AP Euro - Unit 3: Absolutism and Constitutionalism (1648-1815)
1/30
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Fronde (1648-1659)
A series of violent uprisings during the early reign of Louis XIV triggered by growing royal control and increased taxation.
Mercantilism
A system of economic regulations aimed at increasing the power of the state based on the belief that a nation's internal power was based on its wealth, specifically its supply of gold and silver.
Divine Right
the idea that monarchs are God's representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God.
Jean Baptiste Colbert
An economic adviser to Louis XIV; he supported mercantilism and tried to make France economically self-sufficient. Brought prosperity to France.
Louis XIV of France
He ruled through absolutism and believed in divine right. He was the "Sun King" because he reigned from 1643-1715, the longest in European history. He restored the Palace of Versailles. He revoked the Edict of Nantes because he did like division within his realm. He carried out the expansionist policy to the full extent. He was at war 33 years of his 54-year personal rule. Believed in absolute monarchy. He ruled absolutely.
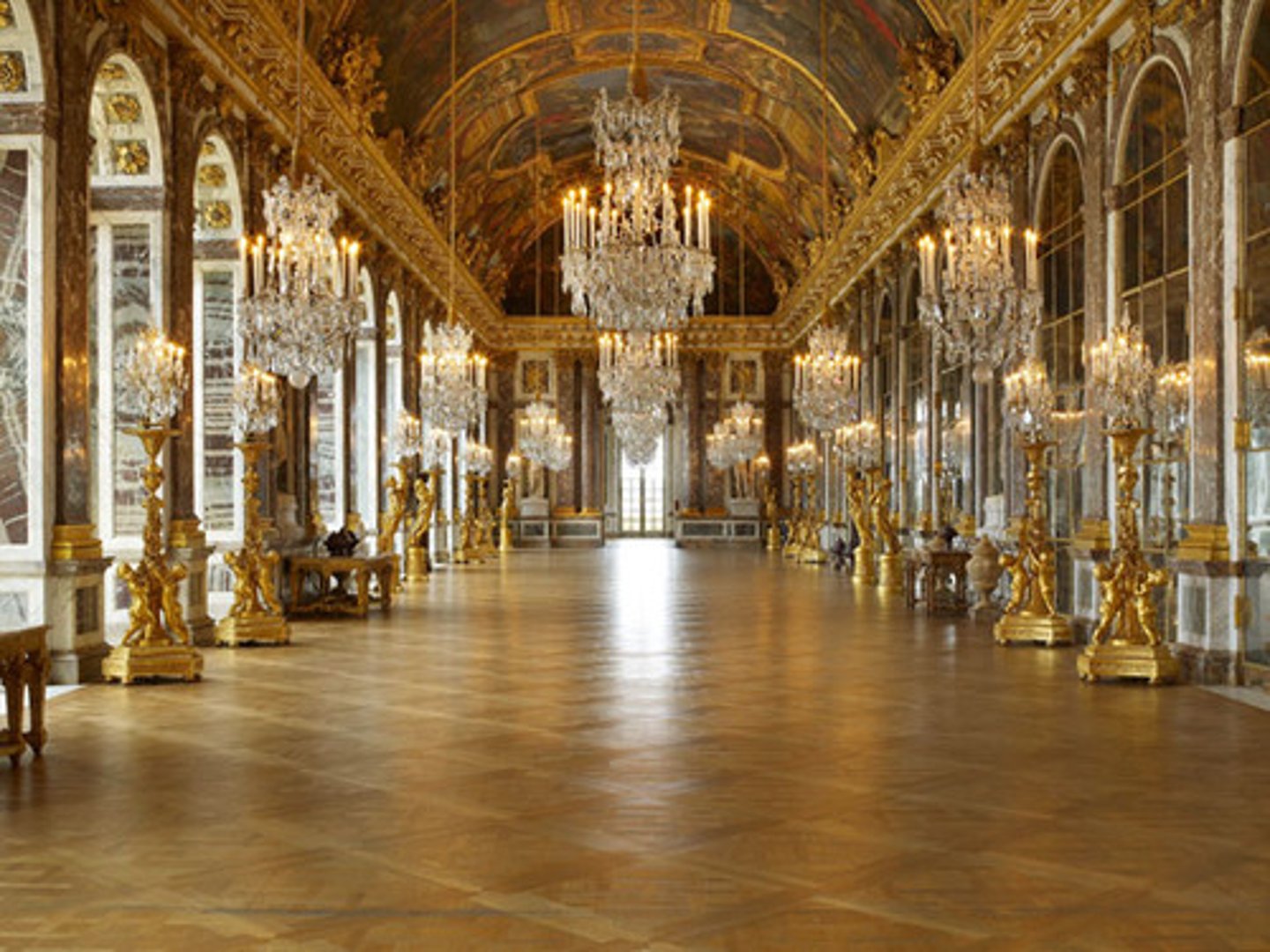
Palace of Versailles
Lavish palace constructed by Louis XIV to reflect his power and might, but also as a way to control and limit the power of Nobles by requiring their attendance there where he could keep a watchful eye on them.

Junkers
The nobility of Brandenburg and Prussia, they were reluctant allies of Frederick William in his consolidation of the Prussian state.
Peace of Utrecht (1713)
A series of treaties, from 1713 to 1715, that ended the War of the Spanish Succession, ended French expansion in Europe, and marked the rise of the British Empire.
War of the Spanish Succession (1701-1713)
A war fought over the Spanish throne. Louis XIV wanted it for his grandson and fought a war against the Dutch, English, and the Holy Roman Empire to gain the throne for France. The Peace of Utrecht ended the war.
Boyars
The highest-ranking members of the Russian nobility.
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
The Romanov czar who initiated the westernization of Russian society by traveling to the West and incorporating techniques of manufacturing as well as manners and dress.
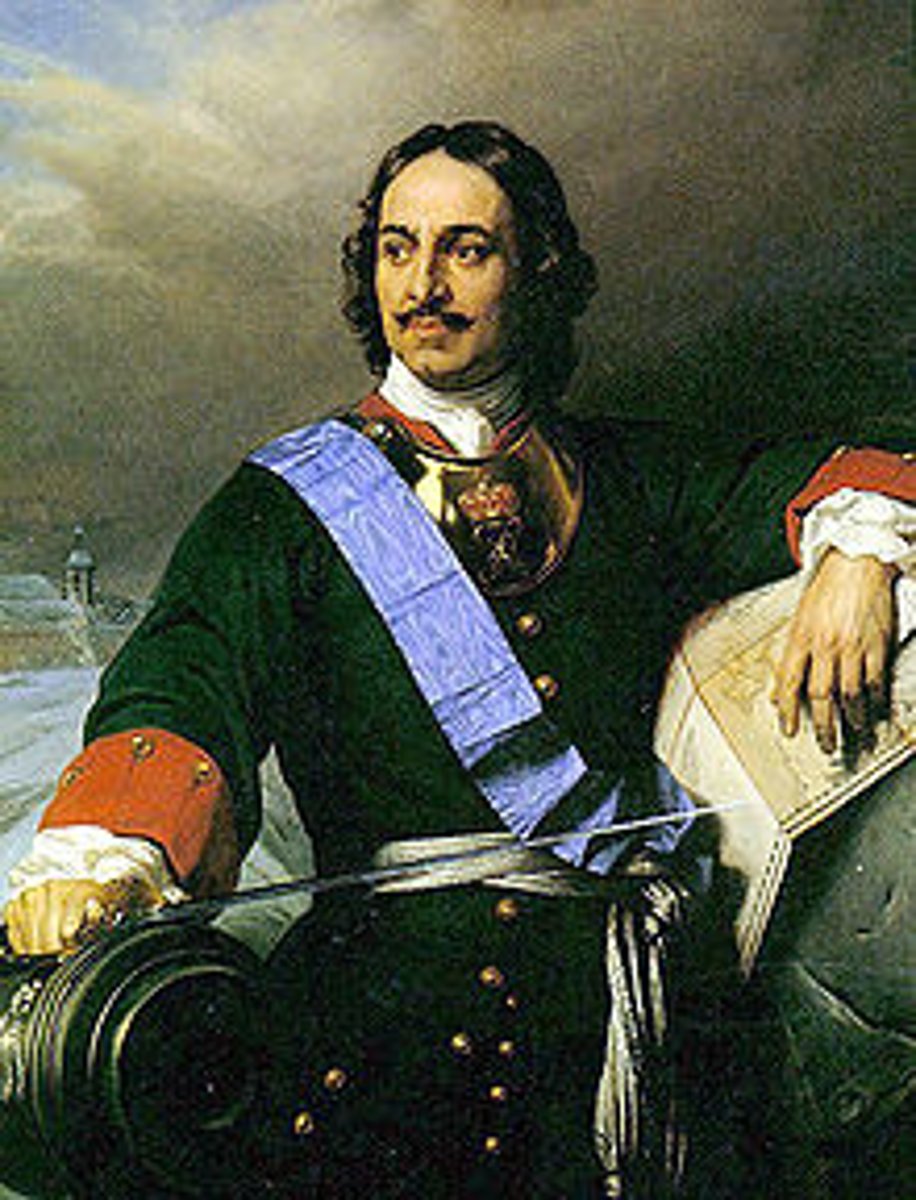

Westernization
An adoption of the social, political, or economic institutions of Western Europe by Peter the Great.
Constitutionalism
A form of government in which power is limited by law and balanced between the authority and power of the government on the one hand, and the rights and liberties of the subjects or citizens on the other hand; could include constitutional monarchies or republics. (Great Britain!)
Republicanism
A form of government in which there is no monarch and power rests in the hands of the people as exercised through elected representatives.
Puritans
Members of a sixteenth- and seventeenth-century reform movement within the Church of England that advocated purifying it of Roman Catholic elements, like bishops, elaborate ceremonials, and wedding rings.
English Civil War
Conflict from 1640 to 1660; featured religious disputes mixed with constitutional issues concerning the powers of the monarchy; ended with restoration of the monarchy in 1660 following execution of previous king.
James I of England
The son of Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots, he succeeded the childless Elizabeth as James I of England. He upheld a belief of Divine Right and Absolutism. He was not popular and was an outsider. He inherited a large royal debt and a divided church. He would alienate parliament as well as Puritans who represented a significant amount of nobles in parliament.
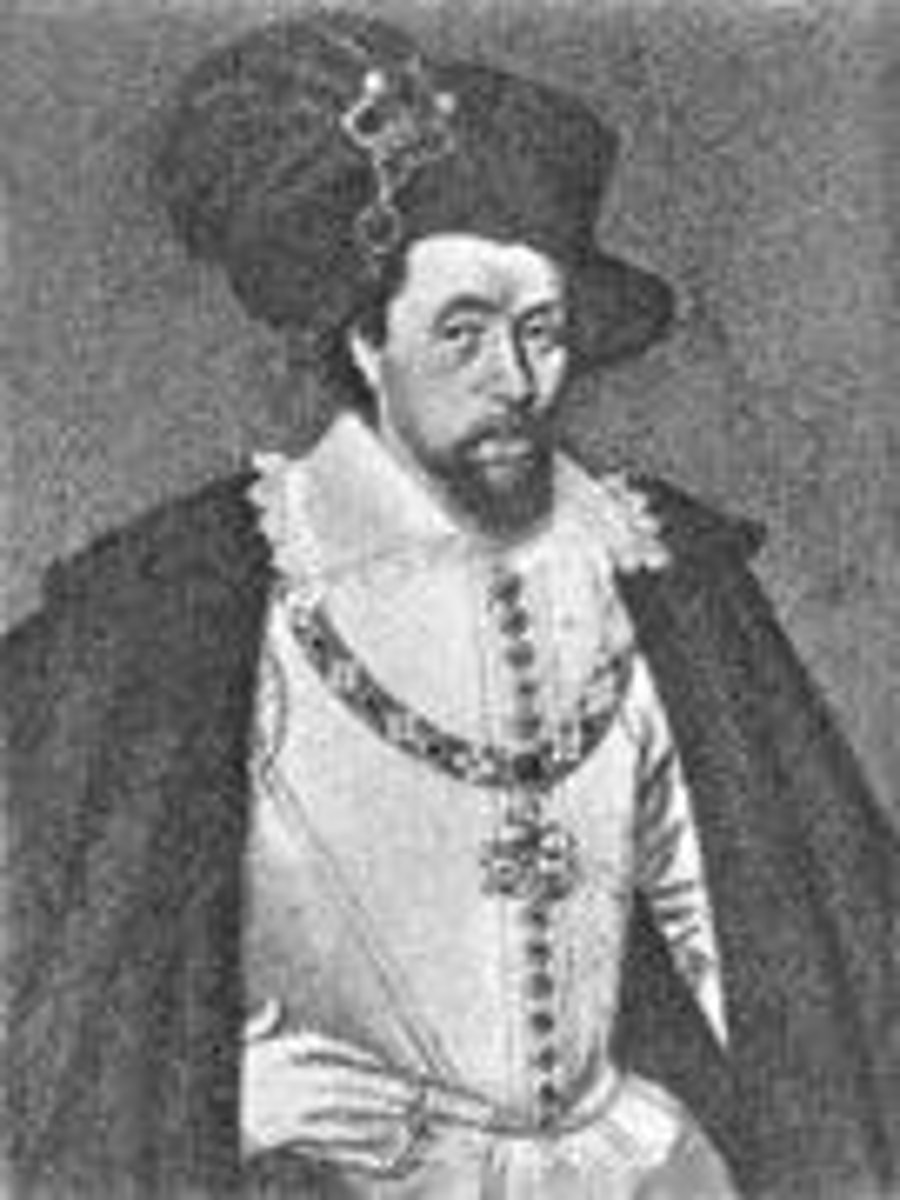

Charles I of England
1600-1649; King of England 1625-1649; numerous conflicts with Parliament; fought wars with France, Spain, and Scotland; eventually provoked Civil War, convicted of treason, and beheaded. First example of regicide by nobles/parliament, which sent shock-waves through the European continent.
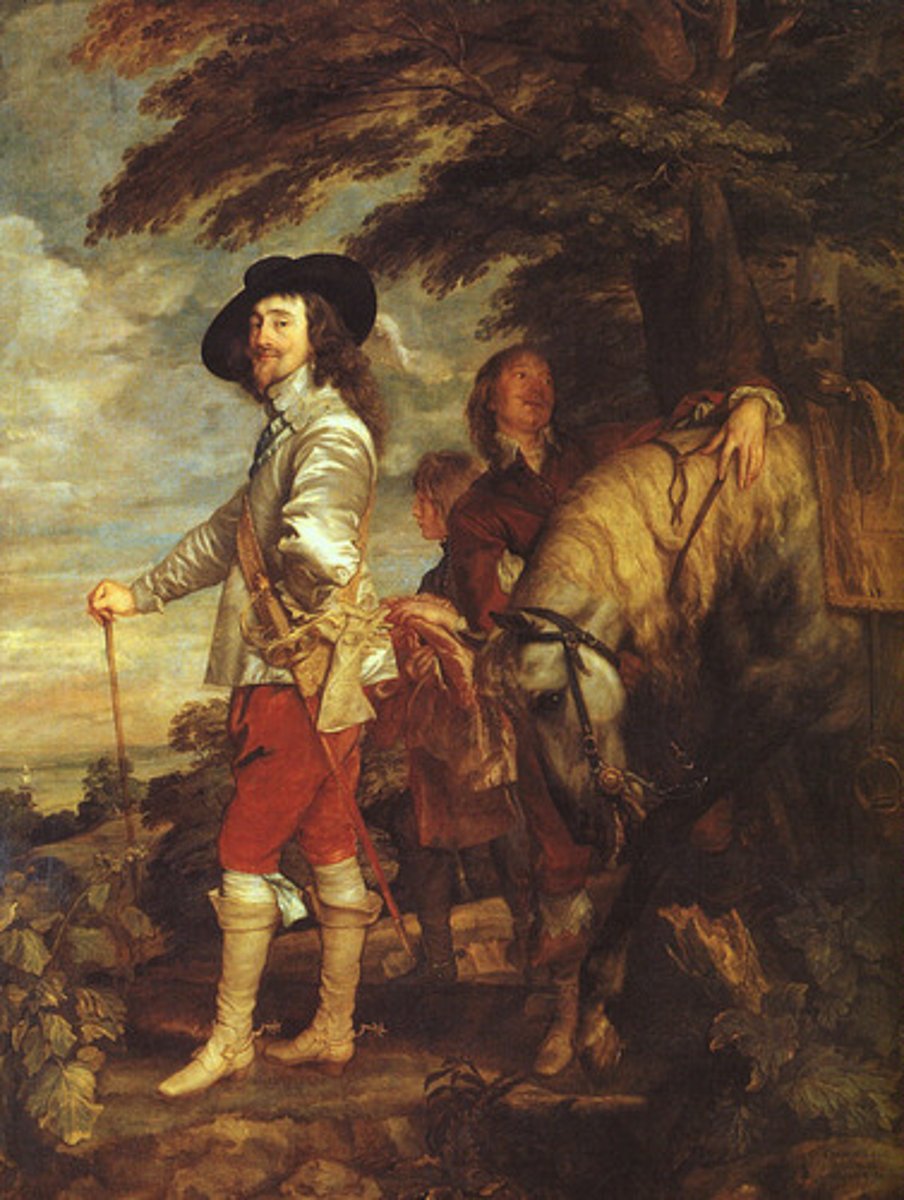

Oliver Cromwell (1599-1658)
Puritan general who helped lead parliamentary forces during the English Civil War, and ruled England as Lord Protector from 1653 until his death in 1658.
Protectorate (England)
The English military dictatorship (1653-1658) established by Oliver Cromwell following the execution of Charles I.
Treaty of Dover 1670
The agreement between Charles II and King Louis XIV of France without the knowledge of Parliament in which he promised religious toleration for English Catholics and his conversion to Roman Catholicism.
Charles II (1660-1685)
Charles was one of the most popular and beloved kings of England, known as the Merry Monarch, in reference to both the liveliness and hedonism of his court and the general relief at the return to normality after over a decade of rule by Cromwell and the Puritans.
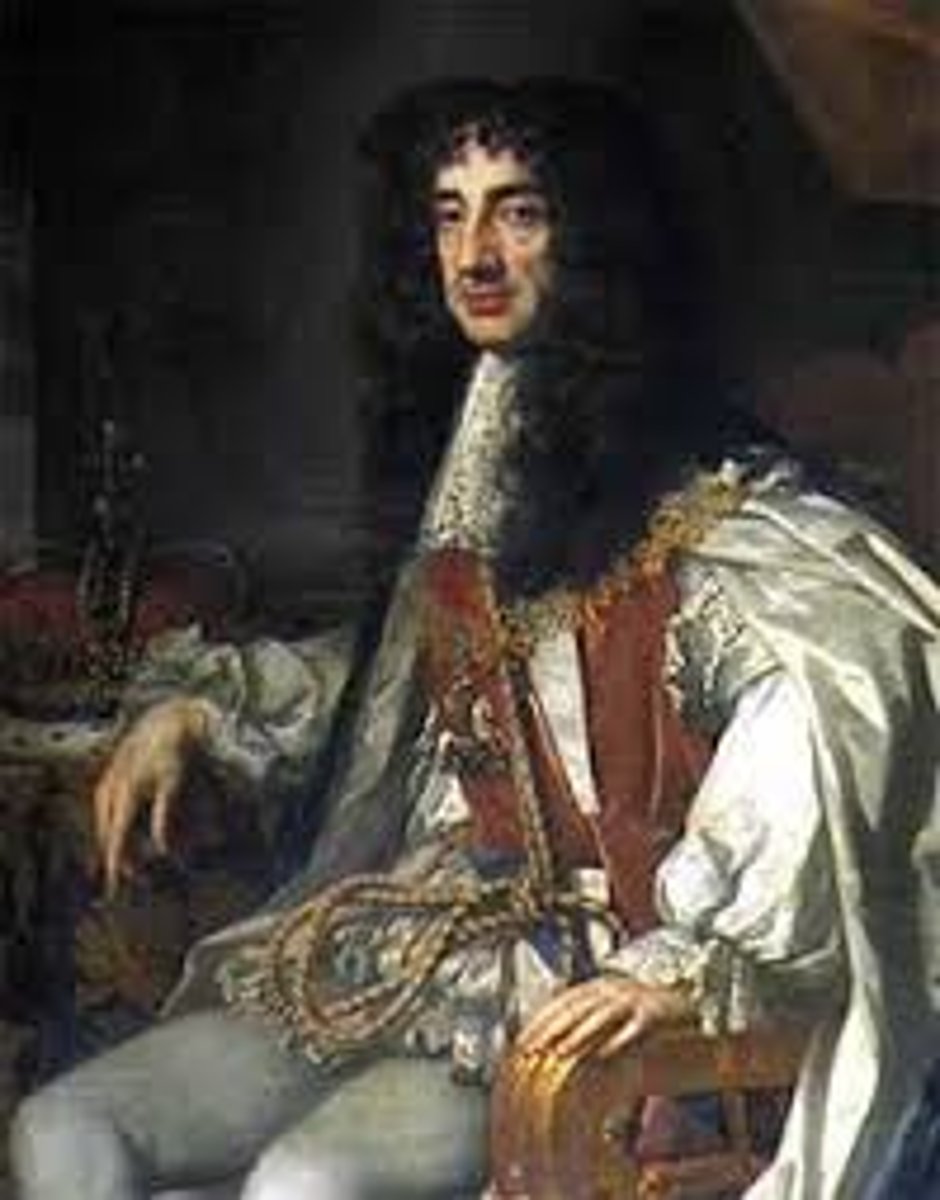

Constitutional Monarchy
A King or Queen is the official head of state but power is limited by a constitution.
Test Act (1673)
Legislation, passed by the English Parliament in 1673, to secure the position of the Anglican Church by stripping Puritans, Catholics, and other dissenters of the right to vote, preach, assemble, hold public office, and teach at or attend the universities.
James II (1685-1688)
The last Roman Catholic monarch of England, Scotland and Ireland, his reign is now remembered primarily for struggles over religious tolerance. However, it also involved the principles of absolutism and divine right of kings and his deposition ended a century of political and civil strife by confirming the primacy of Parliament over the Crown. Deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688.
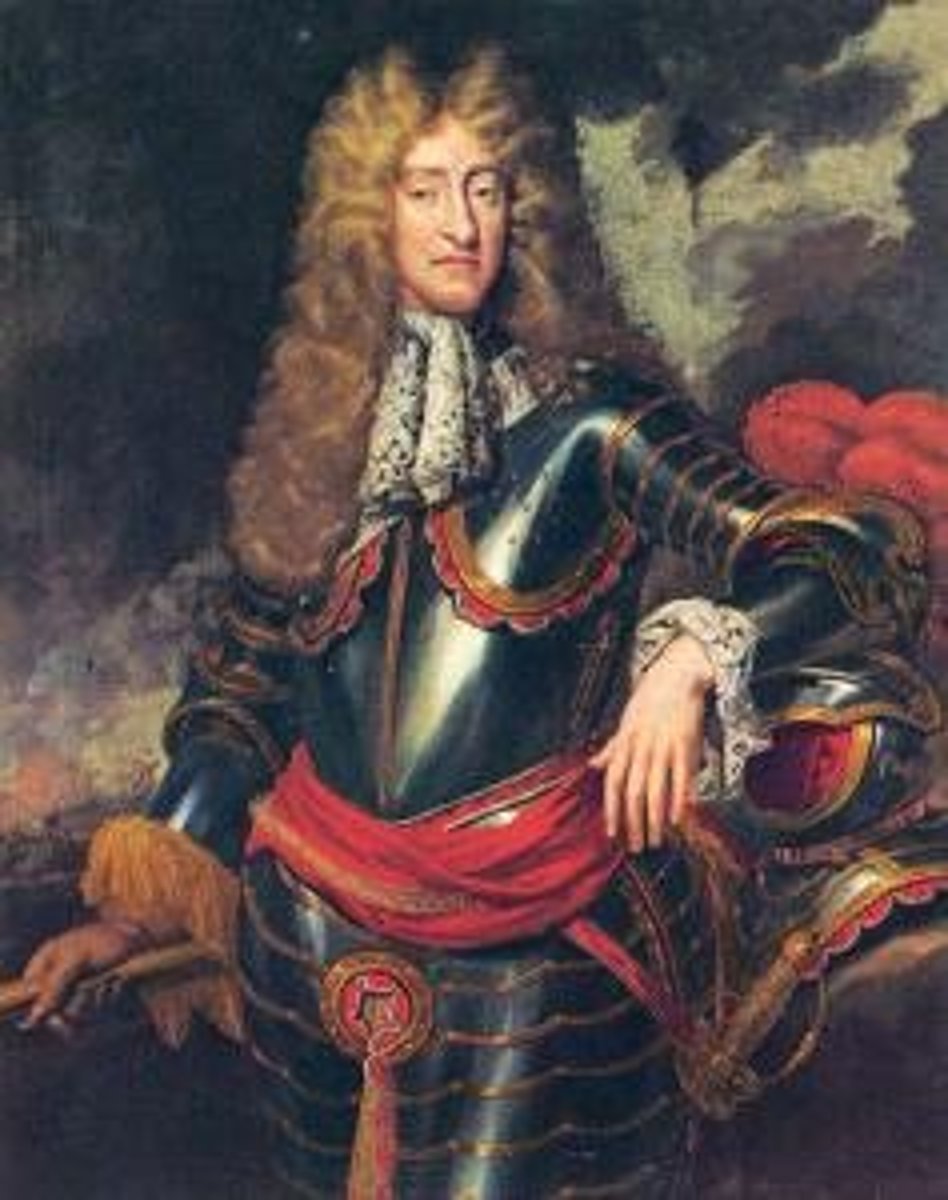

Glorious Revolution (1688)
The bloodless coup in 1688 in England when James II (a Catholic) gave up the throne and his daughter Mary and her husband William of Orange (of the Netherlands) - both Protestants - replaced James II to reign jointly. No Catholic monarch has reigned in England since.
Stadholder
The executive officer in each of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, a position often held by the princes of Orange.
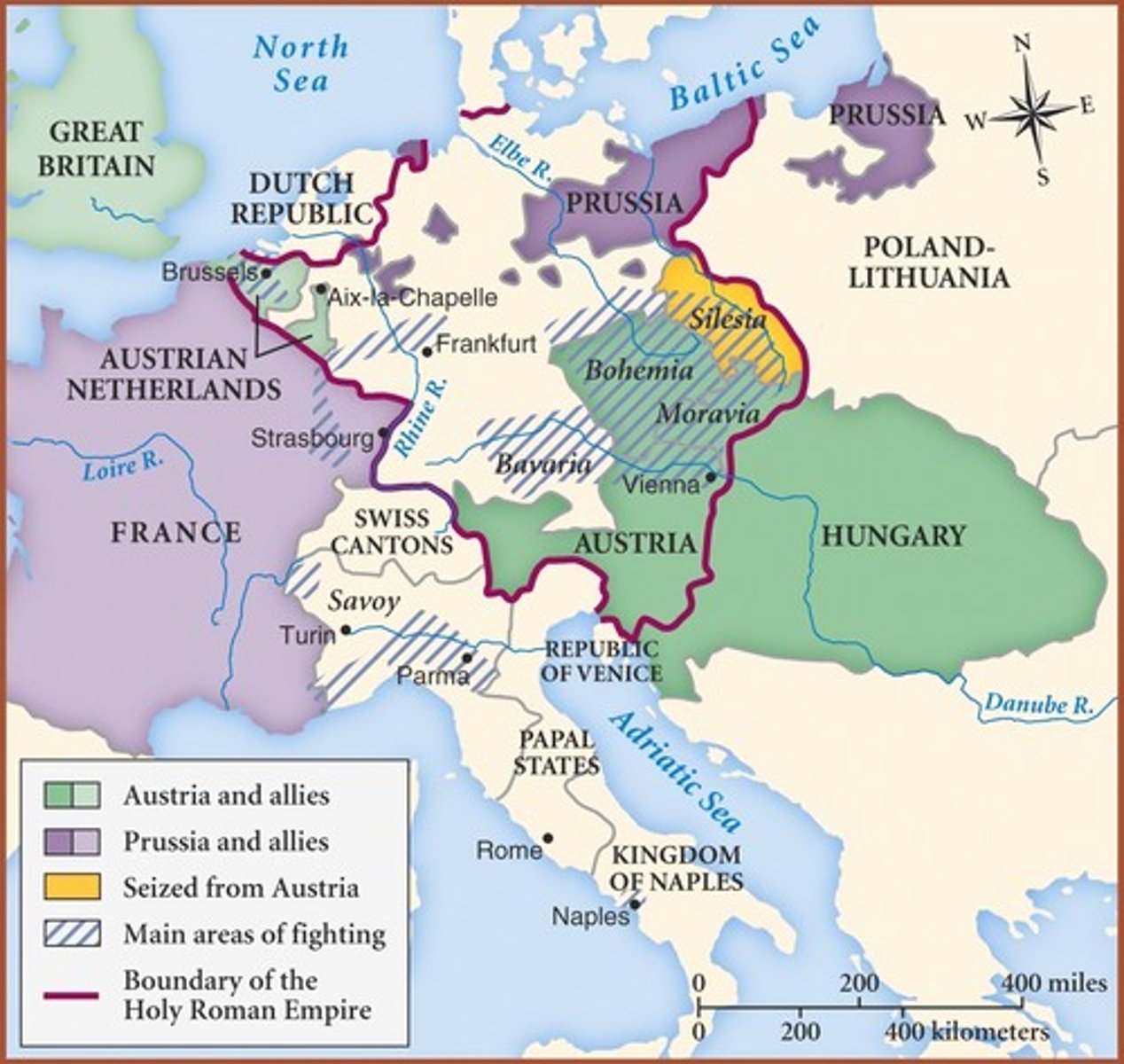
War of Austrian Succession (1740-1748)
War over the control of Austria due to the fact that Charles VI left Maria Theresa (a girl) as heir to the throne. Frederick II of Prussia invaded due to a want for Silesia and France helped him in order to humiliate their enemy (Austria.) Great Britain allied with Austria to prevent France from gaining more land. The colonies of France and GB began to fight also. Austria gave Silesia to Prussia and the Peace of Aix-la-Chapelle ended the war.
Maria Theresa of Austria (1717-1780)
Daughter of Charles XI of the Austrian Habsburgs, she was to succeed him after his death by way of the Pragmatic Sanction. When Frederick II seized Silesia out of her grasp, she failed to return the province to the Austrians, but successfully managed to preserve Habsburg power. She won support from her subjects, as well as the Magyar nobility in supporting her in the war.
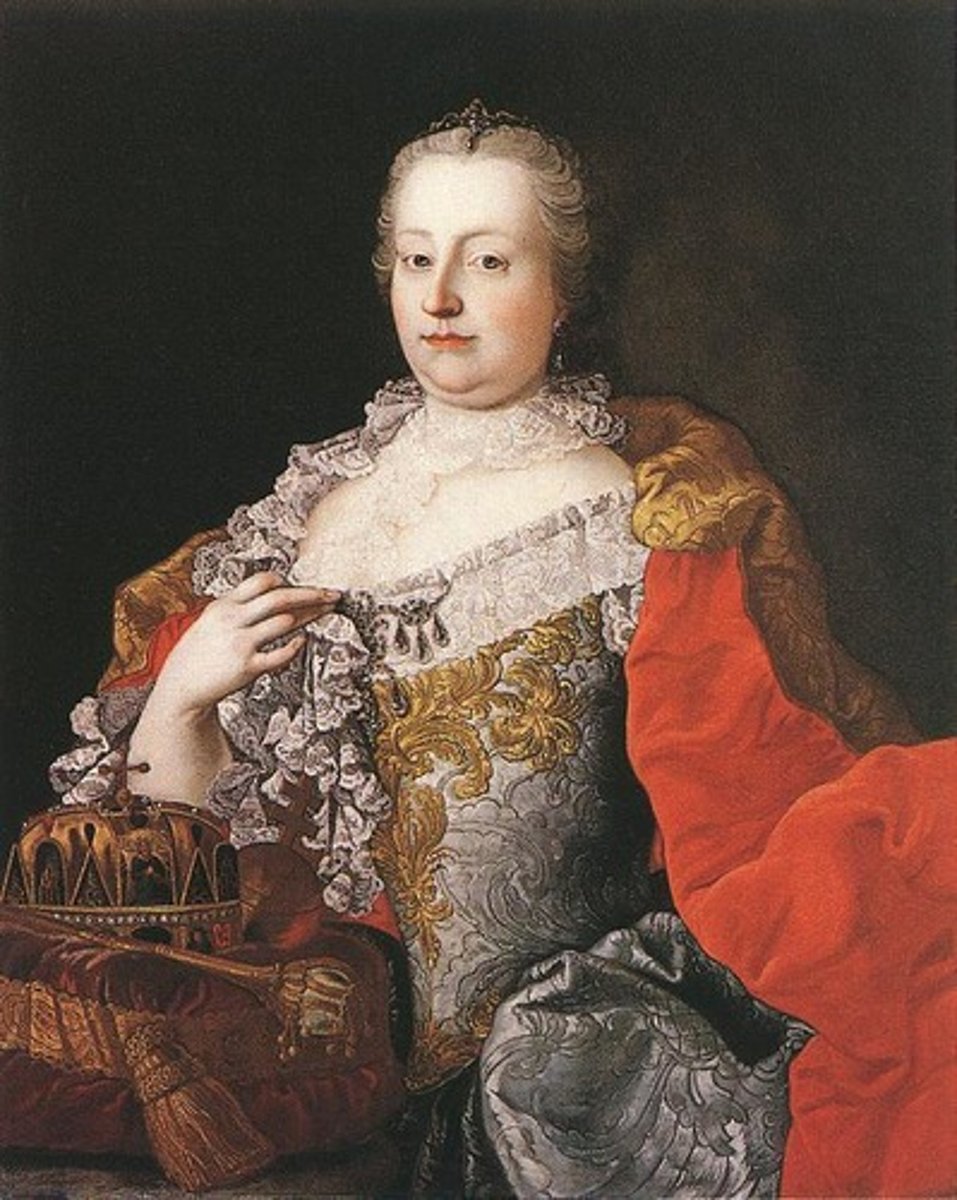

Peace of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748)
The peace treaty which ended the War of the Austrian Succession. Recognizes Maria Theresa as heiress of Austria and her husband as HRE. Prussia got Silesia, but colonial fighting between Britain and France continued even after the war ended.
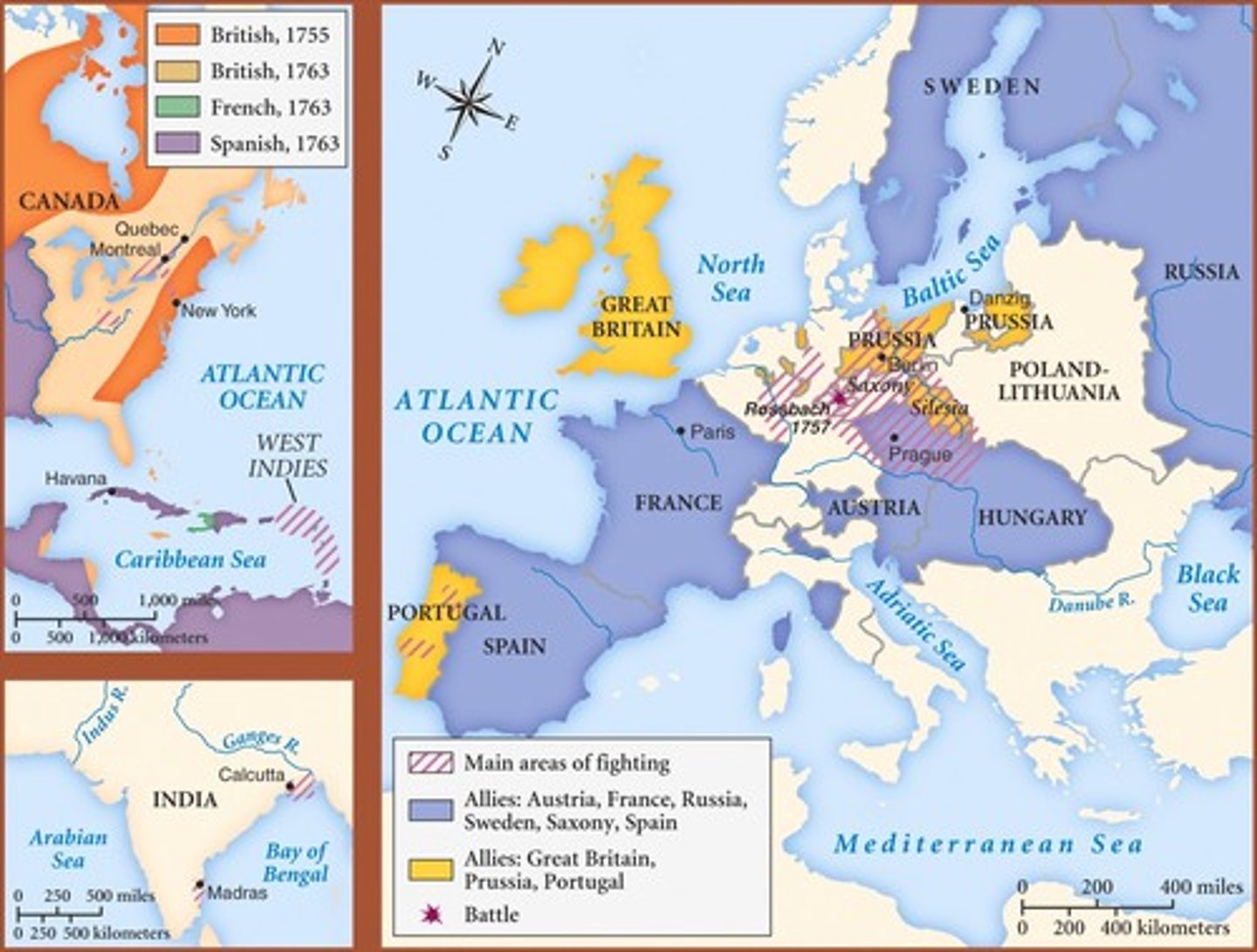
Seven Years' War (1756-1763)
A global conflict fought between 1756 and 1763. It involved every European great power of the time and spanned five continents, affecting Europe, the Americas, West Africa, India, and the Philippines. The conflict split Europe into two coalitions: one was led by the Kingdom of Great Britain and included the Kingdom of Prussia, the Kingdom of Portugal, the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg, and other small German states; while the other was led by the Kingdom of France and included the Austrian-led Holy Roman Empire, the Russian Empire (until 1762), the Kingdom of Spain, and the Swedish Empire. Meanwhile, in India, some regional polities within the increasingly fragmented Mughal Empire, with the support of the French, tried to crush a British attempt to conquer Bengal.