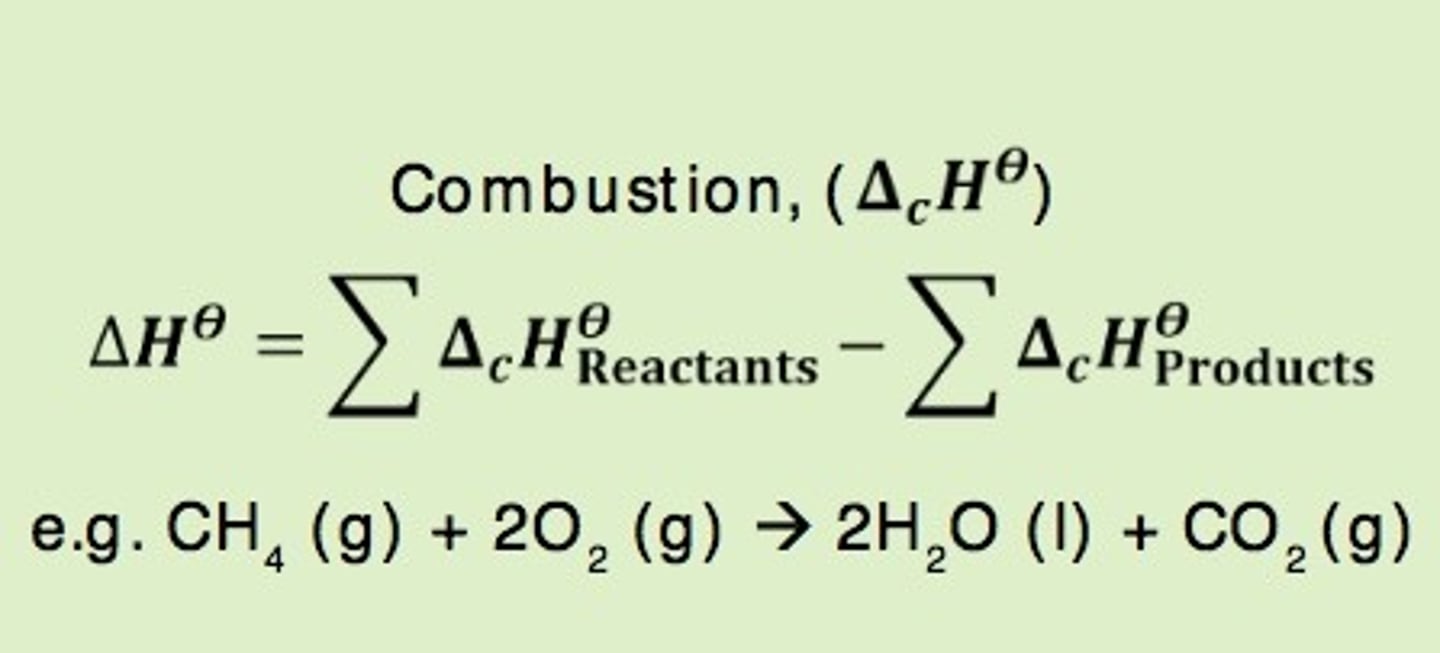IB Chemistry definitions
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What is an element?
Elements are the primary constituents of matter, which cannot be chemically broken down into simpler substances.
What is a compound?
2 or more elements chemically bonded in a fixed ratio
What is a pure substance?
A substance that has definite chemical and physical properties and a uniform composition. A chemical reaction is needed to separate it into its constituent components
What is a mixture?
more than one element or compound in no fixed ratio, which are not chemically bonded and so can be separated by physical methods.
What is a homogeneous mixture?
a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout and all the components are in one phase
What is a heterogenous mixture?
No uniform composition and the components are in different phases
What does miscible mean?
Two liquids which can mix together
What is temperature?
The measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
What is absolute zero?
0 Kelvin, -273 Celsius which is the temperature at which all particles would stop moving
What is sublimation?
solid to gas
What is deposition?
gas to solid
What is relative atomic mass?
The average mass of an atom of an element compared to one twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon 12.
What is Avogadro's constant?
6.02 x 10^23 /mol, is equal to the number of particles in 1 mole.
How do you calculate the number of particles?
Number of moles x Avogadro's constant
What is molecular formula?
The actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule
What is empirical formula?
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
What is an isotope?
atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
What is molar mass?
the mass of one mole of a substance
What is concentration?
the amount of a substance in a given volume
What is Avogadro's law?
equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules
What is an orbital?
a region of space where there is a high probability of finding electrons
What is a sub-level?
A subdivision of a main energy level and consists of one or more orbitals of the same energy
What is the Aufbau principle?
electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first
What is the Pauli exclusion rule?
A full orbital must have electrons of opposite spin
What is Hund's Rule of Maximum Multiplicity?
when in orbitals of equal energy, electrons will try to remain unpaired
What is the first ionisation energy?
The minimum amount of energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms
What is Planck's constant?
6.63 x 10^-34 Js
What is effective nuclear charge?
the net positive charge experienced by valence electrons
What are limiting reactants?
determines the amount of product formed. It gets completely used up in the reaction. All other reactants are excess reactants
What is an ideal gas?
a hypothetical gas with particles that have no intermolecular forces, negligible volume, random motion and elastic collisions
What is Charles' Law?
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 because volume is directly proportional to temperature at a constant pressure
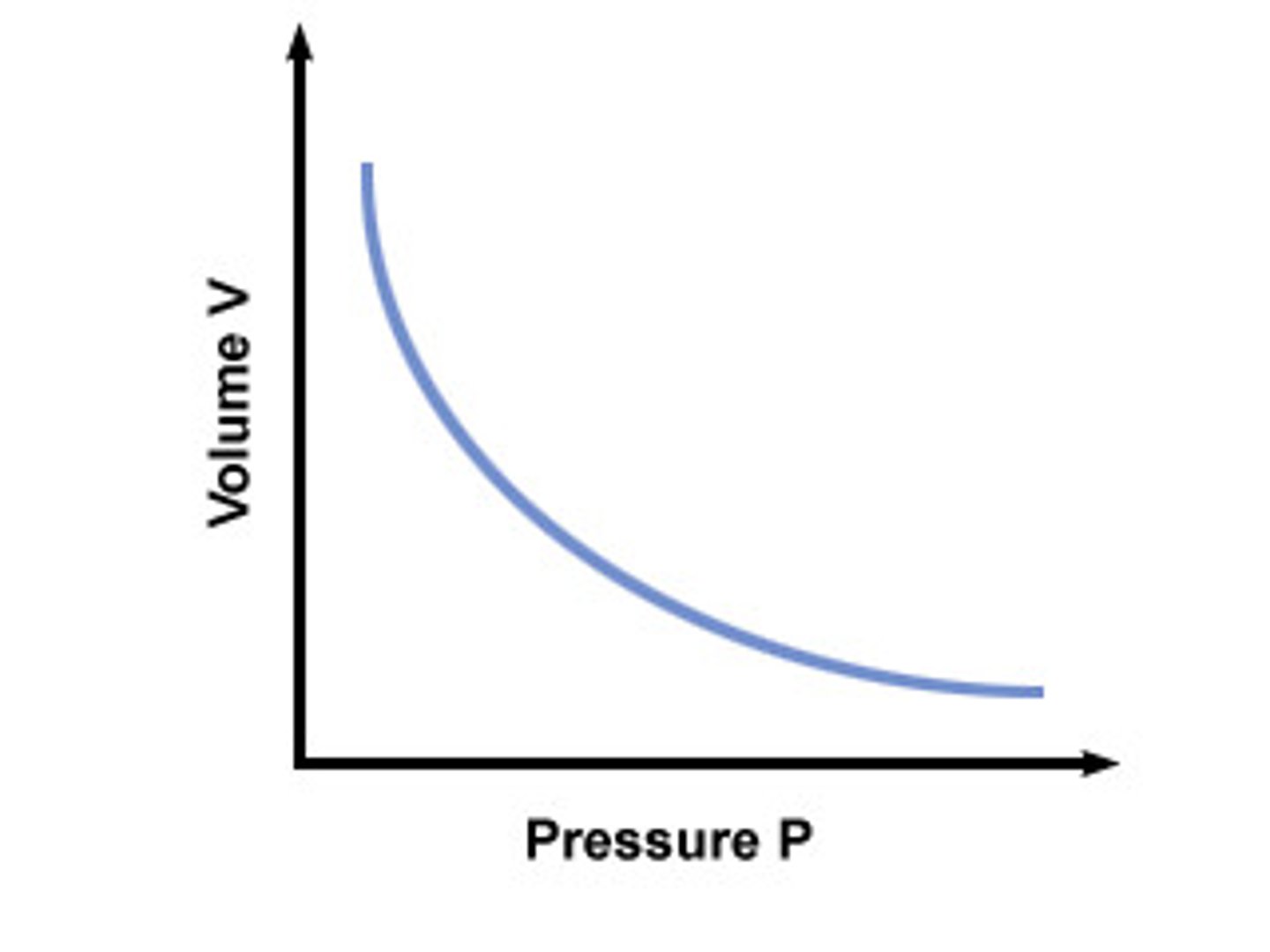
What is Boyle's Law?
pressure is inversely proportional to volume so P1V1=P2V2
What is an exothermic reaction?
A reaction where energy is transferred to the surroundings which causes a temperature increase
What is an endothermic reaction?
a reaction that takes in energy from its surroundings causing the temperature to decrease
What is the octet rule?
The tendency of an atom to achieve stability by gaining, losing or sharing electrons in order to have a full set of valance electrons.
What is a metallic bond?
The electrostatic force of attraction between positive metal ions and negative delocalised electrons in a lattice structure
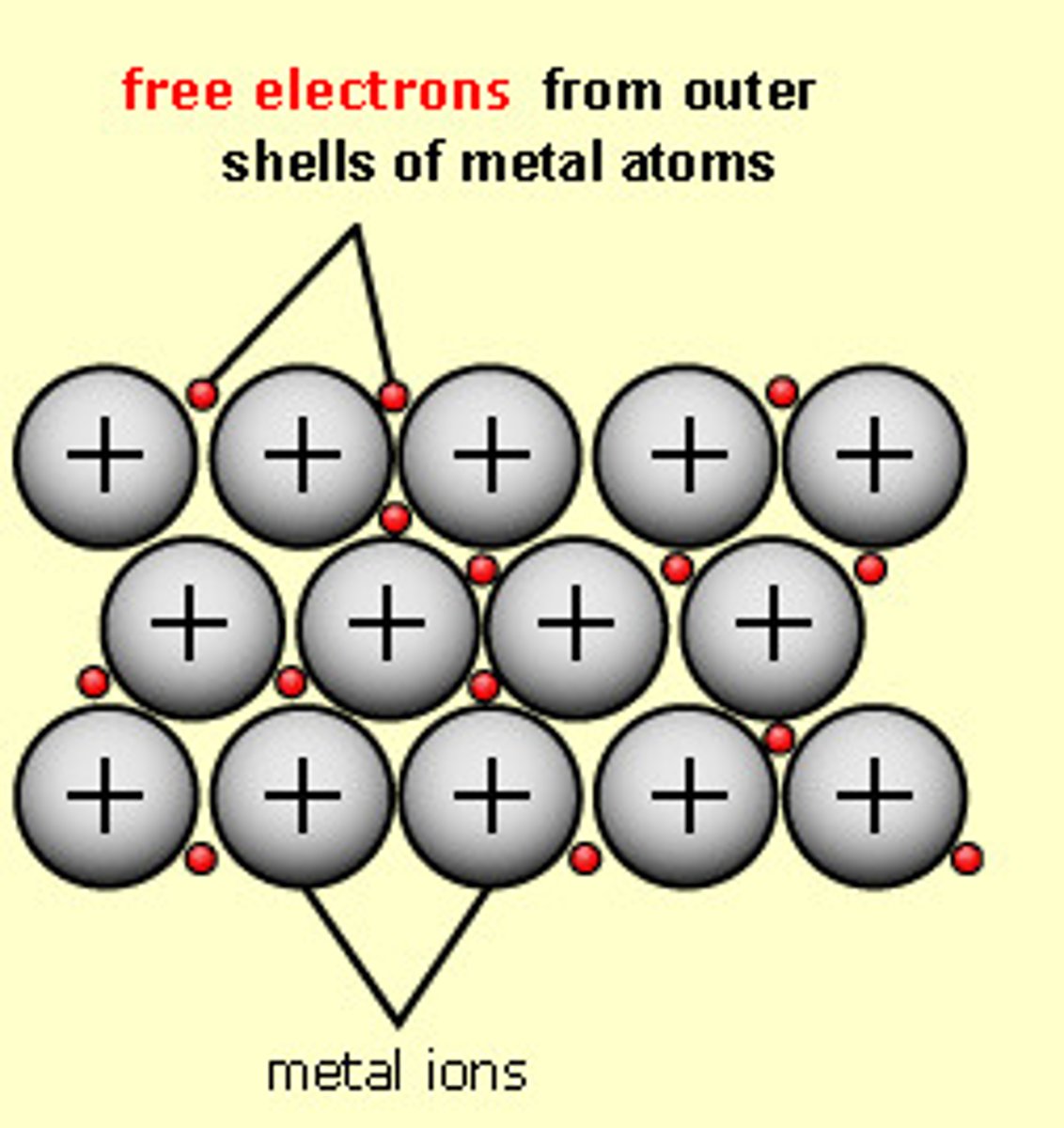
What factors affect the strength of a metallic bond?
Ionic charge, ionic radius and number of delocalised electrons
Describe the structure of a metal?
A giant lattice of metal cations in a sea of delocalised electrons
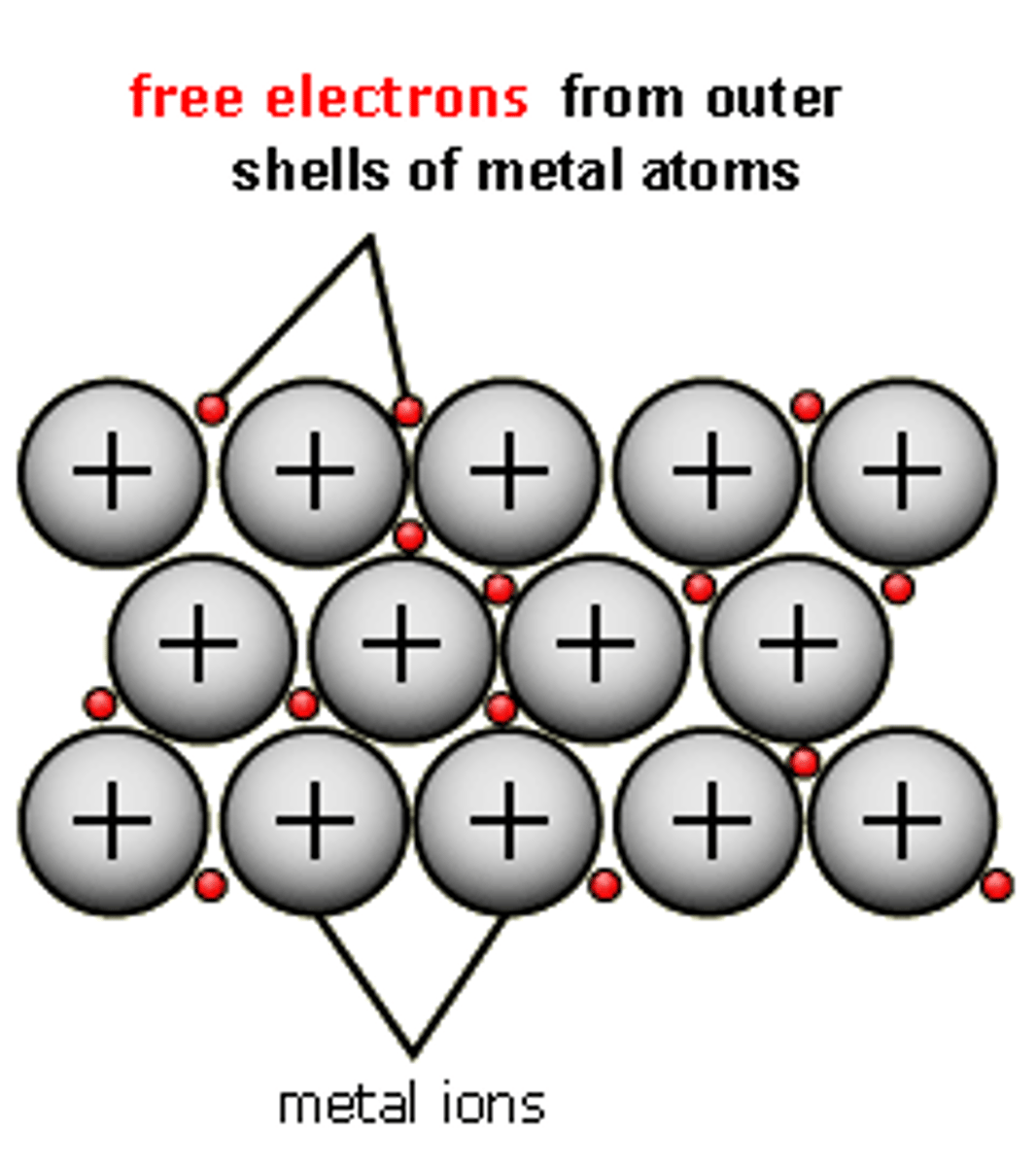
Why are metals good conductors of electricity?
Because the delocalised electrons in the metal carry electrical charge through the metal
Why are metals good thermal conductors?
Delocalised electrons can transfer kinetic energy into thermal energy
Why are metals ductile and malleable?
Layers can slide over each other without breaking up the metal because the forces are non-directional
What is an ionic bond?
The electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
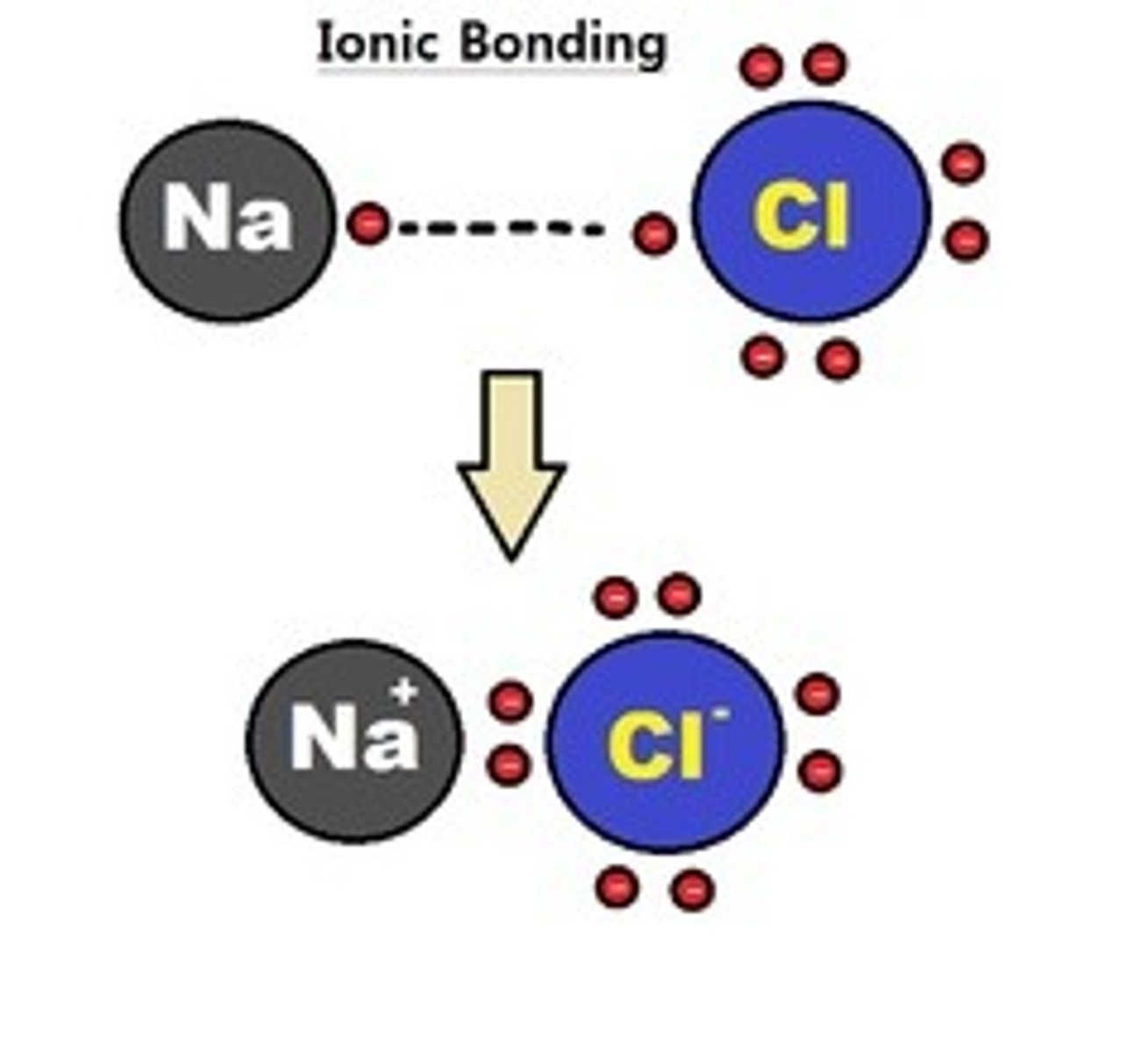
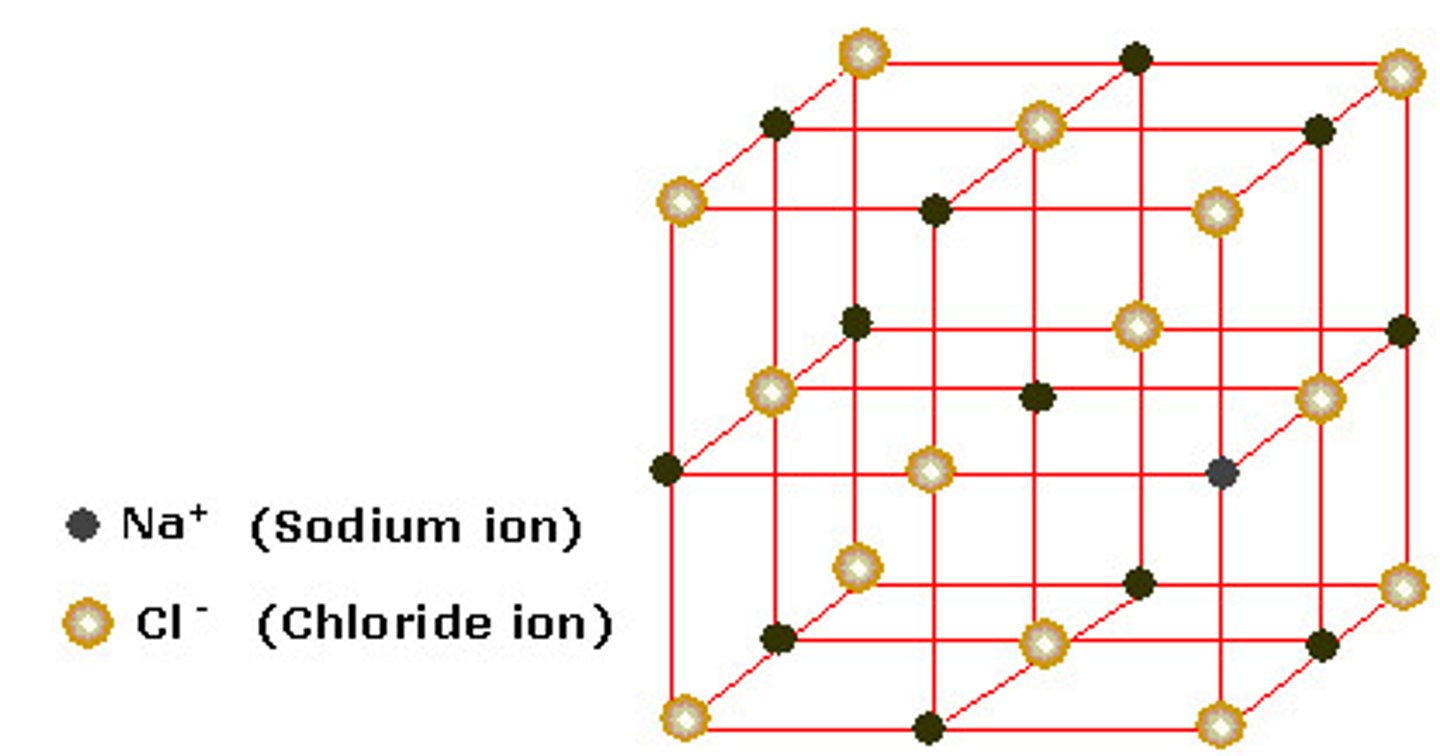
What is an ionic lattice?
a 3D network of repeating units of cations and anions held together by an electrostatic force of attraction between them.
Describe the bonds in an ionic lattice?
Non directional - meaning the attraction between oppositely charged electrons occurs in all directions
What is a covalent bond?
The electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms
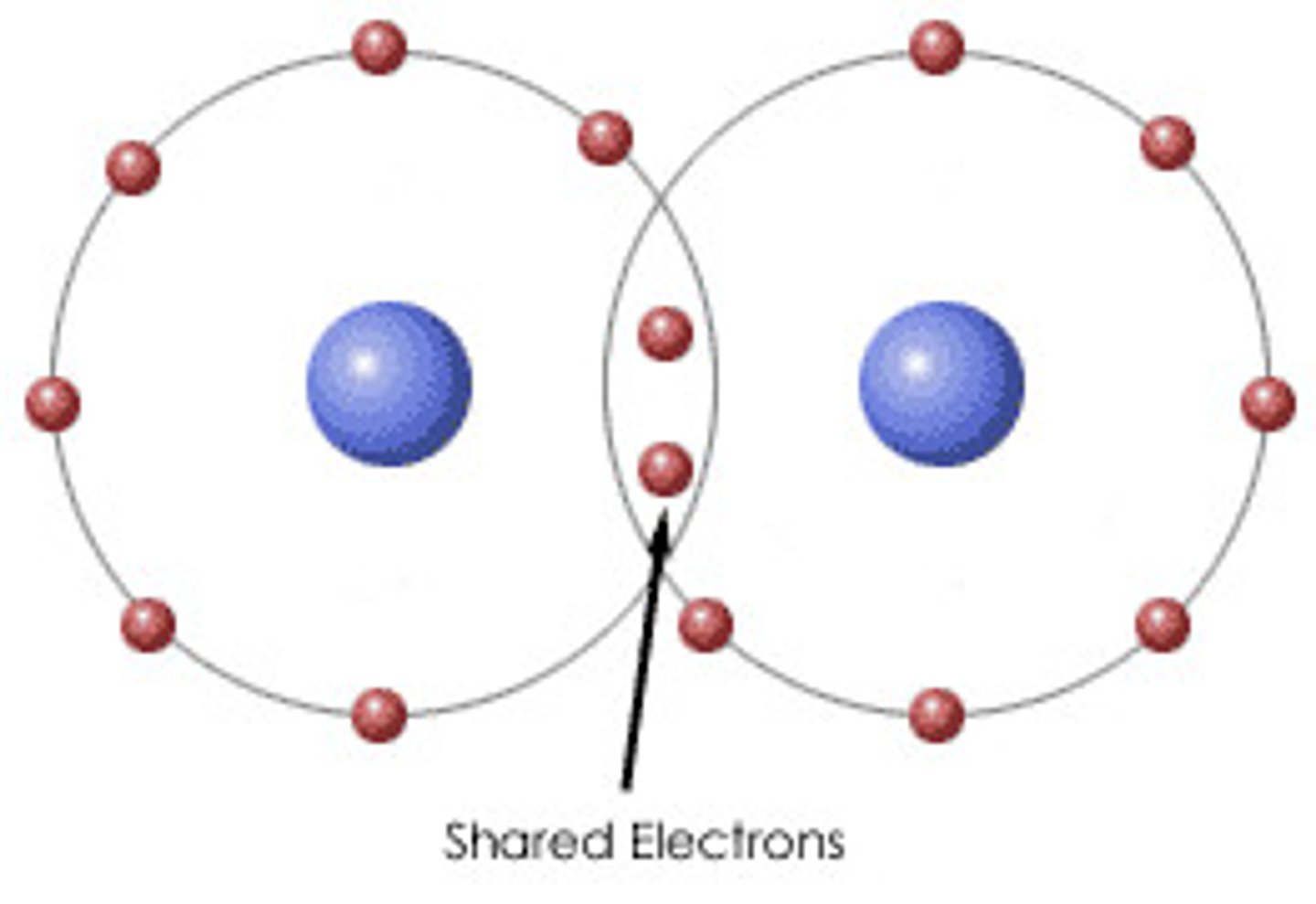
Are covalent bonds directional?
Yes, the force of attraction is only between atoms involved in the bond.
What is bond length?
the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
What is bond strength?
amount of energy needed to break a bond
What is the effect of increasing the covalent bond number (single, double, triple)?
The bond length decreases but bond enthalpy increases
How does atomic radius affect bond length?
The larger the atomic radius, the bond length increases. But, it gets weaker as the valence electrons are further from the nuclei. So, the enthalpy decreases.
What is a non-polar covalent bond?
equal sharing of electrons because the difference in electronegativity is 0.4 or below
What is a pure covalent bond?
when electrons are shared equally. Typically occurs when the bonded atoms are identical
What is a polar covalent bond?
unequal sharing of electrons because the difference in electronegativity is between 0.4 and 1.8
What is electronegativity?
an atom's ability to attract a covalently bonded pair of electrons
Why does electronegativity increase across a period?
because the number of protons increases
Why does electronegativity decrease down a group?
the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus due to a greater number of electron shells so electrons are harder to attract
When is does a difference in electronegativity signal covalence?
If it's 1.8 or less
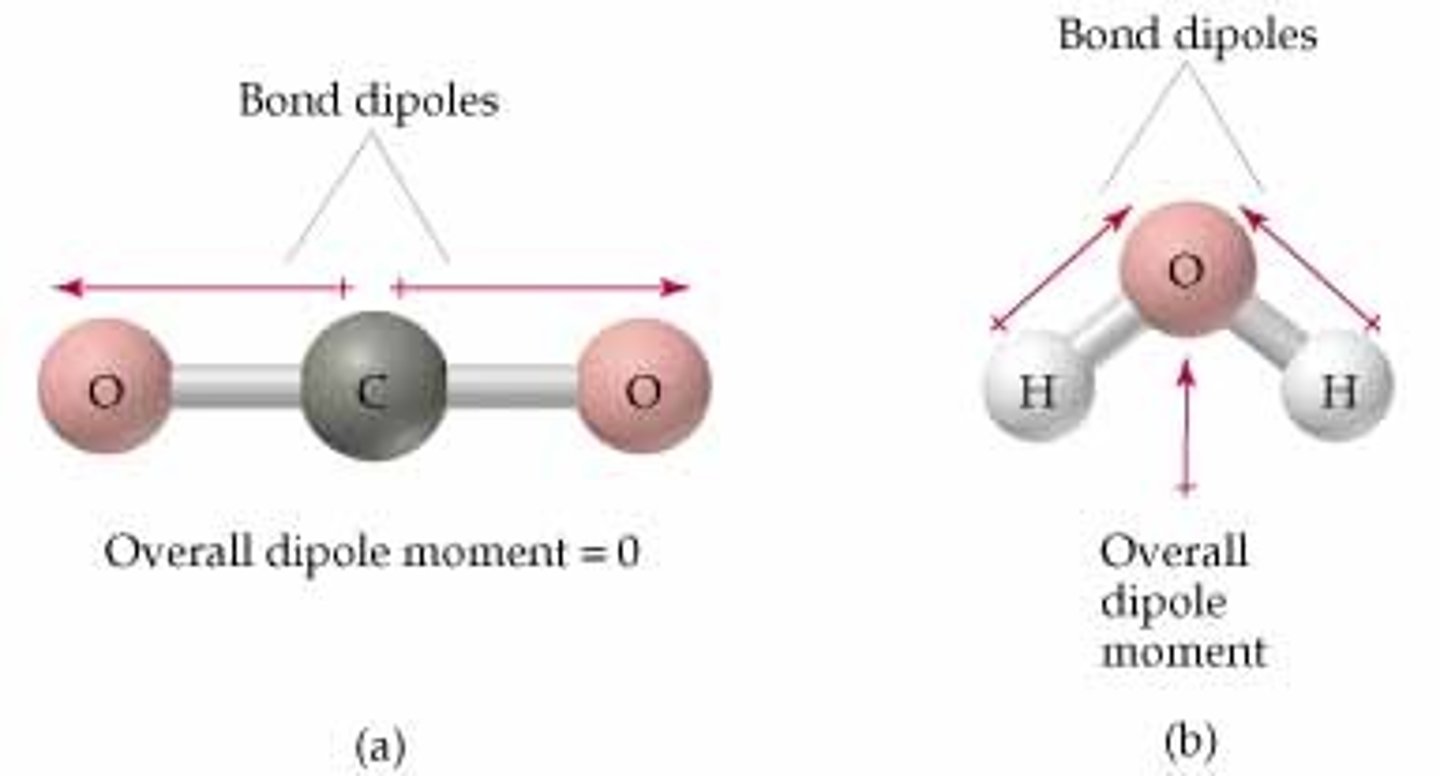
What is a dipole moment?
measure of bond polarity and the separation of charge between two non-identical bonded atoms
What is a dipole?
When the unequal sharing of a pair of electrons causes a buildup in electron density around the electronegative atom. Resulting in a partial negative and positive charges
How can dipoles be shown?
Vectors and partial charges
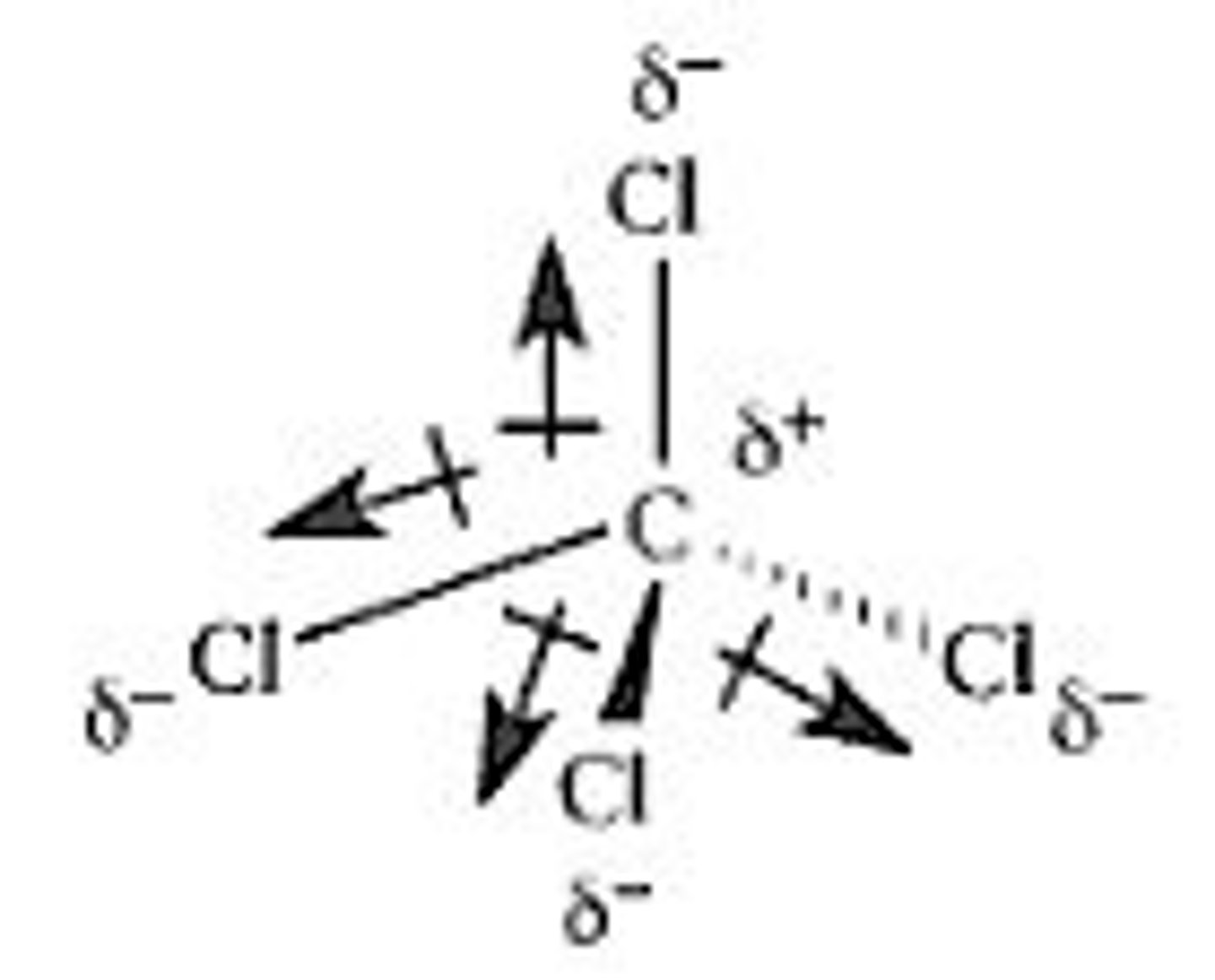
How is molecular polarity determined?
SNAP (symmetry, nonpolar, asymmetry, polar) and if the dipole directions cancel out
What is a coordination bond?
a covalent bond in which both the electrons of the shared
pair originate from the same atom
Give examples of molecules with coordination bonds?
In CO, oxygen donates two of its own electrons to share. In NH4+, nitrogen donates two of its own
How are coordination bonds used in transition metal complexes?
Coordination bonds hold the central metal ion and the surrounding atoms/ions together
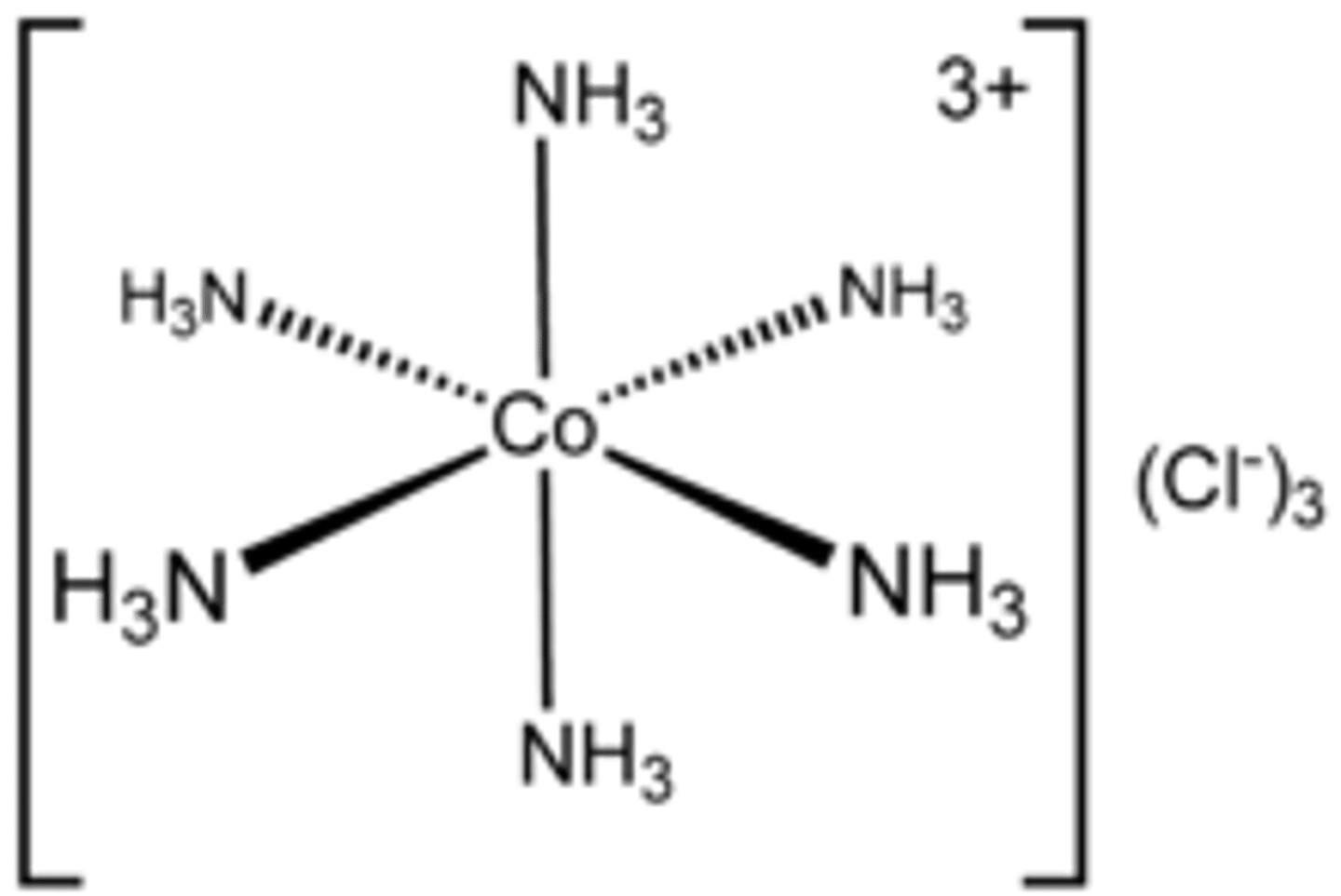
What is an intramolecular force?
Force within a molecule e.g covalent or ionic
What is an intermolecular force?
the force of attraction between molecules e.g hydrogen bonding
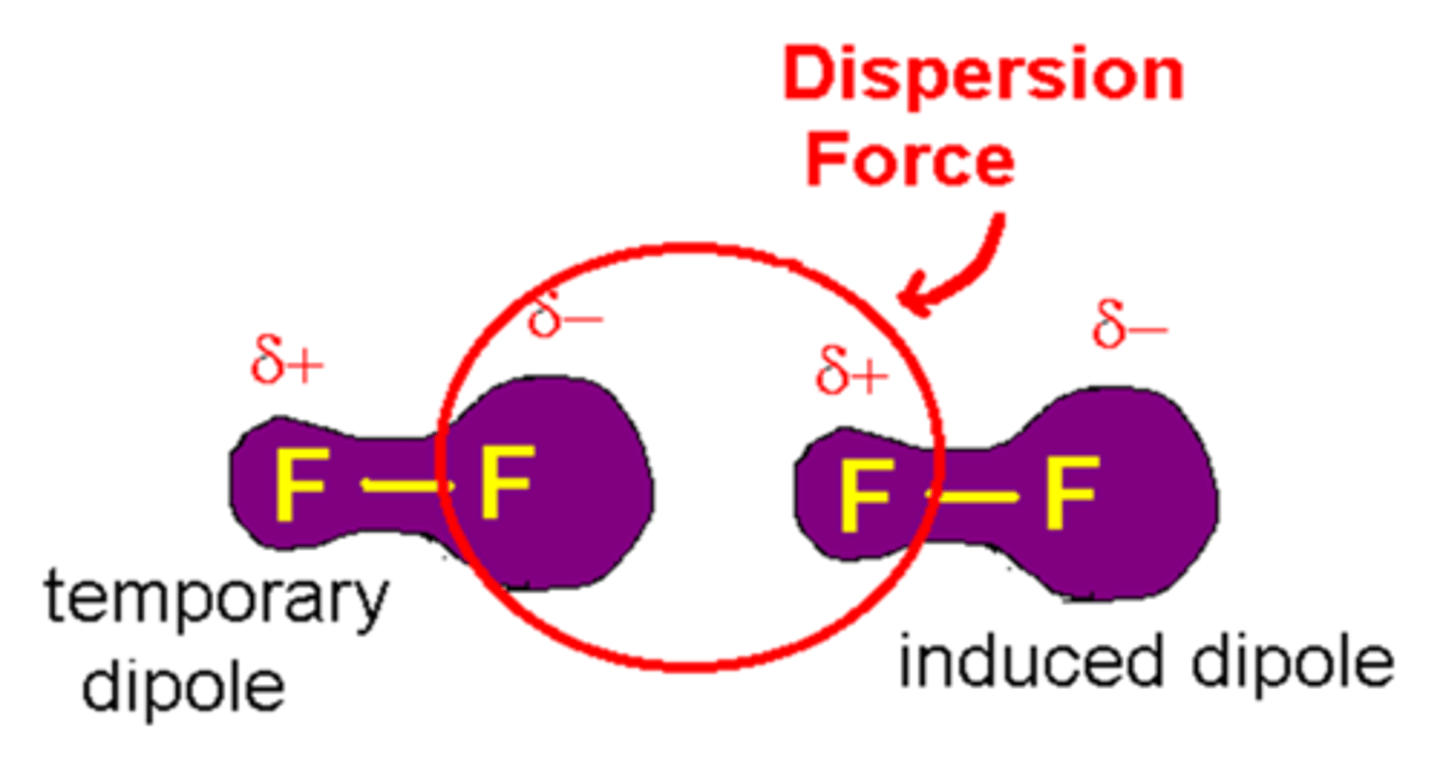
What is an instantaneous dipole?
A brief instance where electron density of a molecule shifts so one region becomes more negative than another.
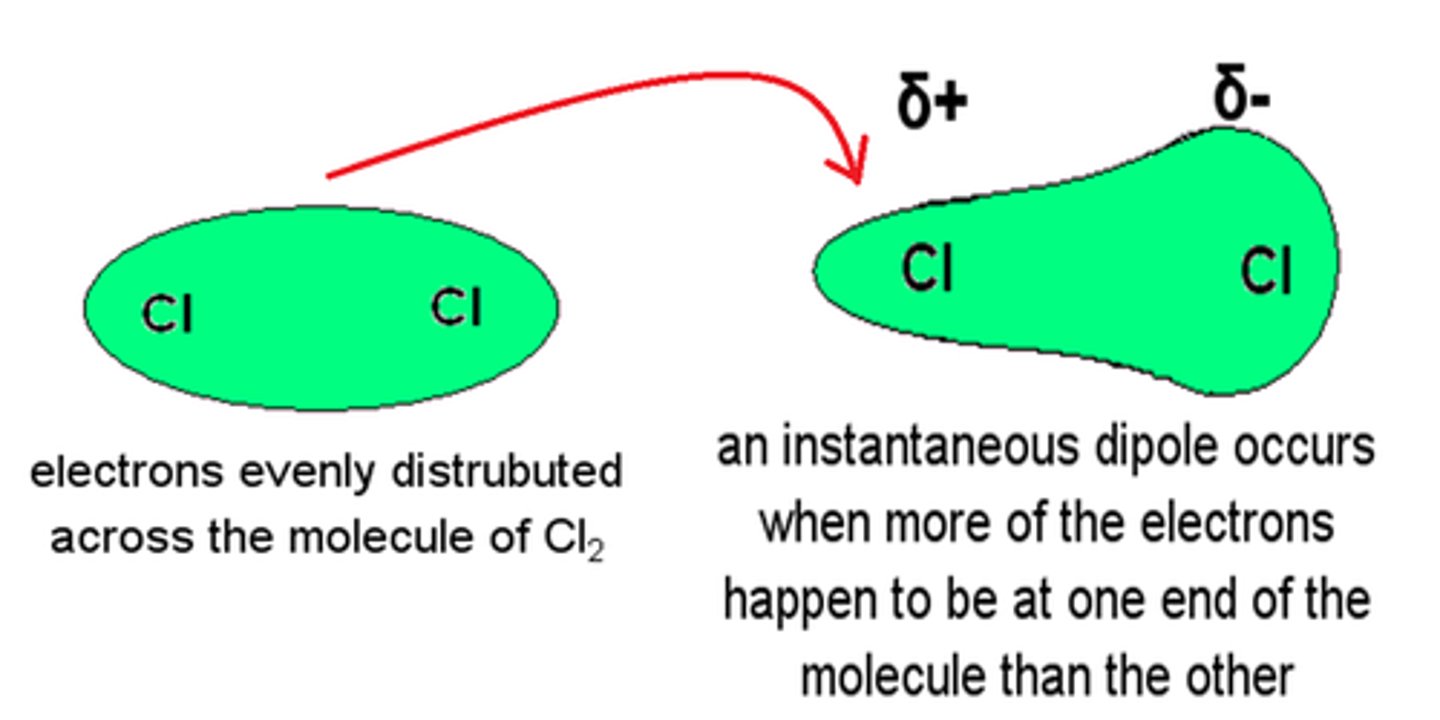
What are London forces?
weak attractive force between an instantaneous dipole and an induced dipole in neighbouring molecules. This is always happening whether molecules are polar or not
Where do permanent dipole-dipole forces occur?
between polar molecules
What is a hydrogen bond?
a dipole-dipole attraction between a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge an electronegative atom from another molecule (N, O, F)

What is chromatography?
a technique used to separate the components of a mixture
based on their relative attractions to mobile and stationary phases due to intermolecular forces
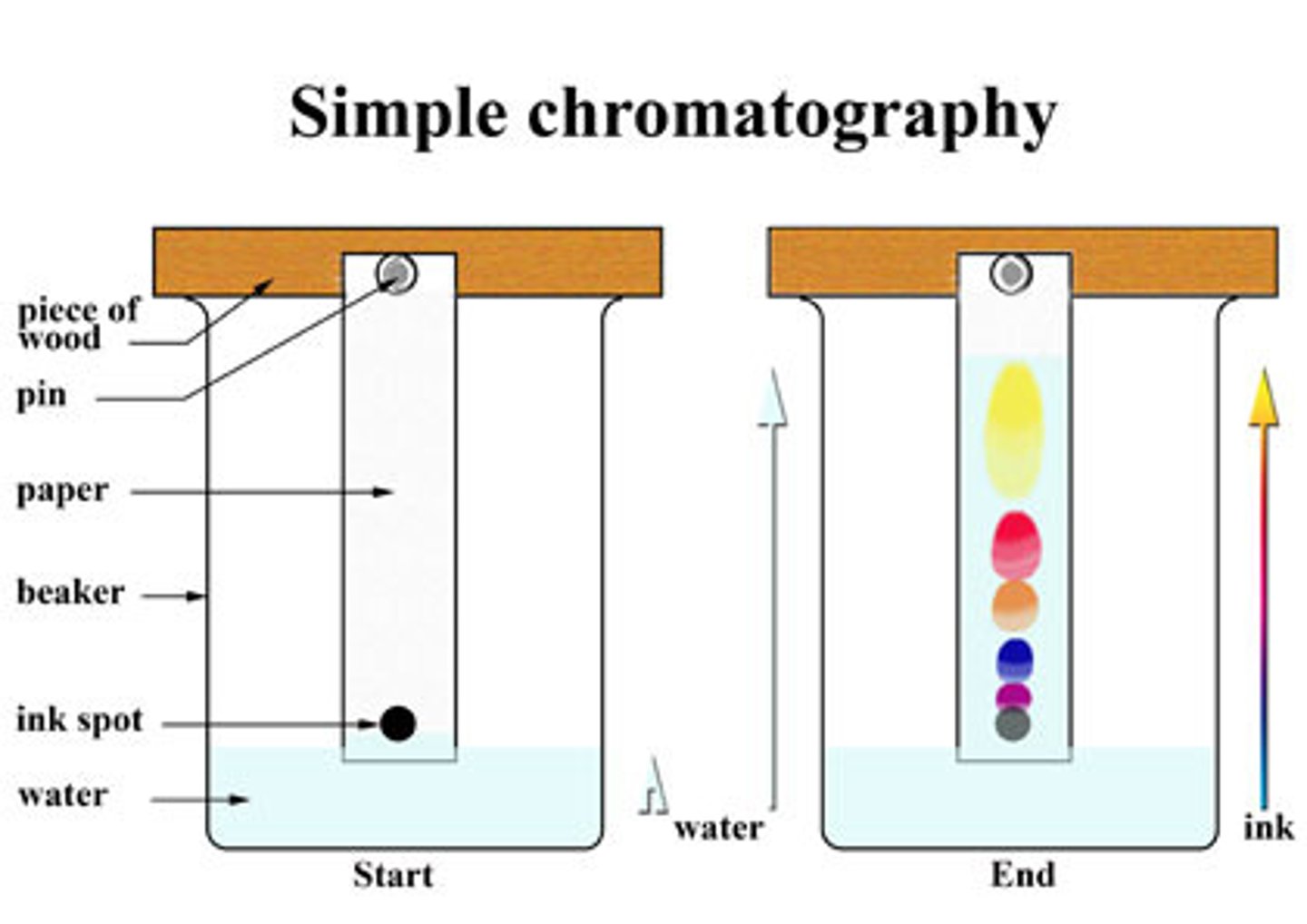
What is an Rf value?
The ratio between the distance travelled by the dissolved substance (the solute) & the distance travelled by the solvent
How do you calculate the Rf value?
= Distance travelled by substance / distance travelled by solvent
What factors affect how far the spot travels in chromatography?
pH, temperature, solvent and type of paper
What do we use the Rf value for?
It's compared to accepted values to identify substances in a mixture
What is a resonance structure?
a structure that occurs when it is possible to draw 1+ valid lewis structure
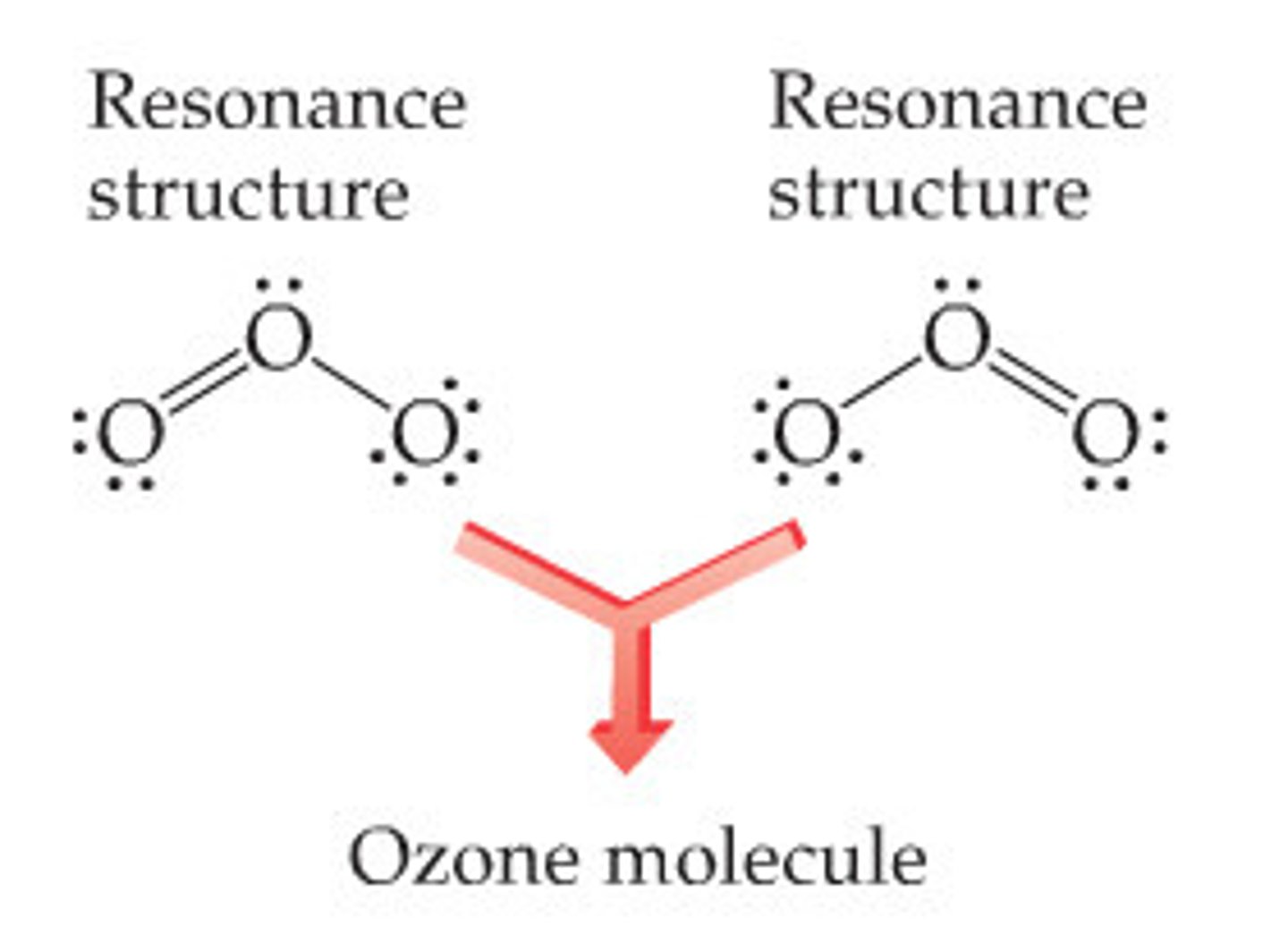
What is a resonance hybrid structure?
The real structure of a molecule with a resonance structure. The bonds have equal strength and length which are intermediates
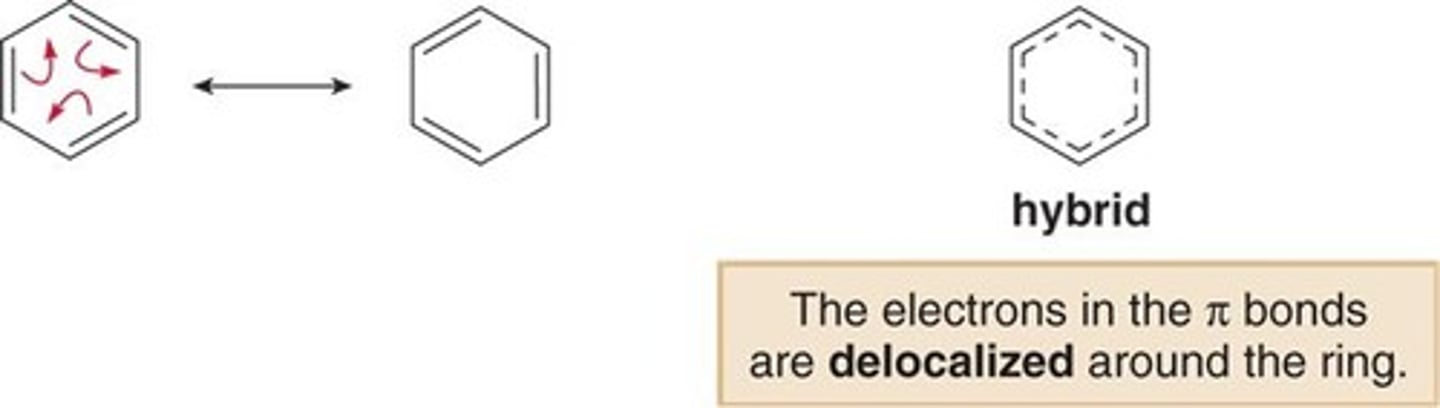
What do the dotted/dashed lines of a resonance hybrid structure represent/
The delocalised electrons spread between 2 positions rather than being fixed (localised) between 2 atoms
What is the chemical evidence of benzene's resonance?
It's stable, unreactive and substitution reactions occur with bromine water rather than addition
What is formal charge?
the theoretical charge of a molecule based on the electron distribution of the atoms it contains
What is the formula for formal charge?
no of valence electrons - no of non bonding electrons - 1/2 no of bonding electrons
Do resonance structures have the same formal charge?
yes
2 multiple choice options
What is the significance of formal charge?
It tells us what the most preferred resonance form is which means it contributes more to the resonance hybrid structure. It must have the smallest formal charge, the most electronegative atom should have a (-) and adjacent atoms don't have the same sign
What is an atomic orbital?
a region of space around the nucleus in which there is a high probability of finding an electron
What is a molecular orbital?
When two atoms combine, their atomic orbitals overlap to produce orbitals that apply to the entire molecule.
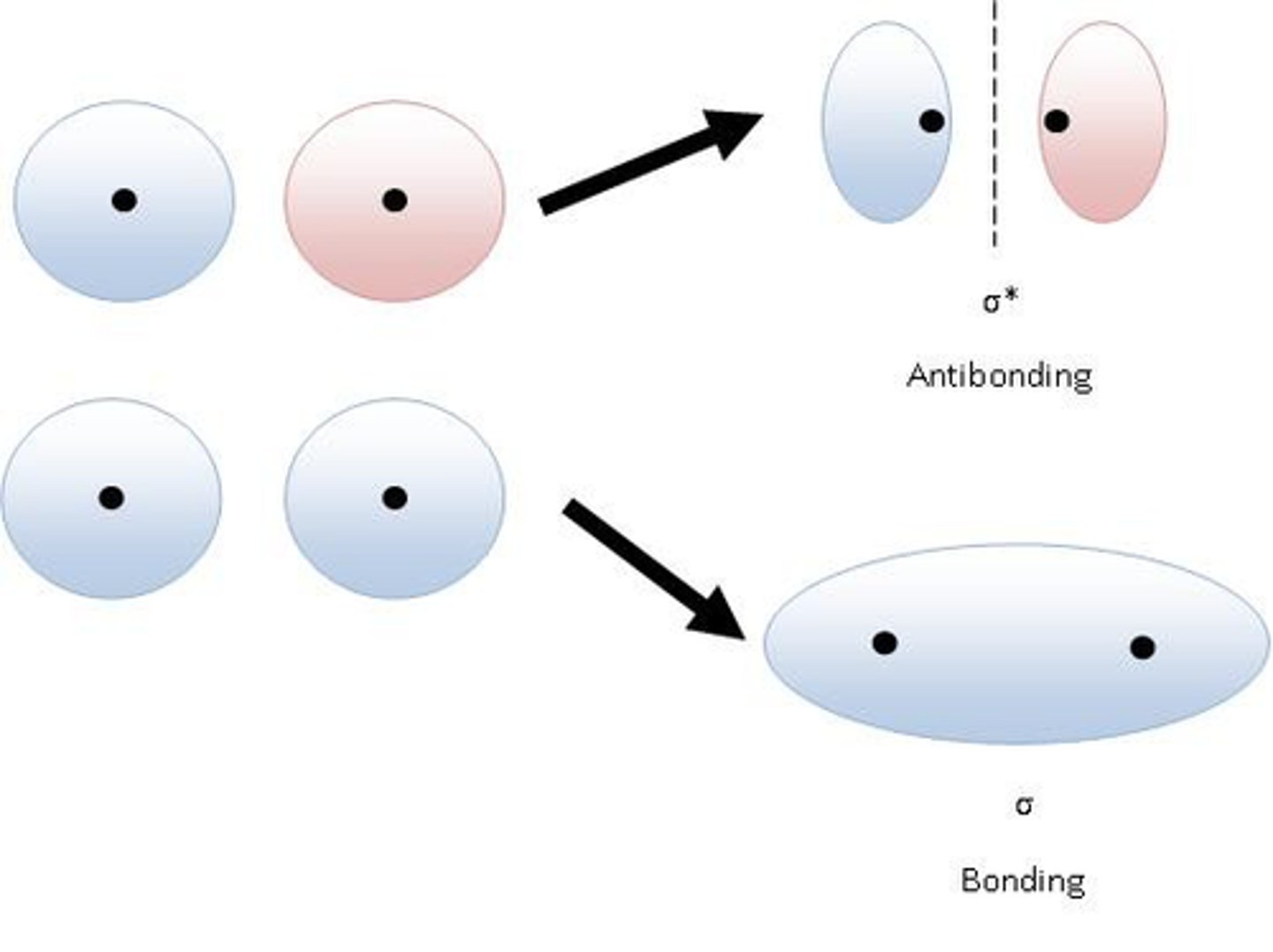
What is a sigma bond?
a single covalent bond formed by the head-on combination of atomic orbitals where the electron density is concentrated along the bond axis
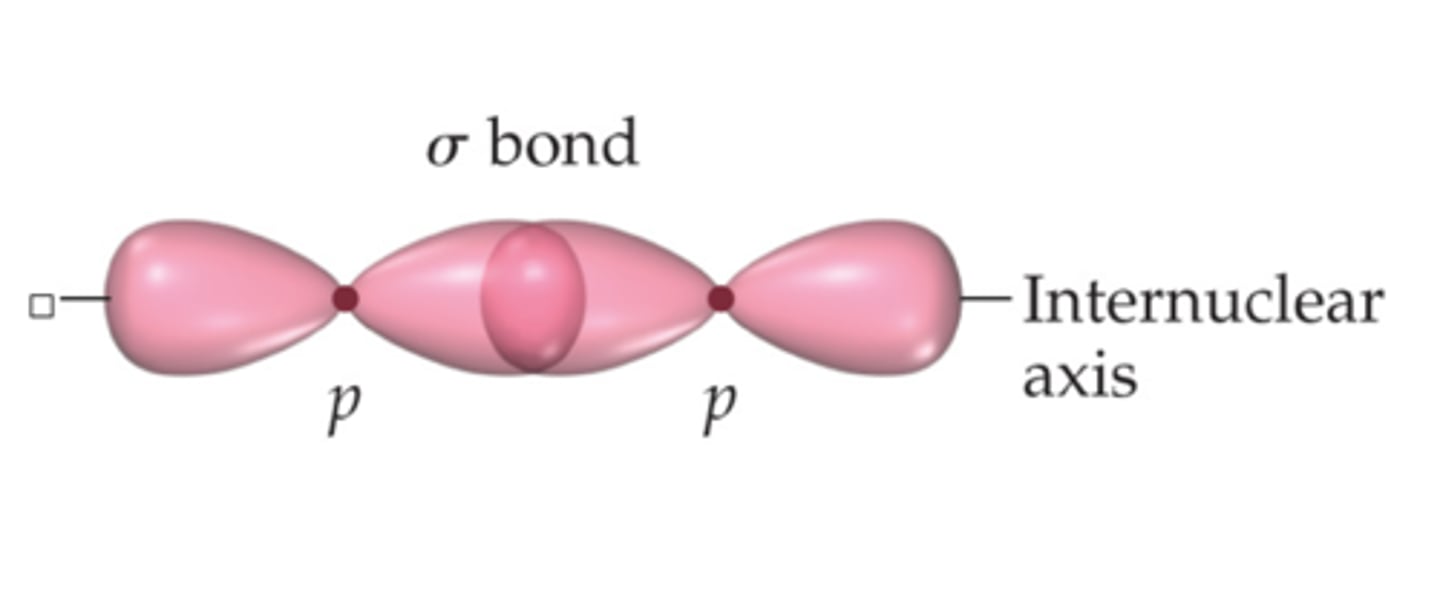
What is a pi bond?
form by the lateral (sideways) overlap of p-orbitals where the electron density is concentrated on opposite sides of the bond axis.
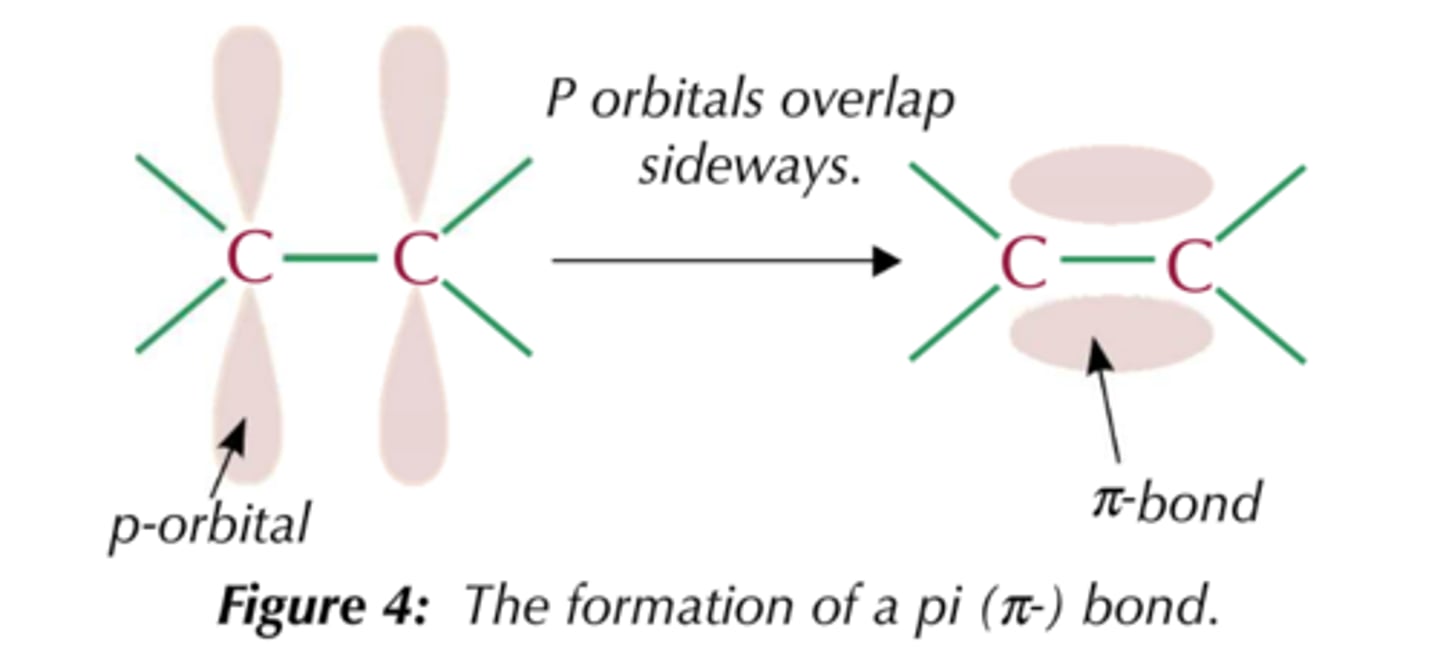
Why are pi bonds weaker than sigma bonds?
The orbitals overlap less so the electron density is more spread out so electrostatic attraction between nuclei and shared pair of electrons is weaker.
sigma bond is a...
single bond
A double bond is made up of...
1 sigma and 1 pi bond
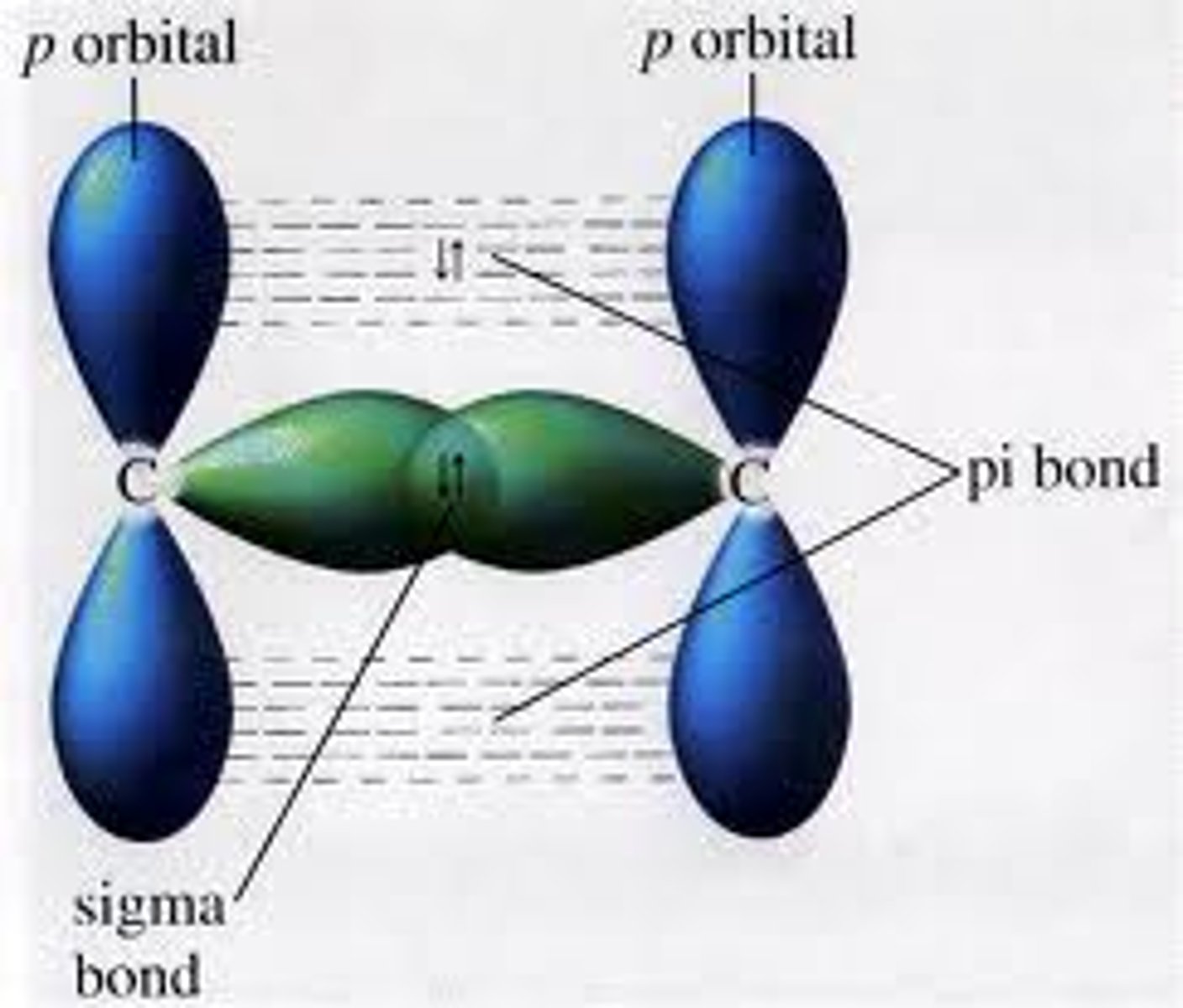
A triple bond is made up of...
1 sigma bond and 2 pi bonds

What is hybridisation?
the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals for bonding
Sp3 hybridisation electron domain geometry is
tetrahedral
Sp2 hybridisation electron domain geometry is...
trigonal planar
Sp hybridisation electron domain geometry is...
linear
What is bond strength/enthalpy?
amount of energy needed to break a bond (kJ mol-1)
What is bond order?
a measure of the number of electrons involved in bonds between two atoms and it's equal to no of bonds / no of possible solutions
The higher the bond order...
the more stable the molecule because the bond is shorter and stronger
Hess' Law
regardless of the route taken by a chemical reaction, the total enthalpy change will always be the same if the initial and final states of the system are the same
Standard enthalpy of combustion
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance in its standard is completely burned in oxygen under standard conditions.