Zoonotic and Vector-Borne Diseases Overview
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Emerging Diseases
Infectious diseases increasing after new host introduction.
Reemerging Diseases
Infectious diseases increasing in existing hosts.
Zoonosis
Infection transmissible from animals to humans.
Zoonotic Diseases
Diseases from animals affecting humans, ~58% pathogens.
Spillover
Pathogen transfer between different host species.
Emergence
Pathogen establishment in a new host.
Superspreaders
Individuals spreading disease more than typical cases.
Transmission Methods
Ways zoonoses spread to humans.
Reservoir
Habitat where infectious agents live and multiply.
Vector
Living carrier transporting infectious agents.

Vector Examples
Rodents, bats, mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas.
Vector-Borne Diseases
Diseases transmitted by vectors like mosquitoes.
Malaria
Disease affecting 40% of the global population.
Malaria Endemic Regions
Areas where malaria is commonly found.
Malaria Death Toll
Annual deaths reach up to 1 million.
Plasmodium falciparum
Most deadly malaria parasite.
Economic Cost of Malaria
$1.8 billion estimated cost in Africa (1995).
Malaria Transmission
Involves mosquitoes and Plasmodium parasites.
Control Methods for Malaria
Treatments, insecticides, bednets, and vaccines.
DDT Use
Indoor insecticide use for malaria control.
GM Mosquitoes
Genetically modified mosquitoes for disease control.
Infectious Agents of Malaria
Includes Plasmodium species causing malaria.
Plasmodium vivax
Second most common malaria parasite.
Plasmodium malariae
One of the malaria-causing parasites.
Plasmodium ovale
Malaria parasite with less severe impact.
Plasmodium knowlesi
Malaria parasite primarily in Southeast Asia.
Malaria Prevention
Includes treated bednets and insecticide use.
Airport malaria
Malaria cases linked to international travel.
Congenital malaria
Malaria transmitted from mother to fetus.
Transfusion-transmitted malaria
Malaria spread through infected blood transfusions.
Arboviral diseases
Viral diseases transmitted by blood-feeding arthropods.
Vectors
Organisms like mosquitoes that transmit diseases.

Acute CNS illness
Severe headache indicating central nervous system infection.
Hemorrhagic fevers
Fever accompanied by bleeding symptoms.
Polyarthritis
Joint inflammation with or without fever.
Arboviral encephalitides
Viruses causing inflammation of brain and spinal cord.
St. Louis encephalitis
Virus causing neurological disease, transmitted by mosquitoes.
West Nile Fever
Mosquito-borne disease with varying health effects.
Dengue Fever
Caused by flavivirus, primarily in tropical areas.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF)
Severe form of dengue with bleeding and shock risk.
Case-fatality rate
Percentage of deaths from a specific disease.
Yersinia pestis
Bacterium causing plague, transmitted by fleas.
Bubo
Swollen lymph node characteristic of bubonic plague.
Pneumonic plague
Lung infection transmitted through respiratory droplets.
Incubation period
Time from exposure to onset of symptoms.
Vector control
Methods to reduce disease-carrying organism populations.
Sentinel chickens
Chickens used for surveillance of mosquito-borne diseases.
Standing water
Breeding ground for mosquitoes, should be drained.
Protective clothing
Clothing worn to prevent insect bites.
Insecticide-treated nets
Mosquito nets treated to kill or repel insects.
Dawn/dusk exposure
: Times when mosquitoes are most active.
Rodent reservoirs
Small mammals that harbor plague bacteria.
Flea species
Various fleas that transmit plague to humans.
Case fatality rate
Percentage of deaths from a disease, >50% for plague pneumonia.
Bartonellosis
Infection caused by Bartonella species, includes trench fever.
Trench fever
Caused by B. quintana, transmitted by lice.
Cat-scratch disease
Caused by B. henselae, transmitted by cat scratches.
Signs of Bartonellosis
Fever, headache, fatigue, depression, rashes.
Arthropod vectors
Organisms transmitting diseases, e.g., lice, fleas, ticks.
Risk factors for Bartonellosis
Veterinary work, animal rescue, pet ownership.
Antibiotics for Bartonellosis
Levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, azithromycin.
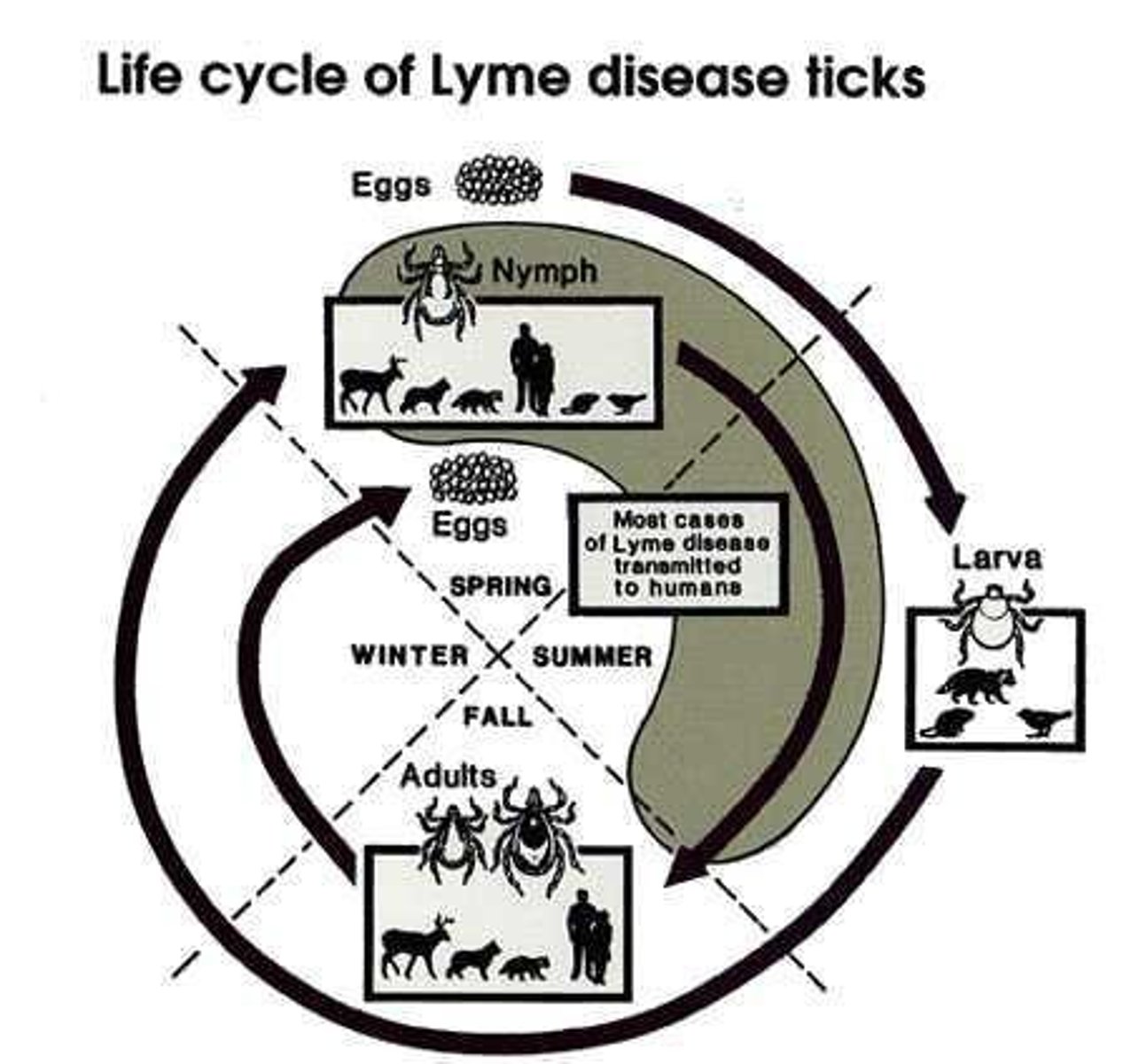
Lyme disease
Bacterial infection from Borrelia burgdorferi via tick bites.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Caused by Rickettsia rickettsii, transmitted by ticks.
Symptoms of RMSF
Fever, severe headache, nausea, rash.
Diagnosis of RMSF
History of tick bites and symptom assessment.
Ehrlichiosis
Infection by Ehrlichia, resembles RMSF without rash.
Anaplasmosis
Infection by Anaplasma, similar symptoms to Ehrlichiosis.
Human Babesiosis
Tickborne disease caused by Babesia protozoa.
Symptoms of Babesiosis
Fever, chills, hemolytic anemia, jaundice.
Diagnosis of Babesiosis
Microscopy, antibody testing, PCR methods.
Emerging zoonoses
New or re-emerging diseases affecting animals and humans.
Factors for zoonoses rise
Ecological changes, population growth, climate change.
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
Severe respiratory disease from hantavirus exposure.
Symptoms of HPS
Fatigue, fever, myalgia, cough, fluid in lungs.
Control of rodent-borne diseases
Remove harborage, eliminate entry points, trapping.
Other zoonotic diseases
Includes Nipah virus, monkeypox, rabies, tularemia.
Control of tick-borne diseases
Avoid habitats, inspect pets, use repellents.
Case fatality rate of HPS
Approximately 38% among infected individuals.
Bartonella species
Includes B. quintana, B. henselae, and others.