MGT FINAL EXAM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Last updated 9:19 PM on 12/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
\*communication
fluid, evolving process involving the sending and receiving of messages between two or more people
2
New cards
sender
person wanting to communicate information the message
3
New cards
receiver
person, group, or organization for whom the message is intended
4
New cards
encoding
translates thoughts into code or language that can be understood by others
5
New cards
selecting a medium
depends on the nature of the message, its intended purpose, type of audience, proximity to the audience, time horizon for disseminating the message, personal preferences, and the complexity of the problem/situation
6
New cards
decoding
occurs when receivers receive a message \n process of interpreting and making sense of a message
7
New cards
model of communication
sender, receiver, encoding, selecting a medium, decoding, feedback
8
New cards
\*effective communication
occurs when the intended meaning of the source and the perceived meaning of the receiver are virtually the same
9
New cards
noise
interference with the transmission and understanding of a message
10
New cards
\*functions of communication
control, motivation, emotional expression, information
11
New cards
\*barriers to effective communication (will be on the exam, give an example of each)
filtering, emotions, information overload, defensiveness, language, national culture
12
New cards
defensiveness
natural response to aggressive communication
13
New cards
language
you have to know your audience, more clarity, don't use loaded words, words have different meanings
14
New cards
national culture
some cultures don't appreciate confrontation \n might come off as rude \n some cultures believe in eye contact, handshake, etc. \n ^ examples of _______
15
New cards
\*other barriers to effective communication
time zone differences, telephone-line static, network problems, crashed computers, office design
16
New cards
overcoming barriers to communication
feedback, simplifying language, active listening, constraining emotions, watching nonverbal cues
17
New cards
nonverbal communication
messages sent outside of the written and spoken word \n body movement and gestures, touch, facial expression, eye contact
18
New cards
\*listening
process of taking in what we hear and mentally organizing it to make sense of it
19
New cards
art of listening
truly listening \n demands attention \n concentration \n effort
20
New cards
\*types of listening
passive, attentive, active or emphatic
21
New cards
\*active listening
most powerful level of listening and requires the largest amount of work on the part of the listener
listener not only hears and reacts to the words spoken but also paraphrases, clarifies, and gives feedback to the speaker about the messages being received.
(actually understanding what ur hearing)
listener not only hears and reacts to the words spoken but also paraphrases, clarifies, and gives feedback to the speaker about the messages being received.
(actually understanding what ur hearing)
22
New cards
\*eight behaviors associated with effective active-listening skills
make eye contact
exhibit affirmative head nods and appropriate facial expressions
avoid distracting actions or gestures
ask questions
paraphrase
avoid interrupting the speaker
don't over talk
make smooth transitions between roles of speaker and listener
exhibit affirmative head nods and appropriate facial expressions
avoid distracting actions or gestures
ask questions
paraphrase
avoid interrupting the speaker
don't over talk
make smooth transitions between roles of speaker and listener
23
New cards
\*passive listening
occurs when one is trying to absorb as much of the information as possible
may not understand the message
one-way communication
"in one year and out the other"
may not understand the message
one-way communication
"in one year and out the other"
24
New cards
\*attentive listening
occurs when one is genuinely interested in the speaker's point of view. The listening makes assumptions about the messages being relayed and fill in the gaps with their own assumptions, etc.
25
New cards
women
are more likely to share credit for success, ask questions, act tactfully give feedback
26
New cards
men
are more likely to boast, to bluntly give feedback, and less likely to admit fault or weakness
27
New cards
\*multicommunication
the use of technology to participate in several interactions at the same time
28
New cards
internet
(on the exam) \n a global network of computer networks
29
New cards
\*intranet
an organization's private internet
30
New cards
\*extranet
connects internal employees with selected customers, suppliers, and strategic partners
31
New cards
\*benefits of email
reduced the cost of distributing information
increased teamwork
reduced paper costs
increased flexibility
increased teamwork
reduced paper costs
increased flexibility
32
New cards
\*drawbacks to email
wasted time and effort
information overload
increased costs to organize, store, and monitor usage
neglect of other media
information overload
increased costs to organize, store, and monitor usage
neglect of other media
33
New cards
videoconferencing
uses video and audio links along with computer to enable people in different locations to see, hear, and talk with one another
34
New cards
\*organizational communication networks
combination of vertical and horizontal flows into a variety of patterns
chain, wheel, & all channel
chain, wheel, & all channel
35
New cards
\*chain network
individuals communicate in a set sequence
(chain of command)
(chain of command)
36
New cards
\*wheel network
most info travels through one central member of the group
37
New cards
\*all-channel network
every group member communicates with everyone else
38
New cards
\*grapevine
the unofficial communication system of the informal organization (usually informal)
39
New cards
telepresence
advanced form of teleconferencing \n requires specially designed rooms with multiple cameras, sound-damping equipment and high-definition video screens
40
New cards
benefits of video conferencing and telepresence
systems can reduce an organization's travel expenses \n allow people working across the world to participate in the innovation process on as as needed basis \n allow employees to speed up the decision making process
41
New cards
group support systems
using computer software and hardware to help people work better together \n have demonstrated increased productivity and cost savings
42
New cards
teleworking
a work practice in which an employee does part of his job in a remote location using a variety of information technologies \n also called telecommuting
43
New cards
blog
online journal in which people comment on any topic
44
New cards
\*motivation
an internal force within the individual that is responsible for the level of effort and drive expended on a job
45
New cards
\*content theories
need based theories which focus on factors that arouse motivation and behavior
46
New cards
\*process theories
these theories compliment the content theories by adding the thought processes involved in motivated behaviors. Emphasize the nature of the interaction between the individual and the environment
47
New cards
\*Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
self-actualization
esteem
love (social)
safety and security
physiological
esteem
love (social)
safety and security
physiological
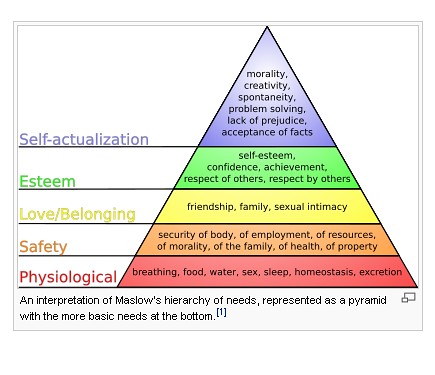
48
New cards
\*Alderfer's ERG theory
existence, relatedness, growth
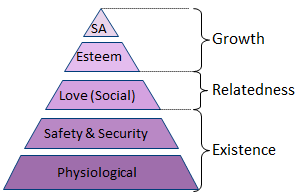
49
New cards
\*McClelland's Need theory
need for achievement
need for power
need for affiliation
need for power
need for affiliation
50
New cards
need for affiliation
a manifest (easily perceived) need that concerns an individual's need to establish and maintain warm, close, intimate relationship with other people
51
New cards
\*Herzberg's two-factor theory
hygiene factor
motivation factor
motivation factor
52
New cards
\*Hygiene Factor (Herzberg)
work condition related to dissatisfaction caused by discomfort or pain
maintenance factor
contributes to employee's feeling not dissatisfied
contributes to absence of complaints
maintenance factor
contributes to employee's feeling not dissatisfied
contributes to absence of complaints
53
New cards
\*motivation factor (Herzberg)
work condition related to the satisfaction of the need for physiological growth
job enrichment
leads to superior performance & effort
job enrichment
leads to superior performance & effort
54
New cards
\*Process Theories of Motivation
(equity and expectancy) these theories compliment the content theories by adding thought processes involved in motivated behaviors. emphasize the nature of the interaction between the individual and the environment
55
New cards
\*equity theory
a theory that states that people will be motivated when they perceive that they are being treated fairly
inputs = outputs
inputs = outputs
56
New cards
equity \n negative equity \n positive equity
___: outcomes A / inputs = outcomes B / inputs \n ___: outcomes / inputs < outcomes / inputs \n ___: outcomes / inputs > outcomes / inputs
57
New cards
valence
the importance that the individual places upon the expected outcome
58
New cards
\*expectancy theory
the belief that an individual chooses their behaviors based on what they believe leads to the most beneficial outcome
59
New cards
instrumentality
the belief that a person will receive a desired outcome if the performance expectation is met
60
New cards
3 causes of motivation problems
1. belief that effort will not result in performance
2. belief that performance will not result in rewards
3. the value of a person places on, or the preference a person has for, certain rewards
61
New cards
theory y
a set of assumptions of how to manage individuals motivated by higher order needs (self-actualization, esteem love (social)
62
New cards
theory x
a set of assumptions of how to manage individuals motivated by lower order needs (safety & security , physiological)
63
New cards
\*Job characteristics model
skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, feedback
64
New cards
\*skill variety
the degree to which a job requires a variety of activities so that an employee can use a number of different skills and talents
65
New cards
\*task identity
the degree to which a job requires completion of a whole and identifiable people of work
66
New cards
\*task significance
the degree to which a job has a substantial impact on the lives or work of other people
67
New cards
\*autonomy
the degree to which a job provides substantial freedom, independence, and discretion to the individual in schedeuling work and determining the procedures to be used in carrying it out
68
New cards
\*feedback
the degree to which carrying out work activities requires by a job in the individual's obtaining direct and clear information about his or her performance effectiveness
69
New cards
\*group
two or more people working together over time to achieve a common goal
70
New cards
\*stages of group formation
forming, storming, norming, performing, adjourning
71
New cards
forming
the first stage of team development, in which team members meet each other, form initial impressions, and begin to establish team norms \n emphasis on interpersonal concern and awareness
72
New cards
storming
the second stage of development, characterized by conflict and disagreement, in which team members disagree over what the team should do and how it should do it emphasis on task planning, authority, and influence
73
New cards
norming
the third stage of team development, in which team members begin to settle into their roles, group cohesion grows, and positive team norms develop emphasis on task accomplishment, leadership, and performance
74
New cards
performing
the fourth stage of team development, in which performance improves because the team has matured into an effective, fully functioning team emphasis on rewards and punishment
75
New cards
adjourning
The fifth stage of group development during which the group finishes its tasks and decides or is forced to dissolve membership work is done, time to move on to other things
76
New cards
\*roles
expected behavior for a given position
77
New cards
\*task roles
perform those activities directly related to the effective completion of the team's work give information, initiate ideas, test ideas, seek information, coordinate activities, summarize ideas, evaluate effectiveness, etc.
78
New cards
\*maintenance roles
roles performed by group members to maintain good relations within the group support others, follow each other's lead, harmonize conflict, set standards, express member feelings, test group decisions
79
New cards
\*norms
shared attitudes, opinions, feelings, or actions that guide social behavior
80
New cards
\*when a group becomes a team
leadership becomes a shared activity
accountability shifts from strictly individual to both individual and collective
the group develops its own purpose or mission
problem solving becomes a way of life, not a part-time activity
accountability shifts from strictly individual to both individual and collective
the group develops its own purpose or mission
problem solving becomes a way of life, not a part-time activity
81
New cards
\*team
small group with complementary skills who hold themselves mutually accountable for common purpose, goals, and approach
task groups that have matured to the performing stage
task groups that have matured to the performing stage
82
New cards
\*characteristics of effective work teams
clear goals, relevant skills, mutual trust, unified commitment, negotiating skills, appropriate leadership, internal and external support
83
New cards
\*groupthink
the practice of thinking or making decisions as a group in a way that discourages creativity or individual responsibility
84
New cards
\*symptoms of groupthink
Invulnerability, inherent morality, rationalization, stereotypes views of opposition, self-censorship, illusion of unanimity, peer pressure, mind guards
85
New cards
invulnerability (groupthink)
members feel they cannot fail, illusion that the group is performing well
86
New cards
inherent morality (groupthink)
a belief that encourages the group to ignore ethical implications (inherently ignoring morality)
87
New cards
rationalization (groupthink)
when team members convince themselves that despite evidence to the contrary, the decision or alternative being presented is the best one
88
New cards
stereotypes (groupthink)
leads members of the in-group to ignore or even demonize out-group members who may oppose or challenge the group's ideas
89
New cards
self-censorship (groupthink)
members of the group withhold dissenting views, keep silent about misgivings and minimize the importance of their doubts
90
New cards
illusion of unanimity (groupthink)
members of the group falsely perceive that everyone agrees with the group decision
91
New cards
peer pressure (groupthink)
influence enacted by a peer that encourages conformity
92
New cards
mind guards (groupthink)
a member of the group who, in an attempt to preserve the central group idea, omits any information which may cause doubts to arise within the group
93
New cards
\*social loafing
decrease in individual effort as group size increases
94
New cards
\*controlling
management function that involves monitoring, comparing and correcting work performance help evaluate whether other functions have been carries out properly
95
New cards
\*the control process
a three-step process of measuring actual performance, comparing actual performance against a standard, and taking managerial action to correct deviations or inadequate standards
1. setting up standards
2. performance appraisal
3. corrective measures
1. setting up standards
2. performance appraisal
3. corrective measures
96
New cards
immediate corrective action
corrective action that corrects problems at once to get performance back on track
97
New cards
basic corrective action
corrective action that looks at how and why performance deviated before correcting the source of deviation
98
New cards
feed forward control
control that takes place before a work activity is done
99
New cards
concurrent control
control that takes place while a work activity is in progress
100
New cards
management by walking around
a term used to describe when a manager is out in the work area interacting directly with employees