AP Psych Unit 2 Cognition Study Guide
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
cognition
all mental activities associated w/ thinking, knowing, remembering, & communicating
metacognition
“beyond cognition”
cognition about our cognition/thinking about our thinking
keeping track of & evaluating our mental processes
concept
mental grouping(s) of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
ex. cataloging
prototype
mental image or best example of a category
ex. feathers to birds
Jean Piaget
studied the development of cognition in children
argued that our intellectual progression reflects an unceasing struggle to make sense of our experiences
schema
understandings
concept or framework that organizes & interprets info
ex. role schema: learned gender roles
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
accommodation
S&P = process by which the eye’s lens changes shape to focus images of near or far objects on the retina
cognitive psychology = adapting our current schemas to incorporate new info
creativity
ability to produce new & valuable ideas
pros: produces new insights & products
cons: may distract from structured, routine work
convergent thinking
ability to provide a single correct answer
divergent thinking
ability to consider many different options & to think in novel (new) ways
Robert Sternberg
believed creativity has 5 components:
expertise — well-developed knowledge
imaginative thinking skills — ability to see things in novel (new) ways, recognize patterns, make connections
venturesome personality — seek new experiences, tolerates ambiguity, perseveres in overcoming obstacles
intrinsic motivation — quality of being driven more by interest, satisfaction, & challenge than by external pressures
creative environment
executive functions
cognitive skills that work together, enabling us to generate, organize, plan, & implement goal-directed behavior
algorithm
step-by-step procedures that guarantee a solution/methodical rule or procedure
pros: guarantees solution
cons: requires time & effort
heuristic
simple thinking strategies, mental shortcuts
pros: allows quick & efficient action
cons: error-prone
insight
sudden realization of a problem’s solution/sudden “aha!” reaction
pros: provides instant realization of solution
cons: may not happen
Wolfgang Kohler
showed that humans are not the only creatures to display insight
experimented w/ a chimpanzee named Sultan
placed a piece of fruit & a long stick outside Sultan’s cage
placed a short stick inside Sultan’s cage, of which Sultan used to try and reach the fruit
Sultan gave up for a moment then began to think and then had an “aha!” moment
Sultan used the short stick to pull in the longer stick, then used the longer stick to obtain the fruit
confirmation bias
tendency to search for info that supports our preconceptions & to ignore or distort contradictory experience
pros: allows for quick recognition of supporting evidence
cons: hinders recognition of contradictory evidence
fixation
(in cognition) inability to see a problem from a new perspective
obstacle to problem solving
ex. mental set
pros: focuses thinking
cons: hinders creative problem solving
mental set
tendency to approach a problem w/ the mindset of what has worked for us previously will work again
intuition
fast, automatic, unreasoned feelings & thoughts
pros: based on our experience — huge & adaptive
cons: can lead us to overfeel & underthink
Amos Tversky & Daniel Kahneman
showed that R&A heuristics can lead even the smartest people to make dumb decisions
representative heuristic
judging likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent/match particular prototypes
may lead us to ignore other relevant info
availability heuristic
judging likelihood of events based on their availability in memory
overconfidence
tendency to be more confident than correct/overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs & judgments
pros: allows us to live happier & make decisions easily
cons: error-prone
belief perseverance
tendency to cling to our beliefs in the fact of contrary evidence
pros: supports our enduring beliefs
cons: closes our minds to new ideas
framing
the way an issue is presented
pros: can influence others’ decisions
cons: can produce misleading results
nudge
framing choices in a way that encourages people to make beneficial decisions
ex. healthier eating, saving for retirement, making moral decisions, becoming an organ donor
memory
persistence of learning over time through encoding, storage, & retrieval of info
recall
retrieving info that is not currently in your conscious awareness but that was learned at an earlier time
ex. fill in the blank questions
recognition
identifying items previously learned
ex. multiple choice questions
relearning
learning something more quickly when you learn it a second time or later time
ex. speak a language used in early childhood
Herman Ebbinghaus
showed our response speed when recalling or recognizing info indicates memory strength & relearning speed using nonsense syllables
ex. JIH XYG HIW JHW
encoding
getting info into the memory system
storage
keeping info in the memory system
retrieval
getting info out of memory storage
parallel processing
processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously
Richard Atkinson & Richard Shiffrin
proposed modal model of memory/multi-store model
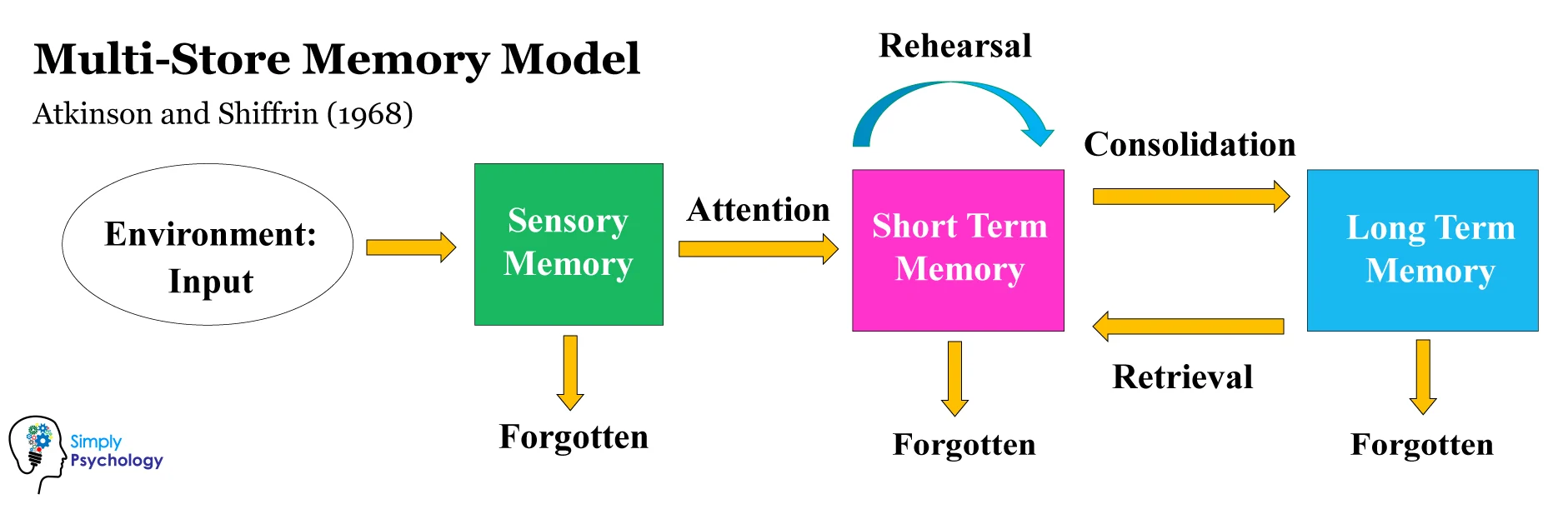
sensory memory
immediate, brief recording of sensory info in the memory system
short-term memory
briefly activated memory of a few items that is later stored or forgotten
long-term memory
relatively permanent & limitless archive of the memory system including knowledge, skills, & experiences
working memory
conscious, active processing of both incoming sensory info & info retrieved from long-term memory
newer understanding of short-term memory
central executive
memory component that coordinates activities of phonological loop & visuospatial sketchpad
phonological loop
memory component that briefly holds auditory info
visuospatial sketchpad
memory component that briefly holds info about objects’ appearance & location in space
neurogenesis
formation of new neurons
Eric Kandel
in order to understand the physical basis of memory/how info becomes embedded in brain matter, recruited the California sea slug
discovered that when learning occurs, slug releases more of the neurotransmitter serotonin into certain neurons
conclusion
experience & learning can increase the number of synapses
long-term potentiation (LTP)
increase in nerve cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation
neural basis for learning & memory
explicit memory
continued possession of facts & experiences that we can consciously know & “declare”
also known as declarative memory
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention & conscious effort
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental info such as space, time, & frequency, of familiar or well-learned info such as sounds, smells, & word meanings
implicit memory
continued possession of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection
also known as nondeclarative memory
iconic memory
fleeting sensory memory of visual stimuli
lasts up to few 1/10’s of a second
echoic memory
fleeting sensory memory of auditory stimuli
lasts 3-4 seconds
George A. Miller
proposed that we can store about 7 pieces of info in short-term memory
chunking
organizing into familiar, manageable units
often occurs automatically
mnemonics
memory aids/helpers
spacing effect
tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention/continued possession than is achieved thru mass study/mass practice
ex. opposite of cramming, studying over a long period of time
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving info
also referred to as retrieval practice or test-enhanced learning
shallow processing
encoding on a basic level based on the structure or appearance of words
deep processing
encoding semantically (in language or topic) based in the meaning of words
tends to yield the best retention
semantic memory
facts & general knowledge
1 of our 2 conscious memory systems
episodic memory
experienced events
1 of our 2 conscious memory systems
hippocampus
neural center located in the limbic system
helps memory storage
memory consolidation
neural storage of a long-term memory
flashbulb memory
clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event
priming
“wakening of associations”/activation of certain associations, leading one’s perception, memory, or response
ex. seeing rabbit then spelling hair as hare
encoding specificity principle
idea that cues & contexts specific to a particular memory will be most effective in helping recalling
mood-congruent memory
tendency to recall experiences that are consistent w/ one’s current good or bad mood
serial position effect
tendency to recall best the last items in a list initially (recency effect) & the first items in a list after a delay (primacy effect)
interleaving
retrieval practice study that involves mixing the study of different topics
reminder: sounds like interweaving
anterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories
retrograde amnesia
inability to remember info from one’s past
ex. stories featuring comas & memory loss
proactive interference
forward-acting disruptive effect of older learning on the recall of new info
ex. misinformation
retroactive interference
backward-acting disruptive effect of newer learning on the recall of old info
ex. it’s like second guessing on a test, mixing up answers
repression
(psychoanalytic theory) basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories
ex. trauma response, inabilty to recall traumatic events
reconsolidation
process in which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again
ex. your memory might not be the real memory
Elizabeth Loftus
“to some degree, all memory is false”
experimented, showed participants pairs of faces — 1 face they had seen earlier & one they had not, then asked them to identify the one they had seen
but in one pair she slipped in included 2 new faces similar to the face they had seen earlier
as a result, participants picked the wrong face when asked to pick the face seen earlier
conclusion
participants had replaced the OG memory w/ a false memory
misinformation effect
occurs when a memory has been corrupted by misleading info
source amnesia
faulty memory for how, when, or where info was learned or imagined
@ the heart of many false memories
deja vu
“i’ve experienced this before”
cues from current situation may unconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience
intelligence
ability to learn from experience, solve problems, & use knowledge to adapt to new situations
Charles Spearman
believed we have 1 general intelligence that lies @ the heart of all of our intelligent behavior
general intelligence
according to Spearman, underlies all mental abilities & is measured by every task on an intelligence test
factor analysis
statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (factors) on a test
used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person’s total score
L. L. Thurstone
one of Spearman’s early critics
gave 56 different tests to people & mathematically identified 7 clusters of primary mental abilities:
word fluency
verbal comprehension
spatial ability
perceptual speed
numerical ability
inductive reasoning
memory
did not rank people on a single scale of general aptitude
conclusion
some evidence of a g factor
fluid intelligence/Gf
ability to reason speedily & abstractly
crystallized intelligence/Gc
accumulated knowledge & verbal skills
Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) Theory
theory that intelligence is based on g (factor) & specific abilities, bridged by Gf (fluid intelligence) & Gc (crystallized intelligence)
Howard Gardner
identified 8 relatively independent intelligences
visual-spatial
verbal-linguistic
musical-rhythmic
logical-mathematical
interpersonal
intrapersonal
naturalistic
bodily-kinesthetic
proposed a 9th possible intelligence: existential intelligence, “ponder large questions about life, death, existence”
influenced learning styles
savant syndrome
condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill
ex. skilled in computation, skilled in drawing
grit
in psychology, passion & perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals
emotional intelligence
ability to perceive, understand, manage, & use emotions
intelligence test
method for assessing individual’s mental aptitudes & comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores
achievement test
test designed to assess what a person has learned
ex. AP psych exam
aptitude test
test designed to predict individual’s future performance
aptitude — capacity to learn
Francis Galton
wondered if it might be possible to measure “natural ability” (is cousin of Charles Darwin), founded eugenics 19th-20th century C.E.
eugenics — discriminatory movement that proposed measuring human traits & encouraging only those deemed “fit” to reproduce
1884 London Health Exhibit, 10k visitors received his assessment of their “intellectual strengths” (eugenics)
Alfred Binet
tasked w/ developing fair testing for children in schooling
evaluated mental age of children
mental age
measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet
ex. 8-year-old who does as well as an average 8-year-old is mentally an 8-year-old
Lewis Terman
measured innate intelligence
revised Binet’s mental age evaluation intelligence tests, ranging ages from 12 to “superior adults”