Neurobiology Exam 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Which plane divides the brain into anterior and posterior sections?
coronal plane
Someone wants to describe brain region A to brain region B. Brain region A is superior to brain region B. What’s another way they can describe the relationship?
Brain region A is dorsal to brain region B.
Damage to which lobe would likely affect auditory processing?
Temporal lobe
What results from damage to Broca’s area?
non-fluent aphasia
Which of the following brain regions is a major convergence area for most sensory input before it sent on to the cerebral cortex?
thalamus
The pons belongs to which major brain region?
cerebrum
Which part of the limbic system is primarily involved in memory formation and consolidation?
Hippocampus
Which part of the spinal cord contains sympathetic neurons and is present only in certain regions?
lateral horns
What is the primary function of Schwann cells in the PNS?
Form myelin sheaths and promote regeneration of damaged axons
What is the primary function of microglia in the CNS?
removing dying cells by phagocytosis
Not all neurons are the same. What type of neuron is this?
multipolar
What is the term for a bundle of axons in the PNS?
nerve
What type of neuron has one process that divides into two branches?
unipolar neuron
Potassium leaves the cell through a channel that is always open. What type of diffusion is this?
Facilitated diffusion—leak channels
Potassium leaves the cell through a channel that opens when there is a change in voltage. What type of diffusion is this?
Facilitated diffusion—voltage gated
If potassium levels were higher on the outside of the cell and sodium levels higher on the inside. What direction would sodium and potassium flow through their leak channels?
Potassium in, sodium out
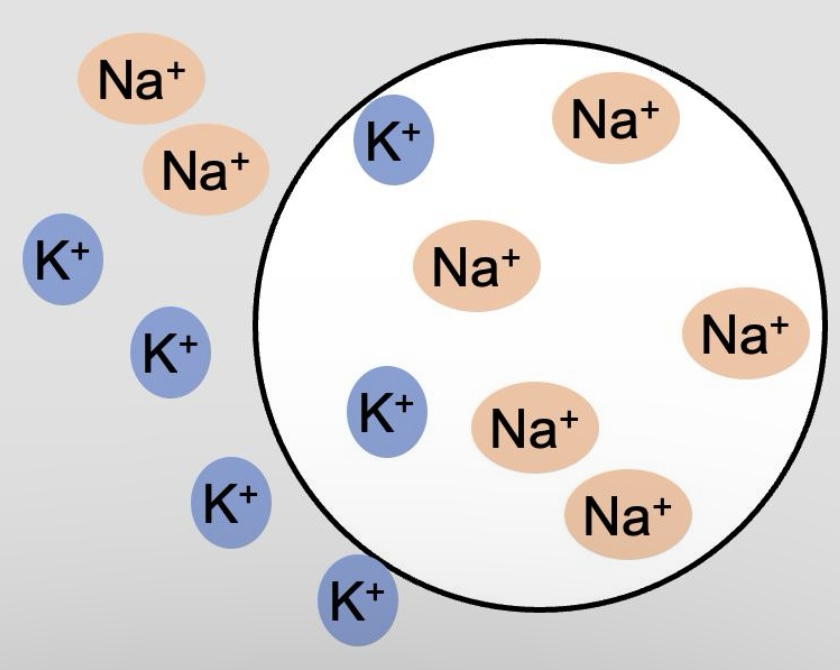
Which is NOT a type of passive membrane transport?
primary active transport
If potassium levels were higher on the outside of the cell and sodium levels higher on the inside. What direction would sodium and potassium move using the sodium potassium pump?
Potassium out, sodium in
When movement of Na+ ions down their concentration gradient drives the transport of other substances across the cell membrane, it is called___
secondary active transport
The sodium-potassium pump____
pumps Na+ out and K+ into the cell
As a general rule of thumb, the greater the potential difference in charge between two points, the ___ the voltage.
higher
When considering Ohm’s law, what will happen to the current if the voltage is increased while the resistance remains unchanged?
current will increase
If a cell only had potassium leak channels, what would be the membrane potential?
-90mV
Depolarization of the neuron refers to___
the membrane potential becoming less negative
What must occur for a graded potential to become an action potential at the axon hillock?
the graded potential must reach a certain threshold
Neurons generally repolarize once the membrane potential reaches approximately +30mV because:
voltage-gated potassium channel gates open
What is the primary difference between continuous and saltatory conduction?
saltatory conduction is faster than continuous conduction
During the events involved in information transfer across a chemical synapse, which of the following steps would be directly interrupted by exposing a neuron to a calcium channel blocker?
Neurotransmitter release from the presynaptic neuron
What differentiates ionotropic receptors from metabotropic receptors?
Ionotropic receptors include an ion channel as part of their structure
Which of the following mechanisms does NOT contribute to the termination of neurotransmitter action?
transport of neurotransmitters into vesicles
A patient presents with difficulty forming sentences. They leave out words, but do not have trouble using the correct words. Which type of aphasia do they likely have?
Broca’s aphasia
Sodium enters a cell along with chloride which exits the cell. What type of transport is this?
secondary active
A patient comes in with memory deficits. Which brain region is MOST likely to have been damaged?
Hippocampus
A cluster of cell bodies in the CNS is a _________ and a cluster of cell bodies in the PNS is a ____________.
nucleus; ganglion
What structure resides within the brainstem?
pons
What structure resides within the cerebrum?
cerebral cortex
What structure resides within the diencephalon?
Thalamus
Which of the following help protect the brain?
The blood brain barrier, the skull, and CSF
What is the primary function of astrocytes in the CNS?
Providing structural support to neurons
Which of the following are types of passive diffusion?
Voltage gated channel mediated, Carrier mediated diffusion, Leak channel mediated, Simple diffusion
A neuron has two processes coming out of it. One is a dendrite which can receive information and one is an axon which transmits information. What type of neuron is it?
Bipolar
The sodium-potassium pump allows___ sodium ___ the cell and __ the cell
3 out of, 2 into
Select the statements which are true regarding the absolute refractory period
It ensures one-way transmission of action potentials, No action potentials can occur during it, It is due to inactivation of Na+ channels
Place the following series of events that take place during chemical synaptic transmission
1) Action potential reaches axon terminals
2) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open.
3) Influx of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal.
4) Synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane.
5) Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft.
6) Neurotransmitter binds to its receptors.
A depolarizing event leads to the membrane potential becoming __ negative and a hyperpolarizing event leads to the membrane potential becoming _ negative
less, more
All graded potentials lead to action potentials
false
What is the action of the neurotransmitter at a chemical synapse?
It acts on receptors in the postsynaptic membrane.
Which consequence of Na+ channels staying open, instead of closing after membrane depolarization, is most plausible?
The membrane would not repolarize (return to a negative value of membrane potential) following depolarization.
The electrochemical gradient of K+ consists of a chemical force that wants K+ to __ the cell and an electrical force that wants K+ to _ the cell.
exit, enter
How would application of a Ca2+ channel blocker affect the function of a synapse?
It would eliminate the postsynaptic potential and the presynaptic Ca2+ current.
Which statement about Na+ permeability during an action potential is most accurate?
It is responsible for the rising phase (upstroke) of the action potential.
Presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons that form _______ synapses are connected via _______.
electrical; gap junctions
What is one function of the Na+ - K+ pump in maintaining membrane potentials?
it maintains the concentration gradient by actively transporting Na+ out and K+ in
Which channel are the main contributors to the resting membrane potential?
potassium leak channel
If K+ was higher on the outside. Na+ and Cl- higher on the inside, what would happen?
K+ will enter (higher on the outside)
K+ will exit inside of cell (positive inside)
Na+ will exit (higher on the inside)
Na+ will exit (positive on inside)
If the cell is only permeable to ion X, what is the resting membrane potential?
Equilibrium potential
A cell is permeable to ion x,y, and z, but it’s much more permeable to y. What can we say about the resting membrane potential?
The resting membrane potential would lean toward the equilibrium potential of y.
Why does the cell not further depolarize once it hits the peak of the action potential?
Na+ channels are inactivated and sodium cannot enter
What type of graded potentials lead to an AP?
depolarizing
When does a graded potential lead to an AP?
when it hits threshold
Why do action potentials travel in only one direction?
voltage-gated sodium channels get inactivated
How do axon diameter and myelination affect conduction velocity?
the bigger the axon, the more myelination, the faster the conduction velocity
What’s responsible for depolarization?
voltage-gated sodium channels opening
What’s responsible for the cell not further depolarizing?
sodium channels closing/inactivating
What’s responsible for repolarization?
potassium channels
What’s responsible for hyperpolarization?
potassium channels staying open longer than needed
What helps bring the cell back to resting membrane potential?
sodium-potassium pump
If dorsal roots are sliced, what is the side effect?
loss of sensation
If ventral roots are sliced, what is the side effect?
loss of motor
If dorsal horn is lesioned, what would happen?
loss somatic and visceral sensory
If ventral horn is lesioned, what would happen?
loss of motor function
Someone is not forming myelin sheaths in the CNS, what cell is involved?
Oligodendroglia