chapter 4: carbs, sugar, starch and fiber
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
what is carb abbreviated as
CHO cuz
Composed of
– Carbon
– Hydrogen
– Oxygen
3 types of carbs
monosaccharides - simple
disaccharides - simple
polysaccharides - complex
list of monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, and galactose
list of disaccharides
maltose, sucrose and lactose
list of polysaccharides
starches and fibers
more complex
contain many glucose units
glucose
AKA blood sugar
-essential energy source
part of every disaccharide
monosaccharide
fructose
monosaccharide
sweetest of the sugars
galactose
only in a few foods (milk)
monosaccharide
disaccharides list
maltose
sucrose
lactose
maltose
disaccharide
made of 2 glucose units
sucrose
disaccharide
made of glucose and fructose
lactose
made of glucose and galactose
disaccharide
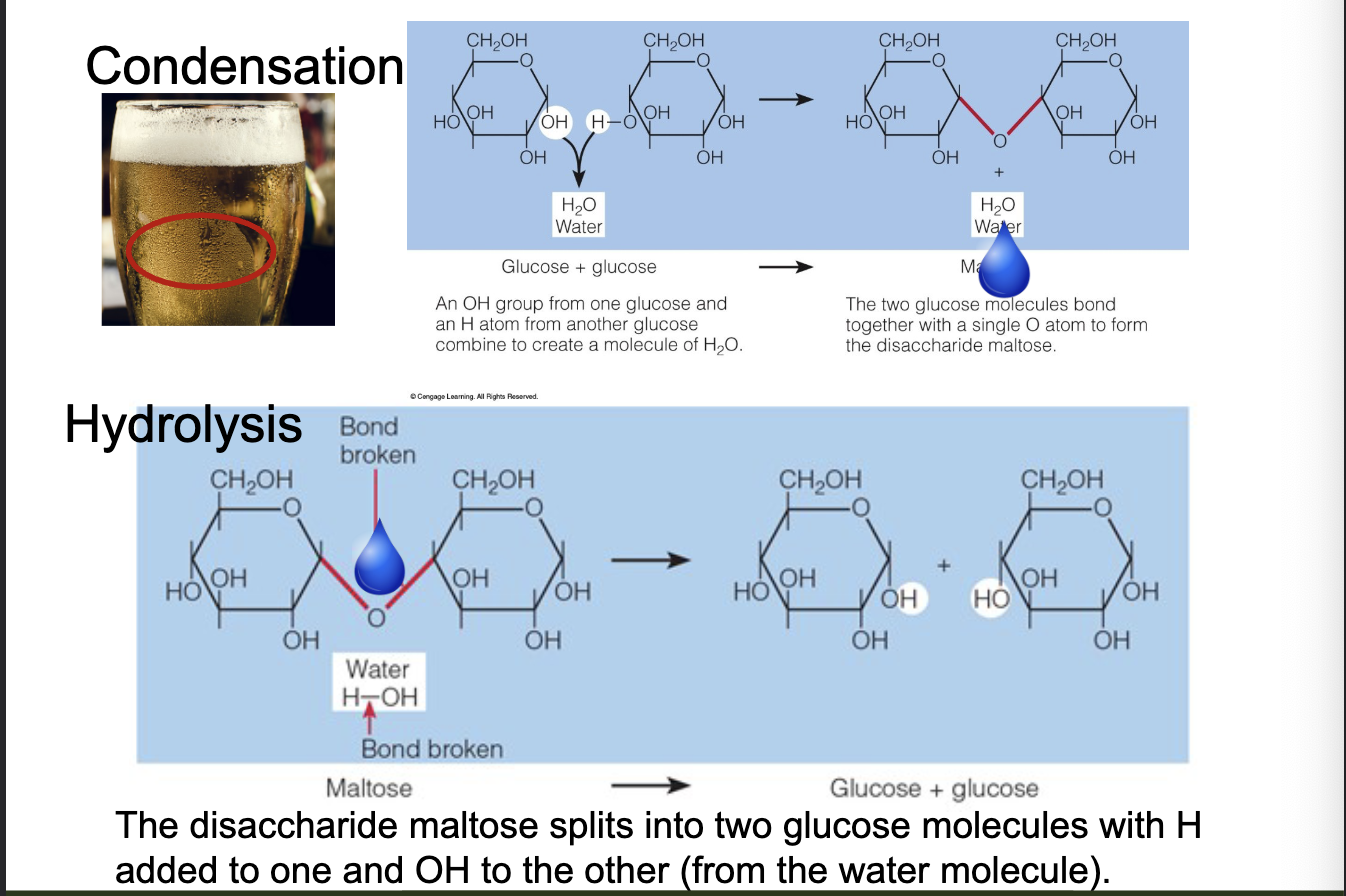
condensation
links 2 monosaccharides together
releases water
hydrolysis
Breaks a disaccharide in two
– Adds the water “back” to break the bond
condensation vs hydrolysis image
specific types of polysaccharides list
glycogen
starch
dietary fiber
glycogen
animal version of polysaccharide
storage form of energy (from CHO in the body)
polysaccharide
contains hundreds of glucose units in highly branched chains
how many grams of glycogen are stored with how many grams of water
1 gram of glycogen is stored with 3 grams of water.
Starch + 2 types of starch
(plant version of polysaccharide)
Amylose linear chain of glucose molecules linked end-to-end.-
—> may resist breakdown and become resistant starch
—→hundreds of glucose molecules in unbranched chains
Amylopectin is a much larger molecule with numerous branches of short
chains of glucose molecules linked to a main chain like the branches—→ hundreds of glucose molecules in occasionally branched chains
dietary fiber
(plant polysaccharide that we cannot
break down in our digestive tracts)
differ from starches cuz we do not have enzymes to break it down
contain soluble and insoluble fibers
—→ soluble fibers dissolve in water, slow gastric emptying time (make u fuller for longer), are fermentable (gut microbes ferment solu fiber and produce short chain fatty acids)
—→ insoluble fibers provide bulk and normalise bowel function
phytic aciid
not a fiber, but associated with fiber
– Binds minerals
– Antioxidant
functional fibers
is a polysaccharide / dietary fiber
e.g. (inulin, cellulose)
• Added to foods
• Used as supplements (psyllium
resistant starch
polysaccharide/ dietary fiber
e.g. chilled amylose
how an enzyme works
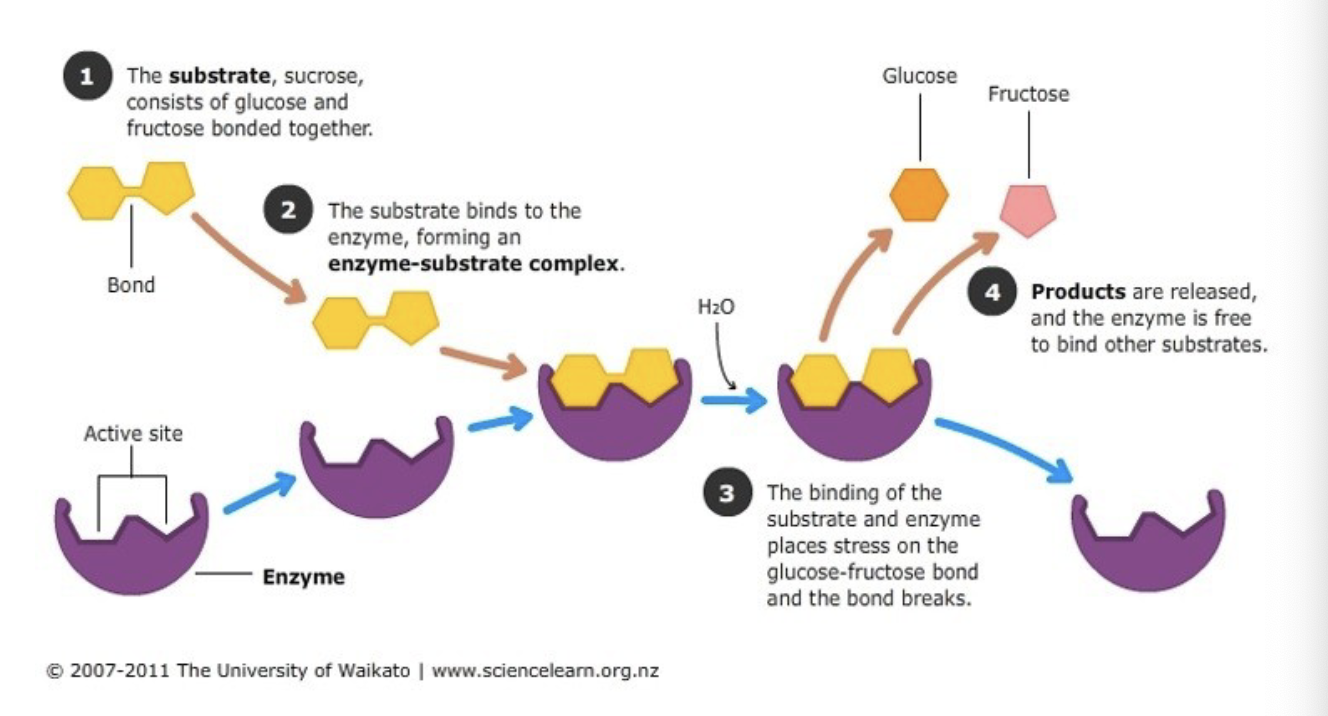
what enzyme digests what carbs
• Lactase digests Lactose
• Amylase digests ___ amylose/amylopectin (starch)
• Maltase digests ____ Maltose
• Sucrase digests ____ Sucrose
• Beano® digests ____ Fiber
• Lactaid® digests ____ Lactose
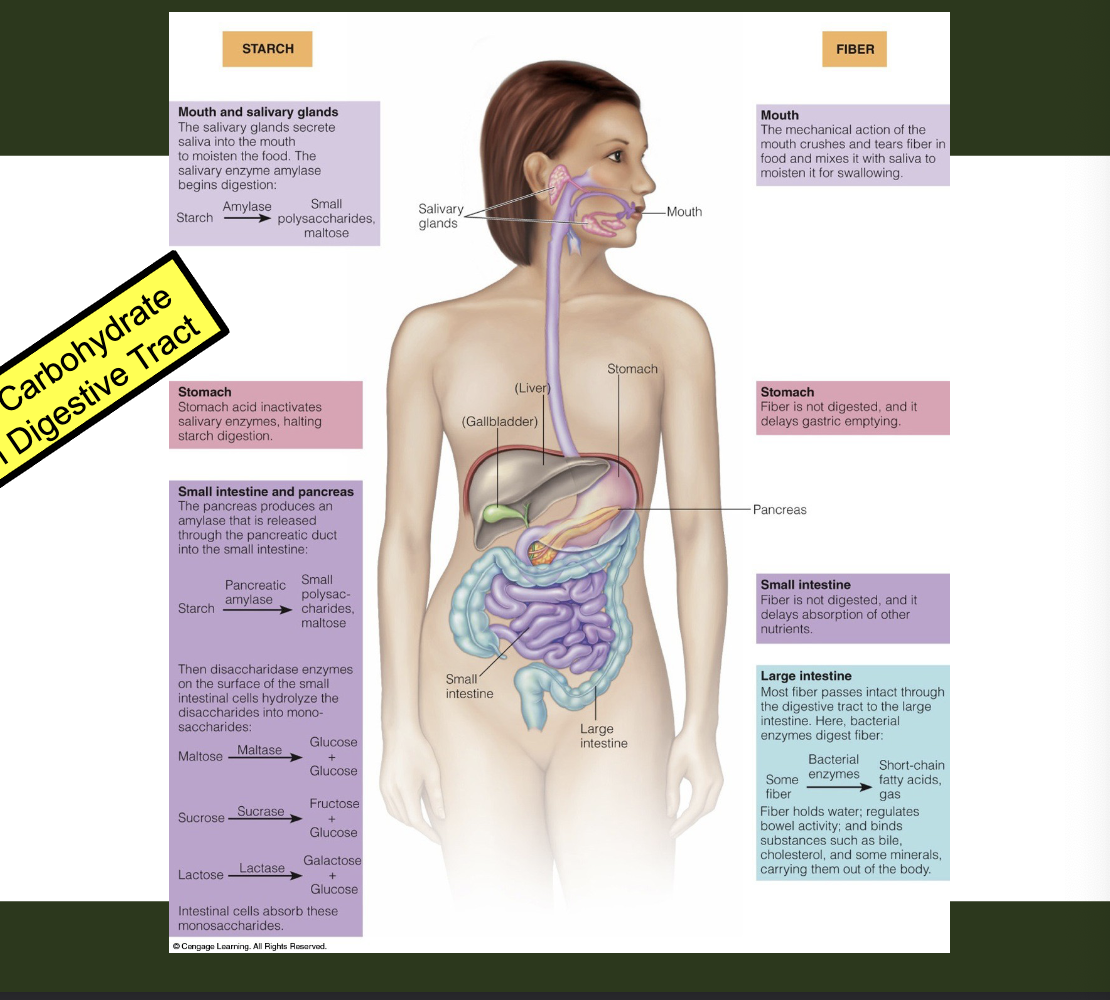
digestion of carbs
goal is to get glucose for absorption and use
digestion of CHO is hydrolysis via enzymes
mouth mechanically breaks down food and mixes with saliva which has salivary amylase that breaks down carbs with enzymes
stomach has stomach acid that has protein digesting enzymes
small intestine has pancreatic amylase
—> specific disaccharide enzymes: maltase, sucrase, lactase
large intestine is where soluble fiber is fermented and insoluble fiber holds liquid and is bulk waste
summary of carbohydrate digestion
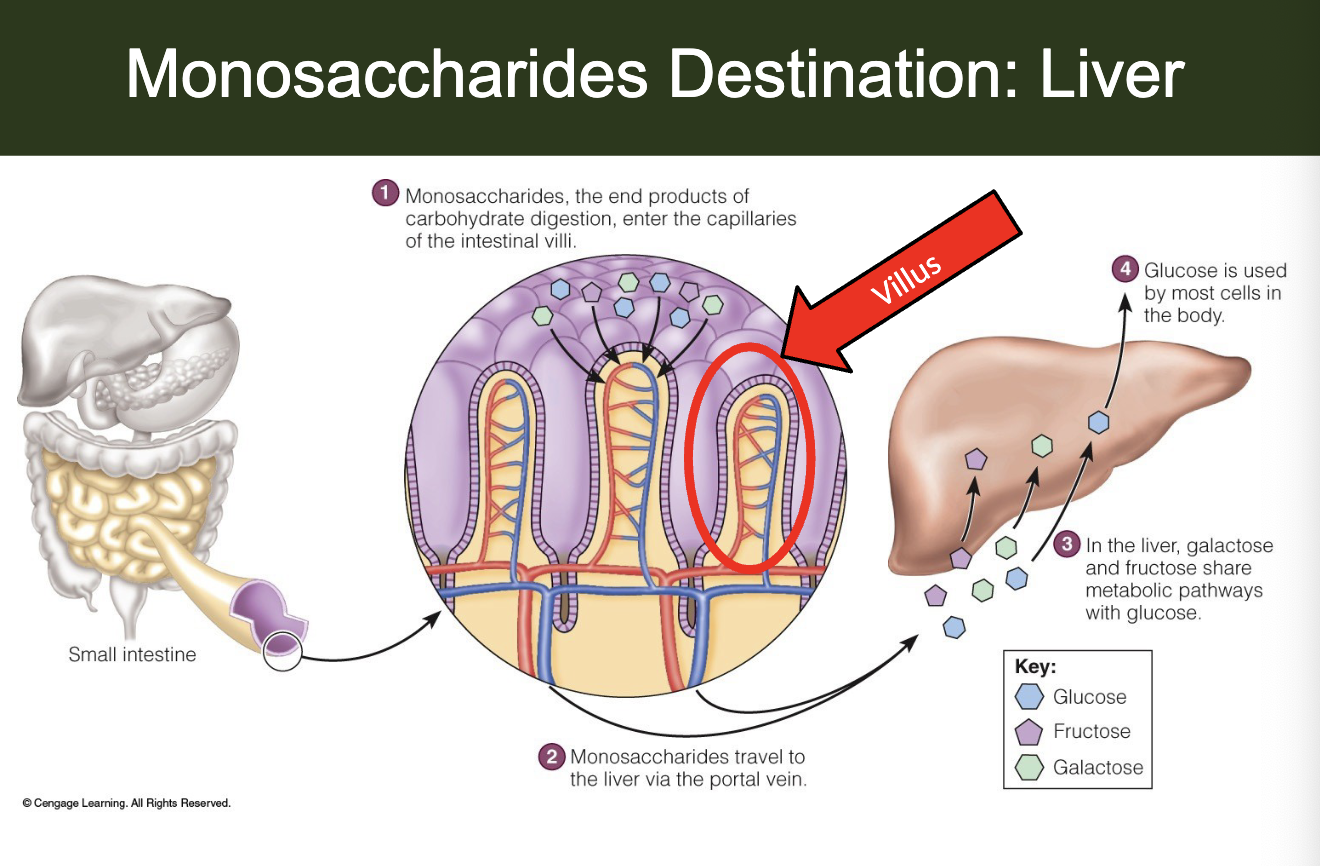
absorption of carbs
most carb absorption (put carbs in bloodstream) happens in small intestine with other nutrients too
glucose and galactose absorbed by active transport
fructose is absorbed by facilitated diffusion
liver:
—→ facilitates conv of fructose and galactose, directs glucose, and stores glucose as glycogen if not need now
lactose intolerance
highest lactase activity is immediately after birth, and declines with age
prevalence determinesd by genetics
to help, make dietary changes
—→ manage dairy consumption by choosing fermented milk products like kefir or yoghurt, getting products with laactose alr digested like lactaid, having an individualized diet
avoidance of lactose can result in riboflavin, vit D, calcium + protein deficiencies
how is glucose stored as glycogen
Liver storage
Condensation into glycogen
Hydrolysis of glycogen for rdelease of glucose when
needed
– Muscle storage
Selfishly hoards glycogen
glucose is preferred source for what cells
Preferred source for brain, nerve cells, and developing red
blood cells
but if not available, can use protein as fuel
how is glucose made from protein
Amino acid conversion (“Glucogenic AAs”)
– Gluconeogenesis (Gluco = Glucose; Neo =
New; Genesis = making)
– Nitrogen is waste product
how many grams of carb per day needed to spare protein and prevent ketosis
50- 100 g carb per day
what happens if inadequate supply of carb
fat metabolism shifts
body breaks down fat for energy and forms ketones (bodies)
ketosis disripts acid base balance
what happens to extra glucose (2 step)
Extra glucose first makes glycogen (stored
form of glucose “body starch”)
• Remaining extra glucose made into fat
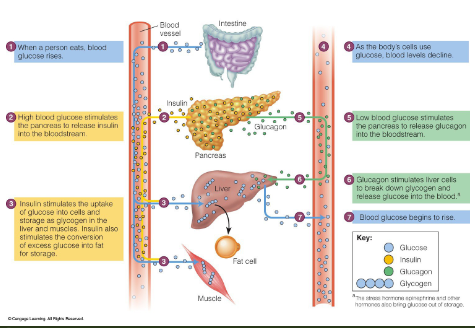
what does insulin do
moves glucose from bloon INTO cells
helps maintain blood glucose homeostasis
what does glucagon and epinephrine do
brings glucose out from storage (from liver glycogen)
helps maintain blood glucose homeostasis
how is a steady supply of blood glucose maintained in blood stream
Intestines – food (use as you go)
– Liver – glycogen (use from stores
between meals)
are things ever digested in pancreas
NO
insulins response in more detail
how high insulin surge is in the body influences how the body stores or uses its glucose
glycemic effect is how quickly and how much a food raises your blood sugar levels - factors that influence this is glycemic index and body weight and other foods
insulin resistance
starts 10 years before diabetes dx
most often caused by obesity (visceral fat)
insufficient sleep (less than 6 hrs) makes it worse
takes more insulin to deliver the glucose
muscles share glycogen…
locally
liver shares glycogen…
to all body parts
Feedback loops for glucagon and insulin
what is the glycemic index
a measure of how quickly or slowly a carb food is digested and increases blood glucose levels
higher glycemic index carbs..
increase blood glucose levels more quickly
lower glycemic index carbs
increase blood glucose levels more slowly.
what is the glycemic response
speed of glucose absorption, how it rises, and the rate of return to normal levels
low glycemic response vs high glycemic response
low glycemic response are long acting - timed release
high glycemic response are fast sugar surge
honey has ___ grams per tso whereas sucrose has __ grams per tsp sucrose
honey - 6 grams per tsp
sucrose - 4 grams per tsp
health effects and recommended intakes of sugars
bacteria ferment sugars producing acid 20-30 min after each exposure
Food factors associated with tooth decay
Time of food in mouth
Sticky foods
Frequency of sugar consumption
Acidity of liquids
– Food choices (natural sugars, fiber, protein, eating occasionally
rather than continuously)
– Factors associated with tooth decay
Poor oral hygiene
Saliva factors
Strep Mutans (does not like Xylitol)e Xylitol)
what are sugar alcohols and what do they do, what problems can come cuz of them!
Sugar Alcohols
• What they are
– Reduced calorie sweeteners 2 – 2.6 cal/gram
– Naturally occur in fruits & vegetables
– Known as “nutritive sweeteners”
• What they do
– Low glycemic response (enter bloodstream
more slowly)
– Do not contribute to dental caries
– Xylitol reduces strep mutans in saliva & plaque
• Problems
– Excessive amounts can cause gas, diarrhea,
and bloating
dietary guidelines for Americans
limit added sugars to 10% of total energy
WHO and FAO recs for added sugar
less than 10% of total energy, so 5-10%
American Heart Association added sugar recs
average is 6%
limit to 100 cal for women (roughly 5% of total daily calories intake)
limit to 150 cal for men (roughly 7% of daily calories intake)
DV for added sugar
50 g
DRI for added sugars
less than 25% of day’s total energy
non nutritive sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners
– Non-nutritive sweeteners
– Large doses and adverse effects
– May not affect weight
• Stevia – an herbal product
– Generally recognized as safe (GRAS)
• Saccharin
– Discovered by accident
soluble fiber
Soluble Fiber
• Soluble fiber produces a thick, viscous liquid
similar to honey in gastrointestinal fluid
• Soluble fiber is readily metabolized by gut
bacteria, which convert much of it into small
molecules called short-chain fatty acids
(SCFA)
• The cells lining the colon obtain about 60-70% of their energy from SCFA
70% of their energy from SCFA
viscous, soluble more fermentable fibers
gums
pectins
psyllium
some hemicellulose
nonviscous, insoluble, less fermentable
cellulose
lignins
resistant starch
hemicellulose
excessive fiber intakes
insufficient energy or nutrient needs
– Abdominal discomfort, gas, diarrhea
– GI obstruction
– Nutrient absorption (phytates bind)
– Dietary goals
Balance, moderation, and variety
Health Effects and Recommended Intakes of
Starch and Fibers
Heart disease
– Whole grains (3 is Key)
Sources
Intact are best
– Soluble fibers (absorb liquid)
Oat bran, barley, legumes
Cellulose, Hemi-cellulose, pectins, gums
Have cholesterol-lowering effect
• Diabetes
– High-fiber foods
– Unprocessed foods
recommended intakes of carb and fiber
Carbohydrates
– AMDR: 45 to 65% of energy requirement
– RDA: 130 grams per day
– DV: 275 grams per day (55% of 2000 cal)
• Fiber
– DV: 28 grams per 2000 kcalories
– DRI: 14 grams per 1000 kcalories (28 gm/2000
kcal)
– No UL
• Protein sparing: 50 – 100 g CHO
Revised!