NUR 317 Exam 5 - Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery (Sprains and Strains)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Soft tissue injury usually results from trauma which includes...
Sprains
Strains
Dislocation
Subluxation
Sprain
Injury to a ligament surrounding a joint
Caused by wrenching, twisting motion
Most commonly affects the ankle, followed by the knee and wrist
First degree sprain
Mild sprain – few fibers torn
Mild tenderness and minimal edema
Second degree sprain
Moderate sprain – partial ligament tissue disruption
Swelling and tenderness present
Third degree sprain
Severe sprain – complete tearing of ligament
Gap in muscle may be palpable
Risk of avulsion fracture
Moderate to severe swelling
Extreme pain
Strain
Excessive stretching of muscle
Most commonly affects lower back, calf, and hamstring
First degree strain
Mild – slightly pulled muscle
Second degree strain
Moderately torn muscle
Third degree strain
Severely torn or ruptured muscle
Sprain and strain clinical manifestations
Pain
Edema
Contusion
Tiny hemorrhage within tissues/bruising
Decreased function
Sprain and strain recovery
Mild sprains and strains are usually self-limiting
Full function usually returns within 3-6 weeks
X-rays of the affected part may be taken to rule out a fracture
Severe sprain can cause
Severe strains may need surgical repair of the muscle, tendon, or surrounding fascia
Sprains and strains health promotion interventions
Before exercise:
Proper fitting shoes
Improve strength, balance, and endurance
Weight control
Sprains and strains injury interventions (ambulatory and home care)
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation for 24-48 hours
Medications:
Prevent reinjury with strength and conditioning exercises
Referral to physical therapy if needed
Repetitive strain injury
Cumulative trauma disorder
Tiny tears in tendon, ligament, muscle leading to inflammation
Etiology
Prolonged force
Repetitive motion – “Nintendinitis”
Awkward posture
Poorly designed workspaces
Repetitive heavy lifting
Prevention
Education
Ergonomics
Dislocation and subluxation
Result of joint instability
Symptoms similar between dislocation and subluxation
Pain
Soft tissue swelling
Loss of functionality
Deformity
Common areas of dislocations:
Upper body – thumb, elbow, shoulder
Lower body – hip, kneecap
Which has less severe symptoms – dislocation or subluxation?
Subluxation
Dislocation and subluxation complications
Fractures within the joint
Blood vessel and nerve damage of adjacent area
Avascular necrosis
Compartment syndrome
Dislocation and subluxation surgery
Open and closed reduction
Dislocation and subluxation nursing care
Dislocation – prompt attention!
Support and protection of injured area
Pain management
Incision/dressing assessments and management
Appropriate positioning/mobility
Coordination with therapy (rehab programs?)
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)
Most common upper extremity compression neuropathy
Compressed median nerve (which passes through carpal tunnel)
Women more likely than men to develop CTS – often occurs during premenstrual period, pregnancy, and menopause
Carpal tunnel syndrome diagnostics
H & P
↓ sensation to light touch in affected fingers
Inflated BP cuff >SBP for 1-2 min
EMG (electromyography)
Median nerve motor conduction
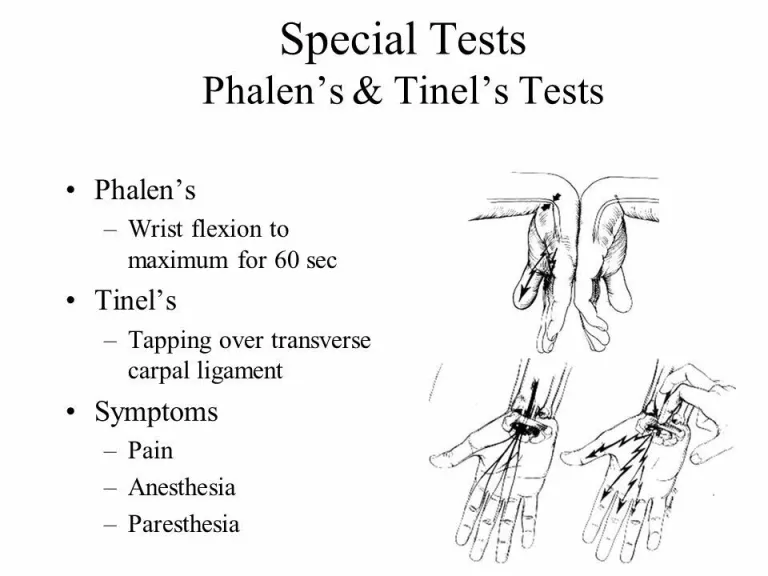
Tinel’s Sign
Tingling over the median nerve on light percussion
Phalen’s Maneuver
Flexion at the wrist for 1 minute and tingling over the median nerve
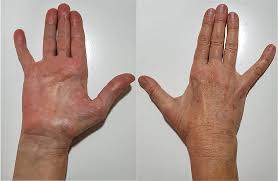
Thenar muscle atrophy
Seen in about 50% of cases
What does Tinel’s Sign and Phalen’s Maneuver test for and how are they performed?
Tinel's sign is performed by tapping over the median nerve at the wrist to check for tingling sensations, while Phalen's maneuver involves holding the hands in a forced flexed position for 30-60 seconds to see if symptoms are triggered
What does Thenar muscle atrophy indicate?
The wasting of the muscles in the base of the thumb due to carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome management
Prevention - adaptive devices, ergonomic considerations
NSAIDS
Physical therapy exercises
Corticosteroid Injection
Surgery
If symptoms last longer than six months
Full recovery may take months
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury
Usually occurs from noncontact injury
Athlete pivots, lands from a jump or slows down when running
Knee may feel unstable after coming down on it, twisting it, or hearing a “pop”
Acute pain, edema
Anterior cruciate ligament injury diagnosis
Lachman’s Test:
Positive if forward motion of the tibia is detected when the knee is flexed 15-30 degrees and tibia is pulled forward while femur is stabilized
Injury confirmed with MRI

Anterior cruciate ligament injury treatment
Conservative treatment
Aspiration of effusion
Immobilizer/brace
Physical therapy
Reconstructive surgical repair – severe injury, graft tissue replaces torn ACL