chem semester 2 final
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
The volume, shape, compression, flow, and diffusion of an object is best said to be influenced by its ___________.
intermolecular forces
Always/Sometimes/Never: Liquids assume the shape of their container.
always
Are liquids compressible?
No, not significantly
Which state has the highest levels of interparticle attraction?
Solids
The state of a substance depends largely on the __________ of the particles and the ________ attractions.
average kinetic energies, interparticle
What is the definition of intermolecular forces?
attractive or repulsive electrostatic forces between molecules
True/False: Covalent bonds are a type of intermolecular forces.
False, they are a type of intramolecular forces.
What are the four intermolecular forces (relevant to this class)?
Dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, ion-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
Which are stronger, intermolecular or intramolecular forces?
intramolecular forces
What is the difference between intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces?
intermolecular forces are between particles in a substance, and intramolecular forces are in a bond. in water, the intermolecular forces are in between the H2O molecules, while the intramolecular forces are in between the hydrogen and oxygen.
Metals have high electrical conductivities because ______.
the electrons in the metal are delocalized.
Which intermolecular force is considered the strongest?
Hydrogen-bonding
Which intermolecular force is considered the weakest?
Dispersion forces
Intermolecular forces determine ___________behavior, while intramolecular forces determine________ behavior.
physical, chemical
True/False: All substances have dispersion forces.
True
What causes dispersion forces?
the constant movement of electrons creates temporary dipole moments, because electrons are not always evenly spaced. the temporary dipole moment in one molecule attracts/effects another
In what type of molecules are dispersion forces the only force present?
nonpolar molecules
True/False: Dipole-Dipole forces are only present in certain types of polar molecules.
false— all polar molecules have dipole dipole forces
Increasing polarity of a substance means __________ dipole dipole interaction.
increasing
Why are hydrogen bonds an especially strong intermolecular force?
Hydrogen’s one electron means the atomic radius is incredibly small, and a shorter ‘bond’ is a stronger one.
Hydrogen bonds always include:
a hydrogen bonded to something electronegative, almost always O F or N
Ion-Dipole forces exist between _____.
an ion and a polar molecule
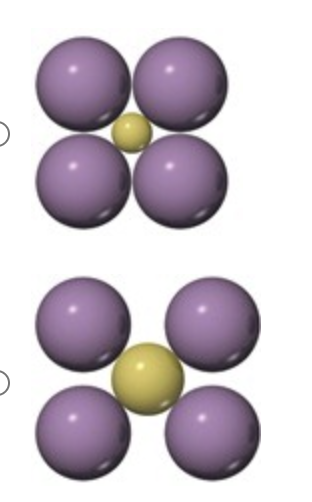
Which arrangement of cations (yellow) and anions (purple) in a lattice is the more stable and why?
the bottom arrangement because in the other structure very close contacts among like-charged particles produce strong electrostatic repulsions.
In molecular solids, the melting point ________ the increasing strength of covalent bonds.
is unrelated to
For molecular solids, the melting point generally_________ increasing strength of the intermolecular forces.
increases with
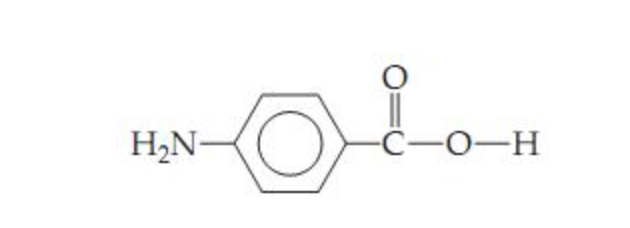
Is this molecule a better starting material for an addition polymer or a condensation polymer? why?
condensation polymer, because The amine group of one molecule can react with the carboxylic acid group of an adjacent molecule to form an amide linkage, and eliminate a water molecule.
Vulcanization is described as____?
The process of making rubber stiffer by forming bonds between the chains.
Hydrogen bonds are a special type of _______ attraction.
dipole-dipole
Viscosity ________ as intermolecular forces increases.
increases
Melting point ________ as intermolecular forces increases.
increases
If a fluid is more viscous, then the fluid moves _________ (faster/slower).
slower
Polarizability is higher in molecules with ______ electrons.
more
Boiling point _______ as intermolecular forces increase.
increases
Surface tension _______ as intermolecular forces increases.
increases
Vapor pressure _________ as intermolecular forces increases.
decreases
Vapor pressure measures _________.
a substance’s tendency to vaporize
Ionic solids dissolved in polar solids have _______ forces and ______ forces.
dispersion, ion-dipole
London forces increase when ____________ or _______________.
the number of e- in a species increases, or molecules without branches have stronger dispersion forces.
Capillary action is ________.
the ability of a liquid to flow in a narrow space against gravity
What are the two forces that drive capillary action?
cohesion and adhesion
In cohesion, intermolecular forces bind _______________.
similar molecules to each other.
In adhesion, intermolecular forces bind ______________.
a substance to a surface.
Why do concaves form in water?
cohesive forces are weaker than adhesive forces
Heat of fusion is _______________.
energy required to change a substance from a solid to a liquid
Critical temperature is ___________.
the highest temp at which a distinct liquid can form.
Critical pressure is ____________.
the pressure required to bring about liquefaction at the critical temperature
The greater the intermolecular force, the ___________ the critical temp of a subtance.
greater
Vapor pressure is ______________.
pressure exerted by the vapor in the space above the liquid
When the temperature and pressure exceeds the critical temperature, _________________.
the liquid and gas phases become indistinguishable from each other
What are the two main features of a supercritical fluid?
it will expand to fill its container like gas, but the molecules are still closely packed together like liquid
Dynamic equilibrium is when ____________.
two opposing processes occur simultaneously at equal rates
A liquid and vapor reach dynamic equilibrium when _____________.
vaporization and condensation occur at equal rates
Substances with high vapor pressure evaporate __________ than substances with low vapor pressure.
quicker
Liquids that vaporize readily are said to be _______.
volatile
The boiling point of a liquid is the _______ at which its _______ equals the ______.
the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the external pressure
The triple point of a phase diagram is when ______.
all three phases are in equilibrium.
Liquid crystals are ______.
a substance that exhibits a viscous milky state in between liquid/ solid state
Metallic solids are described as: ________.
extended networks of atoms held together by metallic bonding
True/False: Metallic solids are insoluble.
True
True/False: Metallic solids are made of only metals.
False— some alloys like steel have non-metals like carbon.
Do metallic solids have strong, weak, or no conductivity?
they have strong electrical AND thermal conductivity
Two common phyiscal properties of metallic solids are _____ and ______.
malleability and ductility
In metallic solids, valence e- are not _______ but ________.
associated with specific atoms/bonds but are spread throughout the solid
An alloy is ___________.
a material that contains more than 1 element and has the characteristic properties of a metal
A substitutional alloy is when _____________________.
atoms of solute occupy positions normally occupied by solvent atoms
Substitutional alloys are formed when ________________,
the solute and solvent atoms have similar atomic radii and chemical-bonding characteristics
Interstitial alloys are formed when ____________.
solute atoms occupy interstitial positions in the “holes” between solvent atoms
In a heterogeneous alloy, components ________________.
aren’t dispersed uniformly
Ionic solids are _______________.
held together by mutual electrostatic attractions between the cations and anions.
True/False: Ionic solids are good conductors.
false— they are poor conductors
Which solid has typically higher melting points, covalent-network or ionic ?
covalent-network
True/false: Ionic solids are malleable.
False— they are brittle
Covalent-network solids are often _______conductors.
semi-conductors
Molecular solids are held together by ___________.
intermolecular forces
True/False: Molecular solids are insoluble.
False— they are often soluble.
Which type of solid has a higher melting point: ionic solids or molecular solids?
molecular solids
Which solid is likely to be a hard, brittle nonconductor?
an ionic solid
What is the second strongest intermolecular force?
dipole-dipole
Most solids are in a ______ structure.
lattice
Why is the melting point of a substance always higher than its boiling point?
when you melt an object, absorbed energy is used to break the intermolecular bonds holding the molecules in their fixed positions… when you vaporize an object, the absorbed energy is used to break the intermolecular bonds holding the molecules together…. that’s a larger energy change.
What particles make of ionic solids
cations and anions
True/False: All solids are solid by intermolecular forces.
false— intramolecular forces are the binding force in solids that are ionic, metallic, or covalent network.
Do ionic solids have high or low melting points?
high melting points
What particles make up covalent network solids?
nonmetal atoms
What particles make up molecular solids?
Polar or nonpolar molecules
True/False: Molecular solids are not volatile.
false
In condensation polymerization, ____ would be taken from a hydroxyl group to create water.
H
In condensation polymerization, ____ would be taken from a carboxyl group to create water.
OH
In condensation polymerization, ____ would be taken from a amine group to create water.
H
What is the difference between condensation polymerization and addition polymerization in terms of chemical makeup?
condensation polymerization always has those functional groups!
is breaking solvent-solvent interactions to form separated particles endothermic or exothermic?
endothermic
Which of the following explanations accounts for the fact that the ion-solvent interaction is greater for Li+ than for K+?
Li+ has a smaller ionic radius than K+
Consider two ionic solids, both composed of singly-charged ions, that have different lattice energies. Will the solids have the same solubility in water?
no
Which solid will be more soluble in water, one with the larger lattice energy or one with the smaller lattice energy?
the one with the smaller lattice energy
True/False: an increase in entropy favors mixing
true
True/False: When a solution is made the enthalpy of mixing is always a positive number.
False, it depends
True/False: NaCl dissolved in water but not in hexane because the enthalpy mixing NaCl with water is more negative that that of mixing NaCl with hexane
True
Nonpolar substances are more likely to dissolve in _____.
nonpolar solvents.
Ionic and polar substances are more likely to dissolve in _____.
polar solvents.
An ionic compound has a very negative ΔHsoln in water. Would you expect it to be very soluble or nearly insoluble in water?
very soluble