CHEM 43A Final (4-7)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Which of the following solvents would be best to separate a mixture containing 2-phenylethanol and acetophenone by TLC? (4)
Hexane and Methylene chloride
methylene chloride or hexane or mixtures of the two might be good choices because the compounds are somewhat polar
Complete the following paragraphs (4)
The stationary phase in TLC is polar. Therefore, the less polar component of the mixture will travel a greater distance up the plate, resulting in a higher Rf value for the component.
When separating a mixture containing 2-phenylethanol and acetophenone, the acetophenone spot would be expected to travel the greatest distance up the plate as it is the less polar component. The 2-phenylethanol would travel the least distance as it is the more polar component.
more polar=smaller distance travelled
What happens if the spots are made too large when preparing a TLC plate for development? (4)
The spots will saturate the plate, show tailing, and/or diffuse into one another.
If the spots are made too large they may saturate the slide, show tailing, diffuse radially outward, or run into one another.
Consider a sample that is a mixture composed of biphenyl, benzoic acid, and benzyl alcohol.
Predict the order of elution of the components in this mixture. Assume that the chromatography uses a silica column and the solvent system is based on cyclohexane, with an increasing proportion of methylene chloride added as a function of time. (4)
Elutes first: Biphenyl > benzyl alcohol > benzoic acid :Elutes last
When using a nonpolar solvent, such as cyclohexane, you should expect the relatively nonpolar substance to elute first (biphenyl), leading to the above order.
SAFETY: Why is it important to handle silica powder in a fume hood? (4)
The powder, if inhaled, can cause serious problems to the respiratory tracts. The powder is fine and easily inhaled.
Silica powder can be carcinogenic if inhaled. It is a very fine powder that readily forms clouds of dust that are easily inhaled.
How long should you run a TLC plate for? (4)
Until the solvent front is just below the top of the plate.
You should maximize the length of the run in order to get good separation; however, be aware that the longer the plate is run, the more diffuse the spots will become.
What type(s) of intermolecular forces are expected between CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH molecules? (5)
dipole forces - yes
induced dipole (London dispersion) forces - yes
hydrogen bonding - yes
Induced dipole forces are always present. Induced dipole forces are also called dispersion forces, or London forces.
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH is a polar molecular compound. Therefore, the intermolecular forces also include dipole forces.
Hydrogen bonding is found in situations represented by D-H---A where both the donor atom, D, and the acceptor atom, A, are one of the highly electronegative elements O, N, or F. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH falls into this category.
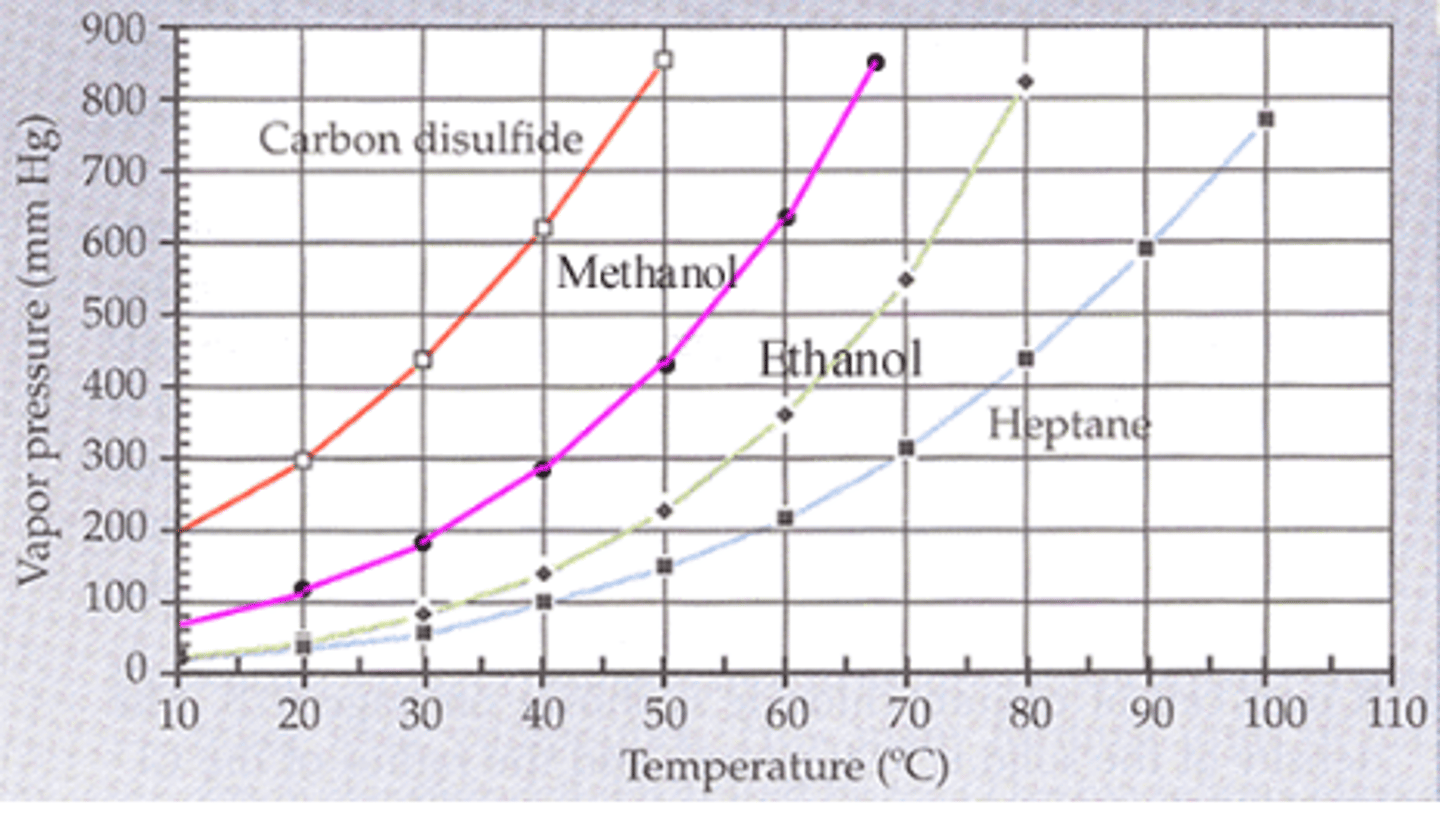
From the plot of the vapor pressures vs temperature above, estimate the boiling point of methanol when the external pressure is 182 mm Hg. (5)
30 C
The boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure is equal to the external pressure. From the graph, the vapor pressure of methanol is estimated to be 182 mm Hg at 30 C.
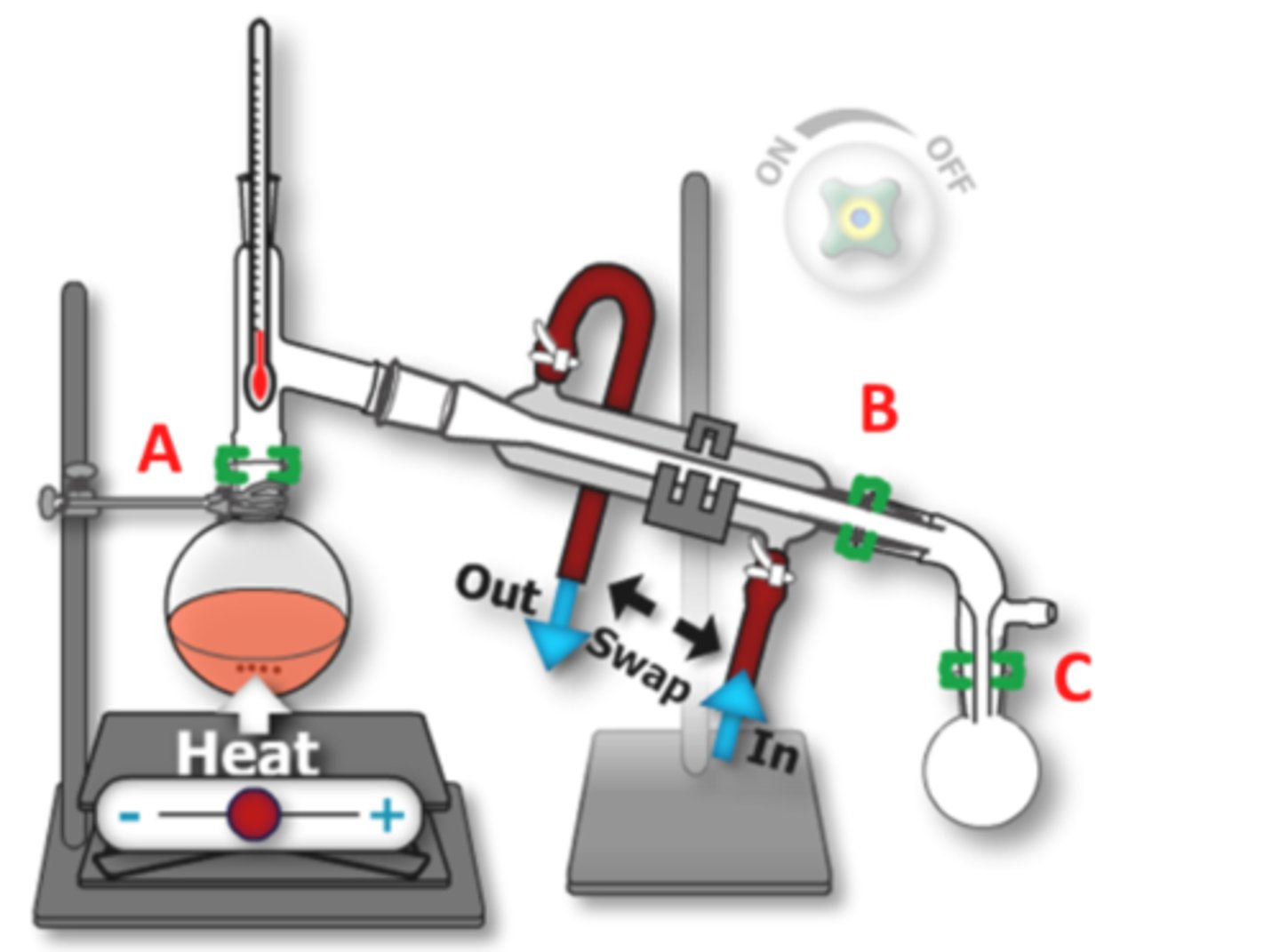
SAFETY: If using plastic joint clips to stabilize your equipment, which clips in the diagram should NOT be used? (5)
B and A
These clips are not heat proof and so can melt if they are too close to the heated part of the apparatus.
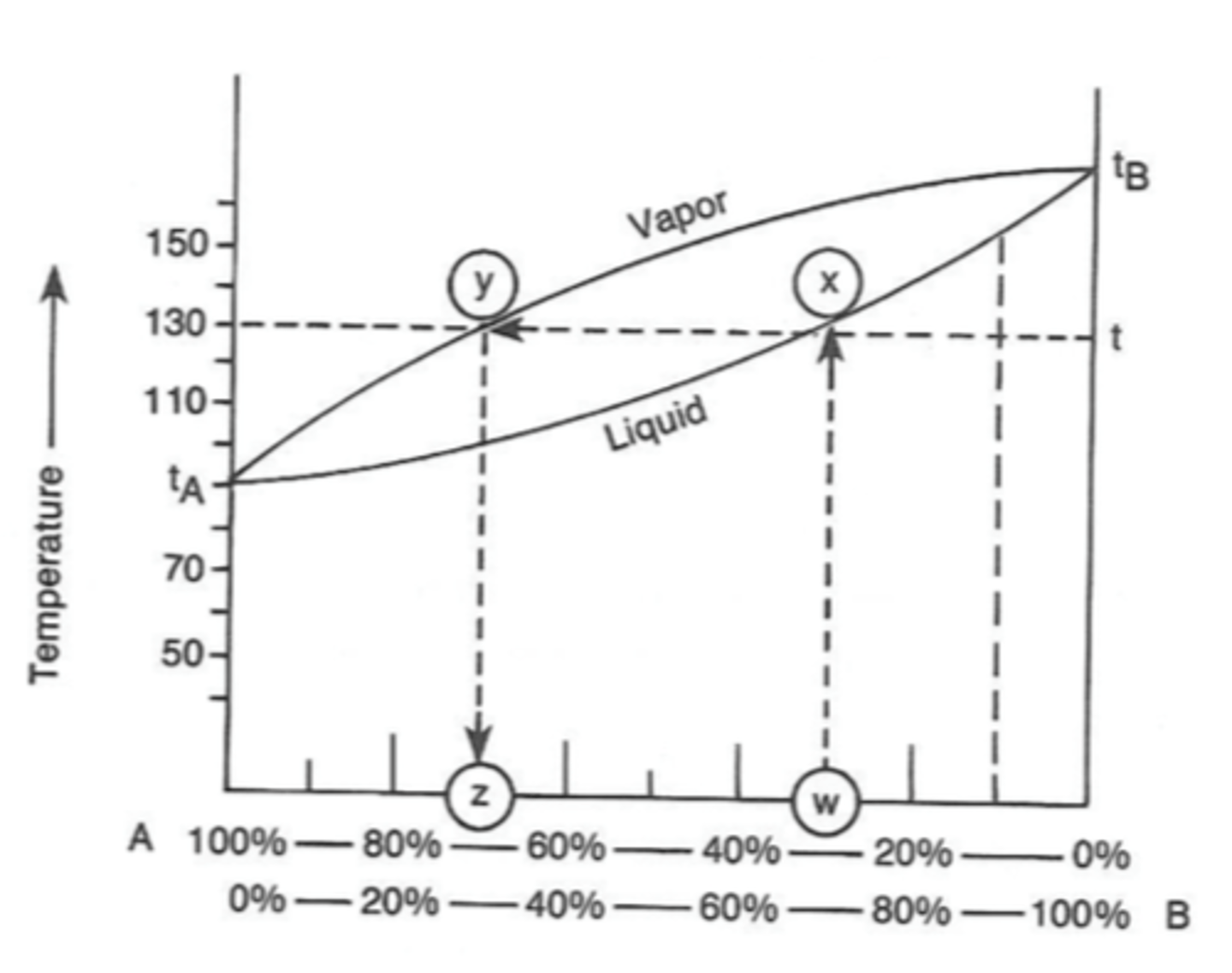
Shown is the phase diagram for a typical liquid mixture of two components, A and B.
a) What is the significance of the horizontal line between points X and Y?
b) Using the phase diagram, determine the molar composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a boiling liquid that has a composition of 80% A and 20% B. (5)
a) A boiling liquid with composition X will produce vapor with composition Y
b) percentage vapor composition A = 98 %
percentage vapor composition B = 2%
What is the boiling point of this liquid? Boiling point = 95 C
The molar composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a boiling liquid that has a composition of 80 % A and 20 % B can be determined by drawing a vertical line from the x axis to the liquid curve at the point where the molar composition of A is 80% (such as line WX on the diagram).
A horizontal line is then drawn from the liquid curve to the vapor curve in the direction of the lower boiling point liquid (such as line XY on the diagram). This point corresponds to the molar composition of the vapor and by drawing a vertical line down to the x axis the values for A and B can be read.
a) If you separated a mixture of benzene, toluene, and m-xylene by gas chromatography, what would be the expected order of retention times?
b) Explain this order of elution (5)
a) shortest retention time: benzene < toluene < m-xylene :longest retention time
b) Gas chromatography separates compounds depending on their polarity and volatility. Benzene, m-xylene, and toluene have similar polarities, therefore, the main basis for separation is volatility.
The more volatile a component the greater its vapor pressure, hence the more time it spends in the gaseous mobile phase, giving it a shorter retention time.
Therefore, components of a liquid mixture will elute in order of increasing boiling point.
SAFETY: Which statement best described how the system should be heated? (6)
Heat gently so that the solvent boils and the vapors extend no more than half way up the condenser.
The height of the vapor can be seen as a ring within the condenser. This should not extend beyond half way up the condenser, and preferably lower, to ensure no vapor is lost from the system.
Why do we use a drying tube in the setup for the Fischer esterification? (6)
To prevent moisture vapors from reaching the reaction
In the Fischer esterification, you will use one reagent in excess. What is the reagent and how will the excess be removed after the reaction? (6)
Carboxylic acid; removed by extraction with aqueous base
After the Fischer esterification, you will preform liquid-liquid extraction to isolate the ester. How will this be accomplished? (6)
The organic and aqueous phases vigorously stirred in the open conical vial to achieve mixing. The aqueous phase is removed with a pipette. The ester is in the organic phase.
The compound from the following list that exhibits the infrared spectrum below is _ (6)
C - alcohol
There is an O-H stretch present in the IR spectrum
Which of the following factors affect boiling point? (6)
Whether a compound is polar or not, and the pressure
The boiling point depends on the pressure, molecular weight, structure, and purity of the liquid.
The vapor pressure of the liquid must equal the external pressure in order for boiling to occur, therefore, the boiling point decreases with decreasing pressure and less energy is required to make the liquid boil.
The structure of a compound determines the strength of intermolecular interactions that hold the molecules in the liquid phase: polar compounds have dipole-dipole and, potentially, hydrogen bonding, whereas, nonpolar compounds have van der Waals interactions.
SAFETY: While setting up a micro-boiling point determination you accidentally break a capillary tube. You should: (6)
Dispose of it in the appropriate glass waste container
Broken glass is sharp and could cause harm to you or others. Capillary tubes are small and could easily be lost so you should put them in the appropriate glass waste container immediately. If you are unsure of where to dispose of broken glass ask your instructor.
Observing the formation of a silver mirror on the surface of a test tube when using Tollen's reagent indicated the presence of: (7)
an aldehyde
The test for an aldehyde uses Tollen's reagent, which is essentially a solution of silver ions in ammonia solution. If an aldehyde is present, a precipitate of silver, which looks like a mirror, forms on the inside surface of the test tube.
What observation would you expect to make if a primary or secondary alcohol reacted with acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution? (7)
The orange solution turns green
What reagent (or compound) causes the observed visual change in a positive Lucas test? (7)
The alkyl halide product is insoluble in water
Which key reagents would you need to use to distinguish between following two molecules? (a primary and secondary alcohol) (7)
Anhydrous zinc chloride and hydrochloric acid
In a recrystallization, the crystals do not always form spontaneously after cooling, even though the solution is supersaturated. Which of the following will help crystals forms? (7)
Scrape the inside of the Erlenmeyer flask with a glass rod below the surface of the solvent
Add some crystals of the compound you are trying to crystallize
In a recrystallization, why are the newly formed crystals washed with cold solvent? (7)
To wash off the film of solvent which contains the impurities
It is part of the purification process. Cold solvent should be used to minimize the dissolution of the crystals.
Which structure best fits the IR with a peak at around 2950 and 1750? (7)
Structure with C=O because of the peak at 1750
Which structure best fits the above spectra with a weak bend at 3300 and peak at 1680? (7)
Structure with C=O and OH because the bend at 3300 is for the OH and the peak at 1680 is for C=O
CAS number
unique identification number; the number carries no information about the structure or properties of the substance
GHS
The first digit of this number refers to specific hazard statement
2 = physical hazard
3= health hazard
4= environmental hazard
Health Hazard
Carcinogen, mutagenicity, reproductive toxicity, respiratory sensitizer, target organ toxicity, aspiration toxicity

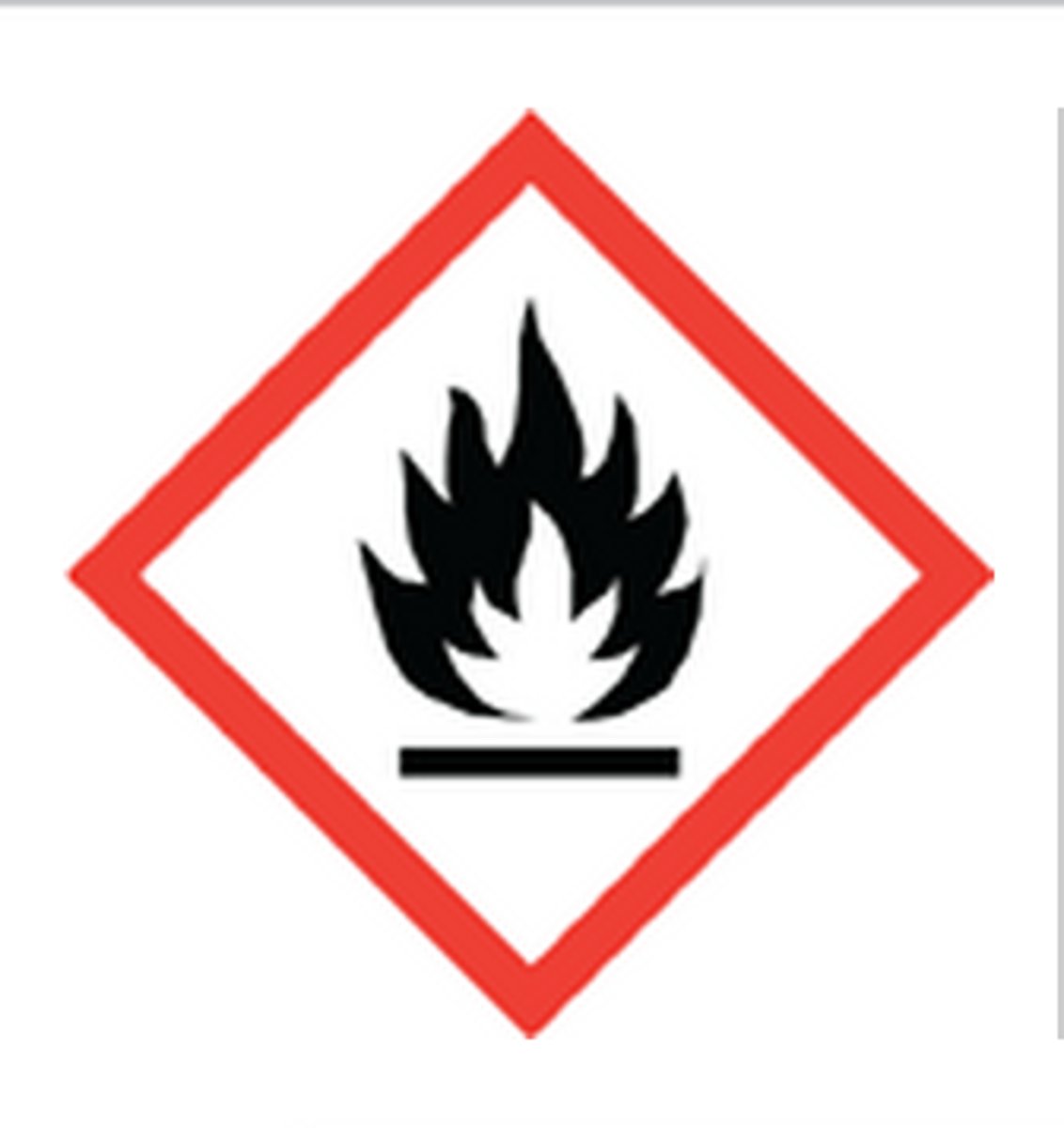
Flame
Flammables, pyrophorics, self-heating, emits flammable gas, self-reactives, organic peroxides

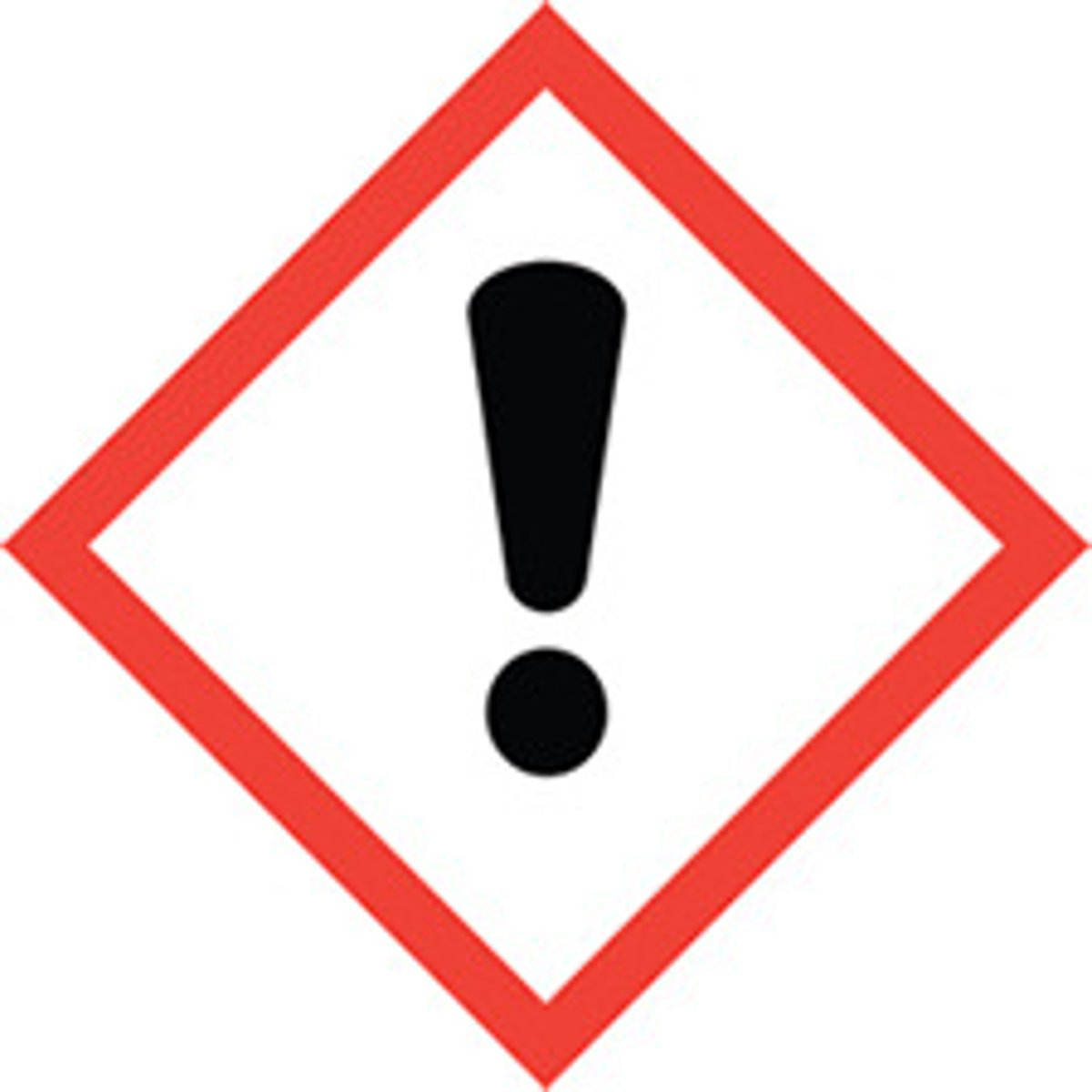
Exclamation Mark
Irritant (skin and eye), skin sensitizer, acute toxicity (harmful), narcotic effects, respiratory tract irritant, hazardous to ozone layer (non-mandatory)

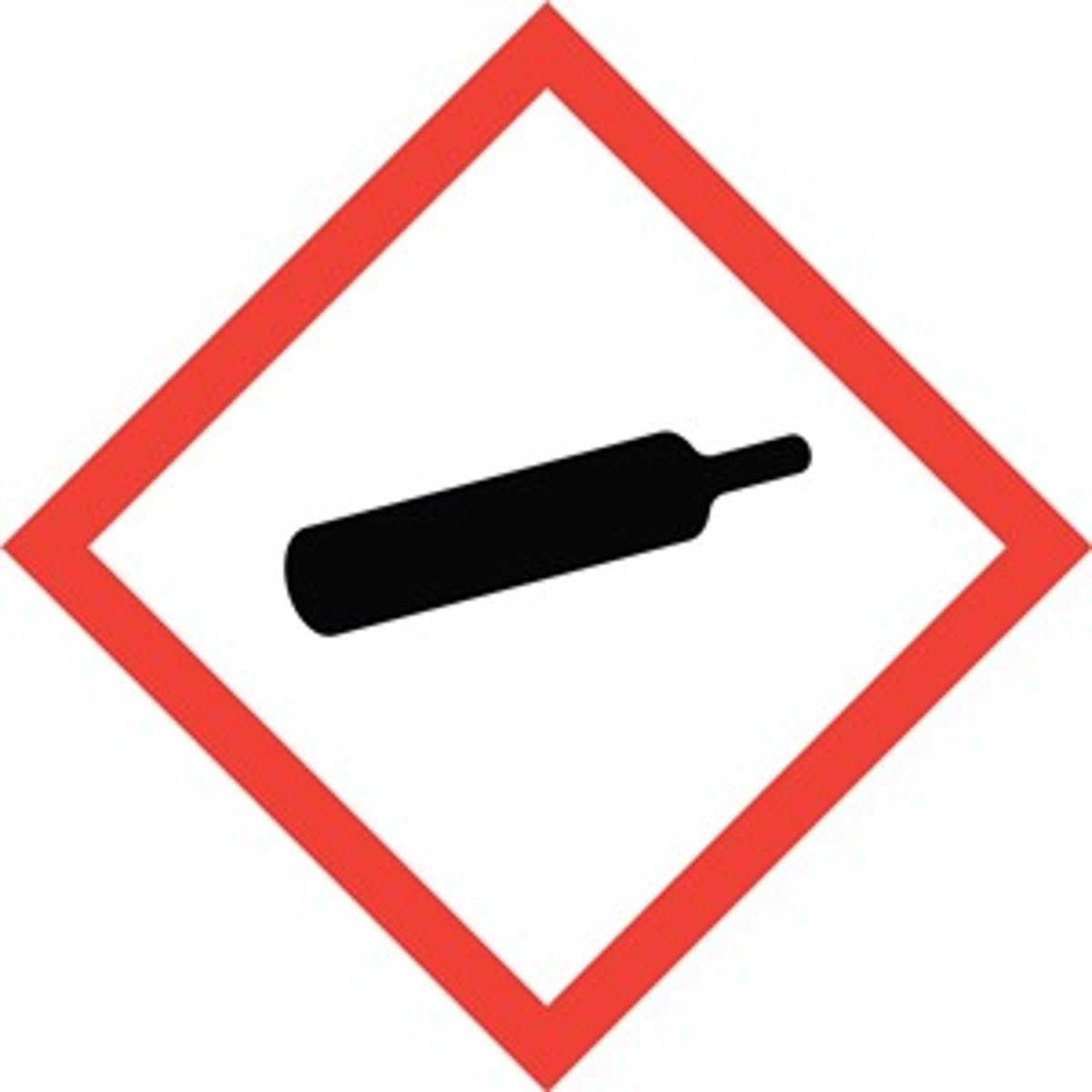
Gas Cylinder
Gases under pressure

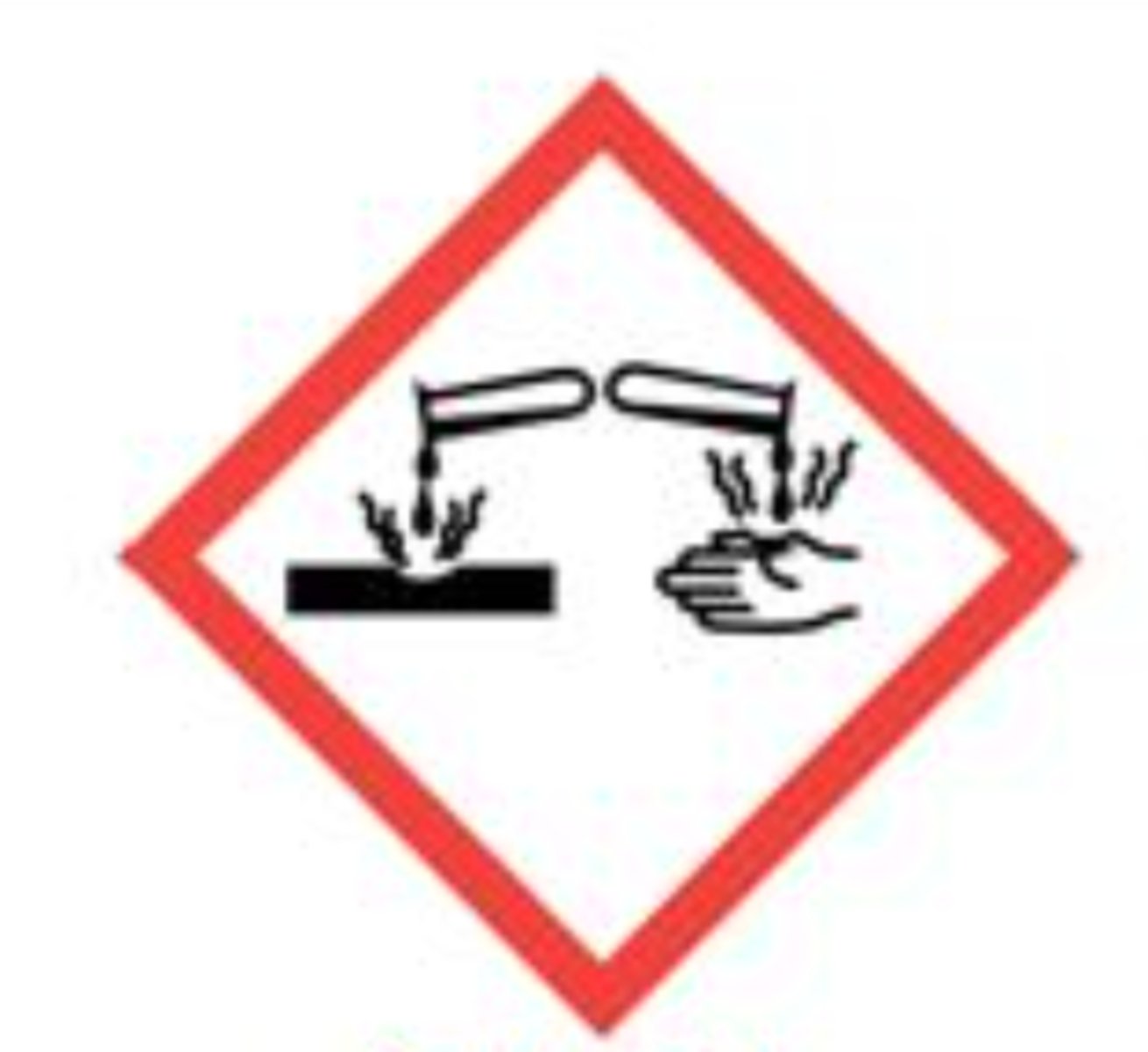
Corrosion
Skin corrosion/burns, eye damage, corrosive to metals

Exploding bomb
Explosives, self-reactives, organic peroxides

Flame over circle
oxidizers

Environment (non-mandatory)
Aquatic toxicity

Skull and crossbones
acute toxicity (fatal or toxic)

PPE
Chemical splash goggles, long hair restrained, knee-length long sleeve lab coat, long pants, closed toed shoes, socks must cover ankles
Students missing PPE must leave and return when properly attired
Sig Fig - Balances and Masses
record and report all masses using thousandths of grams - the third decimal place (1.235 g)
The last two digits are not precise on mass scales
Sig Fig - Graduated cylinders, pipettes and volumes
record and report all volumes using tenths of mL (1.2 mL)
Sig Fig - Thermometers and Temperatures
record and report to tenth of a degree for mel-temps and report whole degrees when using glass thermometer
Sig Fig - Reaction yields
round yields to whole percentages
Sig Fig - Rf values
record and report 2 decimal places (Rf = 0.45)
Sig Fig - GC Peak Area
report to hundreds place (12,345 au is reported as 12,300 au)
Sig Fig - Retention time
report all digits
Sig Fig - IR
report to whole wavenumbers
Jones Test
positive for primary and secondary alcohols + aldehydes (red-orange → blue-green)
Lucas Test
positive for secondary (slow) and tertiary alcohols (fast)
look for separation of layers/cloudiness (if alcohol is miscible in water, then test isn’t inconclusive)
2,4-DNP Test
positive for aldehydes and ketones (red-orange → orange)
Tollens Test
positive for aldehydes (silver precipitate)
3,5-Dinitrobenzoate Ester Derivative
derivative for alcohols
pyridine acts as solvent (good for dissolving unknown)
3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride reacts with alcohol
2,4-Dinitrophenyl Hydrazone Derivative
derivative for aldehydes and ketones
HCl acts as catalyst for reaction
2,4-DNP reacts with aldehyde and ketone
Semicarbazone Derivatives
derivative for aldehydes and ketones
sodium acetate acts as a buffer to ensure reaction proceeds
semicarbazide hydrochloride reacts with aldehyde or ketone
Recrystallization of Derivatives
crude product placed in an Erlenmeyer flask and dissolved in hot methanol/ethanol until dissolved → DI water added dropwise until solution is cloudy → cool solution to room temp → put in ice bath → do vacuum filtration (wash with DI water) → put in desiccator