Chapter 41: Osmotic Regulation and Excretion
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
this results from excessive intake of water too quickly, which disrupts the balance of electrolytes in the body
water toxicity/poisoning
the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane is ___
osmosis
true or false: during osmosis, water moves from an area of low concentration (high solute concentration) to an area of high concentration (low solute concentration)
false. during osmosis, water moves from an area of high concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low concentration (high solute concentration)
this numerical value represents the solution’s total solute concentration
osmolarity
true or false: water moves from an area of low osmolarity to an area of high osmolarity
true
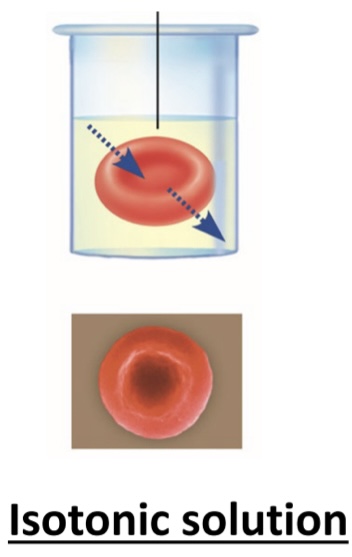
in this type of solution, the concentration of solutes is equal inside and out the cell
isotonic solution
in this type of solution cell shrinkage occurs because the concentration of solutes is lower inside the cell and higher outside the cell, so water leaves the cell
hypertonic solution
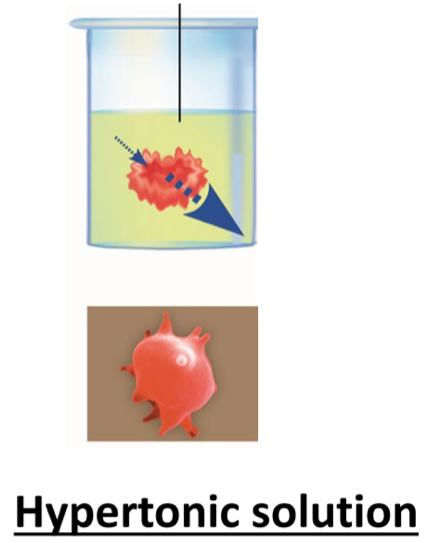

in this type of solution, swelling occurs because the concentration of solutes is higher inside and lower out the cell, so water enters the cell
hypotonic solution

the process of maintenance of salt and water balance (osmotic balance) arose membranes within the body’s fluids (water, electrolytes, non-electrolytes) is defined as ___
osmoregulation
this organ is the primary organs that filters blood, removes waste, maintains osmotic balance, and produces urine in the excretory system
kidneys
this vessel braces into capillaries, and brings oxygenated blood containing waste to the kidneys via the aorta
the renal artery
this vessel branches into venules, and sends filtered blood out of the kidneys via the vena cava
the renal vein
this organ sends urine from the kidneys to the bladder
ureter
this organ collects and acts as a storage site for urine
bladder
this organ sends urine from the bladder out of the body
urethra
the protective face of the kidneys is called the ___
renal fascia
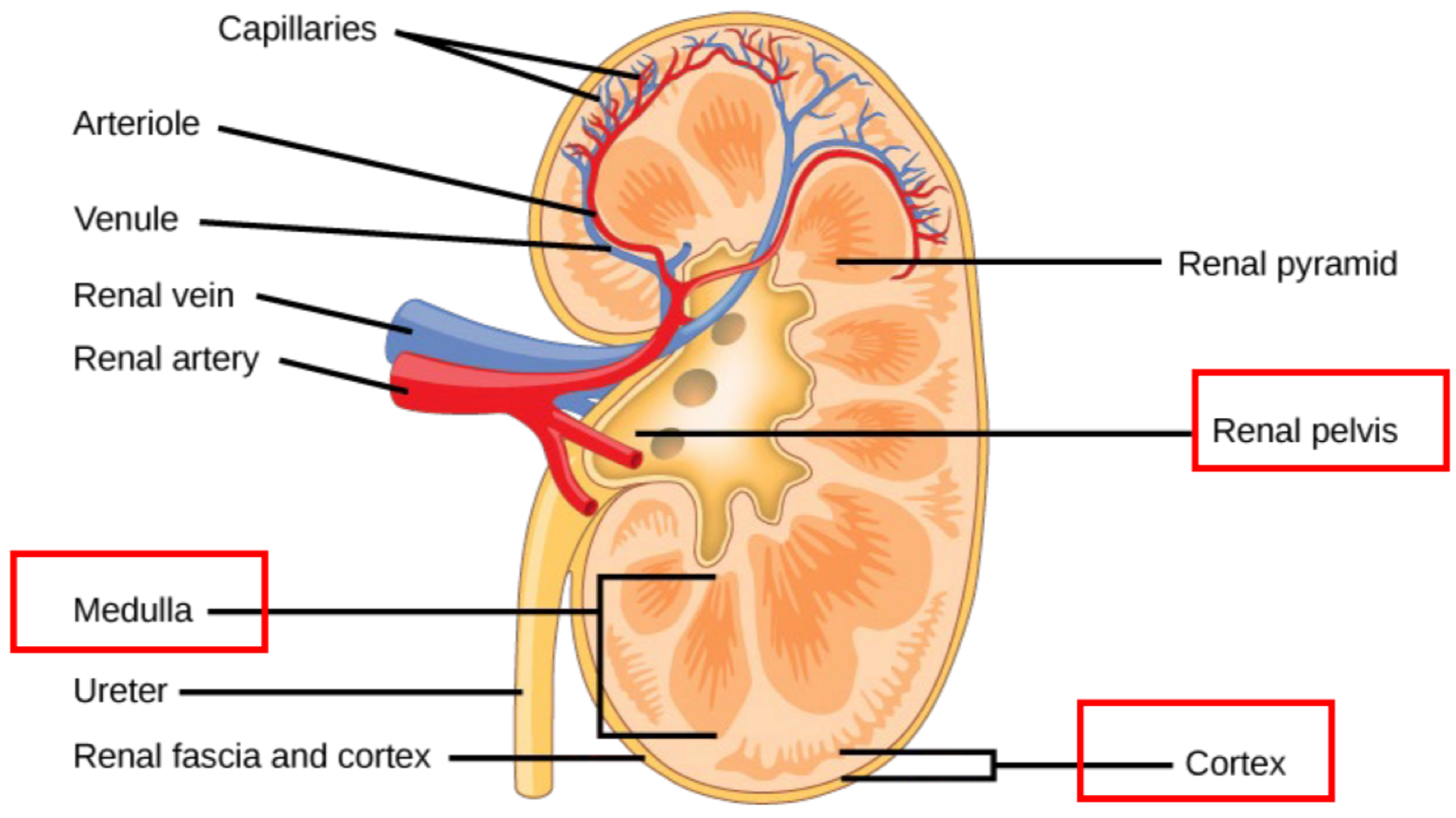
the outer layer of the kidneys is called the ___
cortex
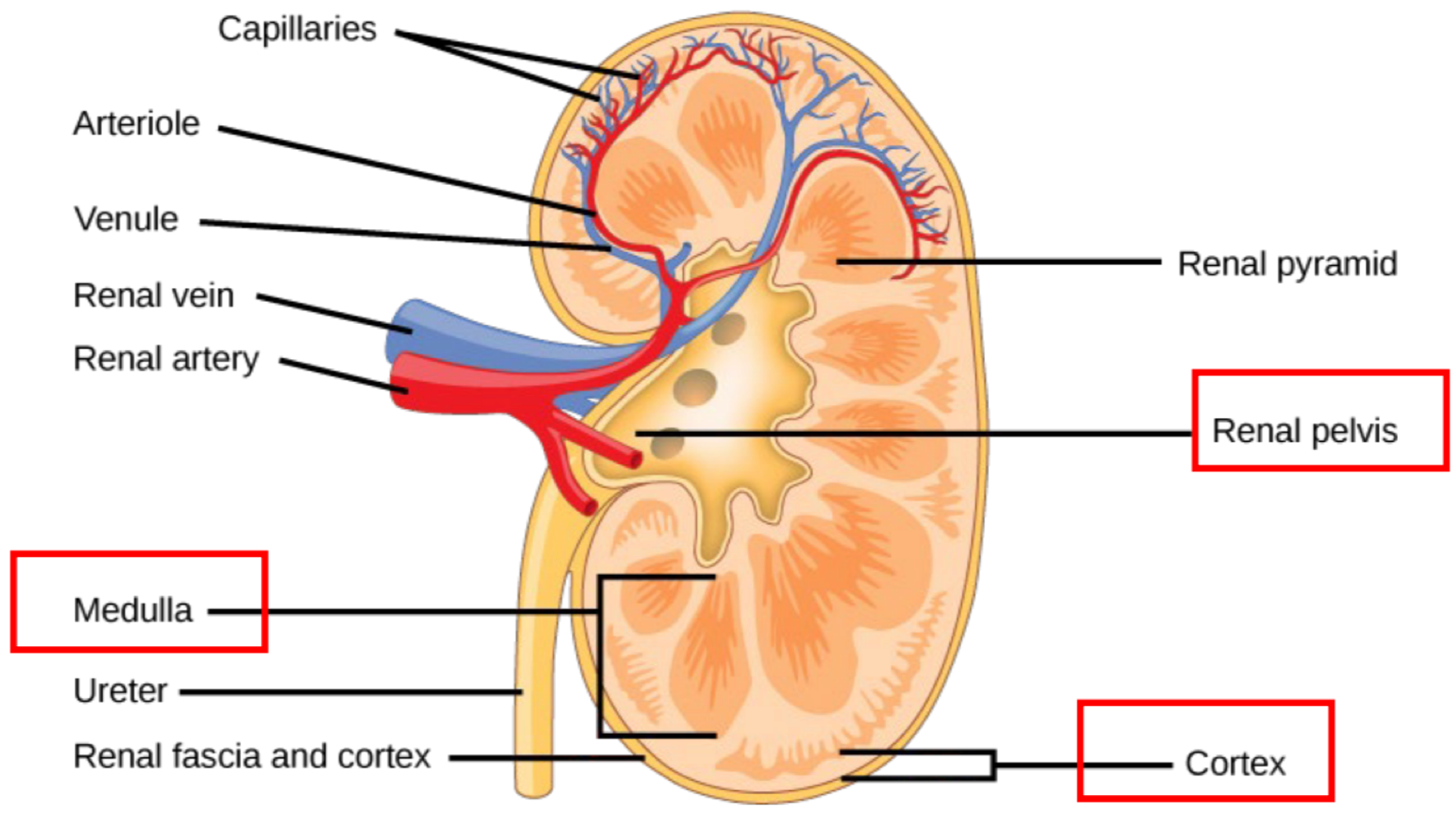
the middle layer of the kidneys is called the ___
medulla
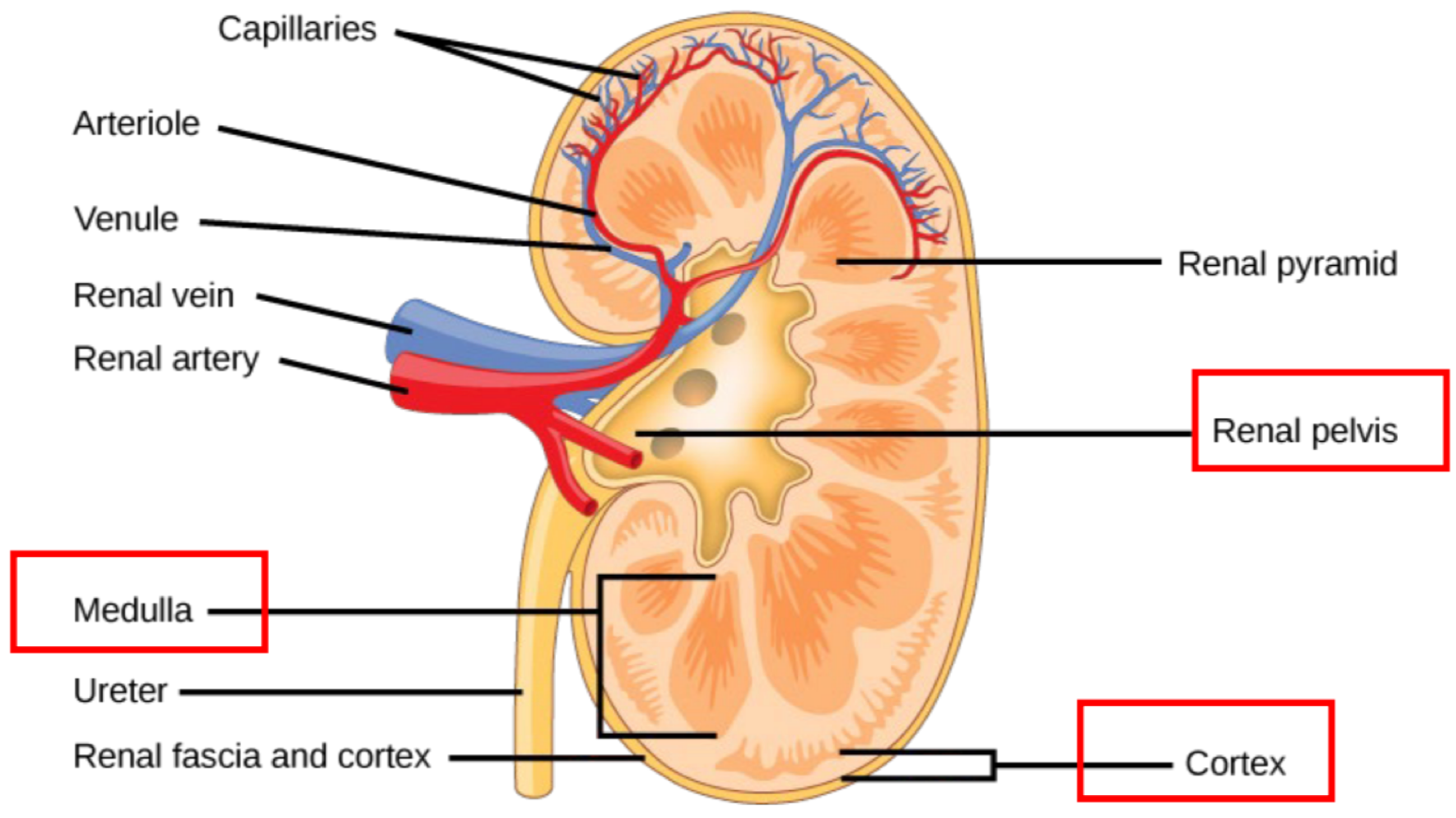
the concave inner section of the kidneys connected to the ureter is called the ___
renal pelvis
the functional unit of the kidneys expanding from the cortex to the medulla that filters blood and removes waste to create urine
nephron
the filtration site of the nephron is called the ___
renal corpuscle
the dense network of capillaries that sends liquid to the Bowman’s capsule via glomerular filtration is called the ___
glomerulus
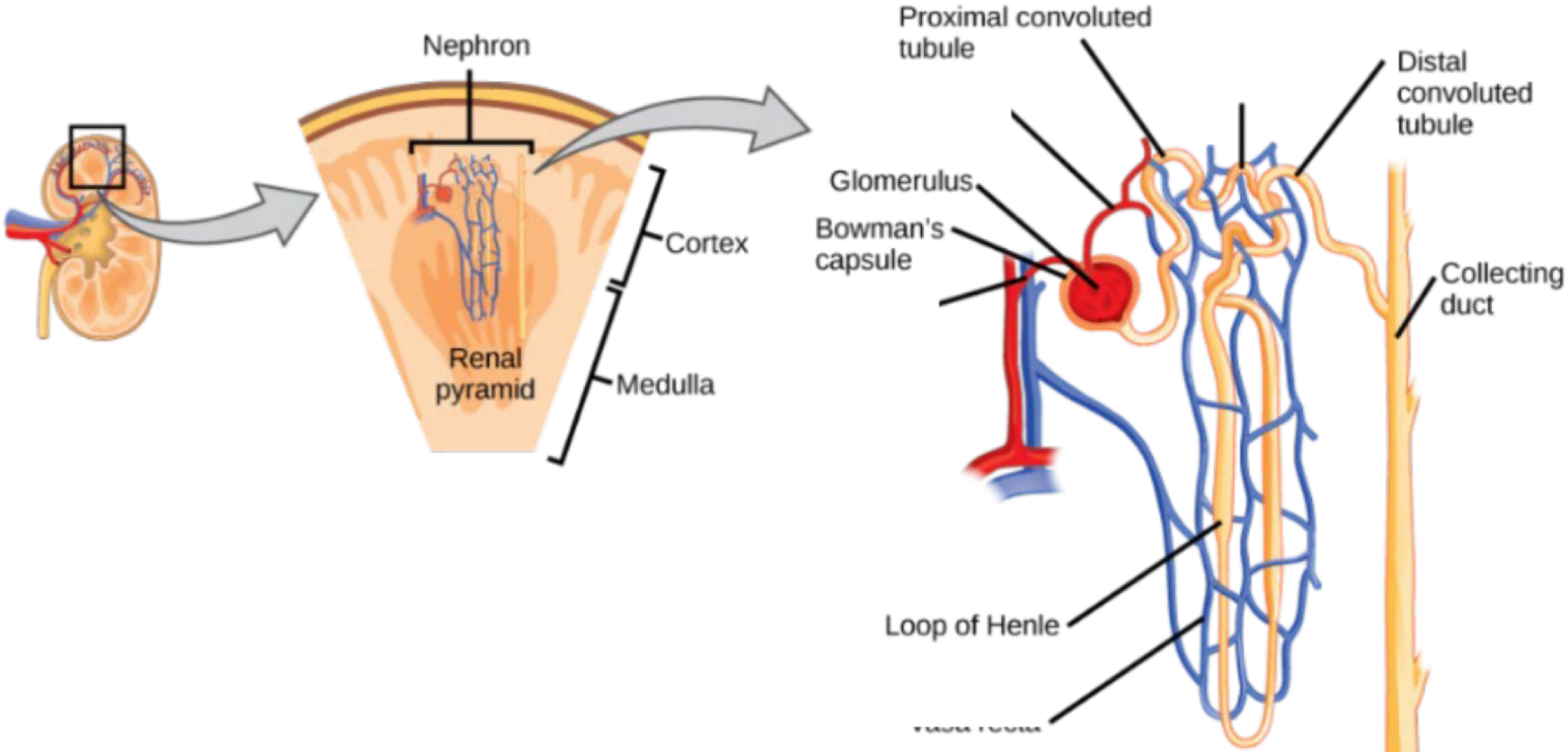
the structure surrounding the glomerulus that receives the liquid (primary urine), which contains water, glucose, salt, etc.
Bowman’s capsule
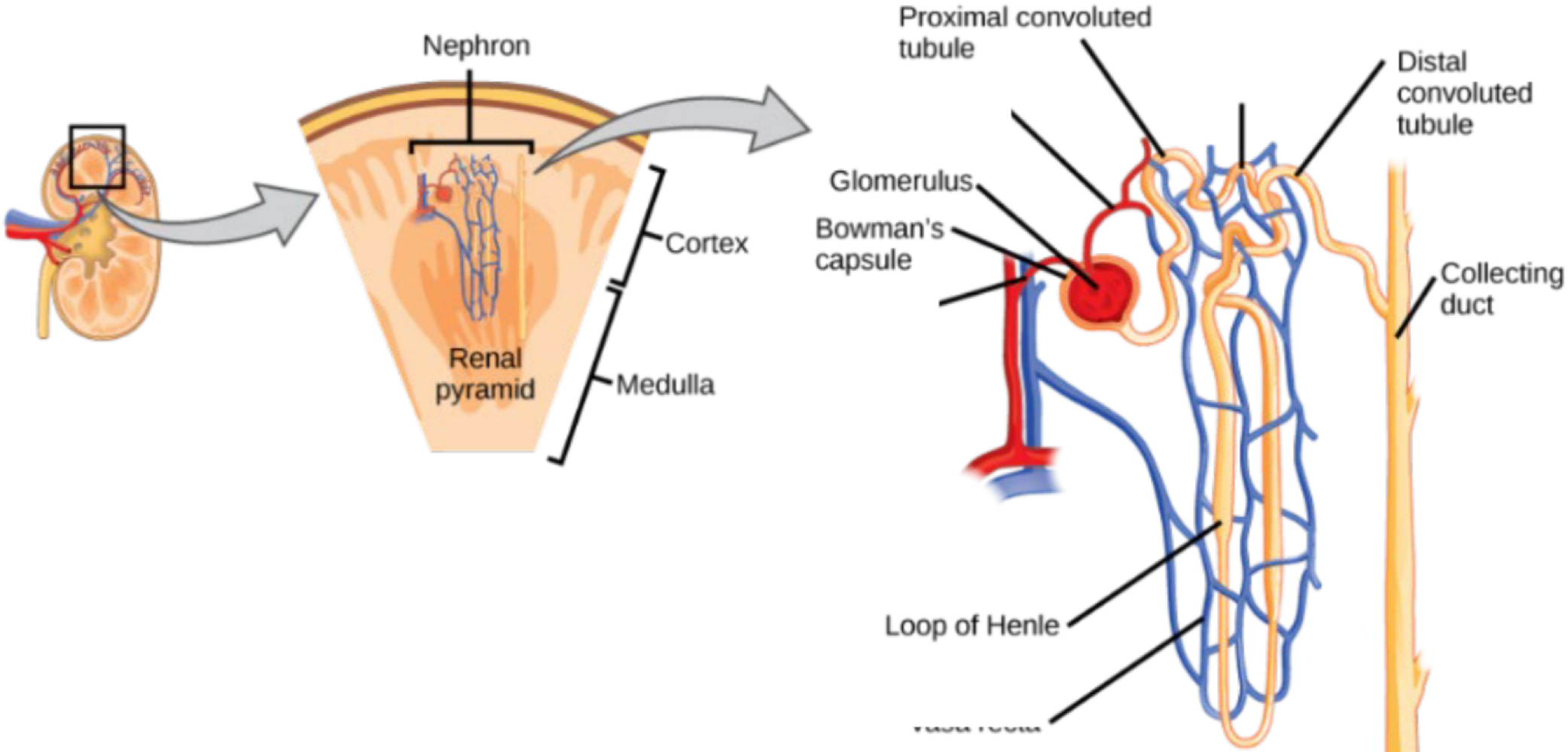
what structure reabsorbs substances in the primary urine?
renal tubule
in which section of the renal tubule is urine the closest to the kidneys?
the proximal convoluted tubule
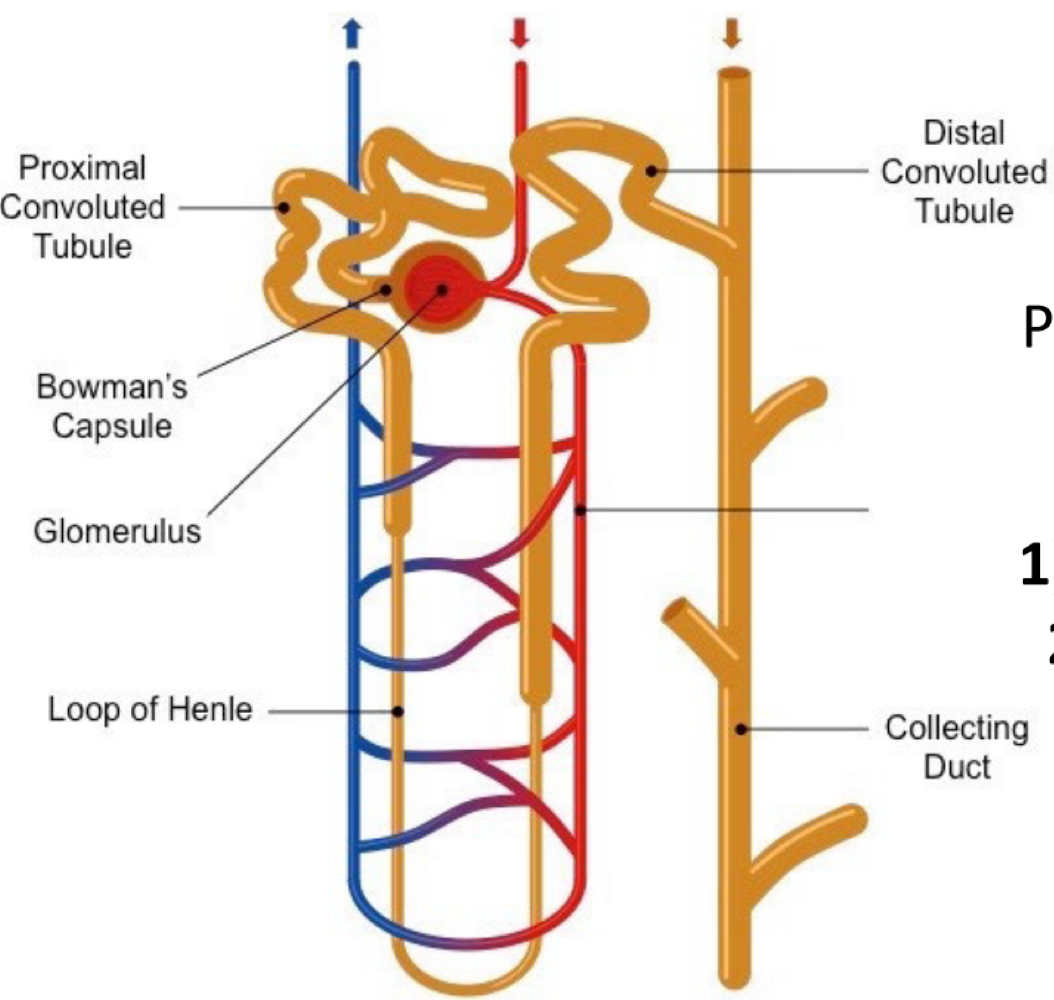
in which section of the renal tubule does urine go down?
the descending loop of henle
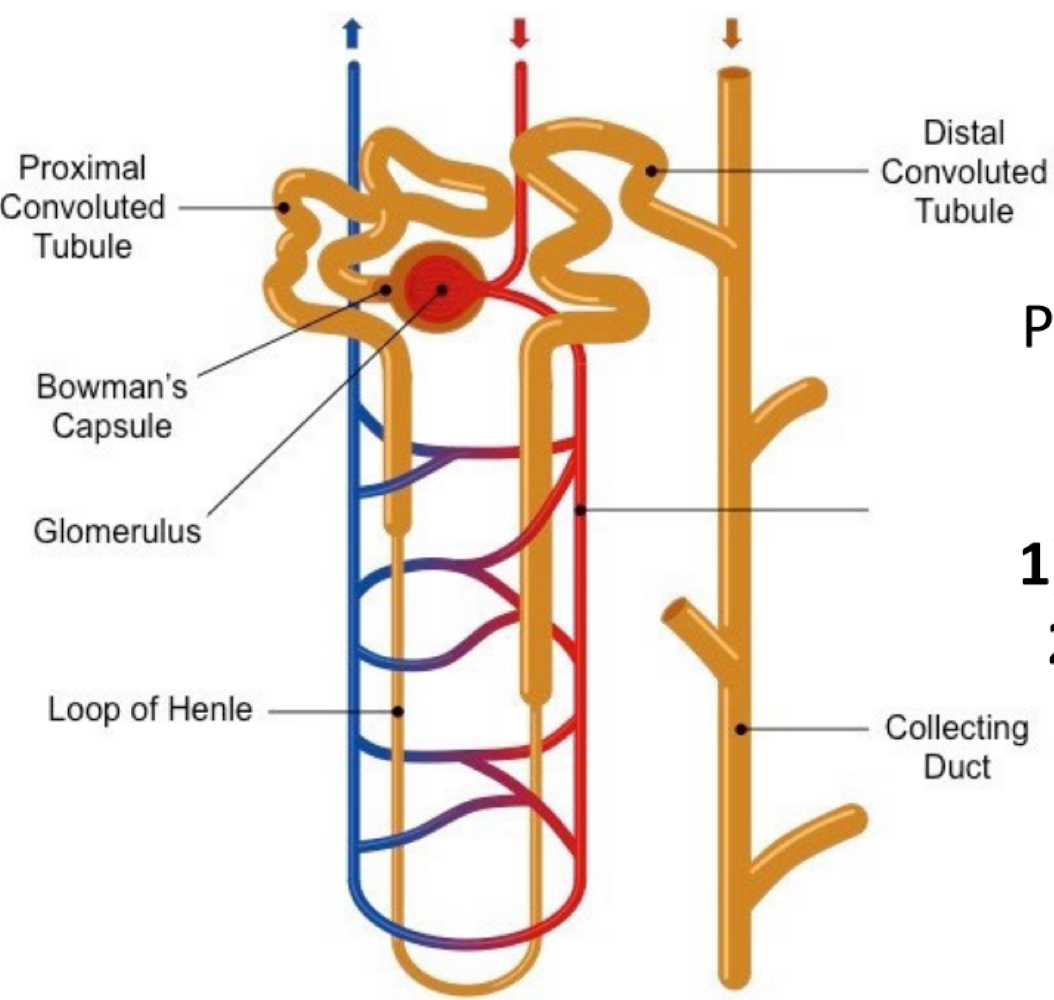
in which section of the renal tubule does urine go up?
the ascending loop of henle
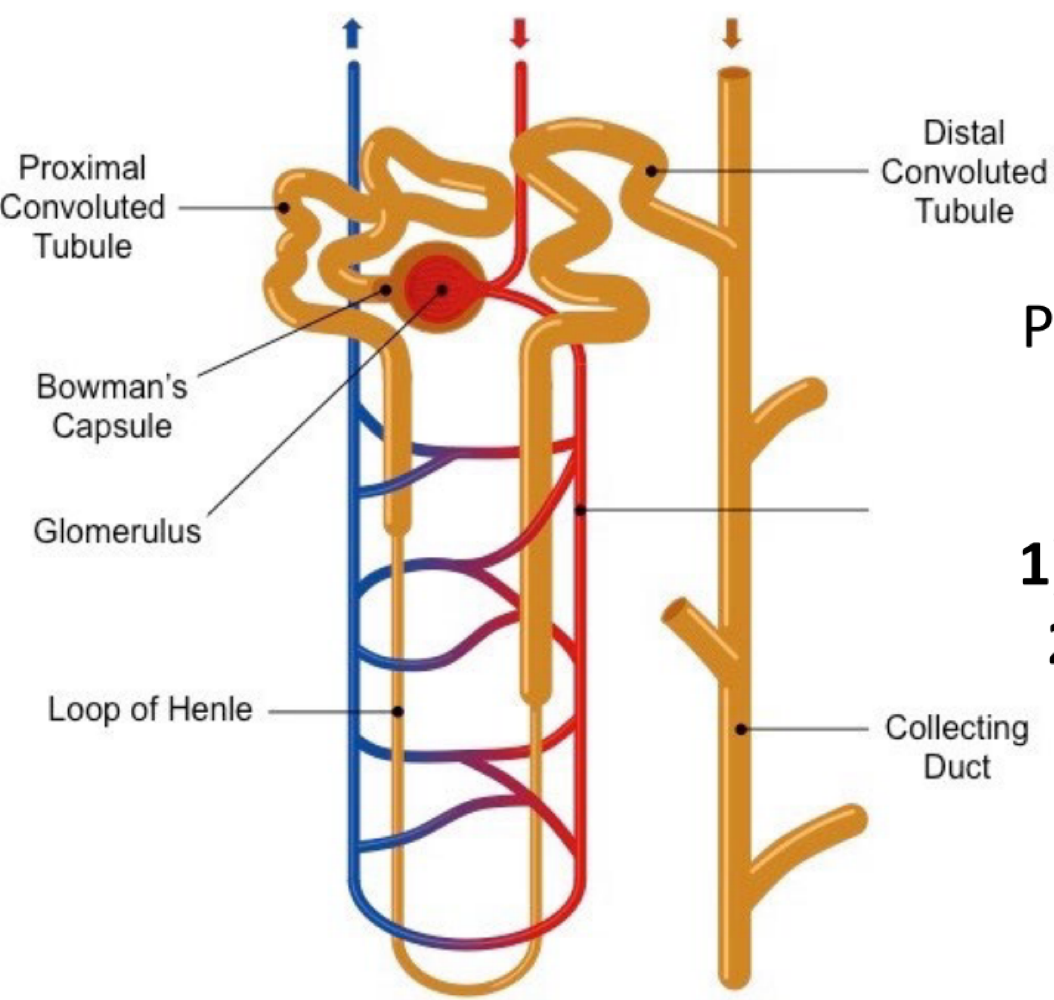
in which section of the renal tubule is urine the furthest from the kidneys?
the distal convolute tubule
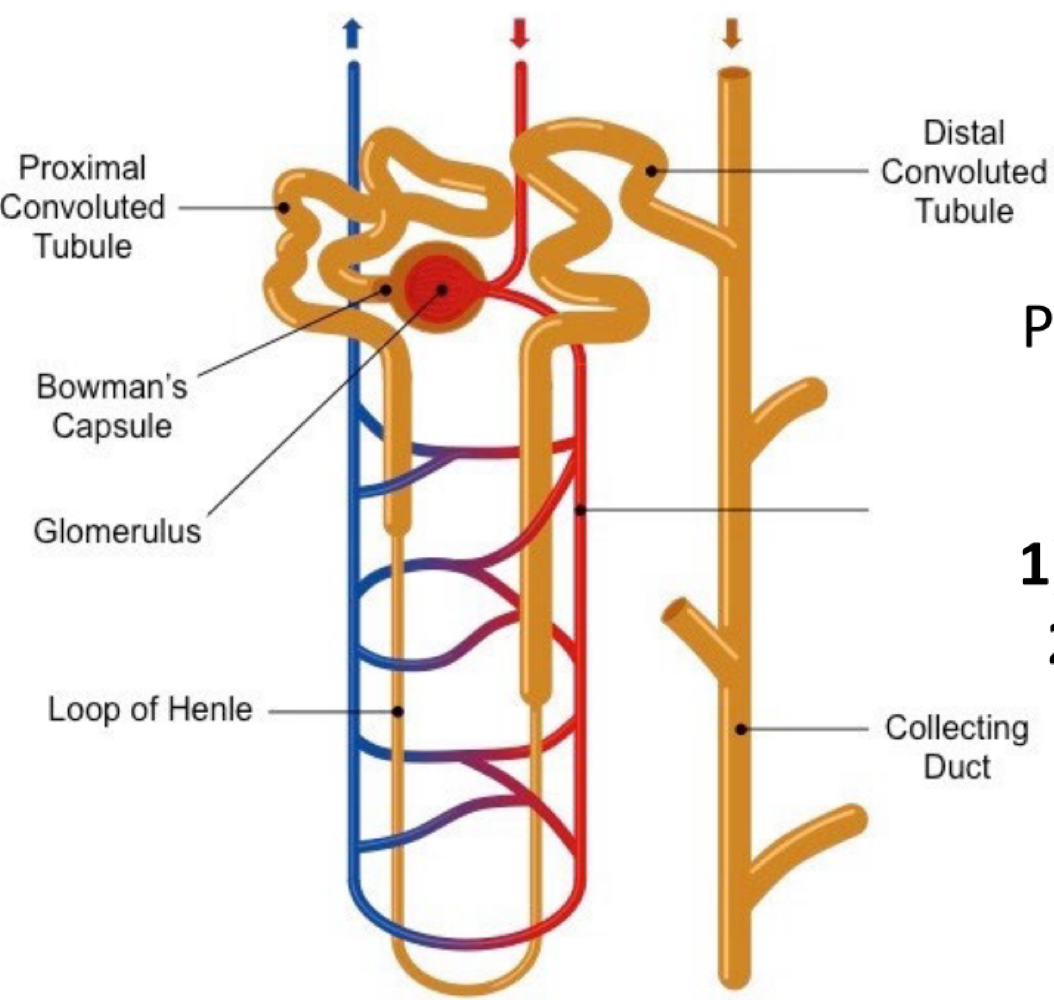
the surrounding capillaries that interact with parts of the renal tube are called the ___
associated capillary network

true or false: more than half of water and ions are reabsorbed in the associated capillary network
true
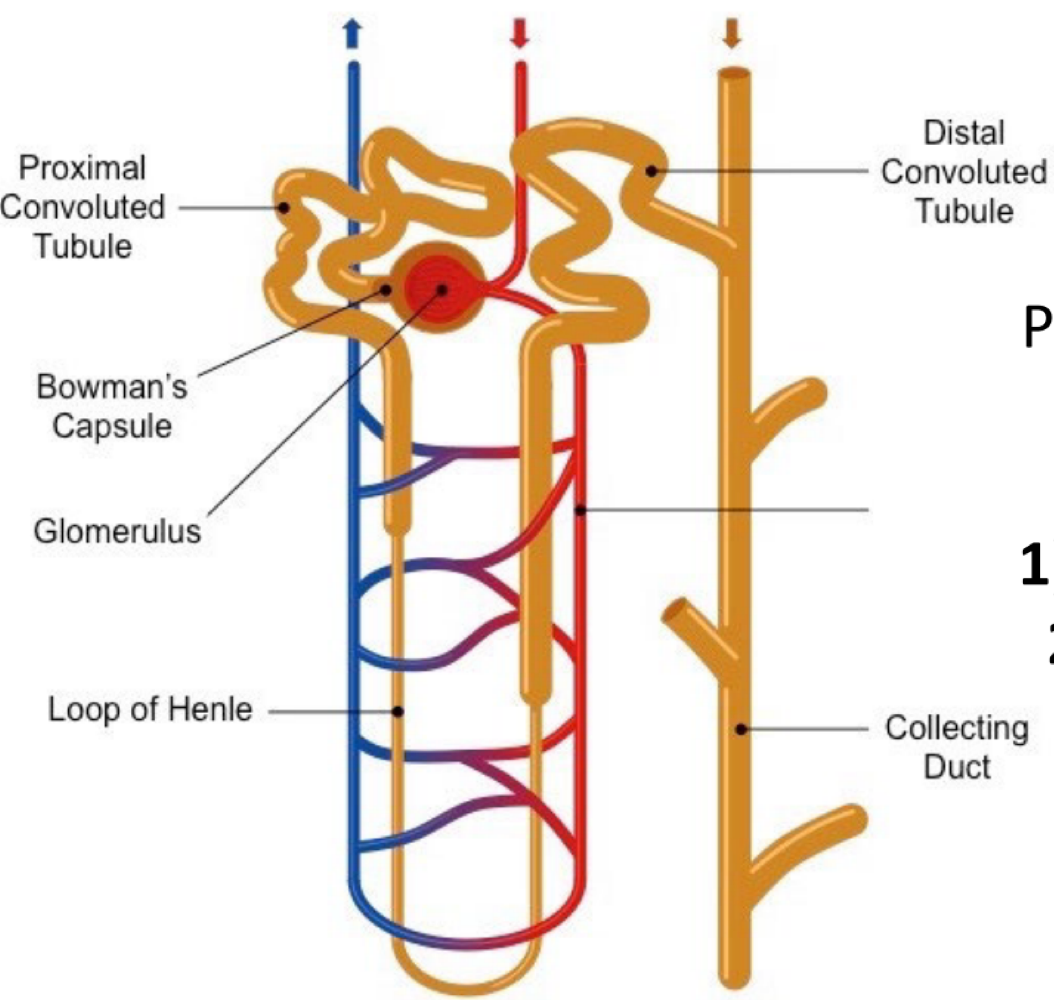
during urine formation, blood pressure forcing solutes into the nephron result in the start of what in the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule?
filtration
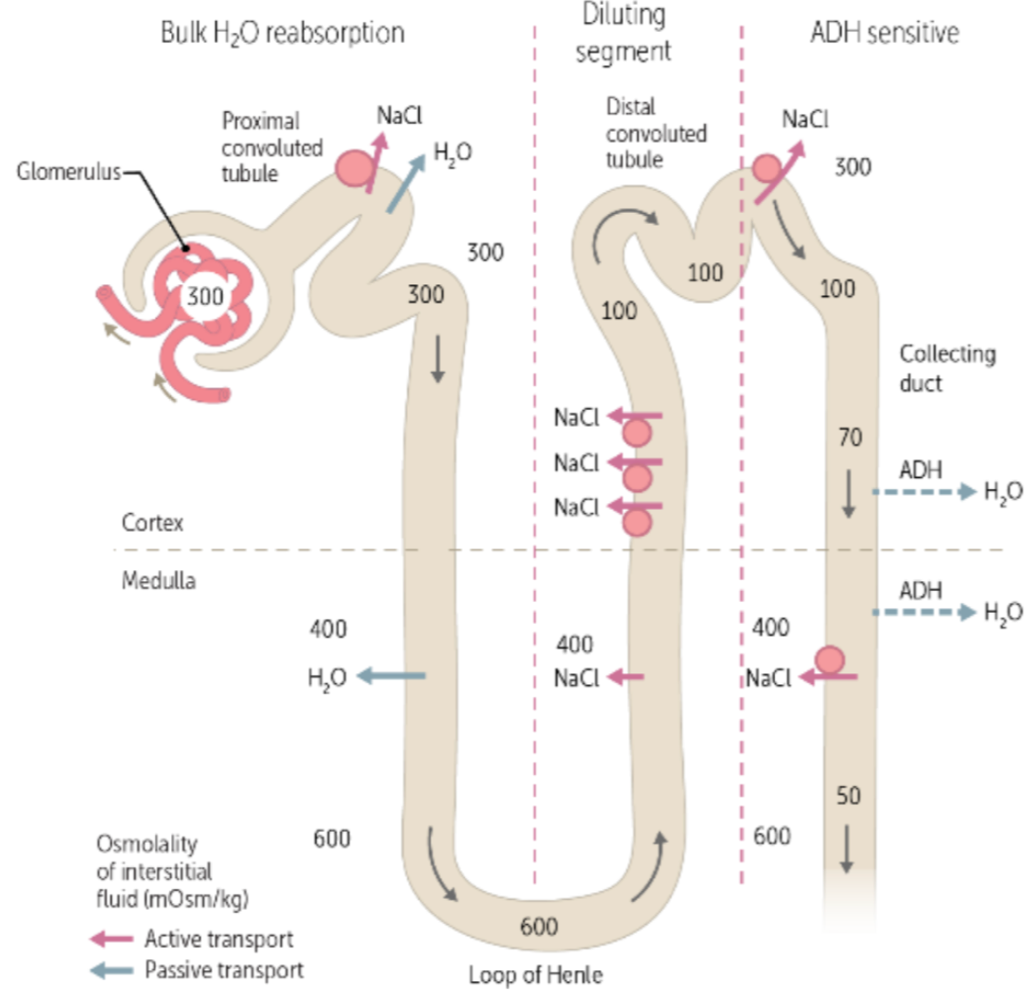
during urine formation, the reabsorption of water, NaCl, glucose, and amino acids, and the secretion of drugs, uric acid, and creatine occurs in the ___, where the osmolarity is ___
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), 300
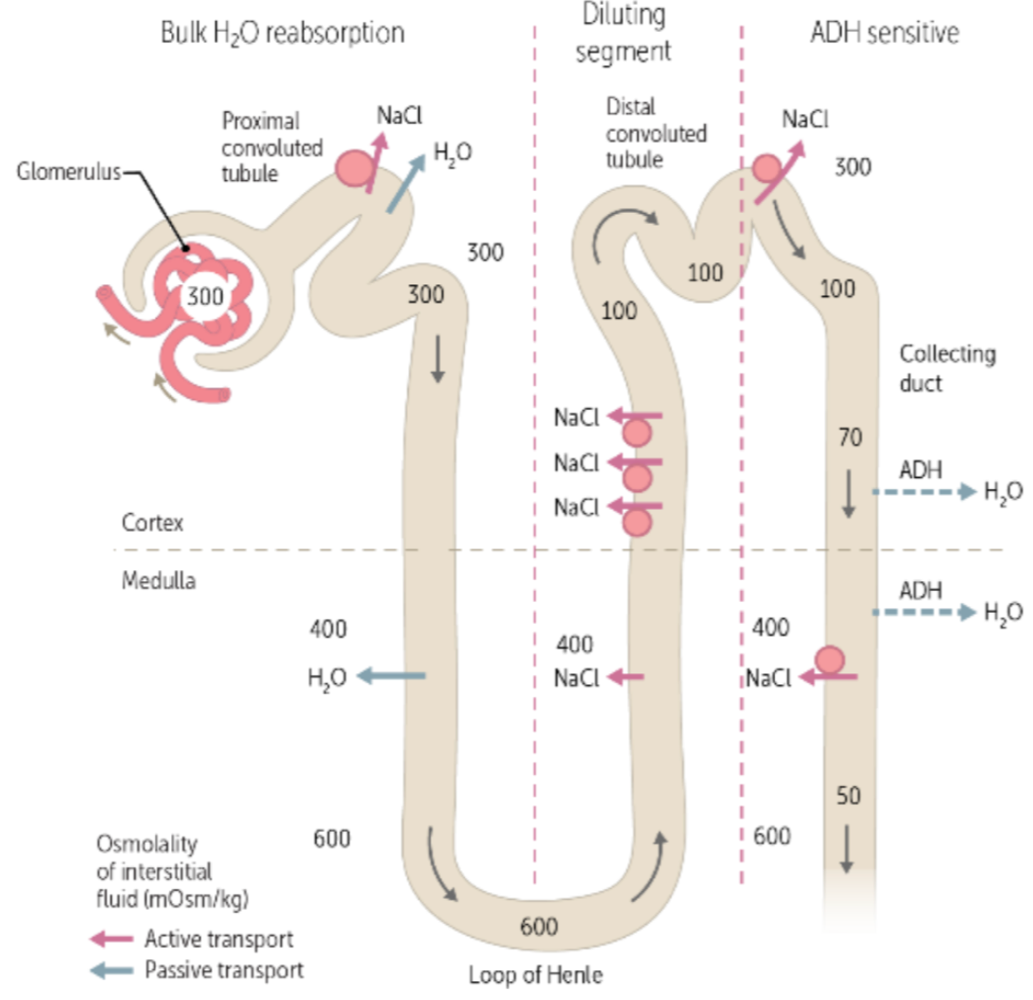
during urine formation, the reabsorption of water via aquaporins (water channels in the cell membrane) occurs in the ___, where the osmolarity increases to ____
descending loop of henle, 600
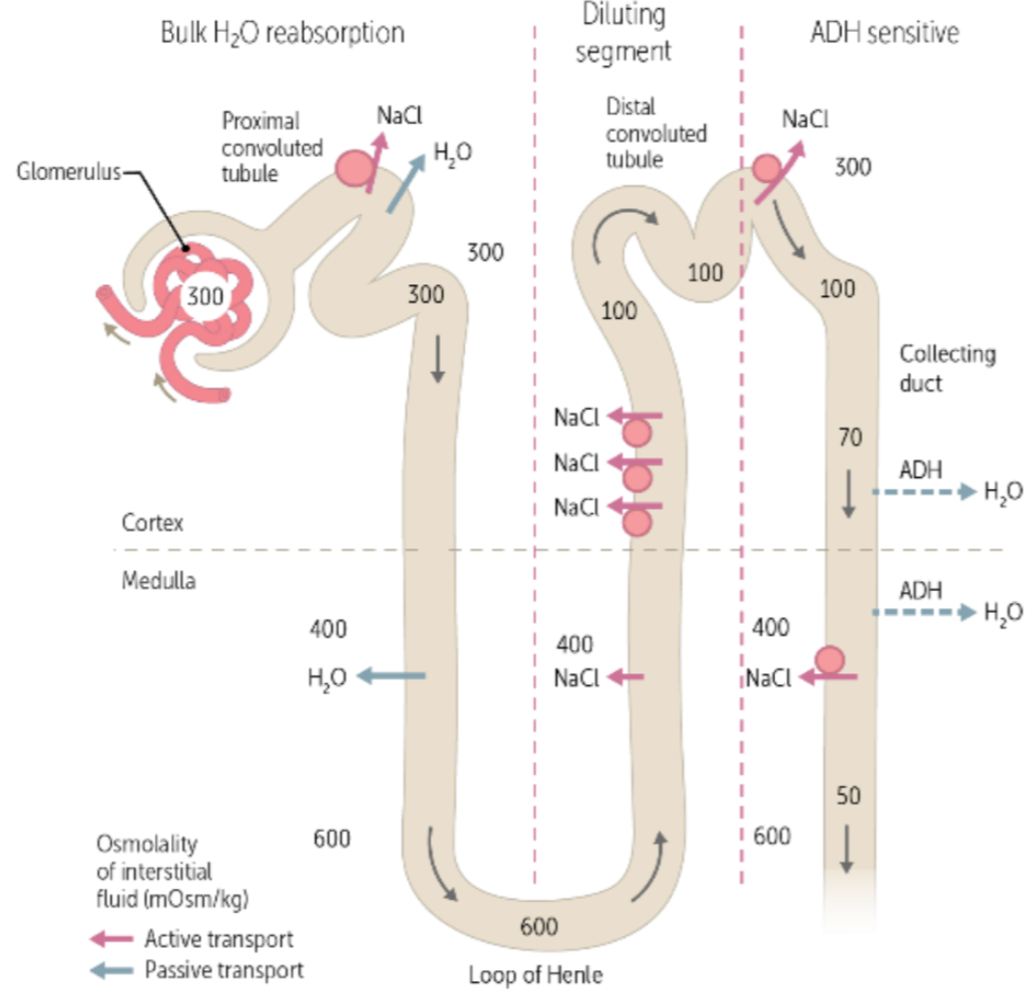
during urine formation, the reabsorption and transportation of NaCl creating an osmotic drive that allows water to be reabsorbed occurs in the ___, where the osmolarity decreases to ___
ascending loop of henle, 100
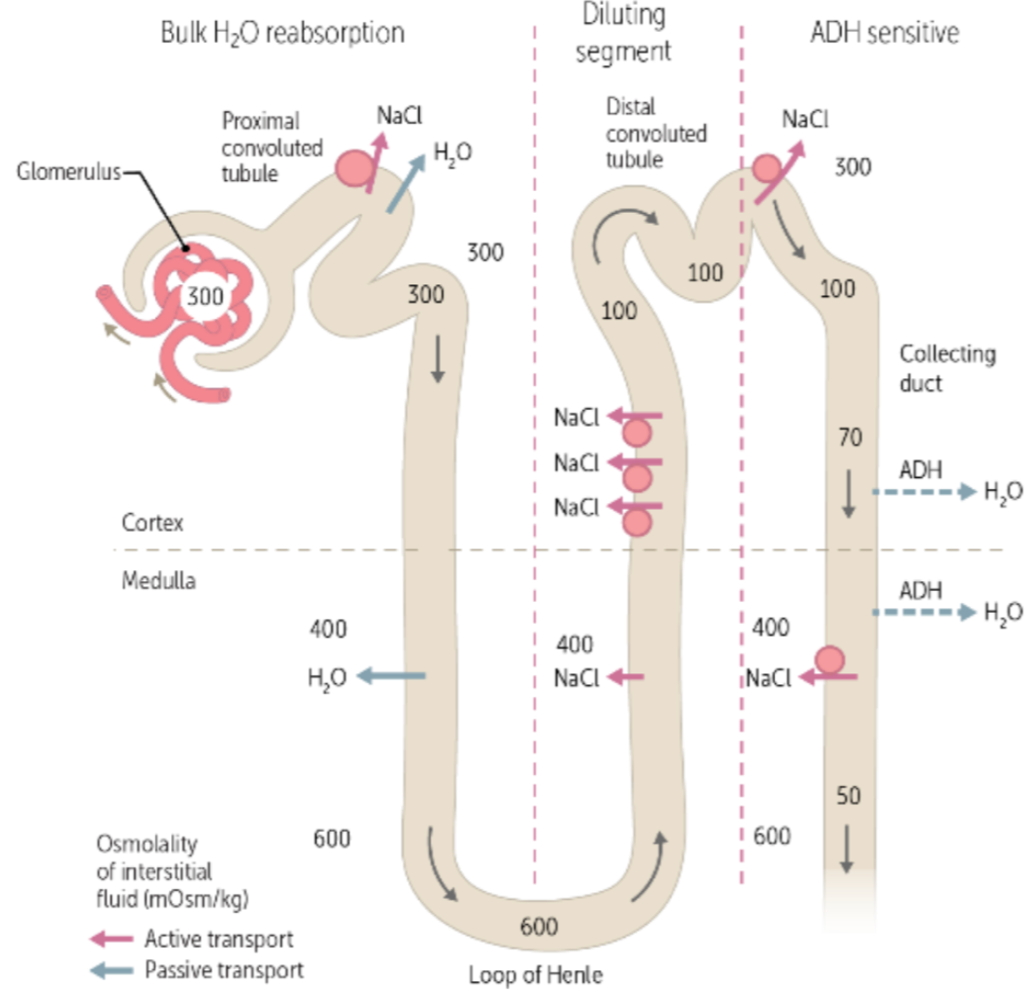
during urine formation, the reabsorption of NaCl and the secretion of potassium and hydrogen occurs in the ____, where the osmolarity is ___
distal convoluted tubule (DCT), 100
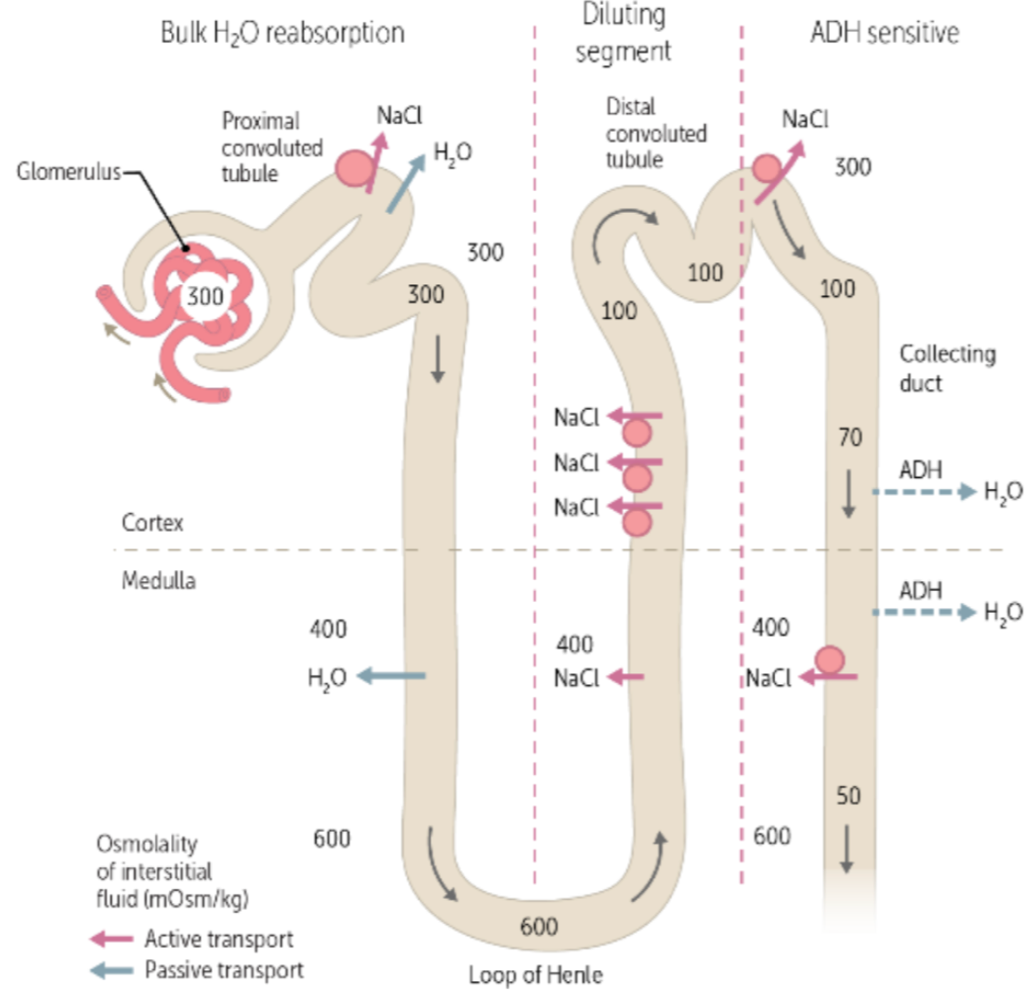
during urine formation, the regulation of urine volume and osmolarity via hormones occurs in the ___
collecting duct
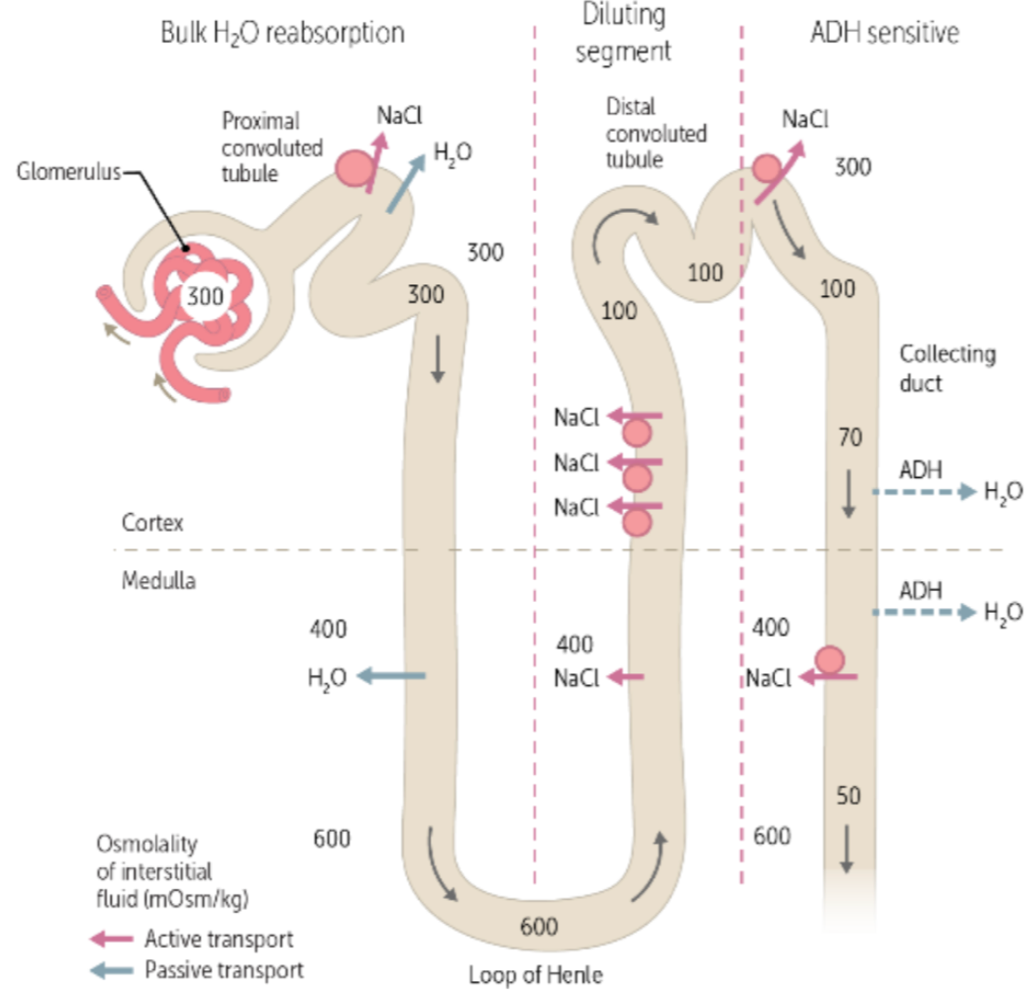
this hormone is produced by the hypothalamus and is critical for osmoregulation in the collecting duct
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
true or false: ADH is released when the brain detects a decrease blood pressure and blood osmolarity
true
true or false: ADH binds to receptors in the collecting duct cells, causing a decrease in aquaporins present there
false. ADH binds to receptors in the collecting duct cells, causing an increase in aquaporins present there