SEG
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To make practice tests
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Clean code
- Ensure source artefacts are readable
- Reduces technical debt
Technical debt
Extra development work required in the future to compensate for taking shortcuts in development time now
How to write clean code
1. Start by writing code that works
2. Refactor code to improve non-functional features
Naming conventions
- Don't leave false cues in your code
- Have good grammar
- Make meaningful distinctions
- No noise words like "the" and "an"
- Use constants to replace magic values
Commenting conventions
- When possible, explain yourself in code
- If function is a bit more complex, write some comments
- Write decorators for specific functions
Function conventions
- Functions should do one thing, they should do it well, they should do it only
- One level of abstraction per function
- Functions should have as few arguments as possible
- Avoid using flag arguments to change the way the function does something
Step down rule
Every line in a function is kept to the same level of abstraction, one level below the name of the function
Command Query Separation Principle
Function should either do something, or answer something, but not do both
DRY vs WET code
- DRY: Don't Repeat Yourself
- WET: Write Everything Twice/ We Enjoy Typing
What does the Boy Scout Rule refer to?
Code refactoring
Boy Scout Rule
Leave it cleaner than you found it
Project delivery
- Delivered end result must be usable, must include source code, and have a deployed system
Deliverables: source code
- Include test suite, installation/config instructions
- Ensure all code and instructions works on recipient machines
Deliverables: deployed system
- Add data, user accounts, necessary docs
- Production env is more restrictive than dev env
Project health assessment
- Review of progress towards deliverables and project as a whole
- Categorises user stories into "in danger", "at risk", "on target"
Project status report
Shows statuses on report and a plan for dealing with the active risk
Scope discovery
- A welcomed scope change that improves result
- Derived from a better understanding of project purpose
Scope creep
- An unwelcome scope change undermining other project constraints
- Increases cost/time without adding value
- Confuses project purpose
- Makes someone happy with no benefit
What package do we use to track coverage in Python projects?
``coverage``
Command to get code coverage of tests
`$ coverage run manage.py test`
Command to get code coverage report
`$ coverage report`
Command to get HTML version of coverage report
`$ coverage report html`
Types of development testing
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- UI testing
- Partition testing
Unit testing
- Test units of code in isolation
Benefits of unit testing
- Fast
- Pinpoint defects with precision
Integration testing
- Test interaction between units
- Testing external units should be done with mocks e.g mock API
UI testing
- Test human interaction with interface
Constraints of UI testing
- Hard to test
- Slow to run
- Time consuming to write
- Have to test whole system so defects are hard to diagnose
Partition testing
Partition tests into general cases
Test coverage
- How much of source is executed during testing
- Proportion of program statements executed during testing
Other types of coverage
- Branch coverage: proportion of branches in which code was run during testing
- Loop coverage: proportion of iterations executed 0, 1, and multiple times
- Path coverage: proportion of possible paths through the code run during testing
Project execution
- After initiation + planning
What can we use to prioritise tasks for project execution?
Urgency-Importance matrix
Urgency-Importance Matrix
- Matrix with urgency on the x axis and importance on the y axis
What is used to check project progress?
Team accountability sessions
Team accountability session
- Meeting to discuss progress
- Everyone talks about individual progress + agrees to new commitments
- Identify barriers to progress
Properties of good software
- Functional suitability
- Maintainability
- Reliability
- Performance
- Security
Quality control
- The strategy for minimising errors by managing each stage of production
- Done through testing + inspection & review
Development testing vs performance testing
- Development testing: testing if the software system output is as expected for a given input
- Performance testing: testing amount of stress the software can take
Inspection/reviews
- Used to assess documentation + code quality
- Inspection is more labour-intensive than review
- Review is not good with new standards/holistic assessment
Code review
- Assess changes in code
- Works well w/ version control software
Code inspection
- Examine whole code in the code
- Requires planning + organisation
- Requires follow-up
What does agile development aim to do?
- Reduce formal documentation
- Refocus on delivery of working software
- Improve adaptability to changing customer requirements
Agile manifesto
1. Individuals + interactions > processes + tools
2. Working software > comprehensive documentation
3. Customer collaboration > contract negotiation
4. Responding to change > following a plan
Agile principles
1. Customer satisfaction
2. Welcome changing requirements
3. Deliver MVPs regularly
4. Business people + dev collaboration
5. Trust
6. Simplicity
7. Team reflection
8. Communication
What does lean development aim to do?
- Eliminate waste
- Design out overburden
- Design out inconsistency
Lean development in one line
Only produce code you need right now
Lean: Heijunka
- Levelling
- All processes should build consistent quantities over time while customer demand varies
Lean: Kaizen
- Change for better
- Continuous improvement of quality and productivity
Lean principles
1. Eliminate waste
2. Build integrity/quality in - reduce technical debt
3. Amplify learning
4. Decide as late as possible
5. Deliver as fast as possible
5. Empower the team
6. Optimise the whole
Agile: product backlog
A list of tasks (user stories) that still need to be started
Agile: what can we use to measure effort?
Task level: story points
Project level: project velocity
Agile: story points
- Story points
- These are relative measurements
- These are based on time: a user story with 2 story pts should take twice as long to complete than one with 1 story pt
Agile: what game can we use to decide story points for a task?
- Planning poker
- Each player has a deck of cards with numbers on them
- Team discusses tasks and then each member chooses a card
- Team members with lowest and highest value explain their choices
- Repeat until everyone chooses the same number
Agile: project velocity
- Story points completed / time unit
- Should aim for constant velocity
Agile: what does a decreasing project velocity mean?
Accumulation of technical debt, quality issue
Agile: Kanban board
- Columns store cards with task description
- Columns correspond to status of task
- Move cards L -> R
Agile: Kanban board principles
1. Visualise project status
2. Limit work in progress
3. Support flow management
4. Discuss policies
5. Listen to feedback
6. Improve collaboration + evolve
Agile: scrum
- Timebox tasks
- Retrospective: feedback on how team work in scrum
- Daily scrum: discuss work ahead in next 24hrs
Agile: roles in scrum
- Product owner: represents stakeholders
- Scrum master: chairs meetings
Agile: PSP
- Potentially Shippable Product
- Produced at the end of every sprint
Agile: scrum timeline
1. Take tasks from product backlog to create sprint backlog
2. Start sprint with daily standup
3. Review PSP in review meeting
Agile: user story
- Brief informal description of a software feature presented from the POV of the stakeholder
Agile: user story structure
As a [PERSONA], I want to [DO SOMETHING] so that [BUSINESS VALUE]
Agile: what acronym can we use to create good user stories?
I.N.V.E.S.T
Agile: I.N.V.E.S.T
- Independent
- Negotiable
- Valuable/Vertical
- Estimable
- Small
- Testable
What is a branch?
Self contained collection of commits on software
What are branches used for?
To reduce impact of changes and experiments on source code
Command to create a new branch
`$ git checkout -b [branch name]`
Command to check what branches exist
`$ git branch`
Command to go to another branch
`$ git checkout [target branch]`
Command to merge 2 branches
`$ git checkout [branch1]`
`$ git merge [branch2]`
What are issues on GitHub?
A way to highlight issues in the code for other people to pick up
What is a pull request?
- A request to merge changes to the main branch
- You should state the changes you've made
- Other team members must approve PRs after reviewing the changes for it to be merged
What does command `git pull` do?
Merges version control network on remote with your local repository
Command to restore the last commit's contents
`$ git checkout -f`
Command to delete a branch
Locally: `$ git branch -D [branch name]`
Remotely: `$ git push -d origin [branch name]`
You can't run these commands on the branch you're currently on!
Command to get a list of commits
`$ git log`
Command to compare 2 commits
`$ git diff [commit1's SHA] [commit2's SHA]`
Command to go back to a specific commit
`$ git checkout [commit SHA]`
Command to find list of unmerged files
`$ git ls-files -u`
Command to find conflicts (it's pretty long)
`$ git ls-files -u | cut -f 2 | sort -u [file name]`
What are the stages of project planning?
1. Identification
2. Definition of tasks
3. Definition of project schedule
4. Do the work and monitor progress against the plan
5. If problems arise, mitigate risk and replan project
Project planning: Identification
First stage
Identify project:
- constraints
- risks
- milestones
- deliverables
What are milestones?
Corresponds to the end of a stage in the project
Requires completion of a set of project activities
Usually, reaching the end of a milestone means you have to write a report
Project planning: Definition of tasks
A task has attributes:
- Description
- Effort: no. of work units a task requires
- Duration to complete
- Elapsed time between start and end of task
- Deadline
- Activities the task depends on
- Defined endpoint: set of conditions to be met for task completion
Tasks
Basic unit of scheduling
Project planning: Definition of schedule
Gantt chart used
On x-axis: Time
On y-axis: Tasks
Shows dependencies of different tasks
What are the stages of risk management?
1. Risk identification
2. Risk analysis
3. Risk planning
4. Risk monitoring
Risk management: types of risks
- Estimation
- Organisation
- People
- Requirements
- Technology
- Tools
Risk management: stages of risk analysis
- Risk probability
- Risk effect
Risk management: risk probability
- Likelihood of risk occurring
- Map different probabilities to their likelihood e.g insignificant = 0 - 2%, low = 2 - 10%, very high = > 50%
Risk management: risk effect
Likelihoods and effects are mapped to categorise risks
Usually done in a *risk assessment matrix*
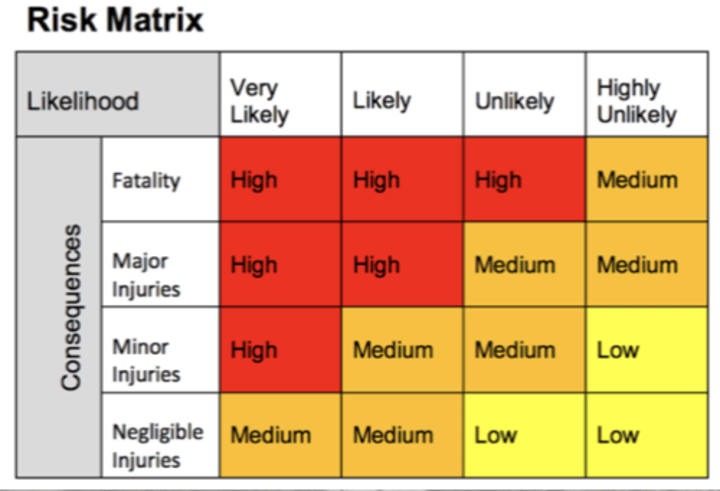
Risk management: risk planning
- After categorising risks, we can decide how to deal with them
Risk management: types of ways to deal with risks
- Acceptance: no action
- Prevention: stop before it occurs
- Reduction: reduce probability of occurrence
- Transfer: transfer risk to someone else
- Contingency planning: no upfront action, plan response in case risk arises
4 principles of project management
- Quantity > quality
- All criticism should be withheld
- Think outside the box
- Build on ideas of others
Requirements for brainstorming
- Record ideas
- Analyse results afterwards
Foundational behaviours of a leader
1. Demonstrate respect
2. Listen first
3. Clarify expectations
4. Practice accountability
What does project initiation aim to do?
To clarify a shared and measurable set of expectations to define the project's purpose
Questions asked in stakeholder analysis
1. Who will this project impact?
2. Who determines how successful the project is?
3. What are their expectations?
4. What are the project limitations?
5. What are the communication needs during the project?