often to the beat of music as if to create a pulsing effect.
Colour Medium
Any coloured transparent material that can be placed in front of a beam to colour the light. They can be of the absorption or reflection type.
Cross Fade
A relatively slow change from one control console setting to another.
Dim
1) To change the intensity of a light.
2) The state of a light at very low intensity.
Fade
To gradually increase or decrease the intensity of light.
Fade In
The gradual increase in intensity of light
Fade Out
The gradual decrease in intensity of light.
Fade-To-Black
To gradually decrease the intensity of all lighting to a blackout.
Flies:
The space above a stage where scenery, lights, etc. are hoisted above horizontal sight lines.
Focal Point
The small region where light is concentrated.
Footlight
A light, often a strip light, which is used from the floor of a stage, runway, or other performing area. This luminaire received its name because it was originally used to illuminate the feet of dancing performers on stage.
Gel
A coloured transparent gelatin material that can be placed in front of a beam to colour the light.
Gobos
A very thin, heat-resistant metal plate with a design cut out of its surface. When placed into the aperture of a spotlight or follow spot, an illuminated representation of the design is projected.
Hard Light
Illumination that has a hard edge and produces sharply defined shadows. Often this light is very intense.
House Lights
General lighting provided for the audience area.
Indirect Lighting
Illumination that falls on an area or subject by reflection, e.g., bounce lighting.
Intelligent Light / Automated Light:
A light that is robotic, i.e., certain functions such as panning, tilting, focusing, dimming, beam shaping and colouring, etc., are motorized and remotely operated from a control console.
Backlight
Illumination on a subject from behind, causing a separation of the subject from the background, often creating a fringe of light around the subject.
Mirror Ball
A sphere whose surface is covered with a plurality of small, individual mirrors, that when rotated and shined upon by a light source, gives the effect of a multitude of moving spots of light swirling and sweeping across surrounding surfaces.
Primary Colours
Colours in terms of which all other colours may be described, or from which all other colours may be evolved by mixtures. In light, the primary colours are red, green, and blue. Combined in pairs, two primary colours give the complementary colour of the third. All three colours combine to form white light.
Punch Light
A high intensity light that floods an area with light whose colour temperature is approximately that of daylight.
Saturation
The aspect of colour that determines the difference from white at a constant hue, i.e., the property of any colour that distinguishes it from a grey of the same brightness. High saturation is one with little or no white light added to the colour, deep red e.g. Low saturation is one with a large amount of white light added to the colour, light pink e.g.
Scrim
A thin, gauze-like curtain. When illuminated from the front, it appears opaque, and when illumination is present behind it but not on it, the scrim becomes almost transparent. It can also appear translucent when there is some illumination directly on it, and some illumination present behind it, in the proper proportions.
Soft Edge:
A beam pattern edge that is not very clear and distinguishable, i.e., one with a fuzzy or blurry perimeter.
Soft Light
Illumination that produces shadows with a soft edge.
Strobe
To cause an intense light source to turn on and off repeatedly at a relatively fast rate. This is usually done in an area devoid of all other illumination to create a flickering, slow motion effect.
Tint
A colour low in saturation.
Warm Colour
Generally, a colour that is in the yellow-orange-red range.
Cold Colour
Generally, a colour that is in the blue range.
Wash
An even, overall illumination over a large area.