4.1 Water systems
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
the main stores of the hydrological cycle are
oceans (96.5%), glaciers and ice caps (1.7%), groundwater (1.7%), surface freshwater (0.02%), atmosphere (0.001%), and organisms (0.0001%)
Hydrological cycle
includes transpiration, evaporation, sublimation, condensation, advection, precipitation, melting, freezing, surface runoff, infiltration, percolation, streamflow, and groundwater flow
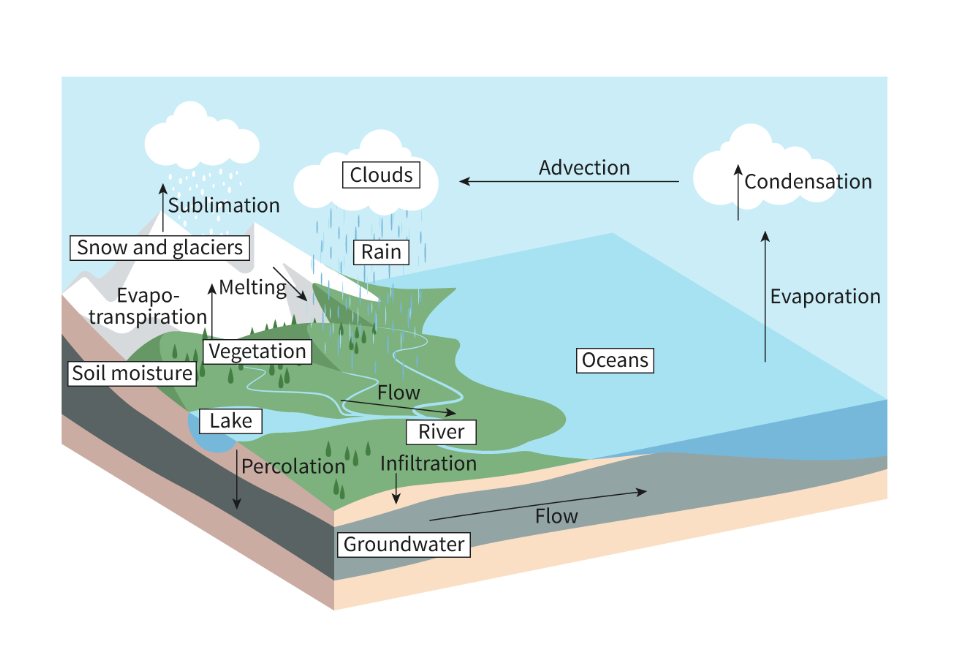
Evaporation
water from storages, such as oceans, lakes and rivers, is transformed as it evaporates from liquid water to gaseous water vapour, Heat provided by the sun is required for evaporation of water
Transpiration
plants take up liquid water from the soil and release it as gaseous water vapour through their leaves. The combined water loss from evaporation and transpiration is known as evapotranspiration.Heat supports transpiration in plants
Advection
in the atmosphere, advection allows for the wind-blown movement of water vapour or condensed water droplets. The energy of the wind derives from solar radiation
Freezing/Melting
Solar radiation provides heat energy that causes solid snow or ice to melt into liquid water. In colder conditions, with less solar radiation and heat, water can freeze back into ice
Sublimation
If the air temperature is below freezing, sublimation of ice directly to water vapour can occur. The solid ice or snow absorbs so much heat energy that it is converted directly to gaseous water vapour
Condensation
As water vapour rises higher in the atmosphere, it cools and condenses into liquid water droplets, forming clouds. Heat is released as water condenses
Precipitation
The downward force of gravity allows liquid water to return to the Earth's surface as precipitation, in the form of rain, snow, sleet or hail
Infiltration
Part of the water that falls on the surface enters the soil through infiltration,
Percolation
water movement in the soil
Runoff
The water not absorbed into the soil enters rivers, lakes or oceans as surface run-off. This process eventually restores streamflow
in rivers and lakes as well as groundwater flows
Human activities such as agriculture, deforestation, and urbanisation can alter these flows and storages
Can lead to reduced evapotranspiration and increased runoff, resulting in flash floods
Impacts of human activities
reduced vegetation cover, reduced interception, more ground compaction, more overland runoff, increased flooding, decreasing amounts of permeable surfaces
When a system is in steady state for a body of water
Total Input = Total Output