Reproductive and Urinary Systems Overview
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Reproductive System
System responsible for producing new individuals.
Testes
Male reproductive glands producing sperm and hormones.
Scrotum
Pouch containing the testes outside the body.
Sperm Cells
Male gametes that determine baby's sex.
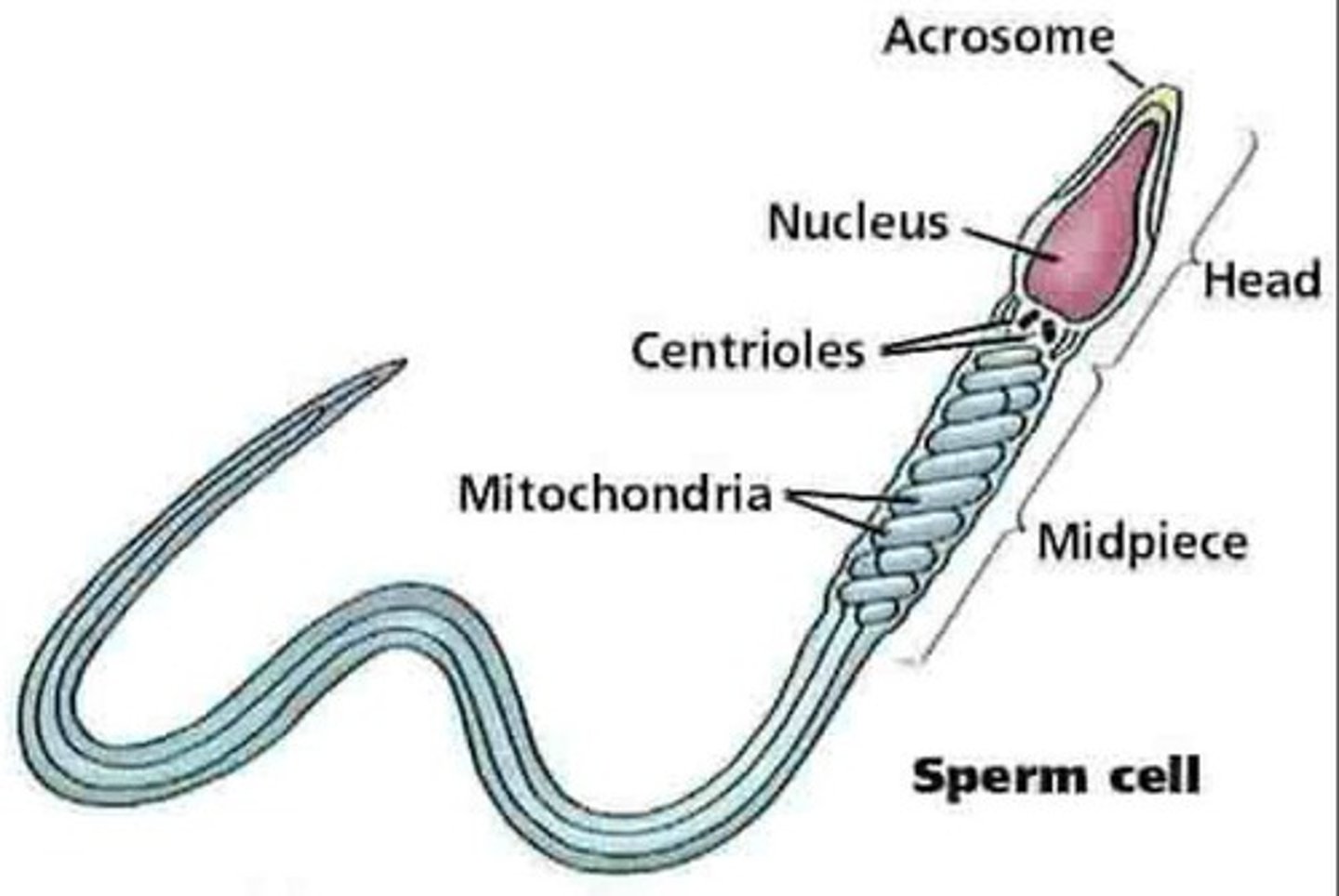
Acrosome
Cap of sperm containing enzymes for egg penetration.
Epididymis
Storage site for mature sperm cells.
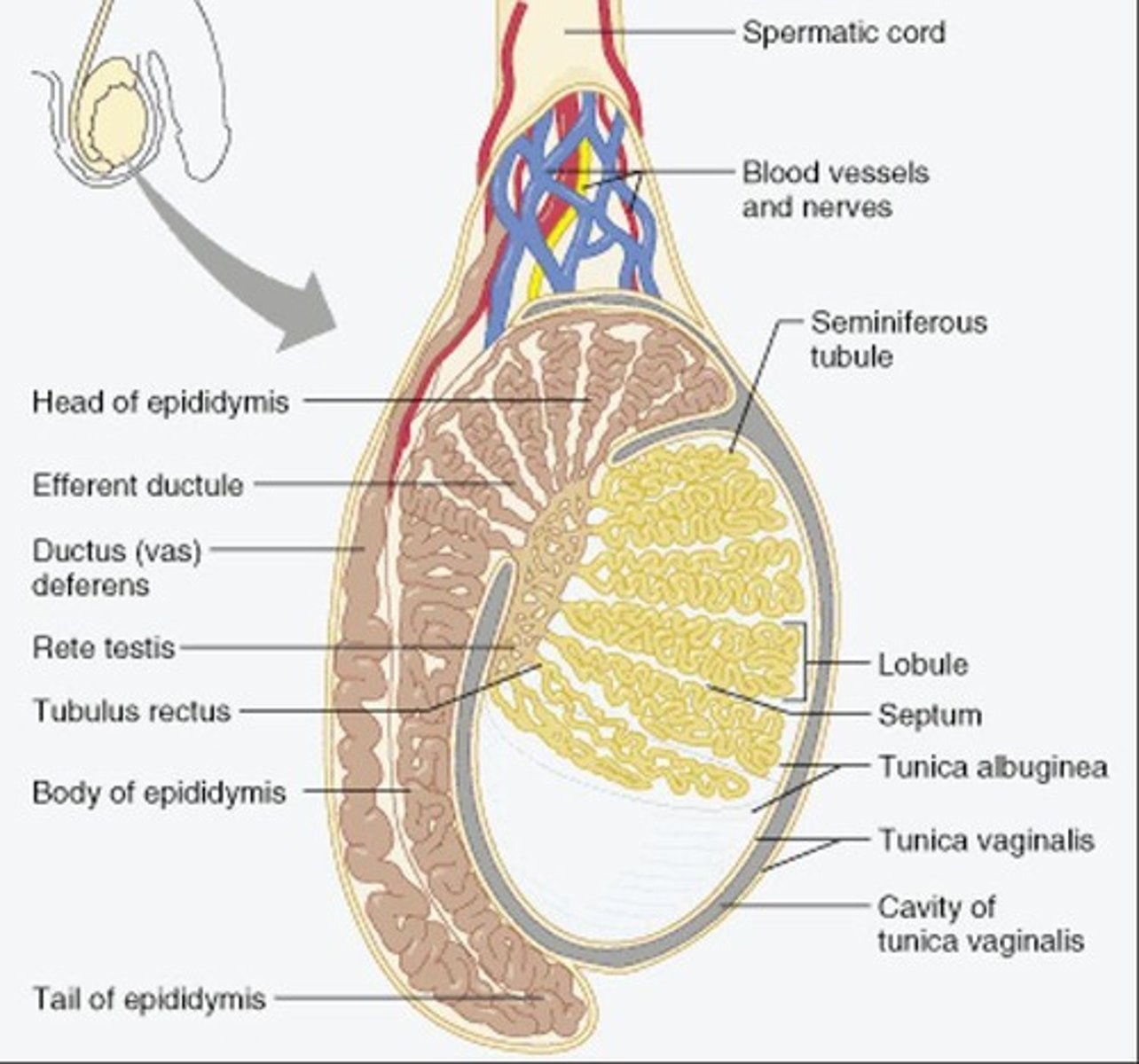
Vas Deferens
Tube transporting sperm from epididymis to urethra.
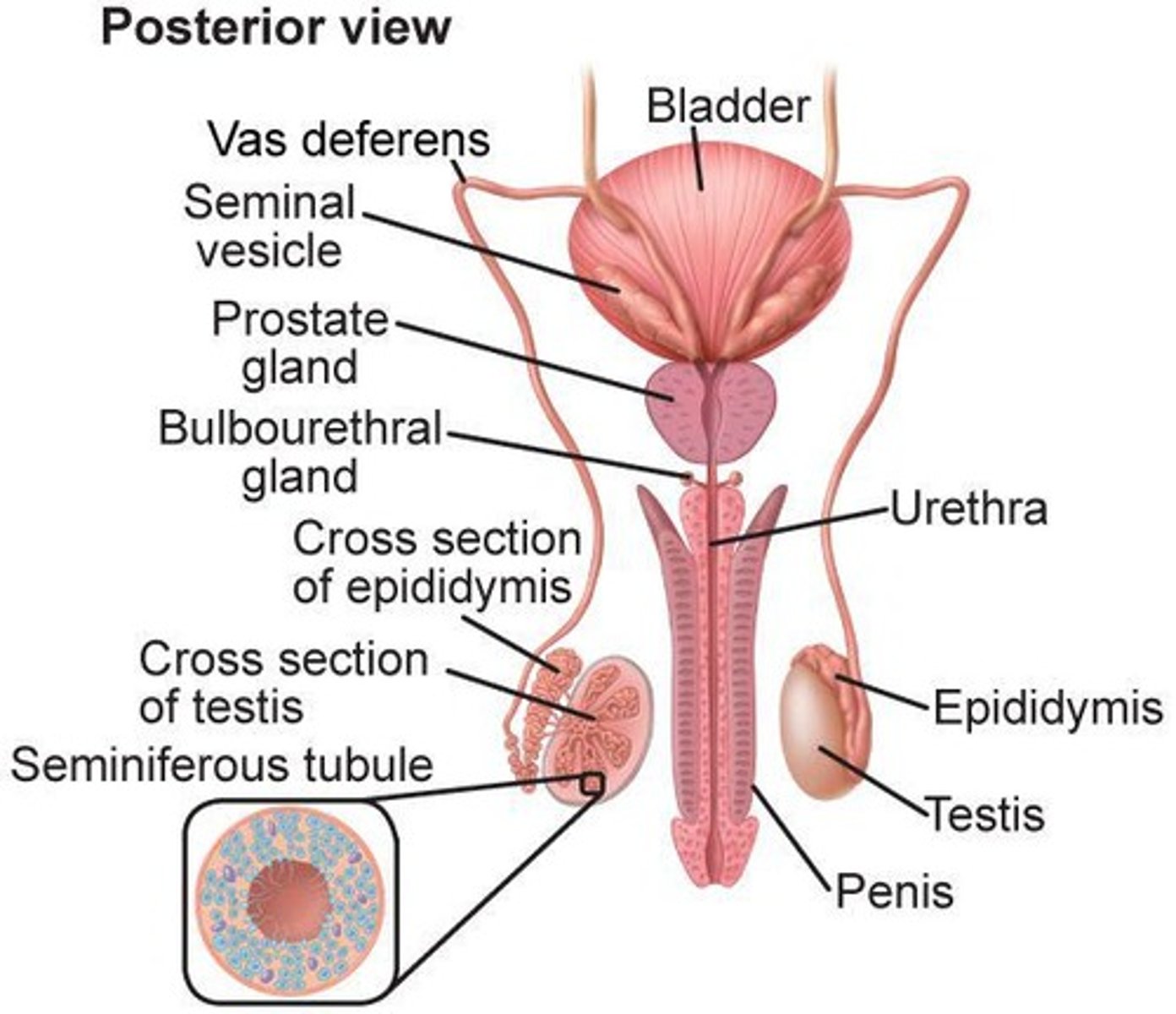
Seminal Vesicles
Glands secreting fluid to nourish and protect sperm.
Prostate Gland
Gland producing fluid that nourishes sperm.
Bulbourethral Glands
Glands secreting fluid to neutralize acidity.
Testosterone
Steroid hormone essential for sperm production.
GnRH
Hormone stimulating testosterone production in males.
FSH
Hormone stimulating egg development in females.
LH
Hormone triggering ovulation and hormone production.
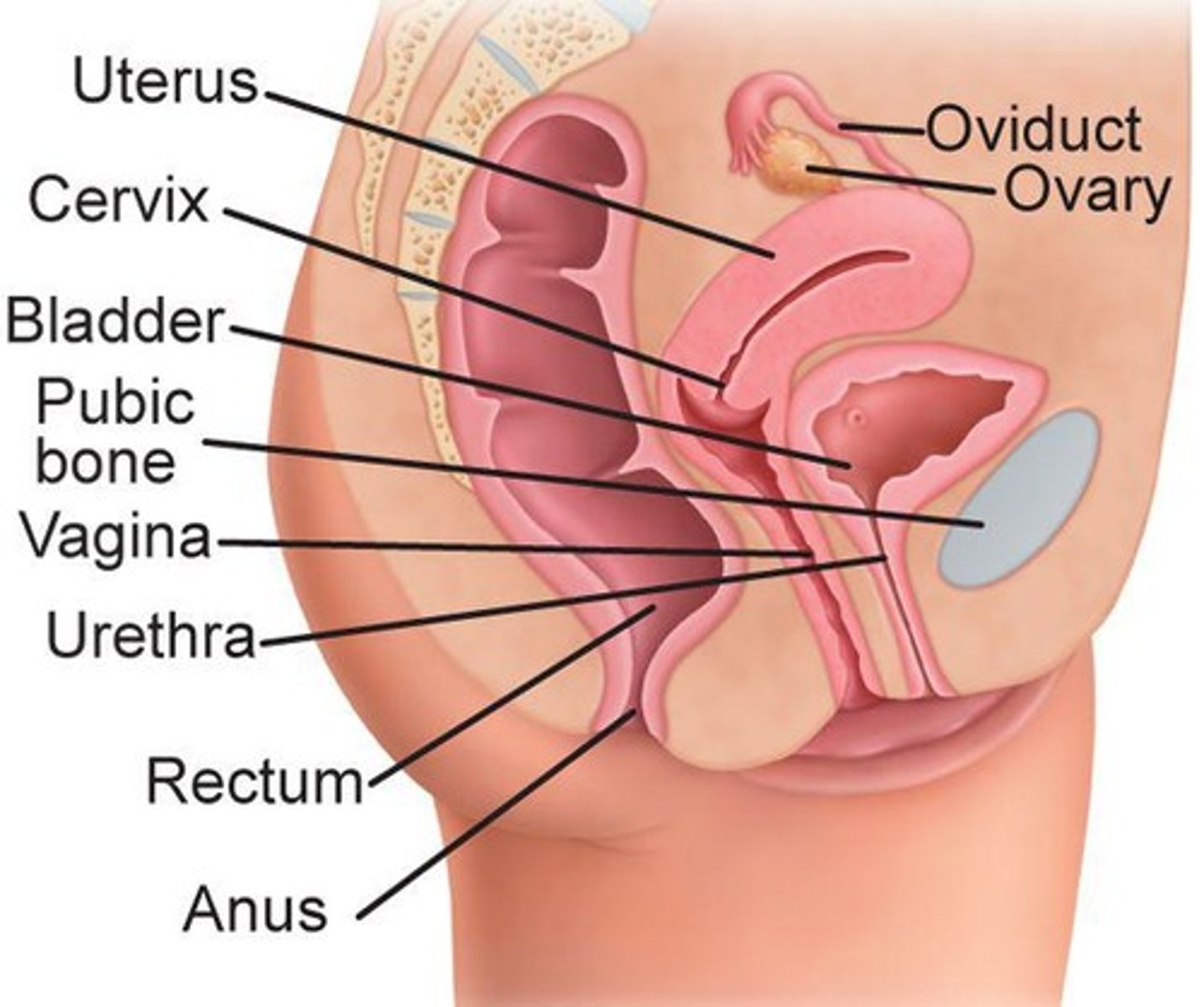
Ovaries
Female reproductive glands producing egg cells.
Oocytes
Immature egg cells in the ovaries.
Oviduct
Tube transporting egg from ovary to uterus.
Cervix
Narrow opening from uterus to vagina.
Estrogen
Hormone promoting uterine lining growth and ovulation.
Progesterone
Hormone maintaining uterine lining post-ovulation.
Menstrual Cycle
Monthly cycle involving egg development and shedding.
Fertilization
Process where sperm and egg unite.
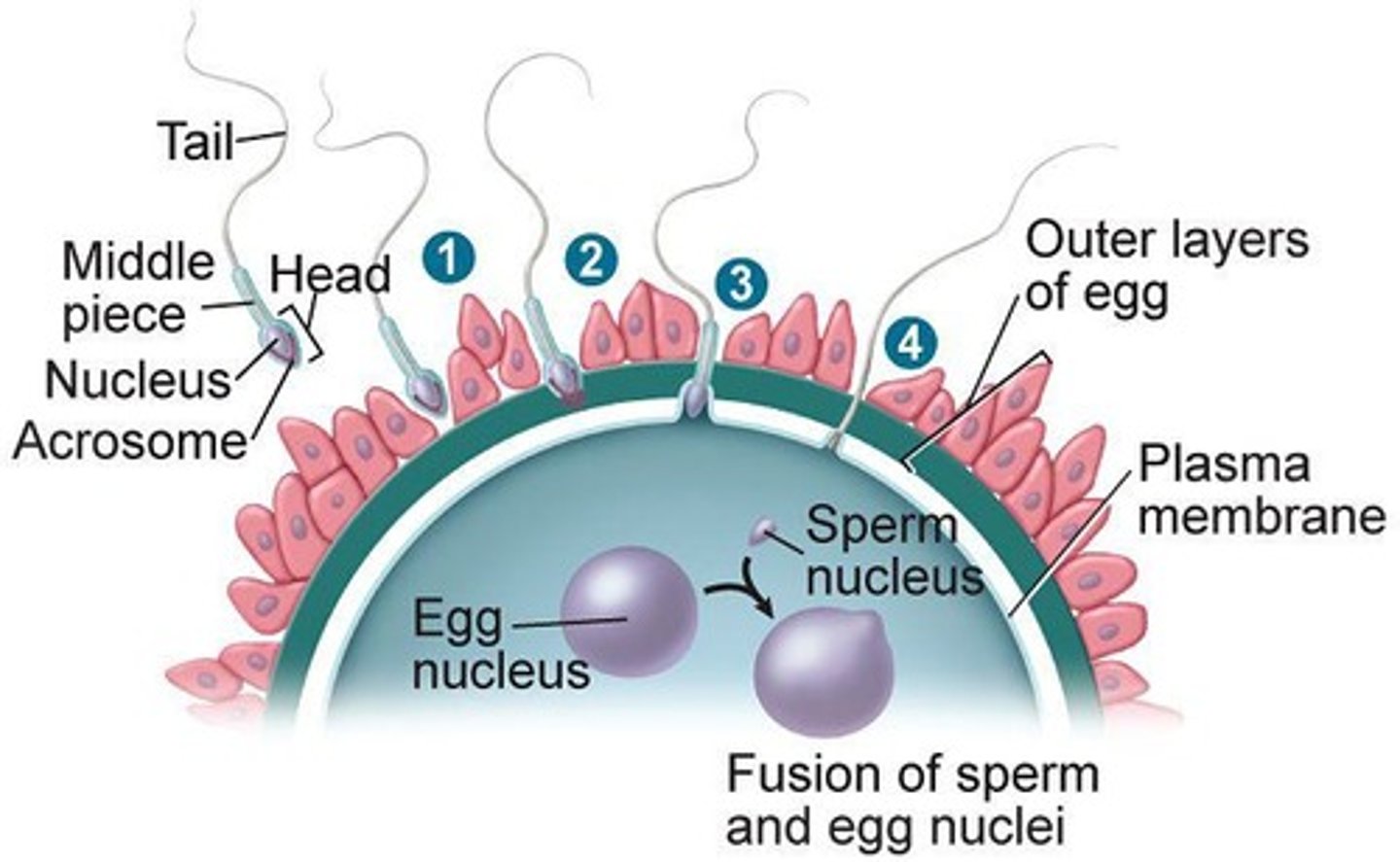
Zygote
Fertilized egg formed after sperm penetrates egg.
Zygote
Fertilized egg undergoing first mitosis after 30 hours.
Morula
Solid ball of cells formed by day three.
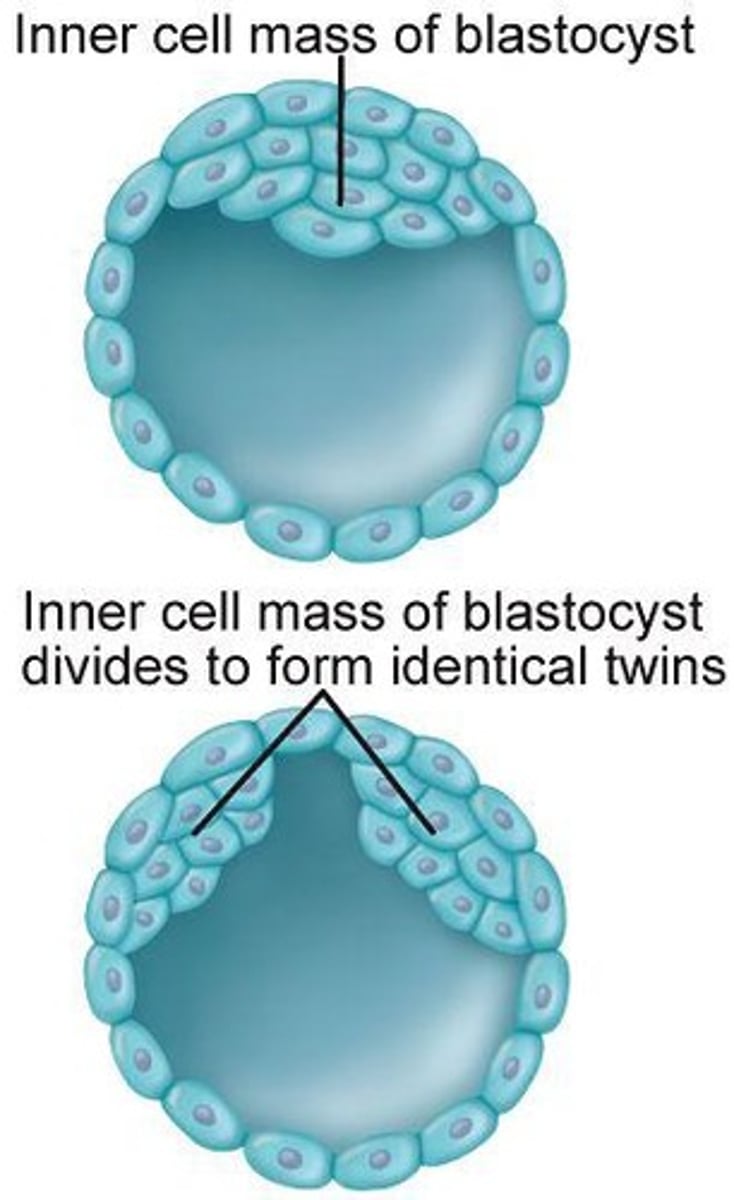
Blastocyst
Hollow ball of cells by day five.
Endometrium
Uterine lining where blastocyst implants.
Implantation
Blastocyst fully attaches by day ten.
Extraembryonic membranes
Four membranes supporting embryo development.
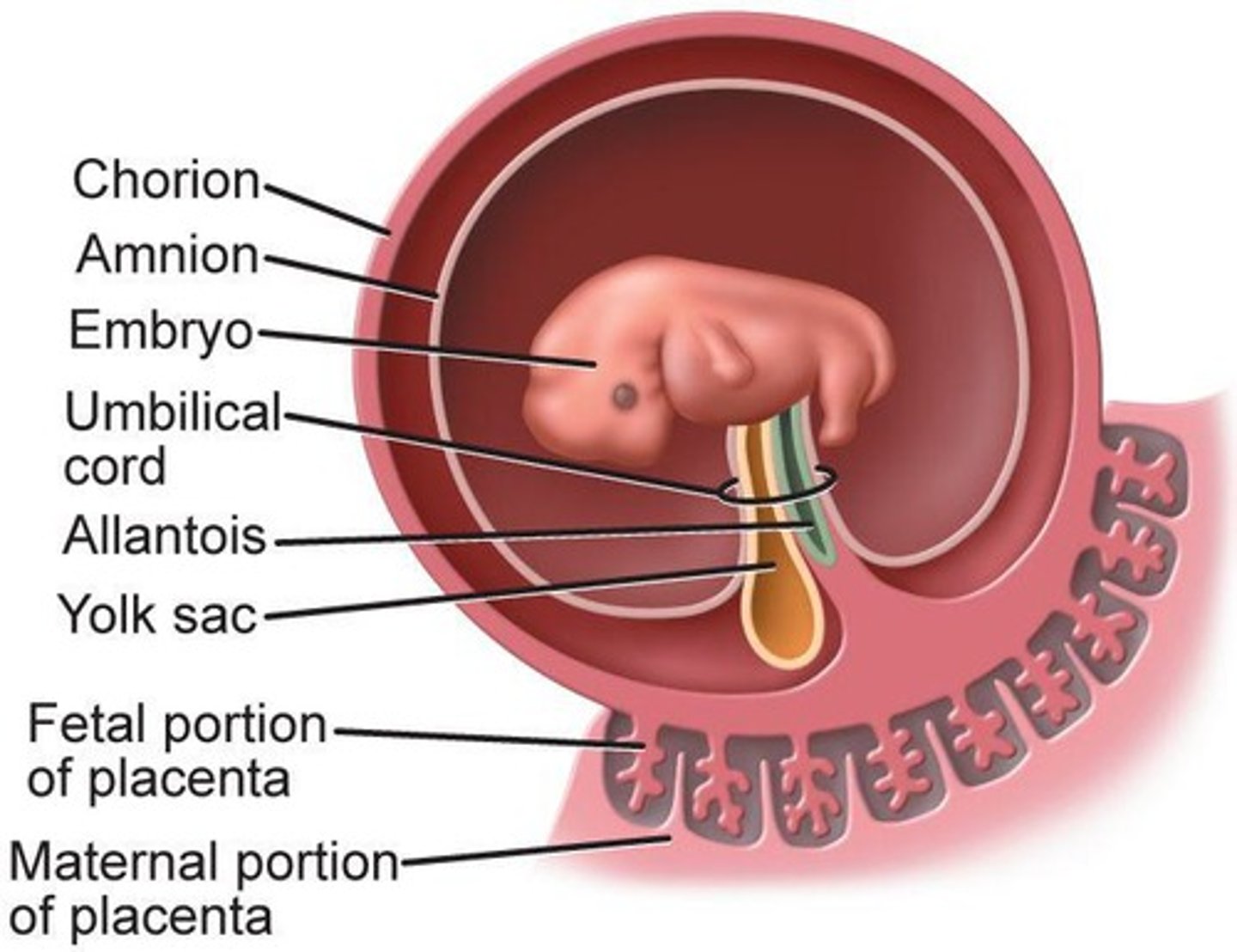
Amnion
Membrane surrounding the embryo, providing protection.
Chorion
Outer membrane forming part of the placenta.
Yolk sac
Provides nutrients to the embryo in early stages.
Allantois
Membrane involved in waste management for embryo.
Placenta
Organ providing nutrients and oxygen to fetus.
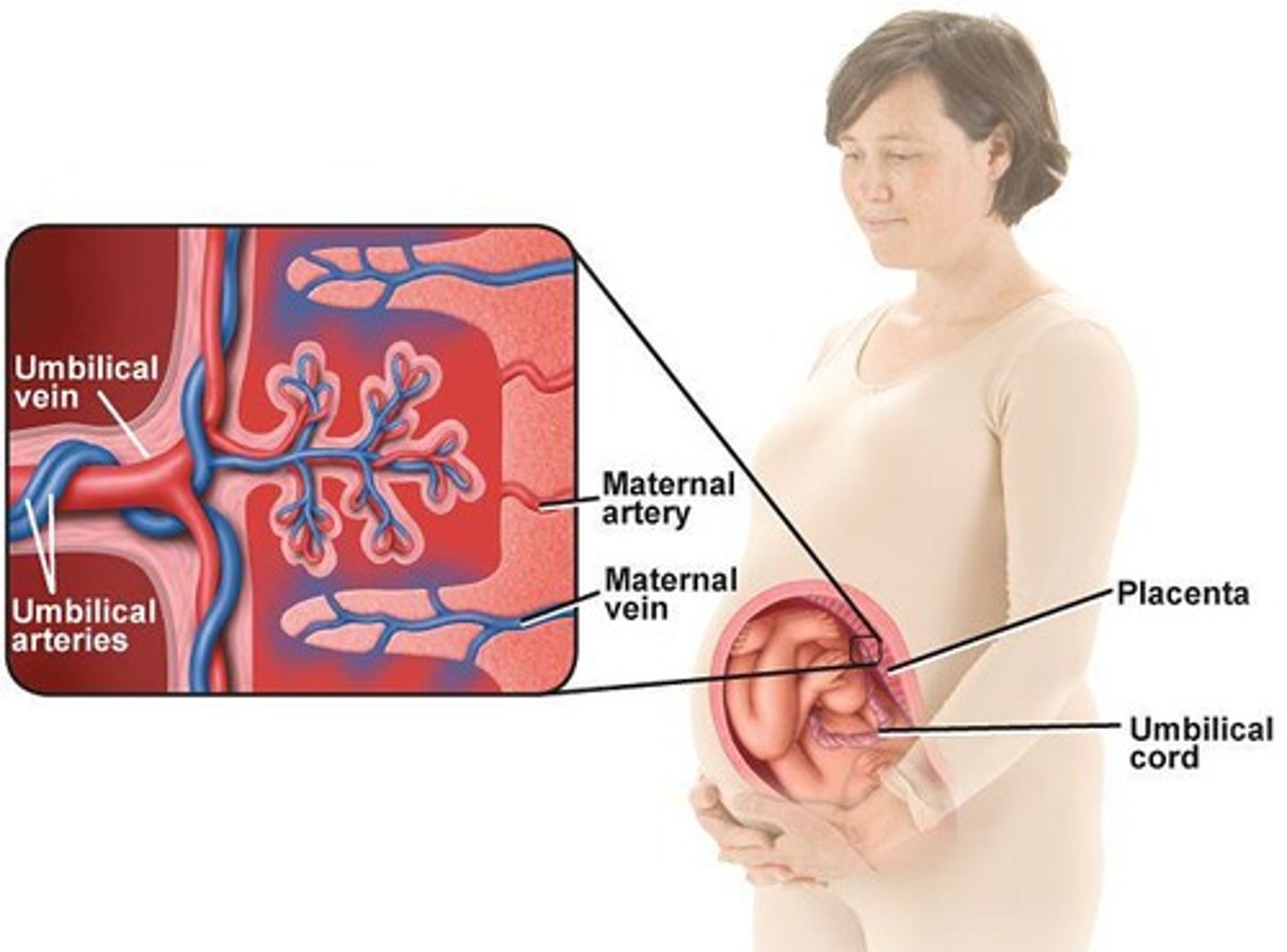
Chorionic villi
Finger-like projections into uterine wall for nutrient exchange.
Umbilical cord
Connects fetus to placenta for nutrient transport.
First trimester
Period of organ and tissue development.

Fetus
Term for embryo after eight weeks.

Second trimester
Growth period with detectable fetal heartbeat.
Third trimester
Rapid growth and fat accumulation in fetus.
Ultrasound
Sound wave procedure to monitor fetal health.
Amniocentesis
Fluid analysis from amniotic sac in second trimester.
Chorionic villus sampling
Cell analysis from chorion in first trimester.
Labor
Beginning of the birthing process.
Dilation
Cervix opening in preparation for birth.
Expulsion stage
Mother pushes baby through vagina.
Placental stage
Detachment of placenta and membranes post-birth.
Infancy
First two years of human life.
Adolescence
Growth period from childhood to adulthood.
Puberty
Developmental stage marking adolescence onset.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Infections transmitted through sexual contact.
Urinary System
Also known as the excretory system.
Kidneys
Bean-shaped organs that filter blood.
Bladder
Stores urine until excretion.
Urethra
Tube through which urine exits the body.
Ureters
Tubes that carry urine from kidneys to bladder.
Meatus
Opening through which urine is expelled.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of water and pH balance.
Nitrogenous Waste
Toxic byproducts removed via urine.
Reabsorption
Process of retaining essential substances during urine formation.
Nephrons
Functional units of the kidneys, over 1 million per kidney.
Glomerulus
Capillary network where blood filtration begins.
Bowman's Capsule
Surrounds the glomerulus, collecting filtered fluid.
Renal Artery
Supplies blood to the kidneys.
Renal Vein
Carries filtered blood away from the kidneys.
Renal Cortex
Outer protective layer of the kidney.
Renal Medulla
Inner soft portion of the kidney.
Hilum
Depression where blood vessels and ureters enter kidneys.
Urine Production
Filtration of water, salts, and waste products.
Filtration
Process of separating waste from blood in kidneys.
Urine Flow
Pathway of urine from kidneys to bladder.
Daily Blood Filtration
Kidneys filter about 1700 liters of blood daily.
Ureters
Tubes transporting urine from kidneys to bladder.
Urinary Bladder
Muscular organ storing urine until excretion.
Peristalsis
Rhythmic contractions moving urine through ureters.
Trigone
Triangular area where ureters enter bladder.
Urethra
Tube carrying urine from bladder to outside.
Female Urethra
Approximately 1.5 inches long, shorter than male.
Male Urethra
Approximately 8 inches long, passes through prostate.
Micturition
Process of excreting urine from the body.
Urologists
Physicians specializing in urinary and reproductive disorders.
Urinalysis
Examination of urine's physical and chemical properties.
Normal Urine
Straw-colored, clear, with pH 4.6-8.0.
Glucose in Urine
Indicates potential diabetes or kidney issues.
Casts
Microscopic cylindrical structures in urine, indicating disease.
Albumin in Urine
Protein indicating kidney damage or disease.
Blood in Urine
Sign of infection, injury, or kidney disease.
Ketones in Urine
Indicates fat metabolism, often in diabetes.
Phenylketones (PKU)
Abnormal metabolites indicating metabolic disorder.
Bilirubin in Urine
Indicates liver dysfunction or hemolysis.
Dialysis
Process of filtering blood when kidneys fail.
Hemodialysis
Blood filtering using an artificial kidney machine.
Peritoneal Dialysis
Dialysis solution inserted into peritoneal cavity.
Hydronephrosis
Swelling of kidneys due to urine buildup.
Kidney Stones
Hard mineral deposits causing urinary obstruction.
Pyelonephritis
Kidney infection often caused by bacteria.
Incontinence
Inability to control urination.
Neurogenic Bladder
Bladder dysfunction due to nerve damage.
Glomerulonephritis
Inflammation of kidney's filtering units.