small ruminants dairy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
4 ways to dx pregnancy
what to look for? is this a sure mehtod?
two aspects
2 times you can eval
one specific type
behavior
no return to estrus (not definitive)
Physical appearance
size + udder development
Transabdominal Ultrasound
>35d - fluid-filled pockets
>45d - placentomes
± count embryo
Blood tests
ex. BioPRYN for pregnancy specific protein B (glycoprotein)
BioPRYN test
what does it test for
how?
when is it effective + with what accuracy?
false positive rate?
why?
fees for this test
BioPRYN test'
pregnancy!
tests for glycoprotein (Pregnancy Specific Protein B) which is produced by placenta
>= 30 days w/ 99% accuracy
5%
mostly early embryonic death
lab fee = $6.50 + blood tube, needle, + shipping costs
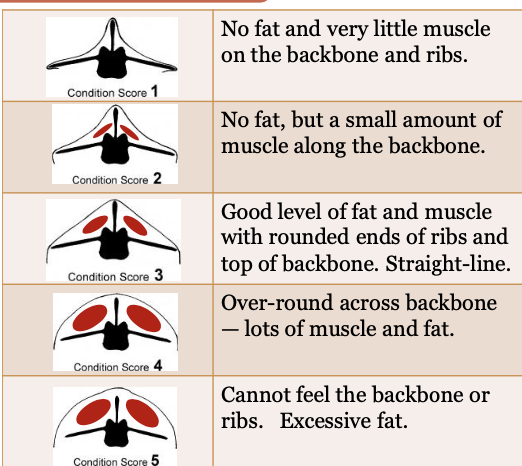
BCS for sheep
two areas examined
scale
BCS for sheep
Transverse spinous processes + dorsal spinous processes
1-5 (1 super low, 5 overweight)
how to prevent NEB 6 weeks pre-lambing/kidding
feed hay + grain w/ rising plane of nutrition - want BCS of 3.5
3 steps taken @ 4 weeks pre-lambing/kidding
how does the second one benefit lambs/kids?
crutch - shear wool from around vulva/udder
vx against Clostridium perfringens,
Clostridium tetani, +/- Rabies.
boosts abx in colostrum
observe frequently + move those w/ larger udders or softening vulvas into ind. jugs
how is normal glucose homeostasis maintained in small ruminants
two ways TGs turned into acetyl CoA
maintained by microbial fermentation of carbs
TGs > glyceral > glucose > pyruvate > acetyl CoA OR TGs > NEFAs > acetyl CoA
last 4-6 weeks of pregnancy
2 increases factors
2 decreases factors
what are they at the risk for?
mentally think of this process
Parturation
change in energy demands
what for?
what is decreased
what is there more of
what do maternal tissues use for energy metabolism? fetuses?
last 4-6 weeks of pregnancy
increased energy demand for fetal growth + lipolysis
decreased rumen capacity + feed intake (due to stress/poor weather/hypocalcemia/dz/poor feed quality)
NEB!!!
Parturation
increased energy demands
for lactation!
feed intake lowers
more lipolysis
mom uses lipids for energy metabolism + saves glucose for fetal demands
how does ketosis occur
possible symptoms of a sick ewe
ewes don’t eat > fat breakdown continues to happen > Ketone bodies (acetone, acetoacetate, + B-hydroxybutyrate) overwhelms use by other tissues > KBs accumulate in bloodstream > spill into urine + milk > suppress appetite > leads to metabolic acidosis AKA KETOSIS
anorexia, weakness, depressed, neuroligc signs like blindness/tremors/ataxia/teeth grinding, recumbency, and death
what happens to NEFAs when ketone bodies accumulate?
what happens once everything accumulates once again?
NEFAs are continued to be broken down, making them be turned into more ketones OR they are esterified back into TGs
these TGs may be stored as fat or exported as very low density lipoproteins (VLDLs)
if body sick of VLDLs, they reform TGs and energy transport decreases
livers export of fat is compromised and begins to store fat (TGs) turning into fatty liver
casual term for liver accumulating fat
medical term
appearance of healthy liver vs unhealthy liver
most common + possibly lethal liver dz in cats
process of the dz in cats
fatty liver
hepatic lipidosis
healthy = dark red/purple
fatty liver = yelllow
fatty liver!
stop eating - allows fat to accumulate - esp in high BCS
usual excess lipolysis = TG accumulation = fatty liver in cats
two things you can test for to see if an animal is in NEB
4 things youd see
6 tx for NEB
urine sample + blood test
ketones in urine
hypoglycemic, increased NEFAs, + increased b-hydroxy ketone body-bw
6 tx
oral propylene glycol + probios
B vitamins
IV dextrose (± Ca)
correct dehydration + acidosis
pump/drench w/ alfalfa meal or transfaunate
induce parturition/C-section
when are cows at risk for NEB vs small ruminants
cows = —> 6 weeks post calving (bc milk production)
sm. rums = 4-6 weeks PRE birth because of multiples
3 stages of lambing
lengths
preparation
1-6 hours
fetus delivery
30 mins-2 hours
placenta delivery
1-12 hours
8 steps to take after delivery of lambs/kids
make sure babies breathing
dip umbilicus
strip ewe’s teats
make sure babies stand + nurse w/in 1 hr
get colostrum! tube if neccesary
monitor that the mom passes placenta by 12 hours
keep babies warm
provide fresh water + hay for moms
keep good records
6 steps of processing for lambs
ear tag
weigh
tail dock
paint brand
± vitamin e + selenium
± castrate
how should food be offered to lambs starting at 7 days of age
desired % protein
what can be provided for immunity
important ratio!
what should be perfomed at 4, 8, + 12 weeks
what determines weaning timeline/weight?
creep feed (separate area mom can’t get in)
18-20% protein
coccidiostat
2:1 Calcium to Phosphorus!
vaccinations! especially for clostridium bacteria
marketing + breeding strategy (ex. winter vs spring born lambs, + market weights)
what is urolithiasis
how does it occur
why is this an issue?
3 causes of urolithiasis
there are stones in the urinary tract - highly saturated solution of solutes/minerals
when a stone becomes too large to pass through a portion of the urinary tract
it becomes a blockage! bad!
3 causes
urine is too concentrated (less water consumed, more water loss)
timing of castration
mineral combos
low Ca:P
high concentrate w/ P + low-roughage diet
alkaline urine
how does diet influence urolithiasis
3 examples
salts become unbalanched
calcium carbonate uroliths (oxalates bind to Ca = precipitates)
Magnesium ammonium phosphate uroliths (High P in diet, Mg, and NH4+ = stones) often in feedlot animals
urine pH (forage-diet = high pH urine = precipitaiton. low pH increases solubility of salts)
4 treatments for urolithiasis
4 methods of prevention
tx
anti-inflammatory + sedation
amputate urethral process
catheterize
surgery
prevention
always clean, fresh water ± salt blocks
delay castration to 6 months
acidify urine (ammonium chloride, biochlor)
adjust diet for low P (limit grain, find substitute)
what type of agent is coccidia
pathogenicity?
how often is it found in flocks
pre-patent period
effect of one coccidial oocyst?
5 CS
dx
typical ages effected?
protozoa
species variable
in most flocks - animals develop immunity
time of ingestion of oocysts to new oocysts being passed = 10-23 days
1 can cause 50 mil intestinal cells to be ruptured
diarrhea (bloody, yellow, strain), loss of appetite, weakness, poor body condition, death
fecal float + egg count
tricky because high pathogenicity may be difficult to find but dangerous
3-7 weeks
two forms of treatment for coccidia
6 methods of prevention
tx
antibiotics
fluid
prevention
avoid overcrowding
don’t house inside/in small areas for long periods of time
minimize strss
good sanitation
avoid overgrazing
feed coccidiostat in creep feed
characteristics of clostridial bacteria
how do they cause dz
2 strains of Clostridium
Obligate anaerobic, Gram (+), spore-forming bacterial rods
release toxins
Clostridium perfringens (B-D) + Clostridium tetani
Clostridium tetani
generic term
source
pathogenesis
5 CS
5 Tx
prevention
Clostridium tetani
tetanus
spores in soil/GIT of healthy animals
spores inoculate a wound - germinate - produce toxin (tetanospasmin) which diffuses in bloodstream > nerves, interferes w/ signaling for muscle relaxation + causes contracted muscles
stiffness, tremors, lockjaw, sawhorse stand, ± death
Penicillin (abx), sedatives, muscle relaxants, supportive care, open/clean wound
vaccinate!
Clostridium perfringens
two general types
source
pathogenesis (for each one)
CS (5 each)
3 Tx
prevention
Clostridium tetani
types B + C —> type D
spores in soil/GIT of healthy animals
pathogenesis
B + C - young ingest spores, germinate in GIT + produce toxins
D = sheep ingest spores in GIT - produce E toxin —> overeating high energy feed promotes bacterial proliferation
5 CS
BC = ulceration, inflammation, GIT hemorrhage —> diarrhea + death
D = necrosis, edema, hemorrhage in brain/kidneys/GIT > diarrhea, death
abx (penicillin), toxoid, supportive care
vx