AP Human Geography Unit 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Agricultural Population Density
Number of Farmers divided by the arable land
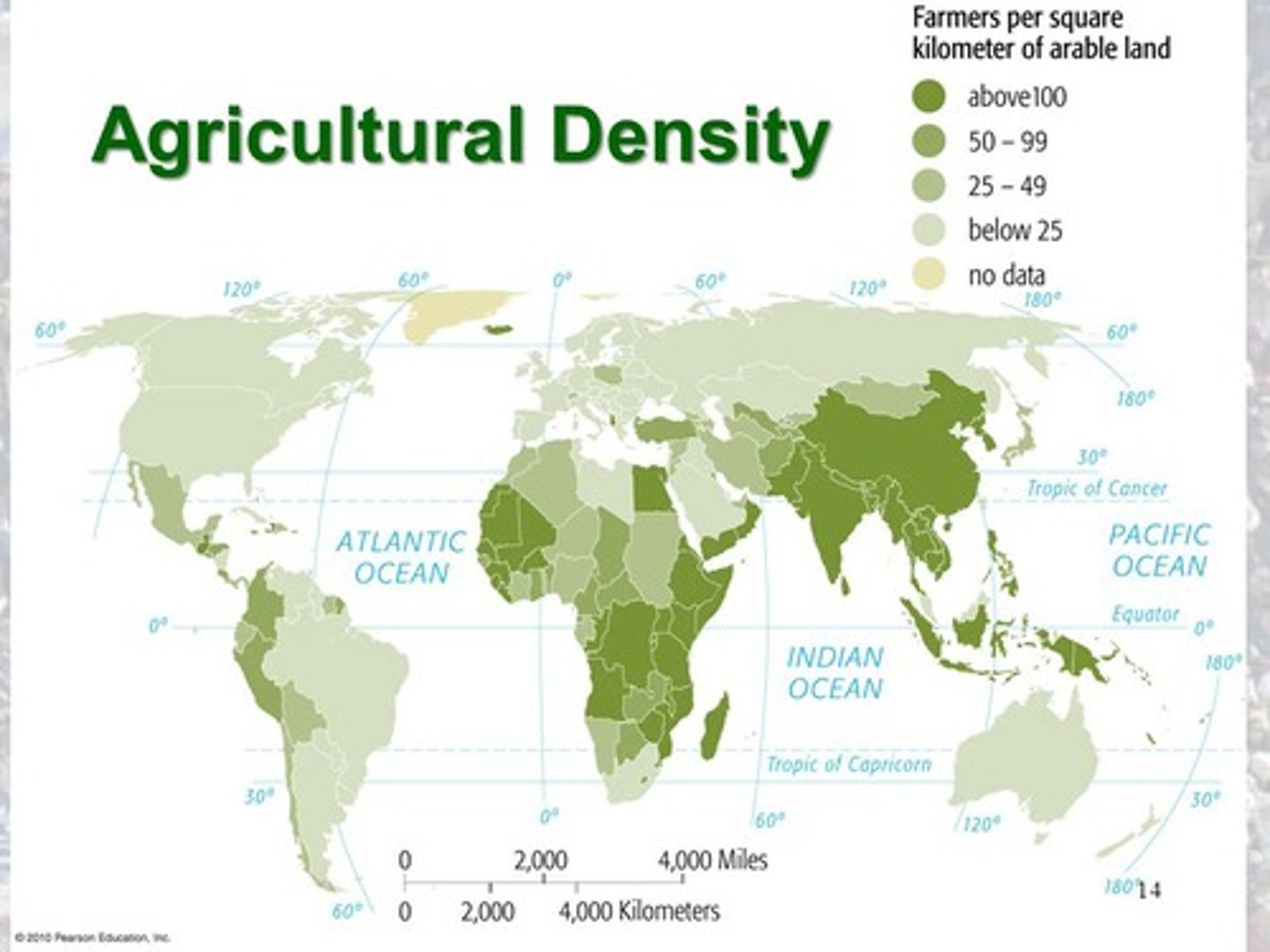
Arable Land
Land suitable for farming/agriculture

Physiological Population Density
Population of a region / arable (farmable) land

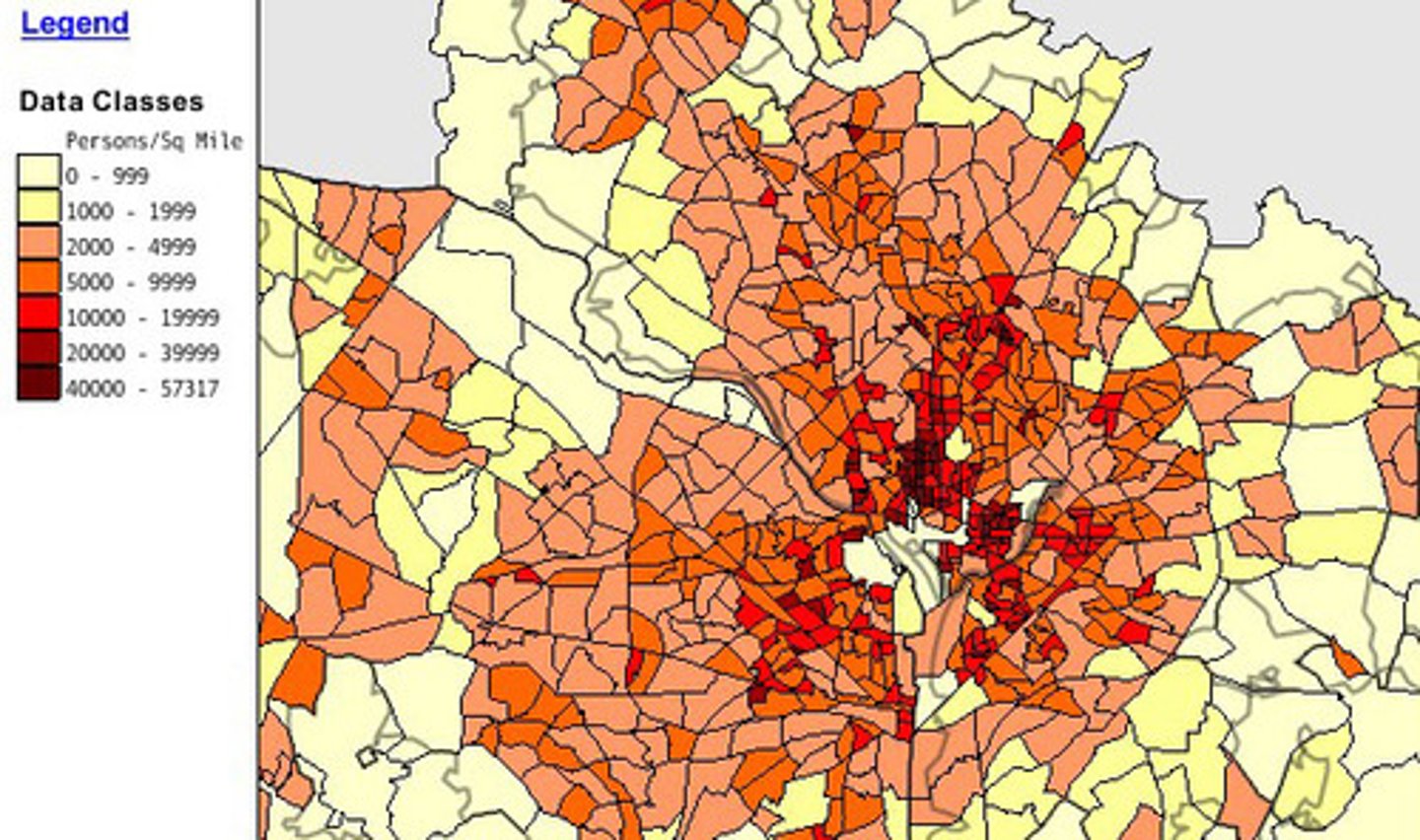
Arithmetic Population Density
Population of a region divided by total land area.
Baby Boom
Temporary marked increase in the birth rate

Census
A complete count of of a population
Child Mortality Rate
Total number of child deaths per 1,000 live births

Crude Birth Rate
Total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people in the society
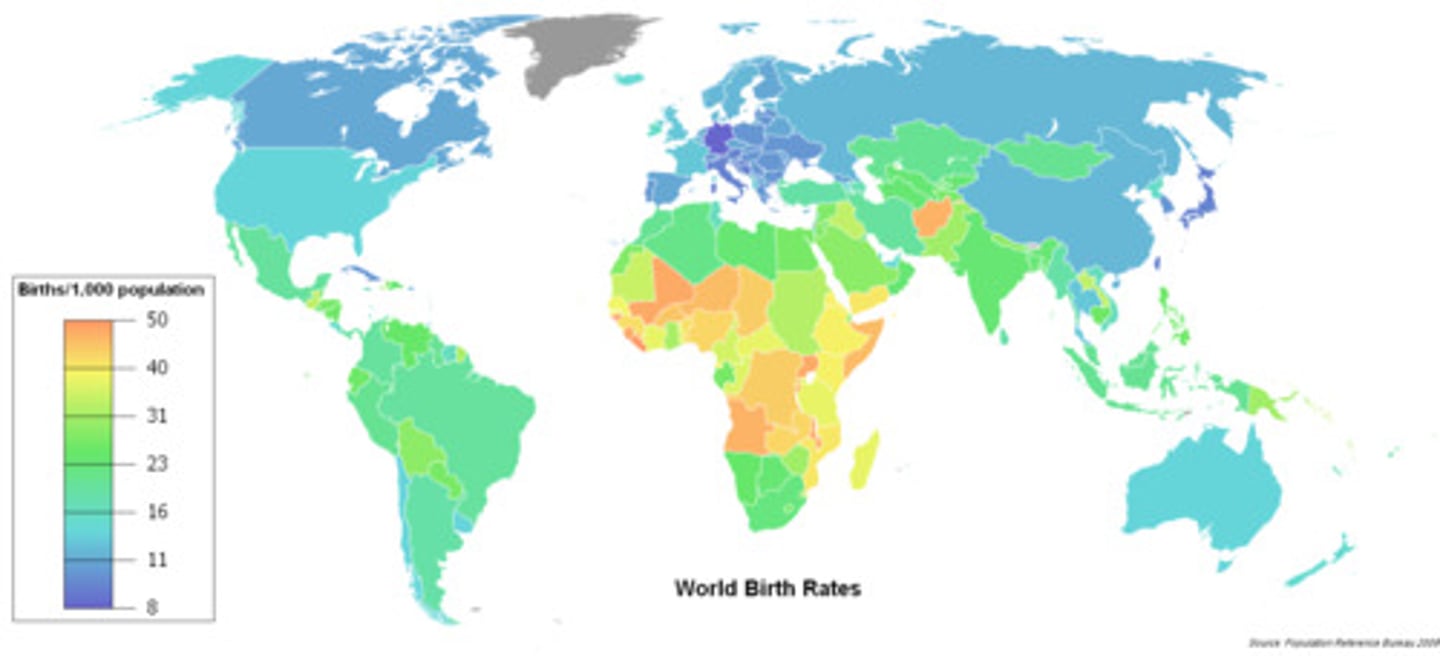
Crude Death Rate
Total number of deaths per 1,000 people in a society
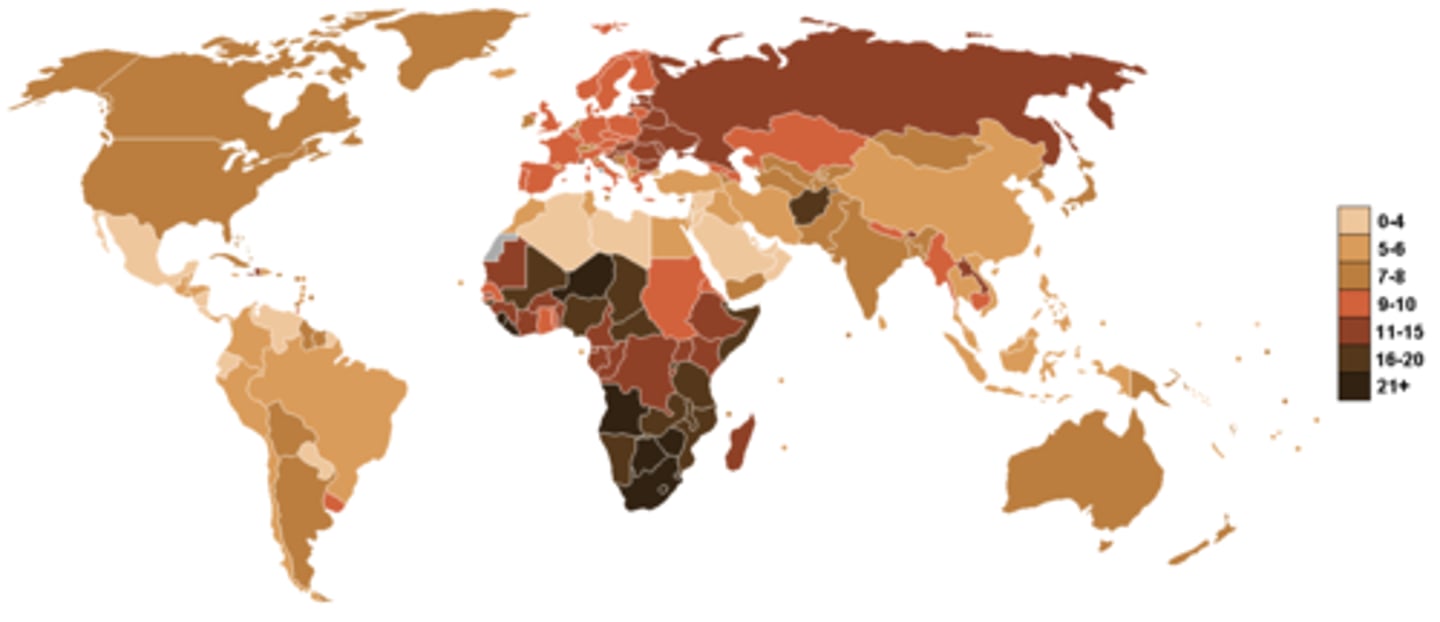
Dependency Ratio
Number of people too young or too old to work compared to workers

More Developed Country (MDC)
Also known as a relatively developed country or a developed country, country that has progressed further along the development continuum

Doubling Time
Number of years needed to double the population

Ecumeme
The areas of earth occupied by human settlement

Epidemiological Transition Model
The theory that says that there is a distinct cause of death in each stage of the demographic transition model. It can help explain how a country's population changes so dramatically.
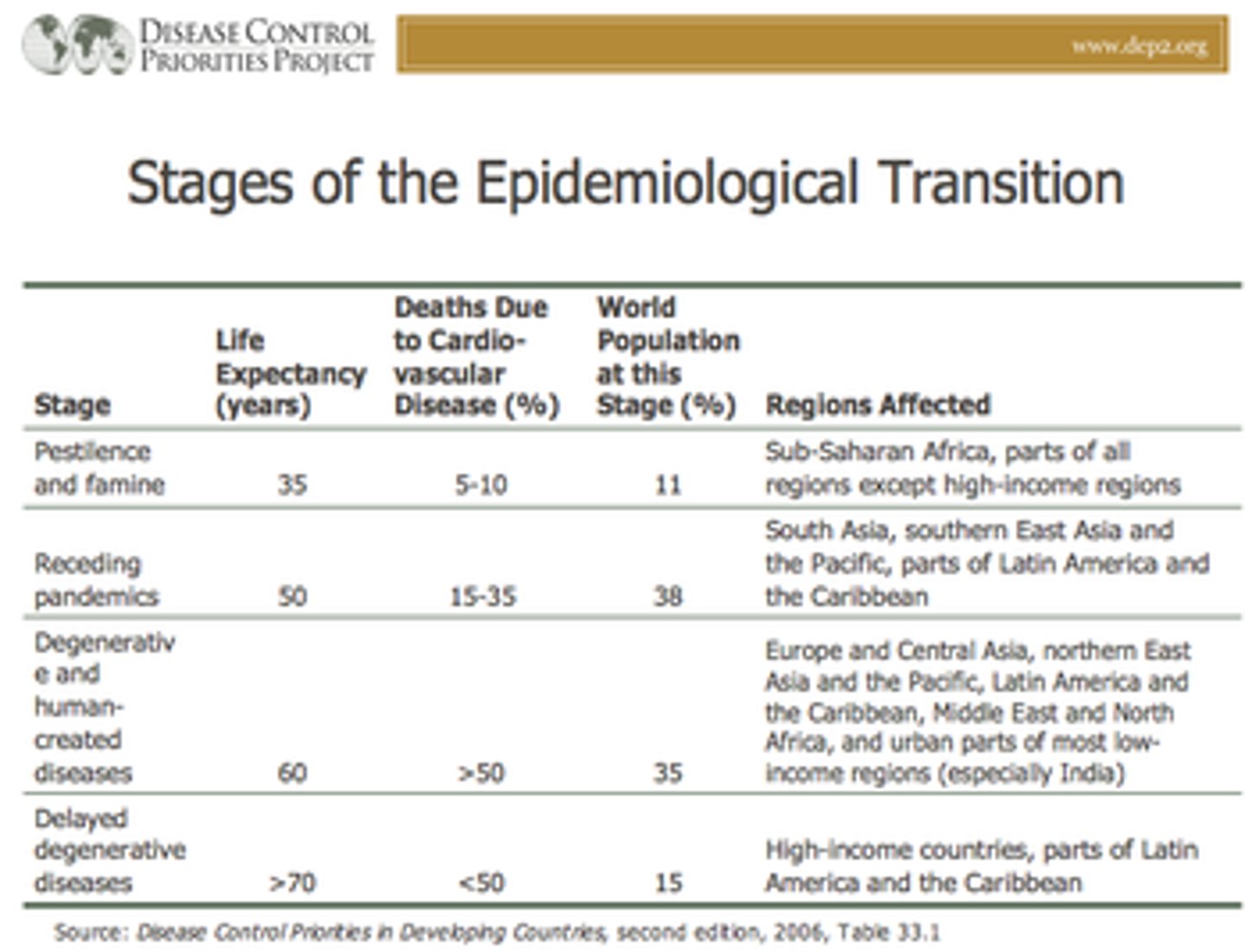
Industrial Revolution
Time during the 19th century, major improvements in manufacturing goals and delivering them to market

Infant Mortality Rates
the number of infant deaths (under age 1) per 1000 live births

Less Developed Countries (LDC)
Non-industrialized/poor countries.
Stage two, early three
Life Expectancy
Average number of years an infant can expect to live

Thomas Malthus
An English economist who was one of the first to argue that the world's population increase was far outrunning the development of food production

Malthusian Theory
The theory that population grows faster than food supply
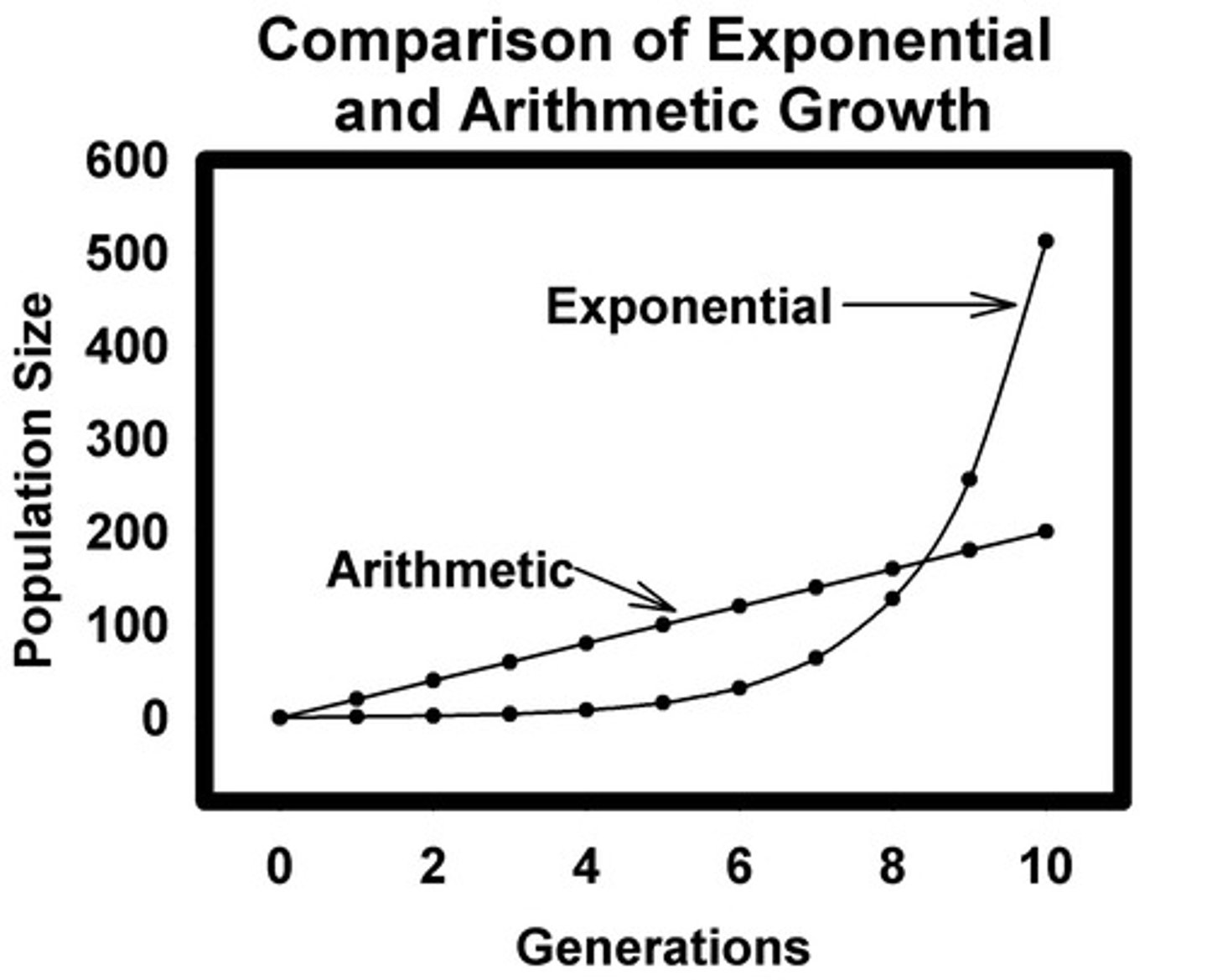
Medical Revolution
Time during the late 20th countries, when medical technology from Europe and North America diffused to developing countries
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
The percentage of annual growth in a population excluding migration.

Neo-Malthusian
A belief that the world is characterized by scarcity and competition in which too many people fight for too few resources. Named for Thomas Malthus, who predicted a dismal cycle of misery, vice, and starvation as a result of human overpopulation
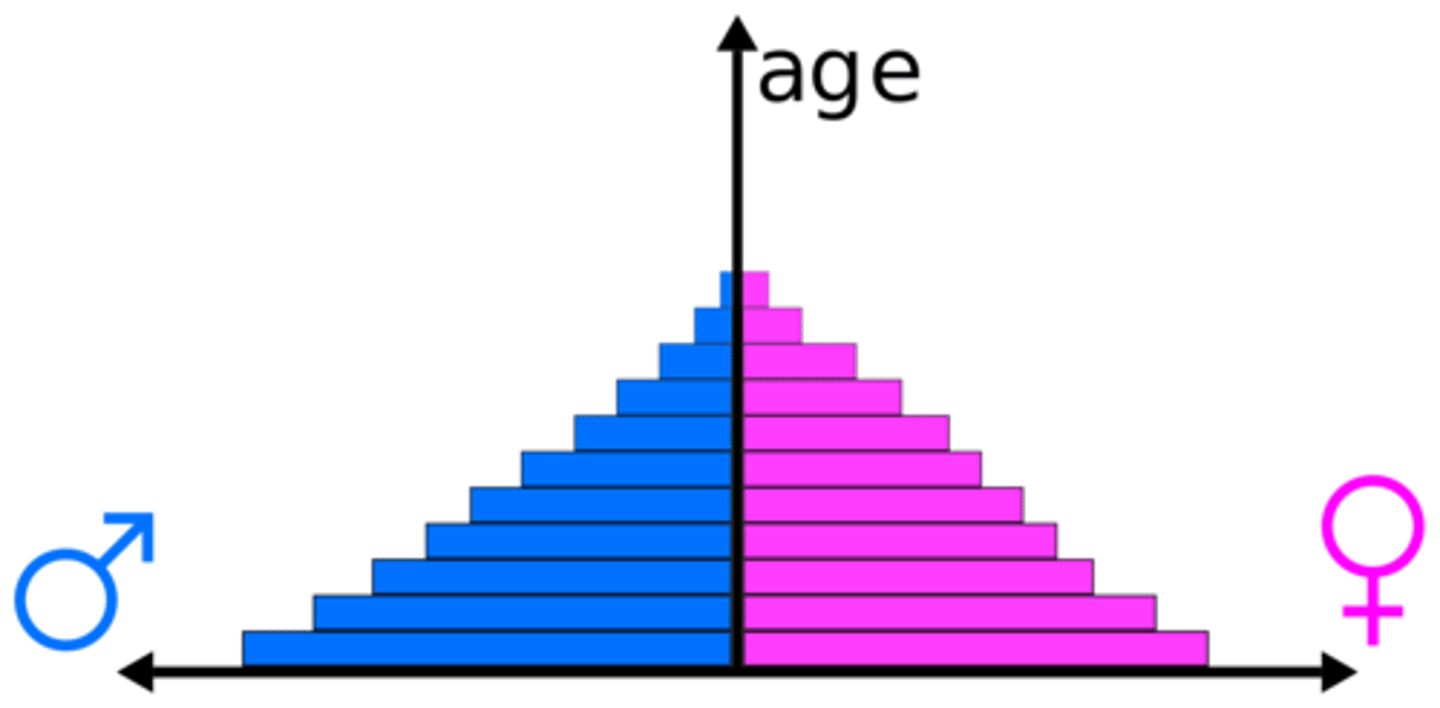
Population Pyramids
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
Anti-Natalist Policies
Government policies to reduce the rate of natural increase

Pro-Natalist Policies
Government policies to increase the rate of natural increase
Sex Ratio
The number of males per 100 females in the population.

Total Fertility Rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
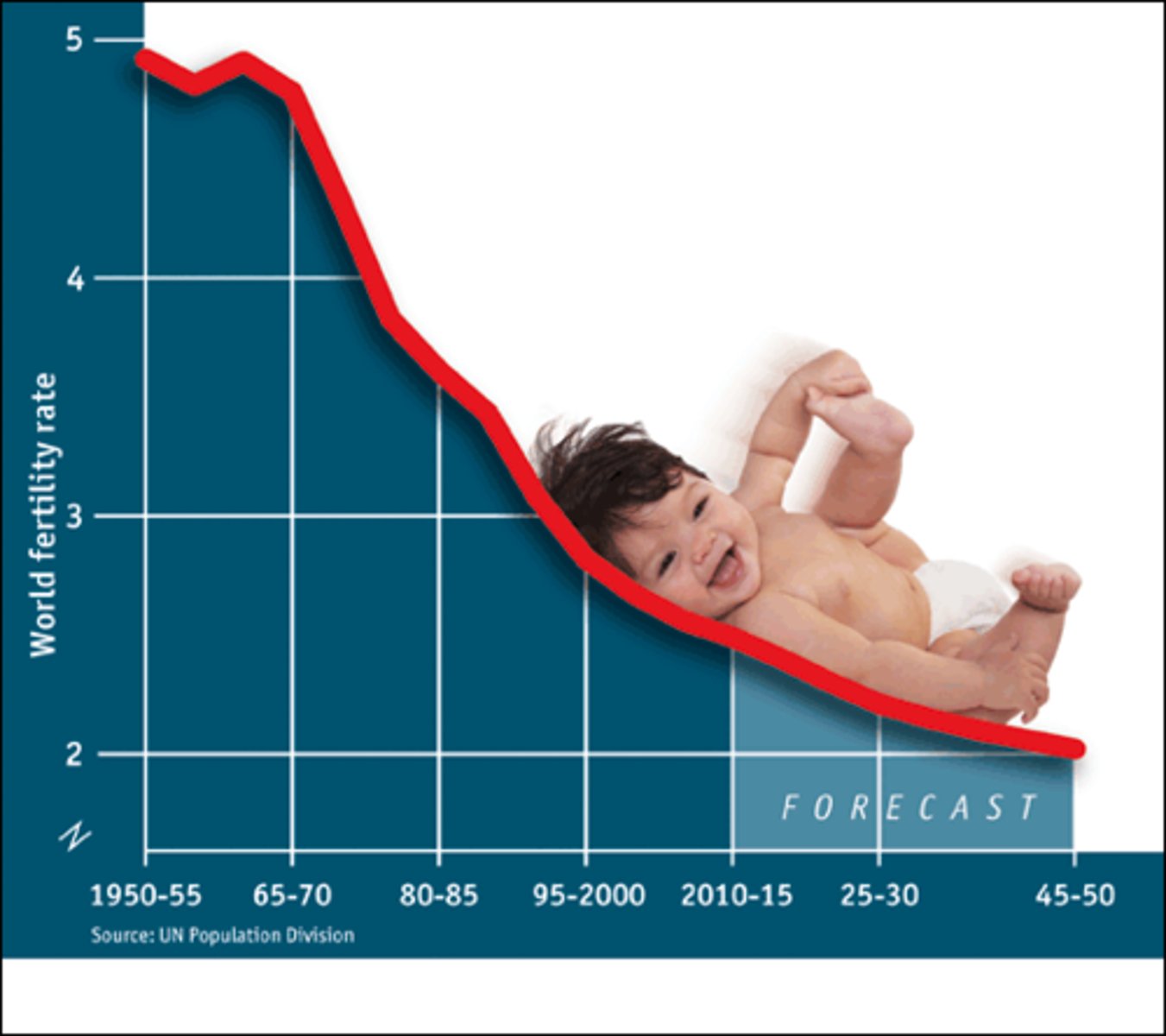
Zero Population Growth
A decline of the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero.

Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics

Overpopulation
The number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living.

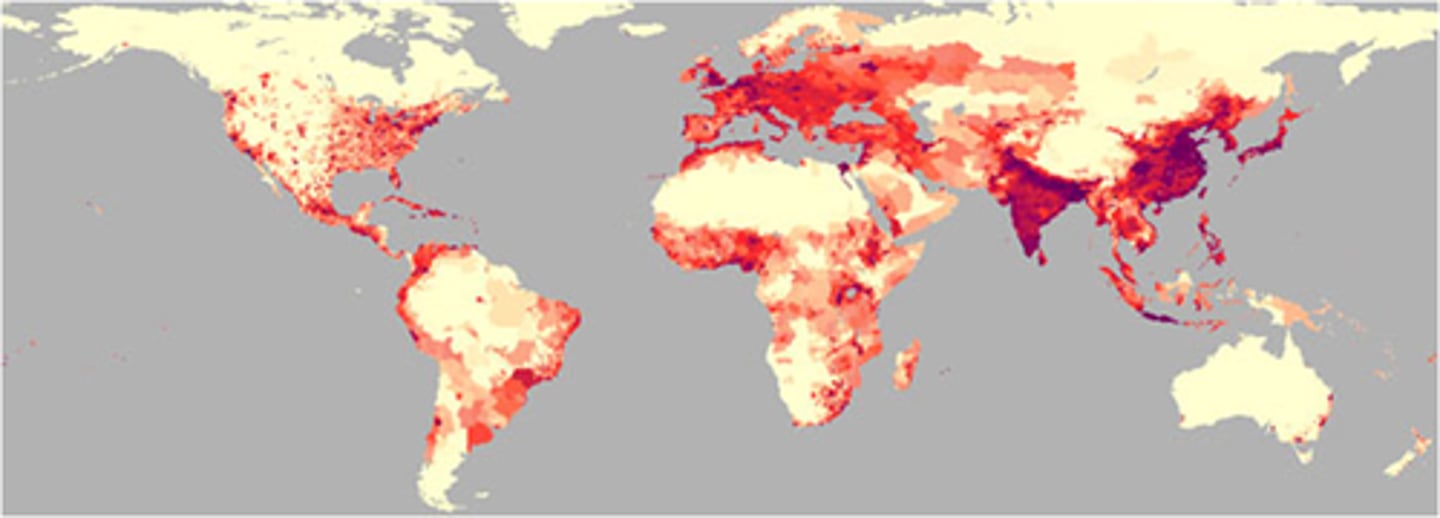
Population Center
An area of land where people are most dense, including East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Europe.
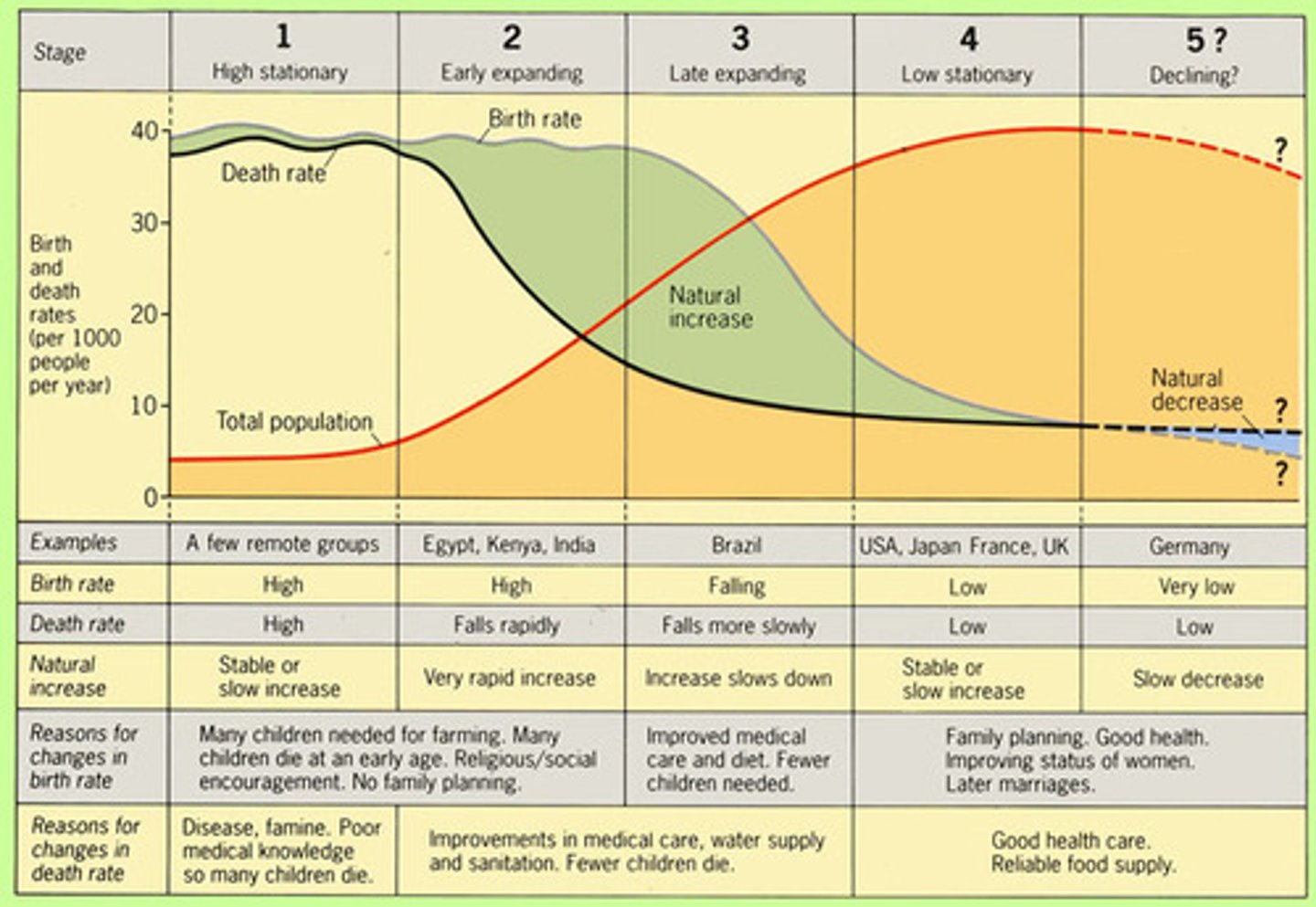
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
Mobility
A general term covering all types of movement from one place to another
Periodic movement
Movement - for example, college attendance or military service - that involves temporary, recurrent relocation

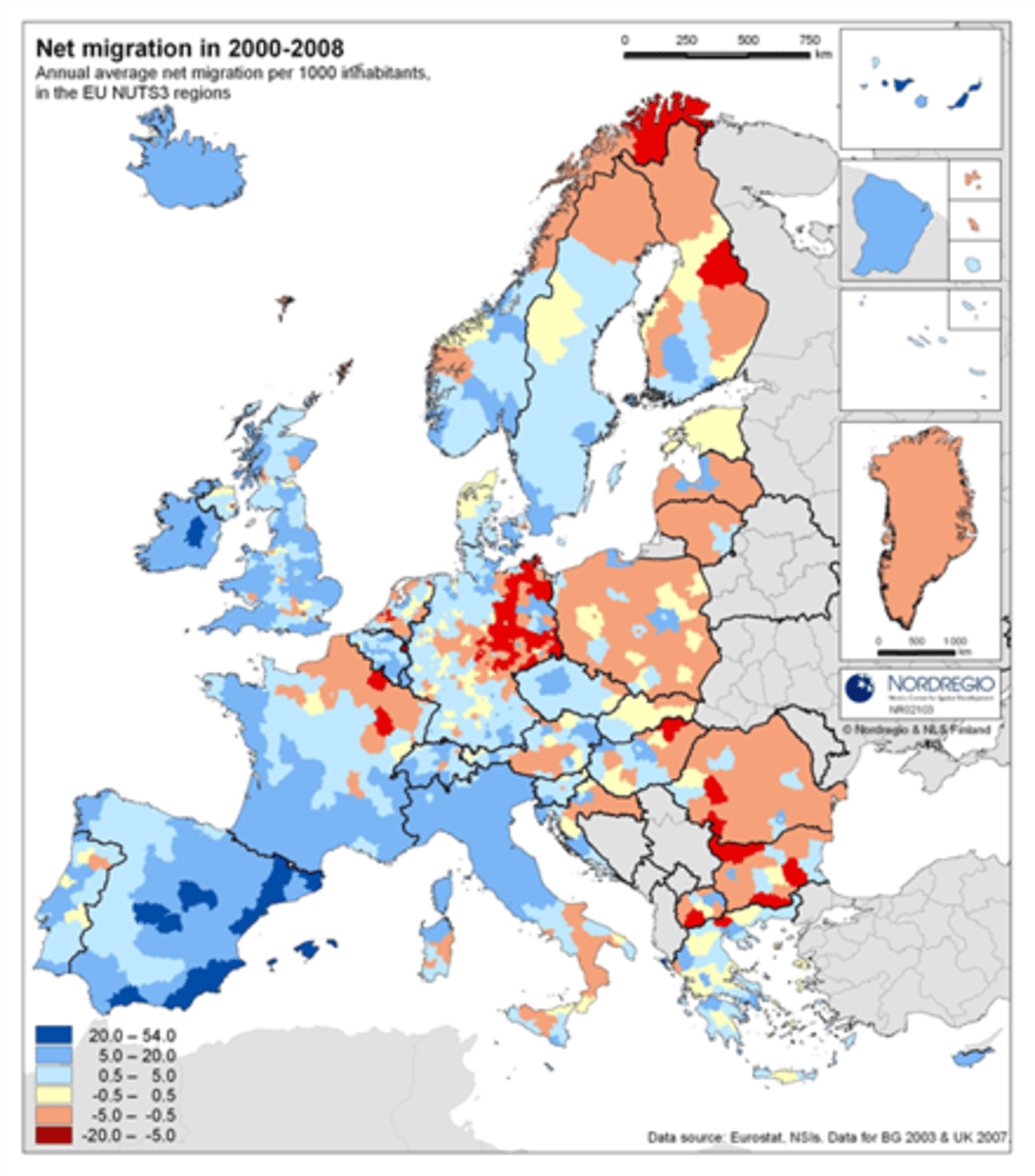
Net migration
The difference between the number of immigrants and the number of emigrants
Push Factors of Immigration
reasons people emigrate and leave their homes such as economic troubles, overcrowding, poverty
Intraregional Migration
movement within a region
Interregional Migration
Movement from one region to another
Migration Transition
Change in migration patterns in a society caused by industrialisation, population growth, and other social and economic changes that also produce the demographic transition

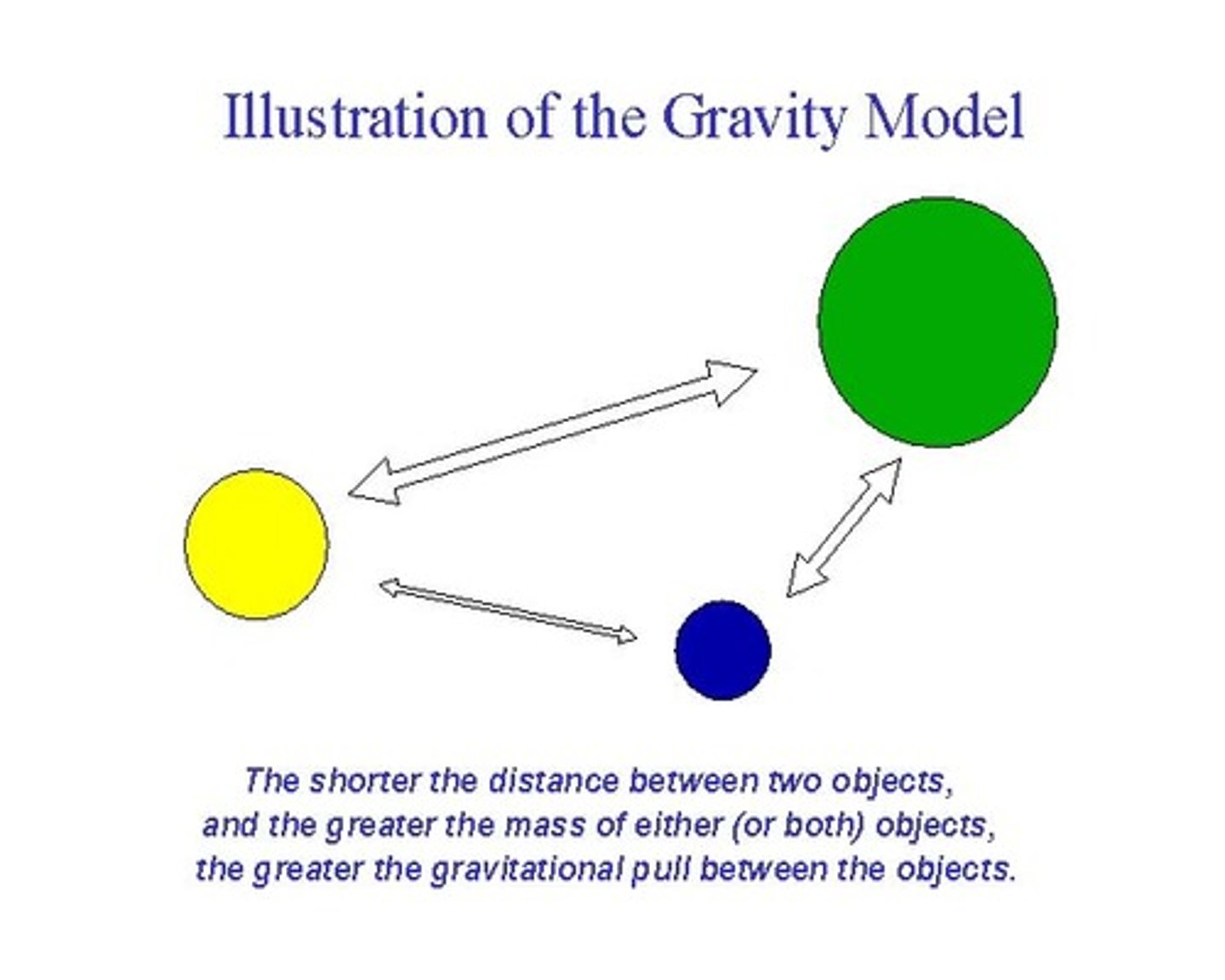
Gravity Model
Predicts interaction between places on the basis of their population size and distance between them.
Migrant Workers
people, typically farmers, who move from place to place to harvest fruits and vegetables

Refugee
a person who has a well-founded fear of being persecuted for reasons of race, religion, nationality, membership of a particular social group, or political opinion
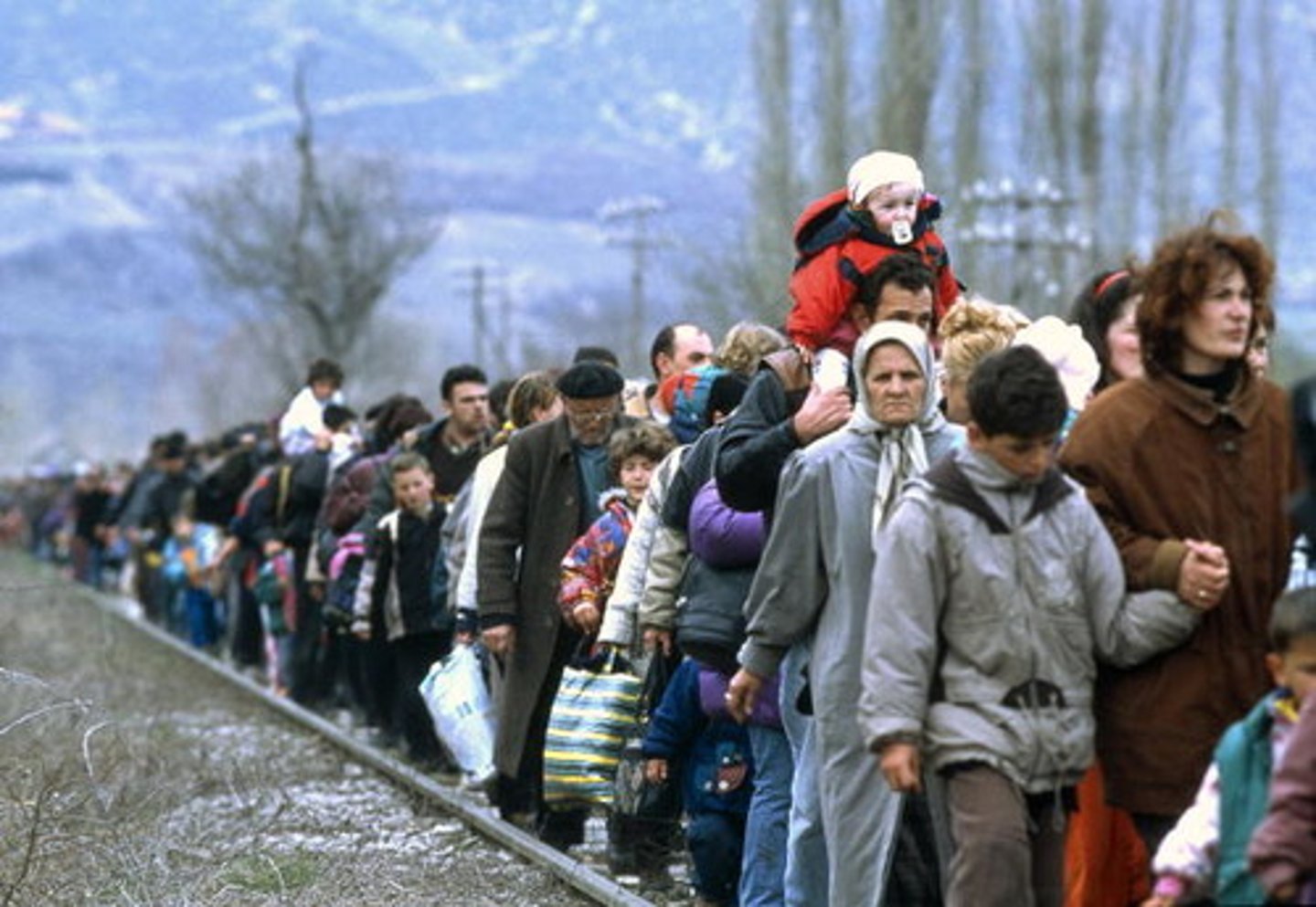

Asylum seeker
Someone who has migrated to another country in the hope of being recognized as a refugee

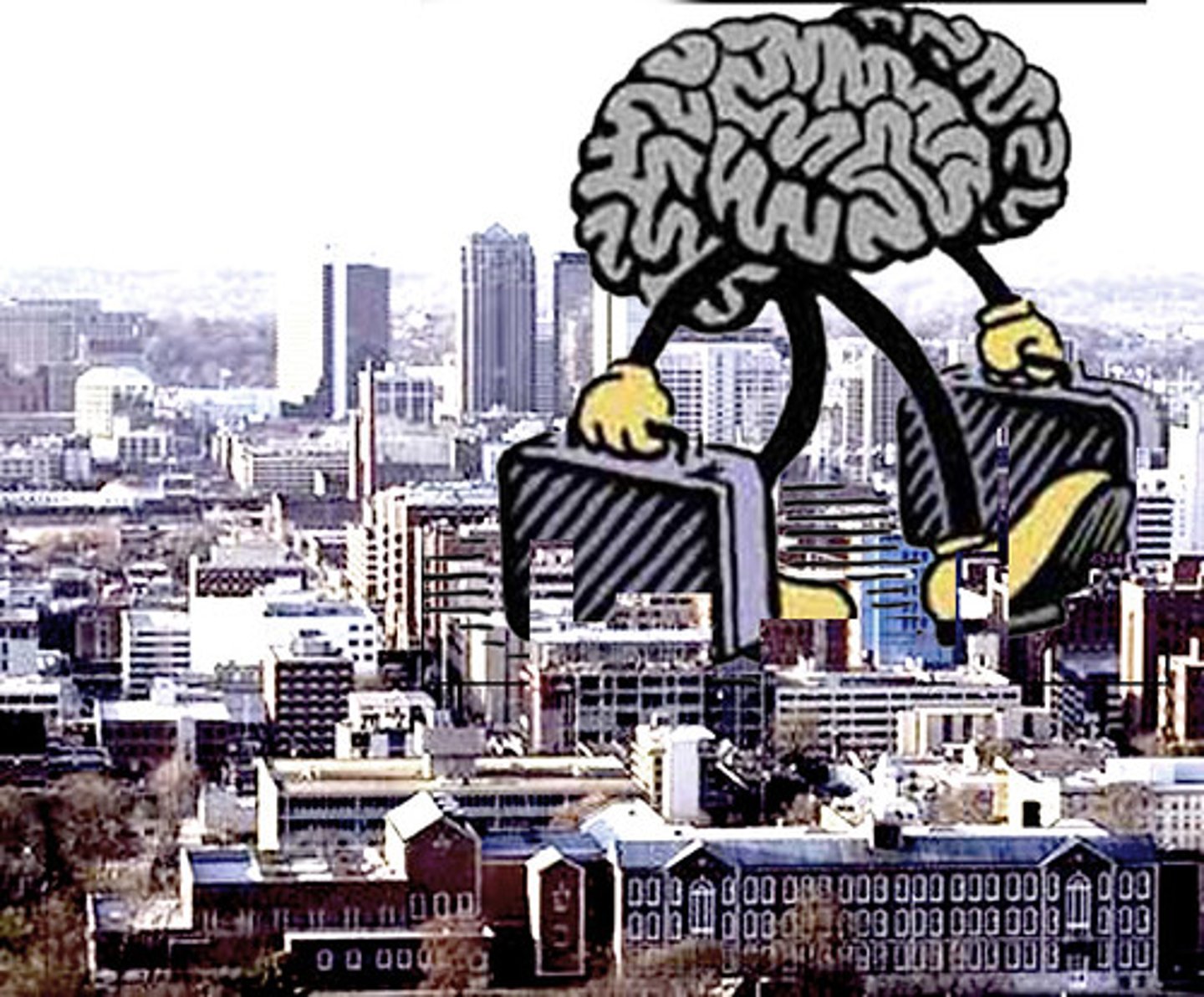
brain drain
the loss of highly educated and skilled workers to other countries

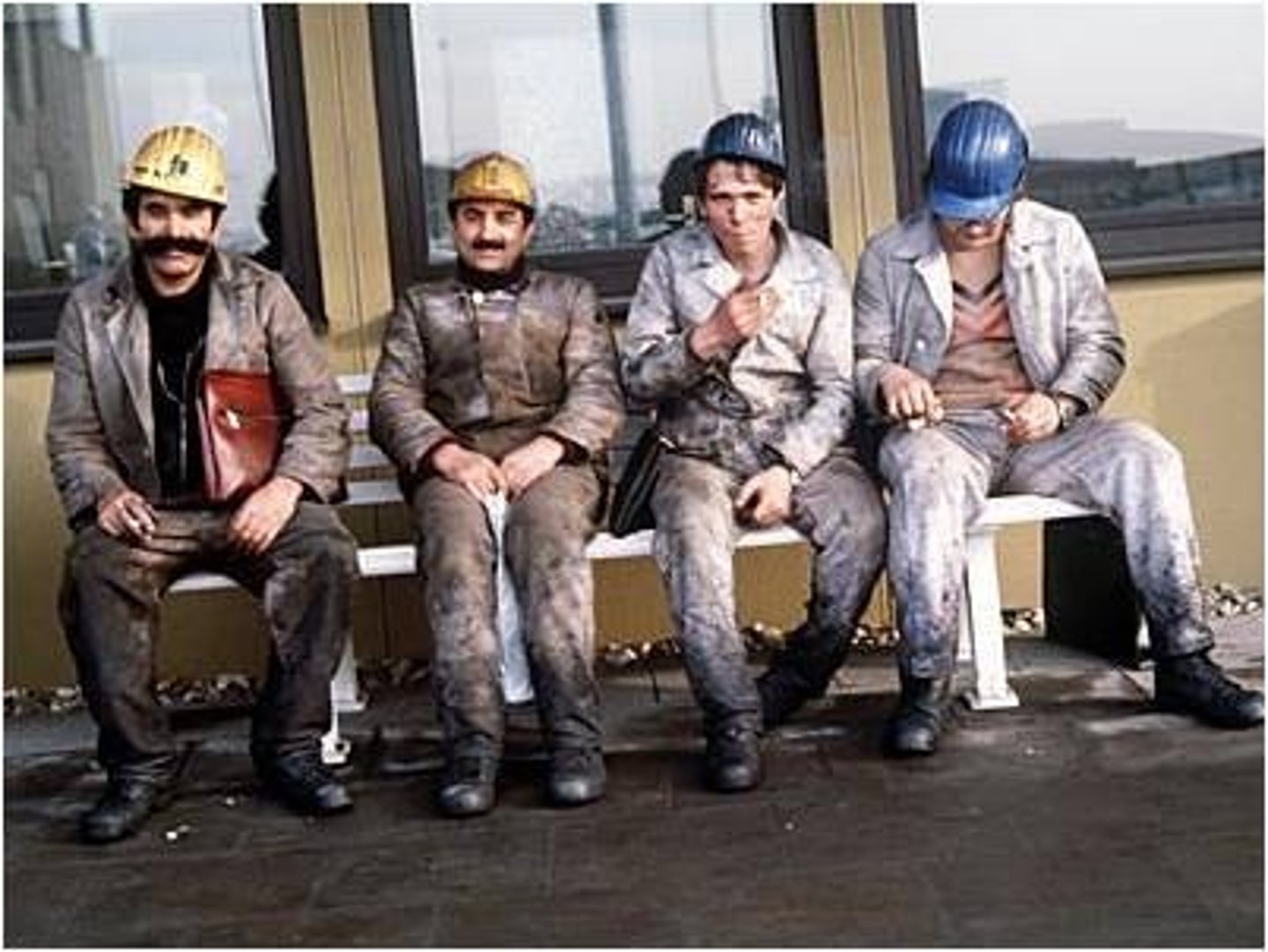
guest worker
a foreign laborer living and working temporarily in another country

intervening obstacle
An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration.

internal migration
permanent movement within the same country

transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.

Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
A set of 11 "laws" that can be organized into three groups: the reasons why migrants move, the distance they typically move, and their characteristics.

remittance
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries
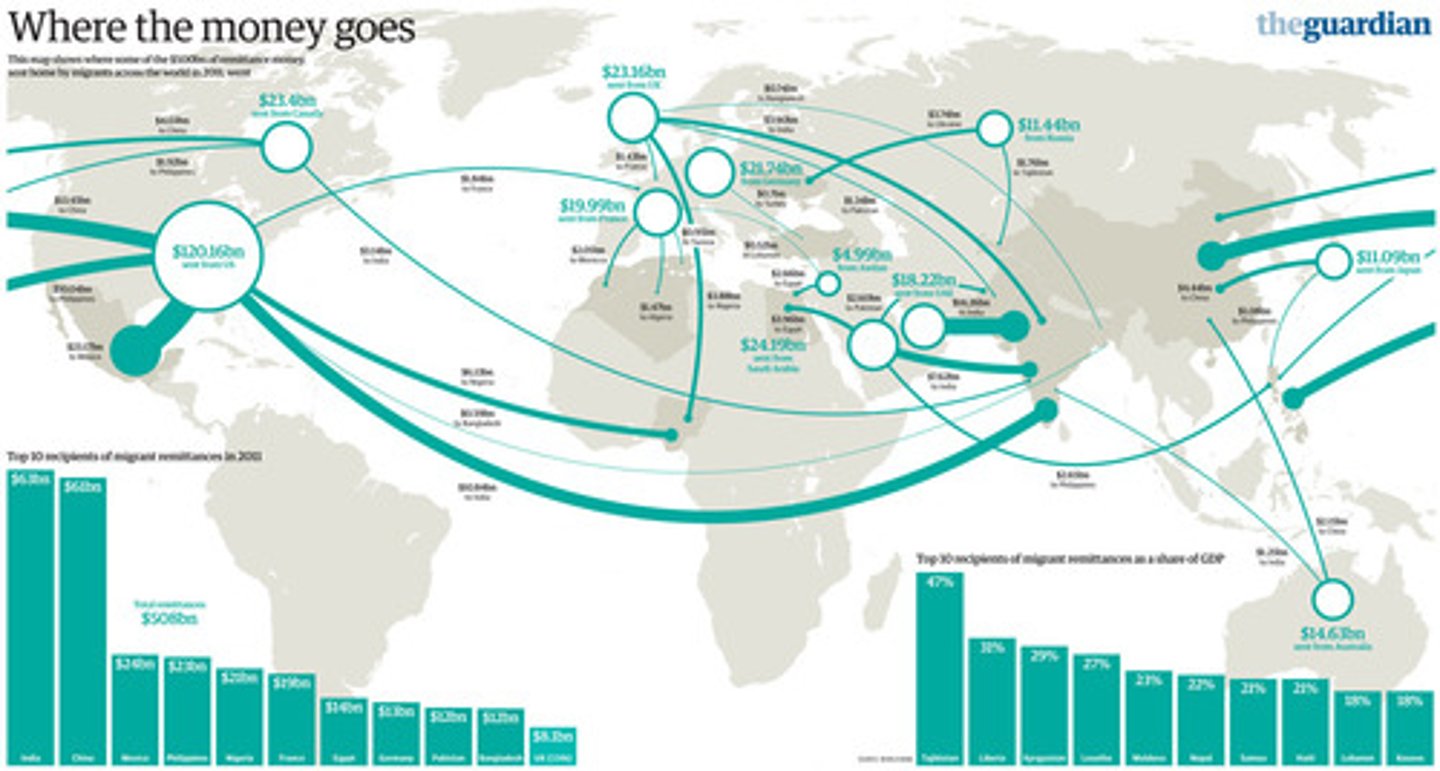
migration selectivity
Only people exhibiting certain characteristics in a population choosing to migrate

step migration
migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages

chain migration
pattern of migration that develops when migrants move along and through kinship links

activity space
The area within which people move freely on their rounds of regular activity

urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.

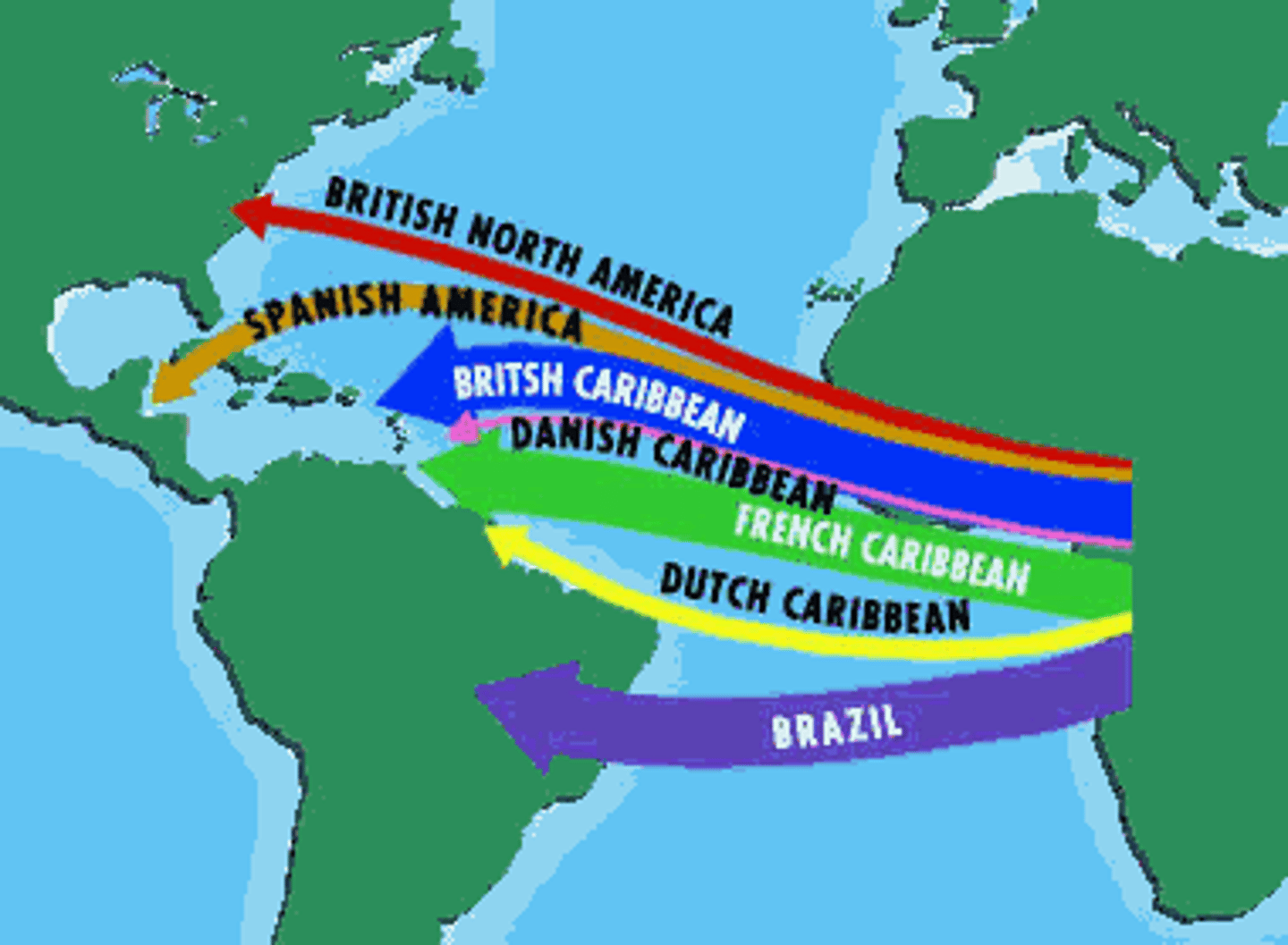
Atlantic Slave Trade
the buying and selling of Africans for work in the Americas
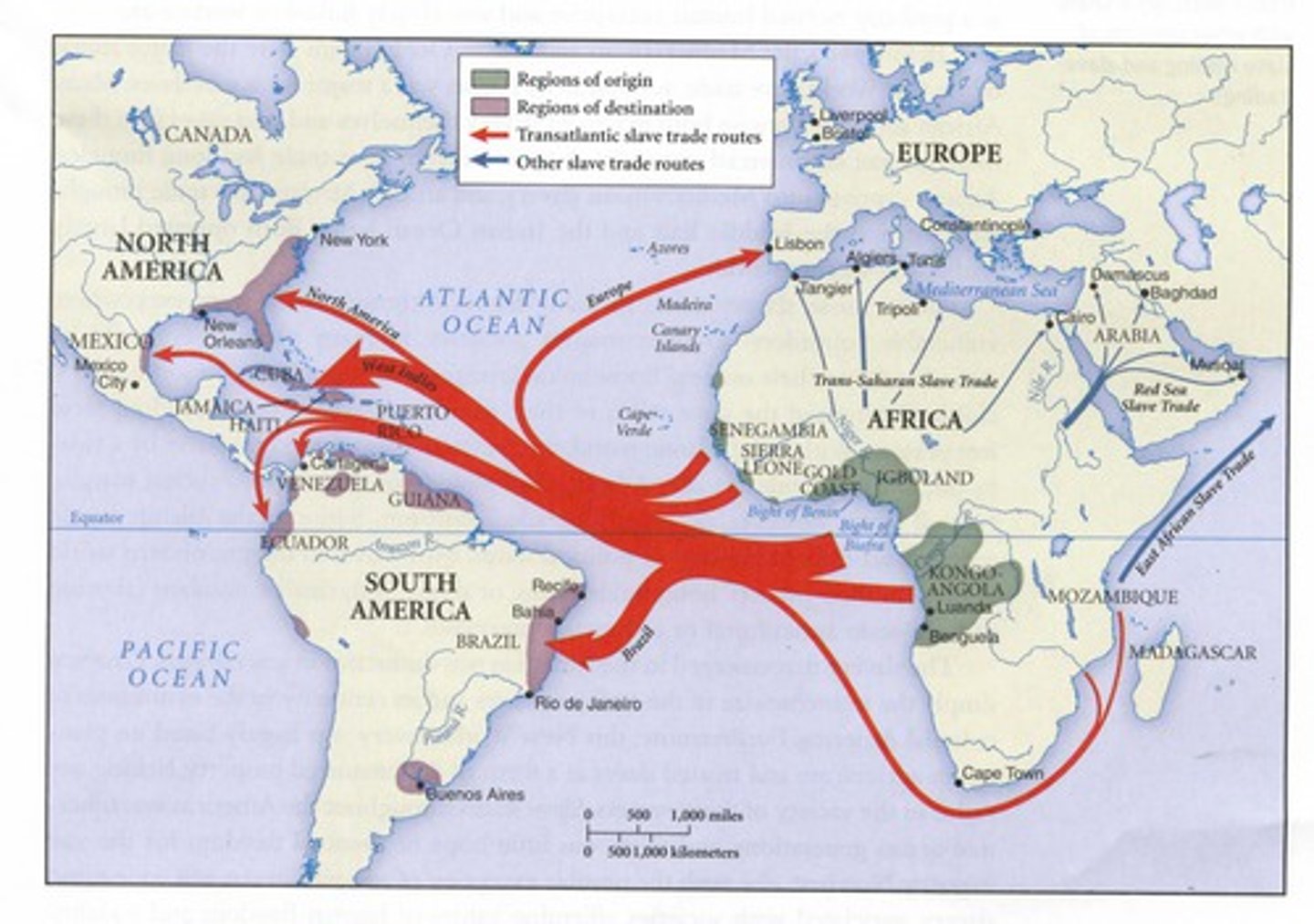
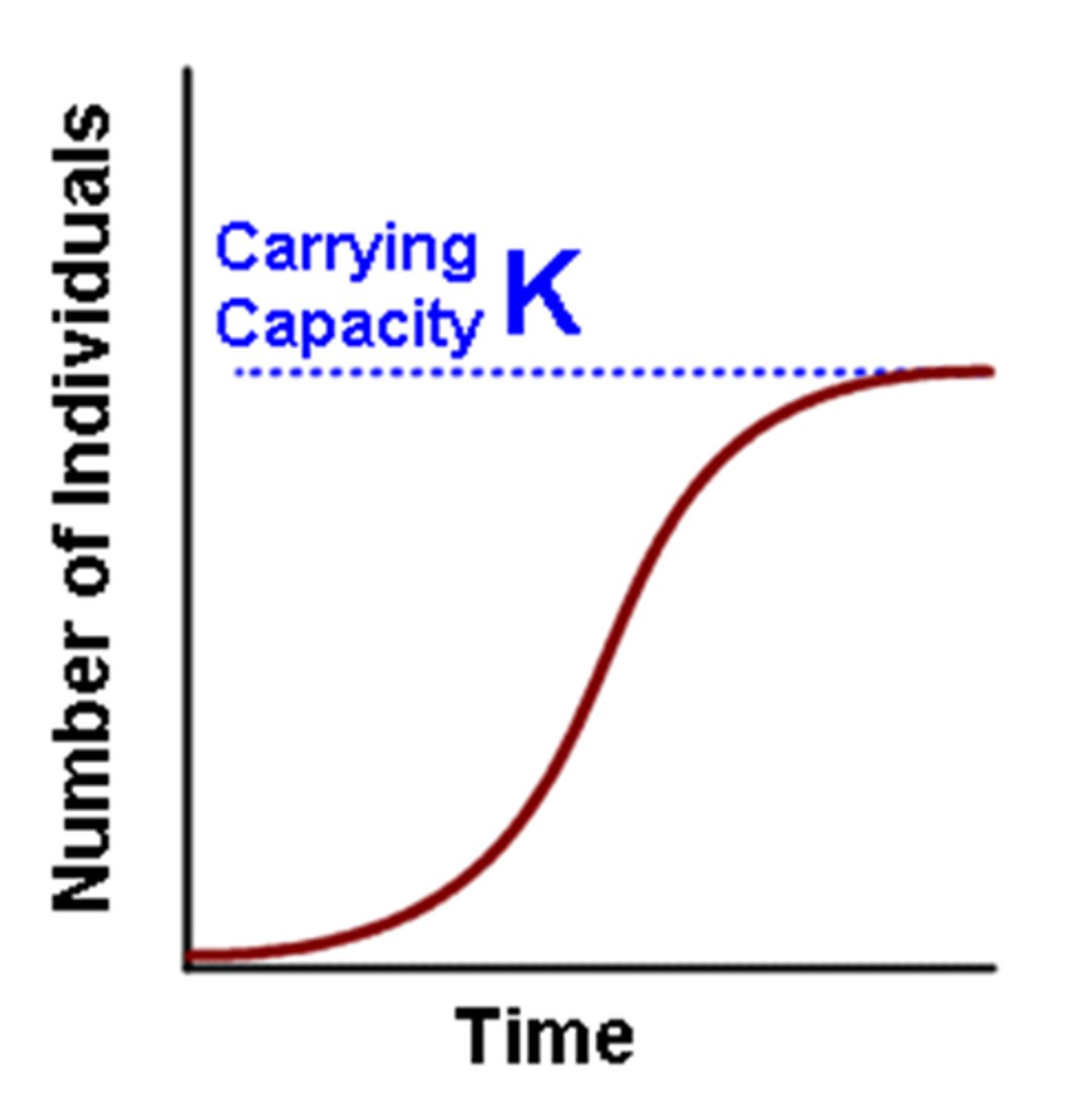
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support

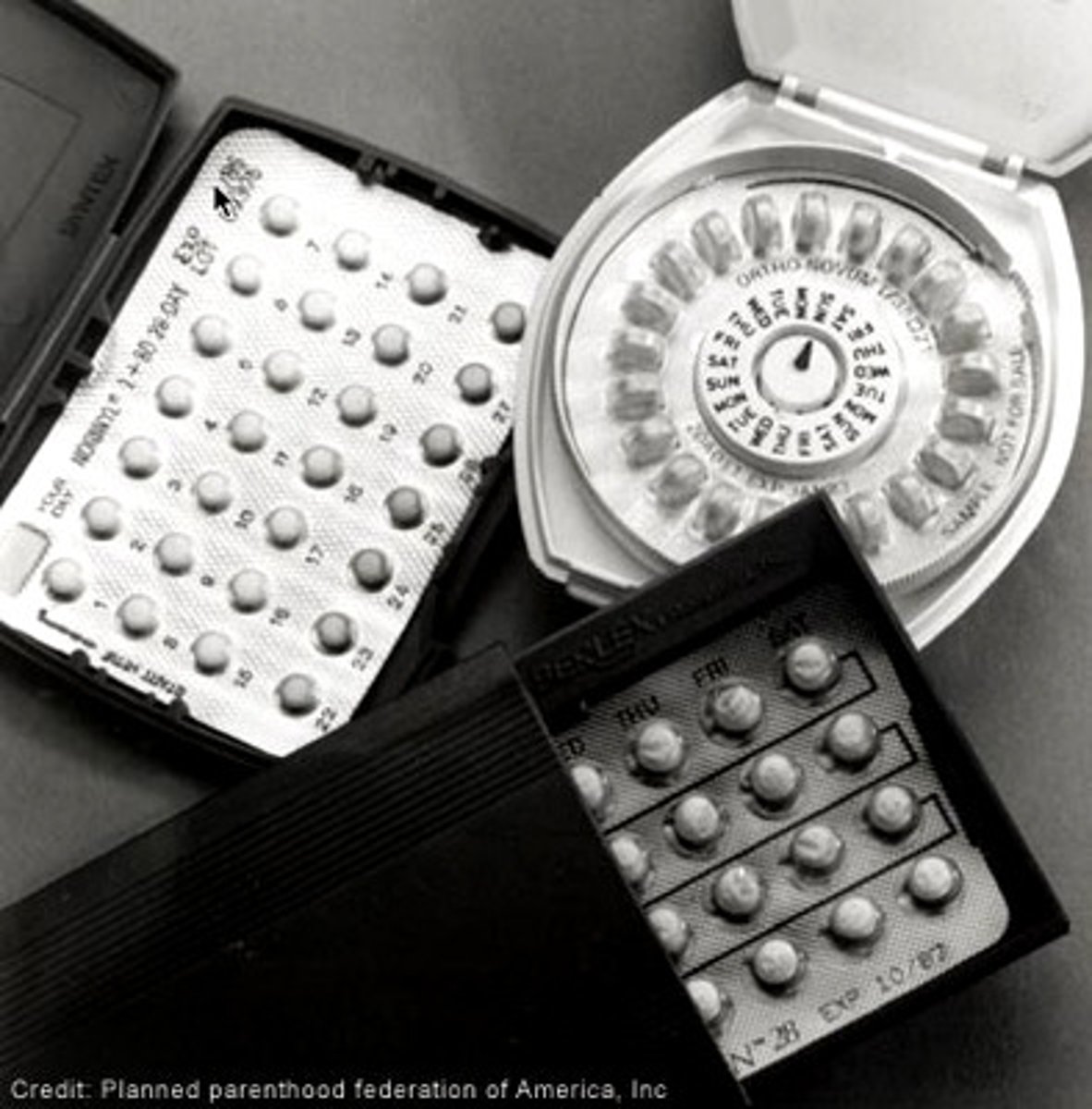
contraception (birth control)
methods of preventing conception
Diaspora
A dispersion of people from their homeland
Distribution
Description of locations on Earth's surface where populations live
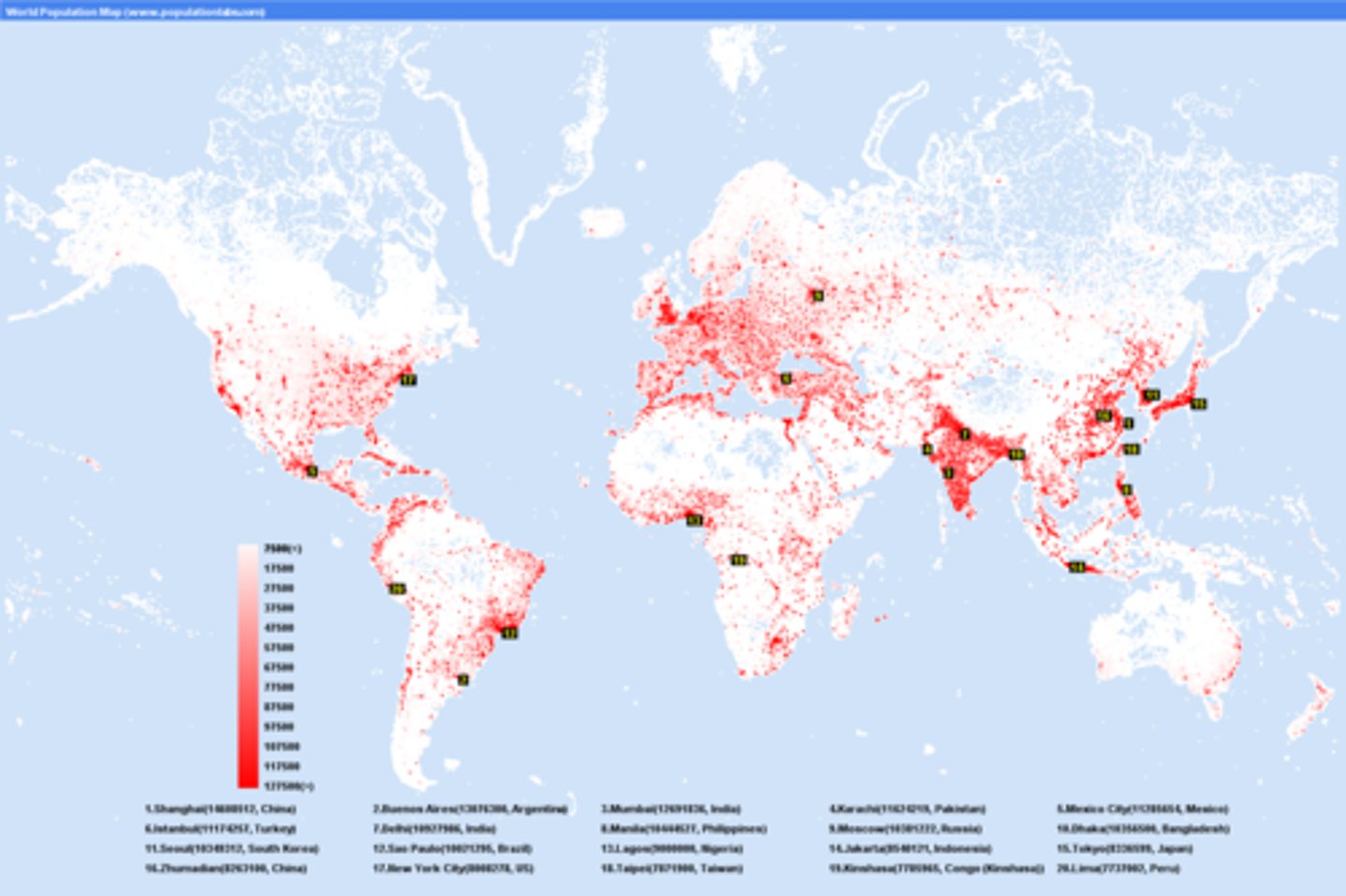
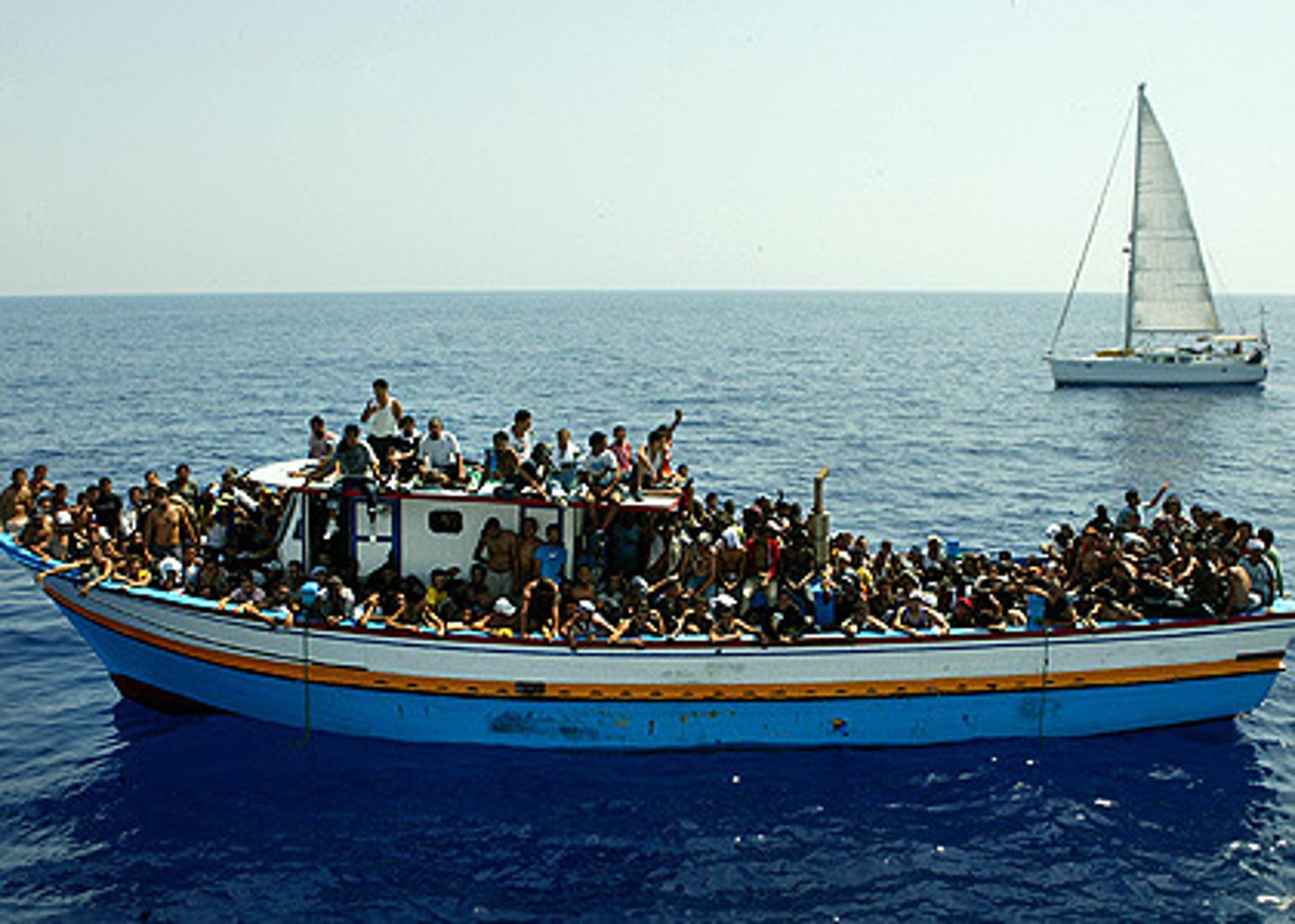
Immigration
Migration to a new location

fertility
The production of offspring within a population

Forced Migration
Permanent movement compelled usually by cultural factors.

Great Migration
movement of over 300,000 African American from the rural south into Northern cities between 1914 and 1920

infrastructure
Fundamental facilities and systems serving a country, city, or area, as transportation and communication systems, power plants, and schools

internally displaced person
Someone who has been forced to migrate for similar political reasons as a refugee but has not migrated across an international border

Migration
Form of relocation diffusion involving permanent move to a new location.
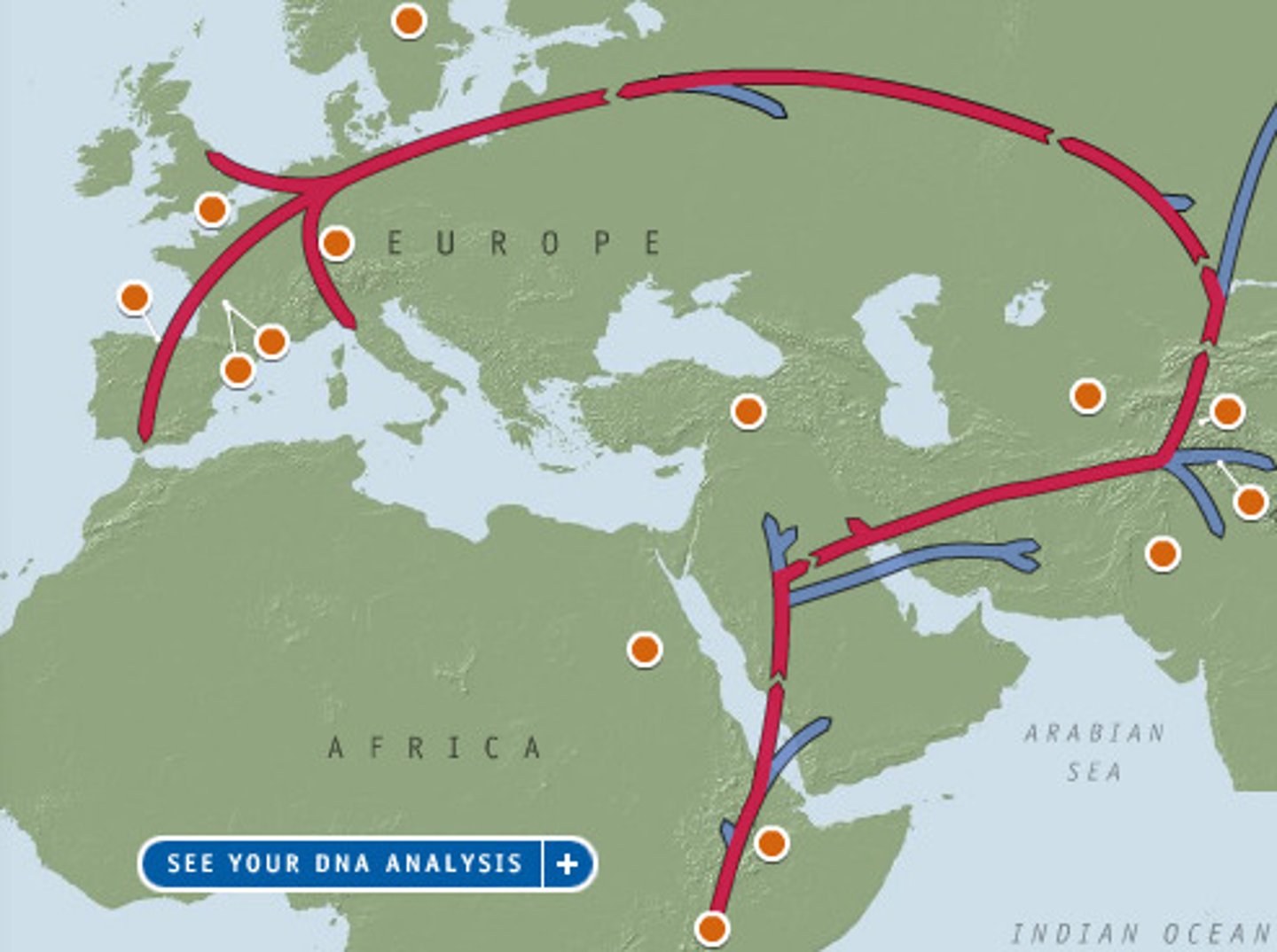
migration stream
the constant flow of migrants from one country into another country
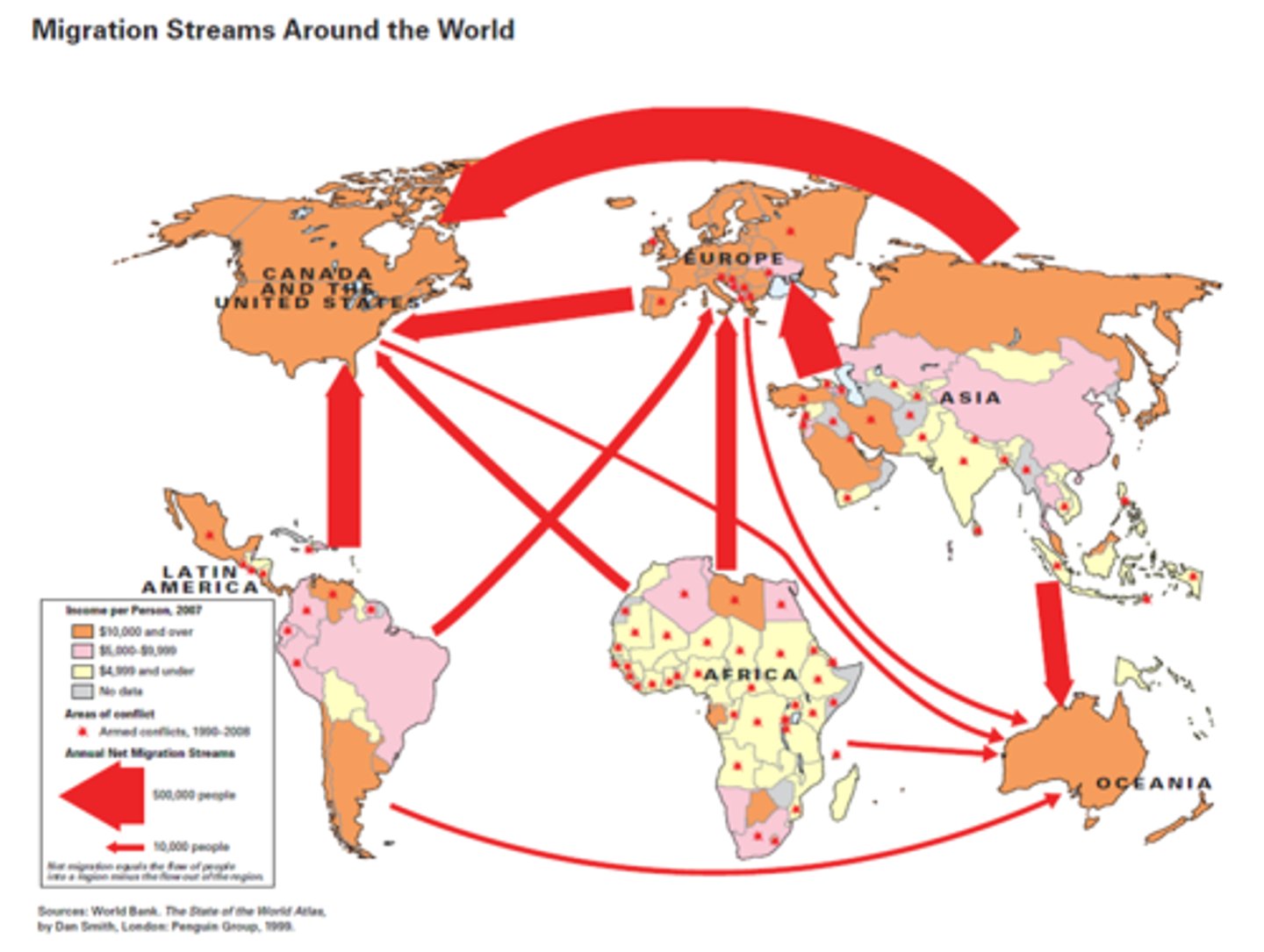
population composition
Structure of population in terms of age, sex and other properties such as marital status and education

Rural-urban migration
Permanent movement from rural area to the urban city area.
S-curve
a curve that depicts growth; shape of an "S." The leveling off of a J-Curve exponential growth.
Voluntary Migration
Permanent movement undertaken by choice.

Pull Factors of Immigration
Reasons to migrate to a new area such as Economic Opportunity ($)
Jobs/ workers were needed
Land
Peace and stability
Freedom to make a better life
degenerative disease
any disease in which deterioration of the structure or function of tissue occurs

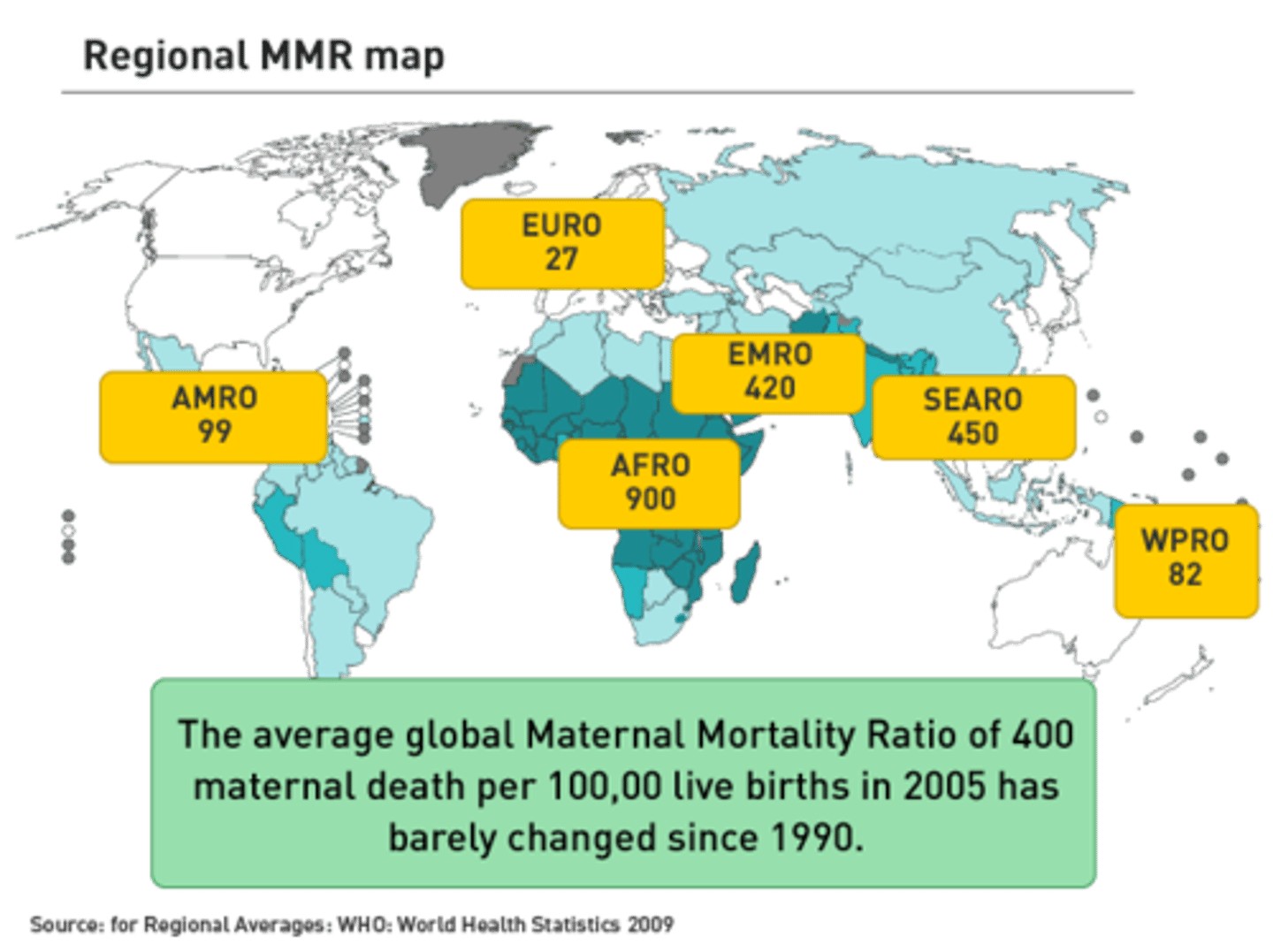
Maternal Mortality Rate
The number of women who die giving birth per 100,000 births