Vet Med Term Chapter 3
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For Quiz 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
The musculoskeletal system consists of what two systems?
Skeletal- Bones, joints, cartilage, and connective tissues
Muscular- Muscles and various connective tissues.
Functions of the skeletal system
Provides support, forms blood cells, aids in movement.
Structures of the Skeletal system
Bones, cartilage, joints, ligaments and tendons, bursa, synovial membrane and fluid.
Bone is
one of the hardest tissues in the body
combining forms for bone
oste/o
oss/e
oss/i
Bones start as
cartilage and fibrous membranes that harden into bone before birth
Ossification is
the formation of bone from fibrous tissue
Cortical bone is
the hard, dense, strong bone that forms the OUTER layer of bone
Cortex means
bark or shell in latin
cortical bone is also known as
compact bone
Cancellous bone is
lighter, less strong bone found in the ends and inner portions of long bone
cancellous is
latticework in latin
cancellous bone is also known as
spongy bone
long bones consist of
a shaft, two ends, and a marrow cavity
examples of a long bone are the
femur, humerus, tibia, and radius
Short
carpal
flat
pelvis
pneumatic
frontal
irregular
vertebrae
sesamoid
patella
Hematopoietic means
formation of blood and blood components
Red bone marrow produces
red blood cells, white blood cells, clotting cells
Yellow bone marrow is for
Fat storage
Cartilage is a form of
connective tissue, and is more elastic than bone
the combining form for cartilage is
chondr/o
Articular cartilage is a type of cartilage that
covers the joint surfaces of bone
The meniscus is a
curved fibrous cartilage found in some joints
Joints are
connections between bones
joints are also known as
articulations
The combining form for joint is
arthr/o
Joints are classified based on
their degree of movements
synarthroses
immovable
amphiarthroses
slightly movable
diathroses
freely movable
Ligaments are bands of fibrous connective tissues that
connect one bone to another
The combining form for ligament is
Ligament/o
Tendons are bands of fibrous connective tissue that
connect muscle to bone
Combining forms for tendon are
Ten/o, Tend/o, and Tendin/o
Bursa is
a fibrous sac that acts as a cushion to reduce friction during movement
synovial fluid
acts as a lubricant for joint movement
The cranium is
the portion of the skull that encloses the brain
The combining form for skull is
crani/o
The skull also has air or fluid filled spaces called
sinuses
The vertebral column supports
the head and body and provides protection for the spinal cord
The vertebral column is comprised of individual bones called
vertebra
The combining forms for vertebra are
spondyl/o and vertebr/o (vertebrae is the plural form)
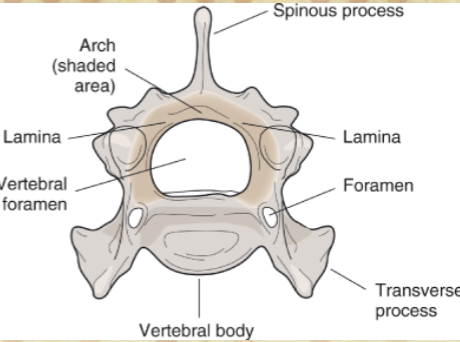
Vertebrae are divided into
body, arch, lamina, vertebral foramen, and processes ( spinous, transverse, and articular)
Combining form of Ribs is
cost/o (think intercostal)
The sternum consists of
Manubrium, body, xiphoid process
The appendicular skeleton is the framework that consists of
the extremities, shoulder, and pelvic girdle
Appen means to
add or hang
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the
front and hind limbs
P1 =
Long pastern bone in livestock
P2 =
Short pastern bone in livestock
P3 =
Coffin bone in livestock
P3 in small animals may be called
the claw or nail
Combining form for claw or nail is
onych/o
The bones of the pelvis are
the ilium, ischium, pubis, acetabulum
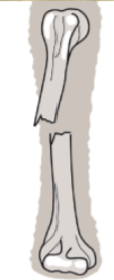
Open and displaced fracture
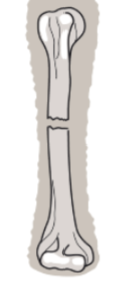
Closed or simple fracture
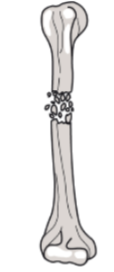
Comminuted fracture
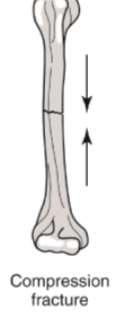
Compression fracture
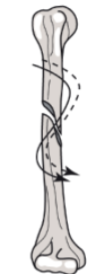
Spiral fracture
Oblique fracture
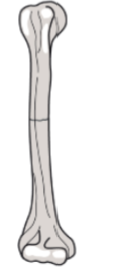
Transverse fracture
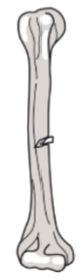
Greenstick or incomplete fracture
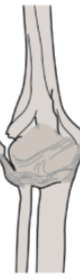
Avulsion fracture
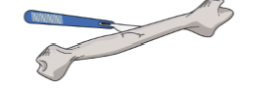
Osteotomy
Cutting into a bone
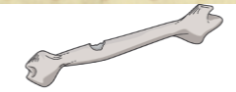
Osteostomy
Making a permanent new opening in a bone
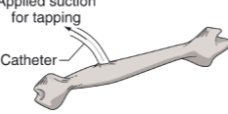
Osteocentesis
Surgical puncture and tapping of a bone
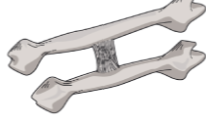
Osteodesis
Binding together of bones
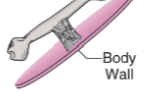
Osteopexy
Surgical fixation of a bone
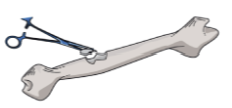
Osteoplasty
Surgical repair of a damaged bone
Ostectomy
Removal of a bone
Muscles are
organs that contract to produce movement
Muscles are responsibe for
ambulation, control of organs and tissues, pumping blood, generation of heat
Muscles are made up of
long slender cells called muscle fibers
Each muscle consists of a
group of muscle fibers in a fibrous sheath
Combining form for muscle
My/o
Combining forms for fibrous tissue
Fibr/o and Fibros/o
Types of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal, Cardiac, and smooth muscle fibers.
Fascia is
a sheet of fibrous connective tissue that covers, supports and separates muscles
Combining forms for fascia
Fasci/o and fasc/i
Aponeurosis is
a fibrous sheet that gives attachment to muscular fibers and serves as a mean of origin and insertion of a flat muscle
Combining form for aponeuroses
Aponeur/o
Anti =
against
Agon =
Struggle
Antagonistic muscles work
against or opposite other muscles
Syn =
together
erg =
work
synergist muscles work
with other muscles to produce movement
Origin =
where muscle begins
insertion =
where the muscle ends
Electromyography
recording of the electrical activity of muscle
Muscle shape terms
deltoid
quadratus
rhomboideus
Muscle size terms
minimus
maxiumus
major
minor
latissimus
longissimus
Muscle fiber directions
rectus
oblique
transverse
sphincter
Number of muscle division
biceps
triceps
quadriceps
Muscle location
pectoral
epaxial
intercostal
infraspinatus
Muscle movement
abductor
adductor
flexor
extensor
levator
depressor
rotator
supinator
pronator