Envi 101 Exam 3 Review
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Geology
The study of dynamic processes taking place on the earth’s surface and in its interior
Three Zones of Earth
Core, Mantle, Crust
Mineral
Naturally occurring chemical element or inorganic compound that exists as a crystalline solid
Rock
Naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of one or more minerals
Sedimentary rock
Made of sediments (pieces of other rocks) and accumulates in layers
Metamorphic rock
Existing rock that’s subjected to high temperatures, pressures, fluids, or a combination. ex. marble and slate
Igneous rock
Forms under intense heat and pressure and then cools, begins as magma
Tectonic plates: Divergent boundary
Plates moving away from each other, ex. earthquakes and volcanoes
Tectonic plates: Convergent boundary
plates colliding/coming together, ex. earthquakes, mountain ranges
Tectonic plates: Transform plate boundary
Plates sliding past each other, grinding against each other, ex. volcanoes, earthquakes
Ore
Solid material that contains profitable concentration of a mineral
High-grade vs. low-grade ore
High grade- high mineral concentration
Low grade- low mineral concentration
Trends with rare earth minerals
China has 1/3 of rare earth mineral reserves but accounts for 90% of production
Fossil fuels
Oil, coal, and natural gas. Exists in finite amounts
Surface and strip mining techniques
Removes shallow deposits and extracts deposits in horizontal beds close to the Earth’s surface (majority of coal is mined from surface mining)
Open-Pit mining- large, deep, open-air pits
Mountaintop removal- uses explosives to remove top of mountain to expose minerals
Environmental issues with mining
Tailings (materials left over after separating the valuable part of the ore from the rest) causes waste, smelting (using heat or chemicals to extract the mineral from the ore) causes air and water pollution
Human health issues with mining
Miners can develop black lung
Gold mining case study in the Ivory Coast
The Ivory Coast (top cocoa producer) was illegally mining gold, it was unsafe, used toxic mercury, the money made from the gold was not being put back into the community
Solutions to Mining
Recycle
Waste less
Use less
Find a substitute
Do without
Biomining- using living organisms to mine, potentially how we can mine in space
Volcanoes
Release molten rock from Earth’s interior, ex. Mt. Vesuvius/Pompeii
Earthquakes
Breakage and shifting of rocks, energy accumulates over time and is released in the form of vibrations. Occurs at faults
seismic waves- vibrations in the crust
focus- where it originates
magnitude- severity, measured by the Richter Scale
Ex. 2010 earthquake in Haiti. but largest ever recorded was in Chile in 1960
Tsunamis
Earthquakes on the ocean floor, a series of huge waves generated when the sea floor suddenly rises or drops
Ex. 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami, 2011 Japan Tsunami (damaged nuclear reactors)
Glaciers
Sheets of ice formed from deep packed snow, most occur on land but can extend out to sea, when they melt or recede they form distinct landforms…
Mounded hills- moraines, drumlins
Bodies of water- Kettle lakes
Difference between weather and climate
Weather- short term, area specific. Includes temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind, cloudiness
Climate- long term
Atmosphere
Composition of gases, 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen
Layers of the atmosphere
Troposphere- closest to Earth’s surface, supports life
Stratosphere- where the ozone layer is located
Ozone layer
Filters 95% of harmful UV radiation, currently on the mend and healing
Greenhouse gases
CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor
traps heat in the atmosphere like a blanket
we need greenhouse gases to keep the Earth warm enough to support life, but we have emitted too much now
Influences on regional climate and seasonal change
At poles of the Earth, the angle at which sun hits Earth is greater and the light spans over a larger distance… temperatures decrease
At the equator, there is no angle from the light, it is direct… temperatures increase
Earth orbits around the sun in 365 days and rotates on its axis in 24 hours, hence seasons and days
Earths tilt puts certain regions closer to the sun than others, so summer when tilted near and winter when tilted away
Hadley cells
Large atmospheric cells or circulations where air rises at the equator and then sinks at medium latitudes, influences precipitation patterns, the reason why it rains so much at the equator
air is colder away from the equator, cold air is denser than warm air, cool air flows to equator, warm air holds more moisture than cold air and and pulls moisture from surface, cold air rushes to equator, forces warm air to rise, warm air rises and cools, now can’t cold as much water, so it rains
Urban heat island effect
Urbanized areas that experience higher temperatures than outlying areas
Albedo effect
How much sunlight is reflected from Earth’s surface. Light surfaces reflect more than dark, ice has a high albedo effect, cities have a lot of pavement and such absorbing heat. solutions? change the color of roofs, paint them, plant trees, etc.
Methods scientists use to understand climate and climate change
Ice cores, real-time atmospheric CO2 measuring, annual tree rings
How we know recent change is caused by humans
Observed changes in temperature are consistent with human (anthropogenic) and natural causes
Effects of climate change
Increasing temperatures, land-based glaciers and sea ice are melting, sea levels rising, too hot to grow normal crops
Paris Agreement and recent discussion at COP27
Each country expected to lower greenhouse gas emissions, goal was to limit Earth’s average temperature increase to less than 2 degrees C, COP27 discussed issues with who will pay for funds for damages from climate change, changed temperature change to 1.5 degrees instead of 2
Solutions to climate change
Clean energy tax credits- you get money for being more energy-efficient
EPA regulations on power plants- lessen pollutants emitted
Auto industry regulations- switching to EV vehicles
Carbon tax- charge people emitting carbon
Carbon cap and trade- government gives companies a permit on how much carbon they can emit, if they emit less than their max they can trade their unused carbon emission permits to other companies
Geoengineering- trying to lesson CO2 absorbed in atmosphere, shooting seawater into air???
Clean Air Act
Set standards and limit for certain pollutants
6 major pollutants
Particulate matter ((dust, soot, pollen, damages lung tissue if inhaled), sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, lead
Primary vs. secondary pollutants
Primary- released directly from the source into the air in a harmful form
Secondary- converted to a hazardous form after they enter the air or are formed by chemical reactions as components of the air mix and interact
Sulfur dioxide and sulfuric acid
colorless, corrosive, can form sulfuric acid if mixed with water—>acid rain
Nitrogen oxides
mainly emitted from electrical power, transportation, and fertilizers, can react with water to create acid rain
Pollutants and fire
Carbon monoxide and particulate matter are created in wildfires
Trends with acid rain
We have seen a major reduction in acid rain since 1986
Indoor air pollutants
Tobacco smoke, e-cigarettes, indoor wood burning (a concern in less developed countries)
Ozone and lead as pollutants
Ozone- when closer to the ground, it can damage vegetation and cause breathing problems
Lead- leaded gasoline was the biggest emitter, exposure is bad, children are especially sensitive, effects nervous system
Effects of air pollution on human health
Causes asthma, chronic bronchitis (inflammation of lungs), and emphysema (permanently constricted airways)
Solutions to air pollution
Rely more on renewables, getting at the source of emissions by putting filters at source (on smokestacks, for example)
Effect of clean air legislation
It works! Emission controls and cap and trade with sulfur dioxide, reduces emitted pollutants
Water breakdown
97.6% of all water is saltwater in oceans
2.4% is freshwater, 87% of which is in ice and glaciers
Hydrologic cycle processes/how humans effect it
evaporation- liquid to gas
precipitation- gas to liquid
surface runoff
we take water and move it around, we overwater plants, don’t use water efficiently, we use up our sources of water and we cause glaciers and snow to melt
Rain shadow effect
explains why one side of a mountain is arid and one is moist with lots of precipitation
warm winds pick up moisture, air rises as flowing up the wayward side of mountain and cools, can’t hold moisture so it rains, winds warm up again as flowing down the leeward side, warmer winds pick up moisture from air making this side even more arid
Zone of aeration
upper level of soil, holds air and water
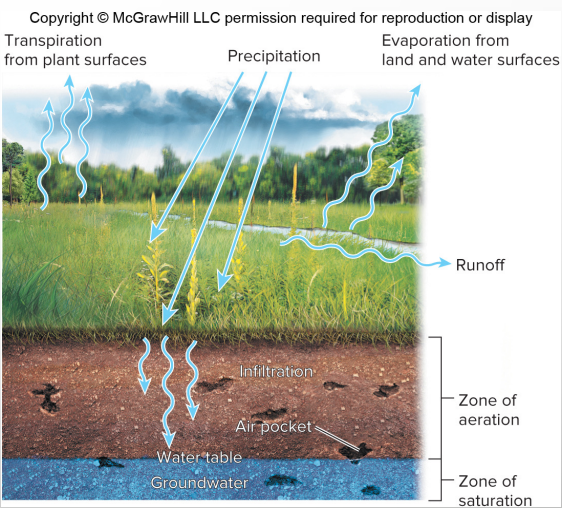
Zone of saturation
filled with water
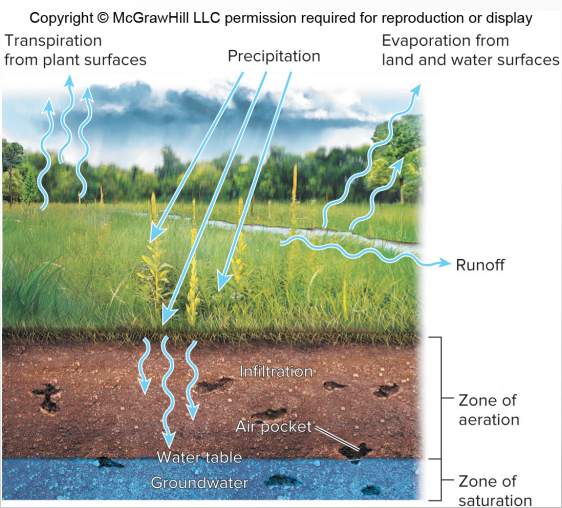
Water table
top of zone of saturation/groundwater layer, falls and rises based on rainfall
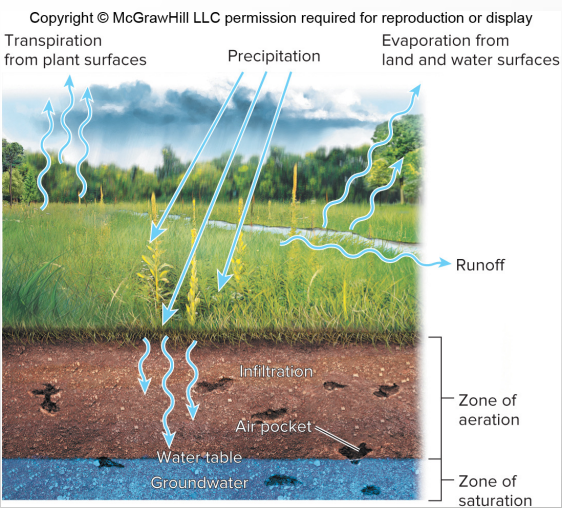
Aquifer
Porous layers of sand, gravel, or rock below the water table
Reservoirs for groundwater, we often make wells for the reserved aquifer water
Problem with groundwater
US is using groundwater up far too quickly, mostly for agricultural
Ogallala Aquifer spans 8 agricultural states and is being used up
land is sinking because we take so much groundwater
The Great Salt Lake, why it’s drying up, effects, what can be done
Water is being diverted away from the lake for development and agriculture, the lake bed is full of arsenic and copper, if it dries up the metals will get into the air and cause health issues, also it’s a habitat for birds, to fix it, policy, rationing water, stop allowing development, wear gas masks
Water out West
The West is facing bad water shortages
Water conservation methods
Recycle water, desalinization to remove salt, sponge cities-lessening blacktop and increasing vegetation to hold more water, cloud seeding- sending planes to force precipitation to fall by releasing silver iodide into air
Water pollution
any physical, biological, or chemical change in water quality that adversely affects living organisms or makes water unsuitable for desired uses
Point vs. nonpoint source pollution
point source- at a specific point, ex. sewage, power plant pollution
nonpoint source- scattered pollution, not a specific source. ex. field runoff, fertilized lawn runoff
Types of water pollutants
infections agents (living pollutants like bacteria, viruses, and parasites), organic/inorganic chemical, radioactive materials, sediment, plant nutrients, etc.
Dead zones
What causes them- eutrophication, not enough oxygen to support fish so they die
Gulf of Mexico-abundance of nitrogen and phosphorus from agricultural runoff from the areas surrounding the Mississippi River accumulates in the Gulf of Mexico
Prevention- planting trees as buffers
Clean Water Act (1972)
national pollution discharge elimination system, upgrade municipal sewage treatment plants, states establish total maximum daily loads, led to significant improvements in surface water quality
“How’s My Waterway” from the EPA
Tells you about the conditions of your local waterways
Critiques of bottled water
Usually just bottled city water, chemicals from plastic can leech into water, increased waste, less strict standards for bottled water than municipal water
Upper Susquehanna Coalition
plants trees along farms to absorb nutrients and lessen runoff, builds a buffer
Municipal wastewater treatment
Primary treatment- physically separating large solids and sludge, uses screens, filters, sediment tanks
Secondary treatment- bacteria and microorganisms catch organic materials, a biological way to break down organic material
Other methods of water treatment
Waterhealth International, duckweed, UV light treatment
Trends in US with energy usage
Increasing the use of renewable energy and decreasing nonrenewable but…
most of our energy is from nonrenewable sources, namely oil and natural gas, only 13% is renewable energy
Coal
solid fossil fuel formed from remains of land plants (peat)
low cost and plentiful
issues- dirty, air pollution, environmental damage extracting it, dangerous for workers
Oil
refining of crude oil, energy used for heat AND to make products such as plastics, paints, chemicals
Offshore drilling… 2010 oil spill in Gulf of Mexico
Canadian oil sands
digging for oil destroys vegetation
transported through pipelines
Natural gas
volatile gas particles sitting on top of oil and coal
chemicals leech into groundwater
extracted through fracking, forcing the fracturing of rock to extract gas
Nuclear power
controlled nuclear fission (splitting apart of nuclei, releases energy) reaction in a reactor
fuel rods and control rods
safety/risk, people generally apprehensive about it, Chernobyl and weapons
nonrenewable source because we have to mine for uranium
expensive
doesn’t produce greenhouse gases, produces a huge energy output
Transition to renewables
must become more efficient with energy while also transferring more to clean energy
passive house- takes advantage of natural light, good insulation, efficient light bulbs, double paned windows
Solar energy
photovoltaic cells convert solar energy to electric energy, can be installed almost anywhere, has become cheaper
solar grazing for agrivoltaics- let sheep graze on areas under panels, panels provide shade for sheep awww
Wind
Kinetic energy captured by wind turbines
China and US use lots of wind energy
offshore windfarms are off the coast
birds? avoid putting turbines in migratory routes, put censor to stop turning when birds flock, paint turbines
Hydropower
produces electricity from flowing water
good- no carbon emitted, produces lots of energy
bad- damming rivers messes up ecology of waterbodies, harms downstream flow of rivers, dams are costly, displaces individuals/community, destroys vegetation, saltwater corrosion and upkeep problems
Biomass
Brazil makes ethanol from sugarcane residue, 40% of corn produced in US used to make ethanol
takes lots of energy, usually from fossil fuels, to turn corn to ethanol
requires lots of land, should be used for food
monocultures
Geothermal
heat stored in soil, underground rocks, and fluids in Earth’s mantle
heat pump system- uses temperature differences between Earth’s surface and underground, similar to how fridges work, fluid carried through closed loop
energy efficient, no CO2 emissions or fossil fuels
could require drilling
Wind Water Solar
We can supply 80% of energy with wind water and solar