Lecture 12 - (Ecological Systems) - Human Impacts: Deforestation, afforestation, mining and agriculture
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is deforestation?
the removal of natural forest, sometimes which hasnt been touched by humans
What is the importance of old growth forests
they have successional dynamics over time, supporting rich ecological communities
Why are trees important for streams?
stabilising temperature - through shading
stabilising soils
provides detritus (e.g leaf litter) - organic matter and nutrients
What are species in river ecosystems largely fed by
terrestrial carbon sources - not aquatic.
Shown by stable isotopes which trace energy flow through the food web
How does large woody debris affect rivers
creates a step profile = creating energy dissipation of the water
provides bank protection
creates debris dam = retention of organic matter
log jams can stop the water from flooding, and force new channels
How does large woody debris impact wildlife in river ecosystems
acts as a food resource e.g for scrapers, tunnelers etc.
Acts as a habitat - some insects bury in the wood
How does large woody debris affect sockeye salmon
they live in old undisturbed freshwaters their whole lives
habitat is a key limiting factor to salmonoid production
large wood debris provides cover for spawning fish
What is the ideal environment for salmonoid spawning
course gravel with little matrix of fine sediments
allows clean, well oxygenated water for egg development
Why is silt problematic to salmonoid production
reduces flow and dissolved oxygen = affects egg development
What is yarding?
dragging the logs to a central area for transport = disturbing the soil and generating sediments
Give an example showing how timber harvest affects salmon
Williamette river - Oregon
logging there has created a more simple flow
more light and nutrients from the soil = more algae
more sediment being washed into the river = reduces permeability of gravels = reduces egg fry survival
20% fine sediment = no survival of fish
What is phase 1 of the effects of timber harvest on streams
high algal growth = more autotrophic
optimal light and nutrients
less CPOM
What is phase 2 of the effects of timber harvest on streams
low to moderate algal growth
low nutrients
nutrient limitation contains patchiness
What is phase 3 of the effects of timber harvest on streams
low algal growthlow nutrients
light nutrient interactions create small scale interactions in patchiness in algae growth
Why would creating a buffer zone help act as a best management practice
most valuable forest in the zone 30m from the bank = would be main source of CWD and leaf litter
the less wood that is in streams = the less fish present
However - the best timber is found in this 30m strip
Why would managing drainage patterns act as a best management practice
to prevent runoff of pollution from roads from deforestation
why would preventing conifers from being planted in catchments sensitive to acidification be a best management practice
prevents the trees from dying
however limestone in areas can make trees less vulnerable through its natural buffering capacity
What are the three main stages of tree production
ground preparation
closure of canopy
felling
Explain ground preparation as a stage of tree production
ploughing, draining and road construction before planting
impacts: high sediment into channels, increased storm flows, leaching from soils
explain closure of canopy as a stage of tree production
increased interception of deposition
reduces temperature extremes
reduces light availability
reduces macroinvertebrate abundance and trout
Explain felling / logging as a stage of tree production
increased sedimentation, altered flow regimes etc.
How does grazing affect freshwater systems
removal of natural vegetation
altered hydrology
reduced inputs of natural organic material
increased sediment erosion
livestock manures
How does arable farming affect freshwater systems
removal of natural vegetation
reduced inputs of natural organic material
increased sediment erosion ploughing
= creates diffuse pollution = more difficult to manage than point sources
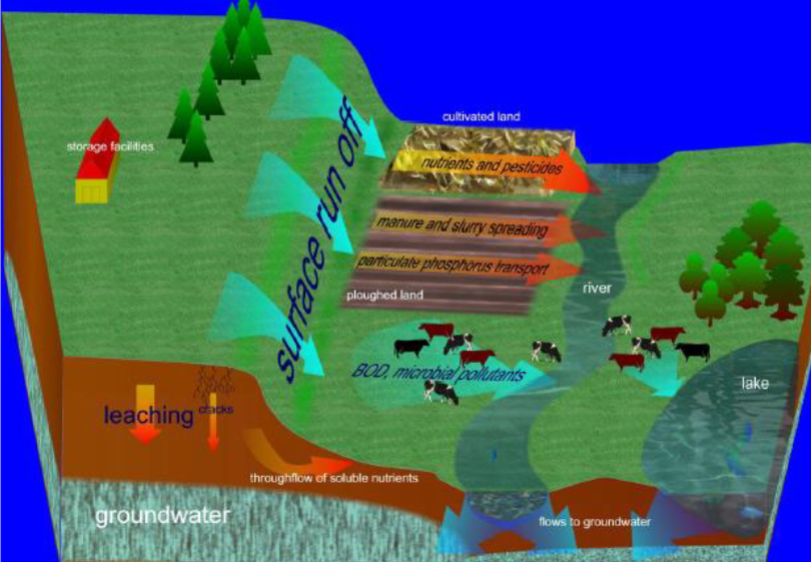
does organic pollutants have high BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) ?
organic pollutants (e.g manures) have very high BOD
clean river water = <5mg L^-1
cattle slurry = 10,000-20,000 mg L^-1
What are the impacts of nutrients?
increased turbidity = limits light = less rooted plants
less biodiversity - some plants can outgrow the others
What are the sources of nutrients and sediments?
sewage works
domestic septic tanks
sediment erosion is increased by seed drilling, livestock trampling
What are the impacts of sediments on streams
reduced space in gravels
reduced flow and dissolved oxygen
reduced light penetration
What are the impacts of pesticides?
death of natural plants, invertebrates etc.
potential increase in more tolerant organisms
Example: chironomids - stress tolerant - can survive in low oxygen environments.
What are neonicotinoids?
= an insecticide which is normally soaked into seeds = has multiple ways of leaching into the river - most of it stays in the soil
largely banned in the UK - but farmers can apply it to increase sugar beet yields
What are the best management practices for fertilisers?
sow autumn crops early
sow cover crops in winter
careful management of farm wastes
fence off livestock
How does mining affect rivers?
huge amounts of sediment generated
abandoned gravel heaps (tailings) = leaches heavy metals into the river
causes formation of ferric hydroxide = impacts on algae, invertebrates etc.
what are the best management practices for mining for protecting rivers?
use settling ponds - traps and removes sediments
recontour streams - to return to its natural course
remove tailings - so it doesn’t leach
replant with natural vegetarian