Overview of the Mesozoic Era and Its Evolutionary Changes
1/222
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
223 Terms
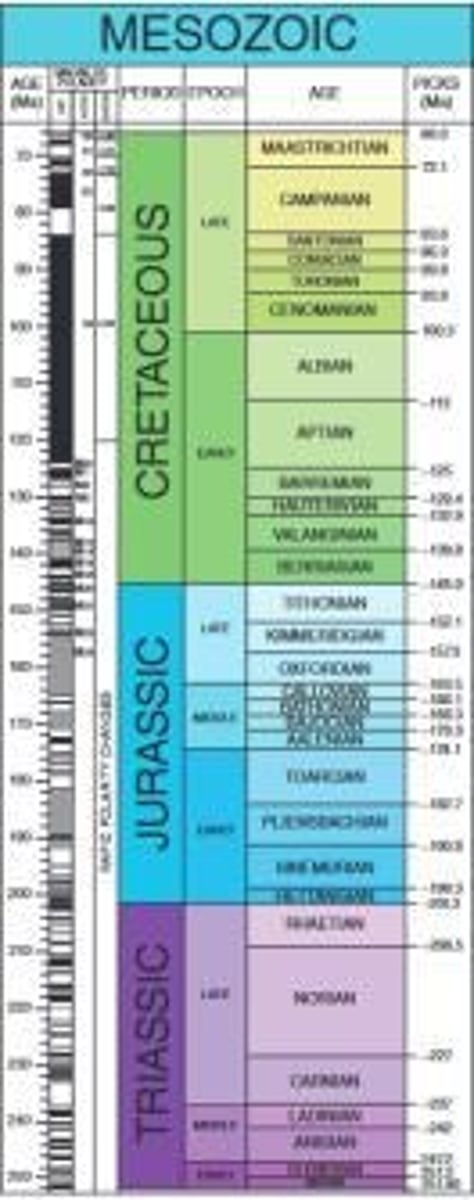
Mesozoic Era
Translates to middle life; Era extends from about 252 to 65 Ma; Begins with significant recovery from mass extinction; Finishes with another mass extinction; Dinosaurs, birds, and mammals appear.
Mesozoic Tectonic Changes
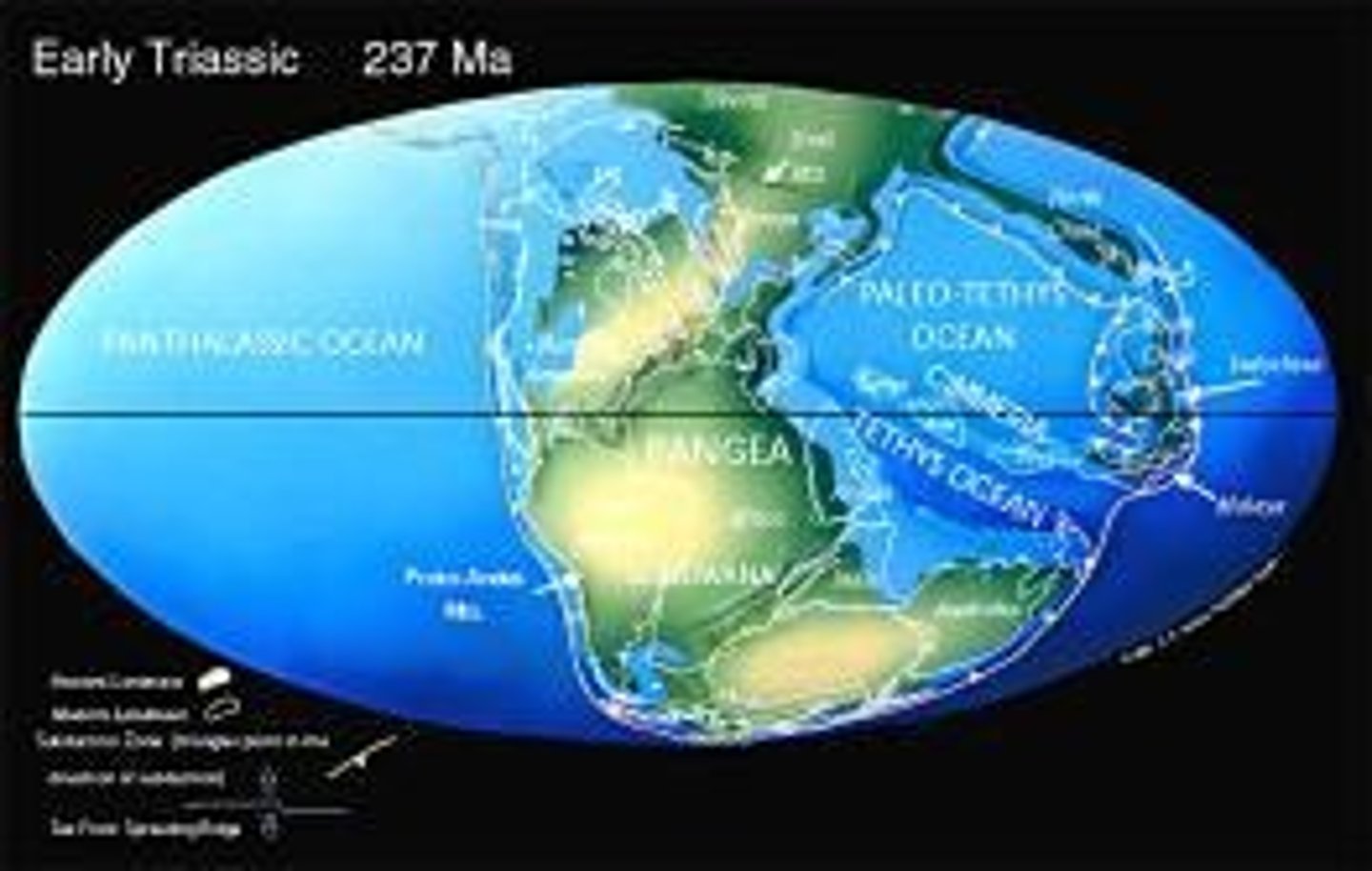
Breakup of Pangaea begins at end of Triassic and splits apart during Jurassic; Divided into 3 periods; Gradually rough modern continental shapes emerge; Begins following Permian-Triassic extinction; India starts becoming an island; Ends in violent mass extinction; Australia still fused to Antarctica; Features numerous geologic and biologic changes; Larger landmasses covered by inland seas.
Triassic Period
Lasts from 252 to 201 Ma; Reptiles continue to evolve; Oceans rebound from mass extinction; Continued amphibian extinction wiping out 96% of marine species; this may have taken 10 Ma; Mid- to late Triassic first modern stony corals; Flying vertebrates appear; Modest reef building in shallower waters; Pangaea breakage begins.
Amphibian Evolution
Amphibians had been around since late Paleozoic and continued to thrive; Progression from semi-aquatic to more land dwelling lifestyles.
Arthropod Evolution
Trilobites and many other creatures didn't make it to Mesozoic; Insects continued evolution; Earliest wasps appear; Earliest flies appear.

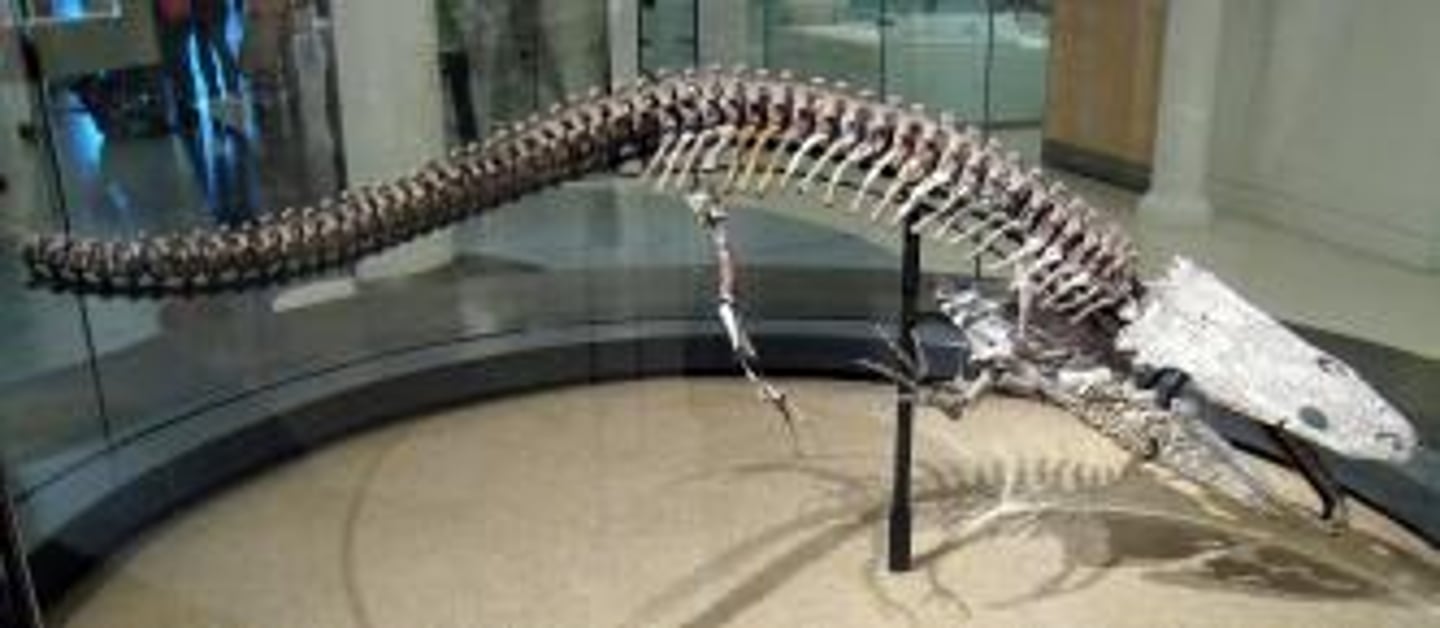
First True Lizards
Stem lizard that lived ~240 Ma; partial skeleton discovered 2003 in Italy; Sizes varied and larger perhaps were dominant predators in earliest Triassic; About 5.9 in (15 cm) long; Gecko group (not iguana group) was earliest squamate.
Eggs vs Live Birth
Reptiles altered between eggs and live birth; Reptiles became dominant during the Mesozoic.
Therapsida
Group of synapsid reptiles who share lineage with mammals.
Prosterognathus
Earliest primitive therapsids appeared early Permian and successfully continued into Triassic.
Archosauria
Reptiles that were stem ancestors to birds, crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs.
Lystrosaurus
Heavily built reptiles; stem ancestor with mammals that likely dug and nested in burrows.
Cynodonts
Suborder of therapsids that includes heavily built reptiles and stem ancestors with mammals.
Cynognathus
Mid-Triassic therapsid that is a stem ancestor to mammals, herbivores or insectivores.
Biarmosuchus
Therapsid with primitive stance still existing in possums.
Archosauria (continued)
Group of diapsids whose members evolved into birds, crocodiles, pterosaurs, and dinosaurs.
Protosuchus
Translated as 'first crocodile', part of the Archosauria group.
Pseudosuchia
One of the major divisions of Archosauria.
Avemetatarsalia
Another major division of Archosauria, includes bird-like foot bones.
Teleocrater
A genus within the Avemetatarsalia group.
Batrachotomus
A genus within the Pseudosuchia group, characterized by 'jammed in' hip sockets.
Rauisuchia
Dominant Triassic land predators, largest discovered in Argentina in 2010, over 20 feet (6 meters) long.
Ankle Difference
Comparison of ankle bone structure between Pseudosuchia and Avemetatarsalia.
Fasolasuchus
A genus within the Rauisuchia group.
Therapsid Survival
Describes the adaptations of therapsids during the Triassic period.
Skull openings
Characteristic of Archosauria, with openings in front of eyes and in jaw.
Socketed teeth
Teeth that are firmly set into the jaw, a feature of Archosauria.
Pelvis and femur orientation
Differences that distinguish some archosaurs from true dinosaurs.
Mid-Triassic
Period during which therapsids like Cynognathus thrived.
Partially arboreal
Describes the lifestyle of some therapsids, indicating they lived in trees.
Triassic
A geological period during which certain reptiles were stem ancestors to dinosaurs.
Cretaceous
A geological period characterized by the presence of dinosaurs.
Jurassic
A geological period known for the dominance of dinosaurs.
Permian
A geological period preceding the Triassic, during which early ancestors of reptiles existed.
Pseudosuchian
A branch of archosaurs that includes modern crocodiles and their ancestors.
Therapsids
A group of synapsids that were stem ancestors to mammals.
Archosaurs
A clade of reptiles that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and modern birds and crocodiles.
Mammals
Animals that evolved from therapsids.
Pterosaurs
Flying reptiles that evolved from archosaurs.
Crocodiles
Modern reptiles that evolved from the pseudosuchian branch of archosaurs.
Birds
Modern avian species that evolved from theropod dinosaurs.
Closed acetabulum
A hip socket structure found in certain reptiles, including pseudosuchians.
Erect and 'plugged' into sides
A description of the hip and leg structure of certain reptiles.
Sprawling with closed acetabulum
A description of the hip and leg structure of some reptiles.
California Dinosaur
Refers to the limited dinosaur fossils found in California.
Ichthyosauridae
A family of marine reptiles known for their dolphin-like features.

Nothosauridea
A group of marine reptiles that returned to the ocean.
Testudinata / Chelonida
A group of anapsids whose members evolved into turtles and tortoises.
Proganochelys
An early turtle known for its shell structure.
Pterosauria
A clade of flying reptiles that includes pterosaurs.
Dinosauriformes
A group that includes the earliest dinosaurs and their relatives.
Dinosauromorpha
A clade that encompasses the ancestors of dinosaurs.
Sharovipteryx
A crow-sized glider with wing membranes attached to long hind legs.
Icarosaurus
A hummingbird-sized pterosaur with wing membranes extending from modified ribs.
Coelophysis
A dinosaur that is possibly the first dinosaur at ~ 246 Ma, smaller than Rauisuchians but likely faster due to more flexible jointed hip and hollow bones.
Nyasasaurus
An archosaur lineage that evolved into dinosaurs, possibly the first dinosaur at ~ 246 Ma.
Chindesaurus
A small carnivorous bipedal dinosaur, whose name translates to 'ghost lizard' from the Navajo word for evil spirit.
Evolving Cynodonts
Reptile-like mammals typically small in size, many laid eggs but clearly had fur or fur-like coats and suckled their young.
Primitive bats
One of the earliest flying vertebrates, characterized by their small size.
Primitive birds
Reptile-like mammals that had characteristics of both birds and mammals.
Pterosaurs
Early flying reptiles that had evolved from reptile-like mammals.
Triassic Climate
Global climate mostly hot and dry, with arid zones covering much of Pangaea's interior.
Cimmerian Orogeny
Created large mountain ranges the size of modern Himalayas in central Asia 250-150 Ma.
Kazakhstania
A landmass that collided with the Cimmerian plate and landmasses of North and South China.
Plant Evolution
During the Cimmerian Orogeny, seed ferns and cycads were the dominant plants.
Hunter-Bowen Orogeny
A geological event that involved the subduction of a divergent plate boundary transitioning into a transform plate boundary.
Permian-Triassic extinction event
An event that led to a rebound in plant evolution, particularly in seed ferns and cycads.
Taxonomic group uncertainty
Scientists are unsure if certain dinosaurs are a sister group to or a subgroup of dinosaurs.
Fossil evidence of first dinosaur
According to fossil evidence, the very first dinosaur was Coelophysis.
Climate shifts
The climate shifted to more humid as Pangaea began breaking apart (~175 Ma).
Large numbers in fossil beds
Some dinosaurs may have been pack hunters due to large numbers found together in fossil beds.
Jaws characteristics
Some early flying vertebrates had jaws showing both mammalian and reptilian characteristics.
Skull openings in diapsid reptiles
A diapsid reptile skull features one high skull opening behind the eye.
Cimmerian Tectonics
The tectonic activity that resulted in significant magmatism and metamorphism in the Triassic.
Sonoma Orogeny
Formed Sonoma Mountains in west central California during Permian-Triassic transition (~ 250 Ma)
Lesser mass extinction
Occurred at end of Triassic; many archosaurs died out; pterosaurs, dinosaurs, and crocodile relatives would progress.
Marine life extinction percentage
34% of marine life went extinct; nearly all large amphibians went extinct.
Accretion event
Thrusting terrain onto continent (process termed obduction); some dispute this interpretation.
Volcanic eruptions, climate change, meteorite impact
Possibly caused the extinction or a combination of these factors.
Pangaea split
Pangaea split into Laurasia and Gondwana (215-175 Ma).
Early Atlantic ocean development
Open via rifting in north, unopen in south.
Gulf of Mexico
Opens during the Jurassic period.
Paleo Tethys Sea
Closes while Tethys Sea opens via rifting.
Climate Shift
As continents continued to split from Pangaea, more coastlines formed, driving climate change from dry to humid.
Ornithischian
A group of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs with a hip bone structure with open acetabulum and pubis bone pointing tailward.
Saurischian
A group containing all carnivorous dinosaurs, modern birds, and some herbivorous dinosaurs with a hip bone structure featuring open acetabulum and pubis pointing forward.
Hadrosaur
Also termed lizard-like hip dinosaurs; translates to bird foot.
Theropods
Characterized by hollow bones and three-toed limbs; translates to wild beast foot.
Sauropods
Mainly herbivorous saurischian dinosaurs; huge 4 legged dinosaurs with disproportionate head sizes; largest land creatures that ever lived.
Brontosaurus
A type of sauropod characterized by its size and structure.
Allosaurus
A theropod characterized by hollow bones and three-toed limbs.
Iguanodon
A bipedal dinosaur that developed quadrupedal habits later in evolution.
Dinosauromorph
Ancestors of dinosaurs from which more dinosaurs evolved.
Crocodylomorph
Ancestors related to crocodiles that progressed during the Jurassic.
Complex jaws
Most complex jaws utilized for chewing AND grinding food.
Cockchafer
A European beetle also known as doodlebug.
Gondwana
A supercontinent that existed during the Late Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic eras.
Laurasia
A northern supercontinent that included North America and Eurasia.
***-tyrant
A species of small Andean tyrant birds.
Hunter-Bowen Orogeny
An orogenic episode that occurred with a terrain colliding with western North America.
Chuckwalla Orogeny
An orogenic episode associated with eastern Australia.