AP Micro Unit 2: Supply and Demand
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
capital goods
Goods made for indirect consumption. Goods that make consumer goods
human capital
the knowledge and skills a worker gains through education and experience
the law of demand
consumers buy more of a good when its price decreases and less when its price increases, inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
quantity demanded
price changes ________ ________, not demand
demand shifters
income, population, price of substitutes, price of complements, expectations, tastes
substitutes
two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the other
complements
two goods that are bought and used together, price of one goes up then demand for other goes down
normal goods
Goods for which demand goes up when income is higher and for which demand goes down when income is lower.
inferior goods
Goods for which demand tends to fall when income rises.

right
demand curve increase shifts _______-
substitution effect
an increase in price makes substitutes more attraction an a decrease in price makes them less attractive
income effect
an increase in price decreases purchasing power and visa versa (if smthg is more expensive, i can't afford it as much)
the law of supply
producers sell more of a good at higher prices and less as its price falls
supply shifters
input prices, government tools, number of sellers, technology, prices of other goods, producer expectations
government tools
per unit taxes, subsidies, regulations
decrease supply
per unit tax
increase supply
subisidies
generally decrease supply
regulations
increase
An increase in the number of sellers in a market generally leads to a _______ in market supply,
increase
an increase in technology also _______ supply
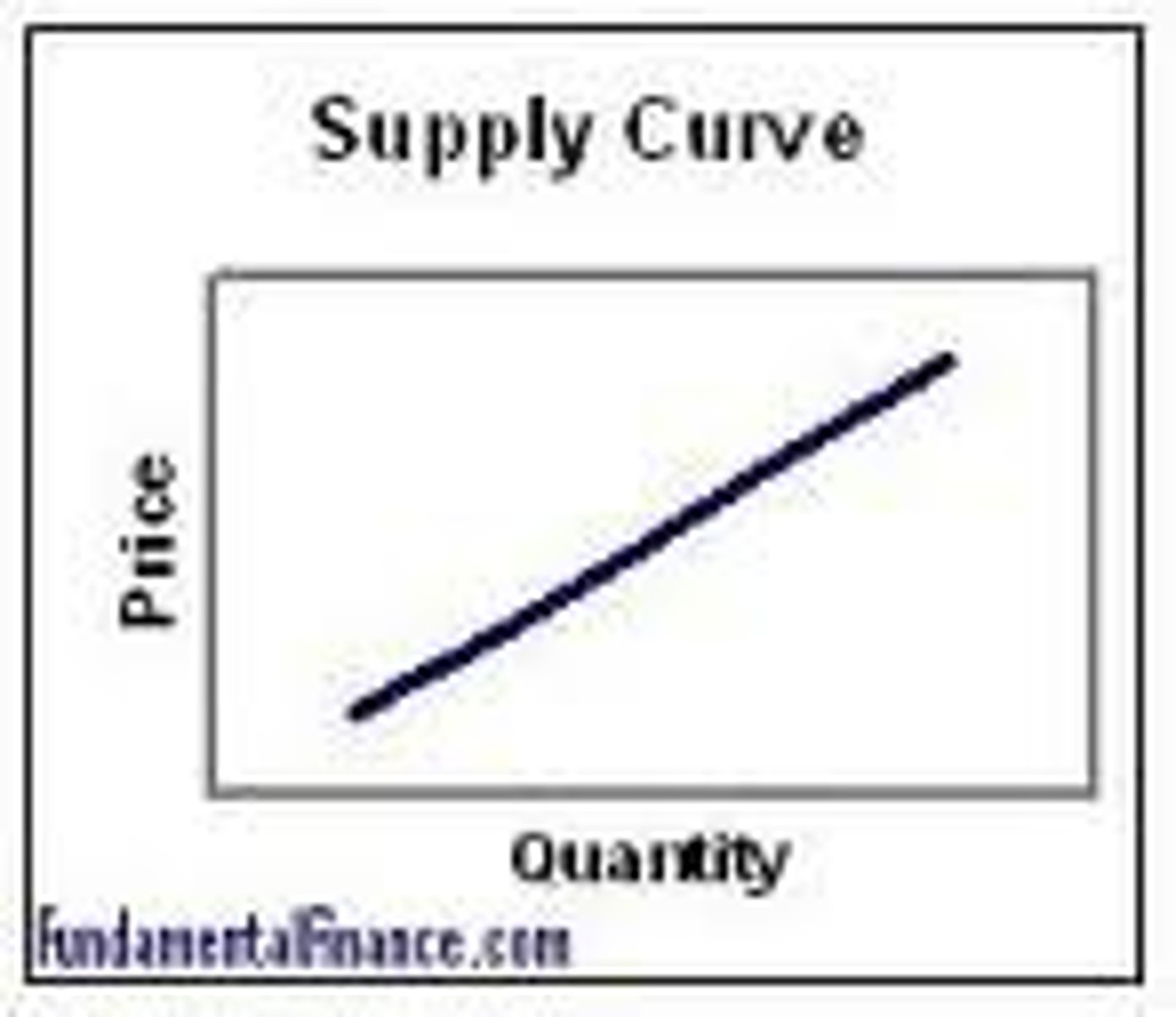
supply curve
upward sloping, positive linear function :)
elasticity
a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded or quantity supplied to a change in price
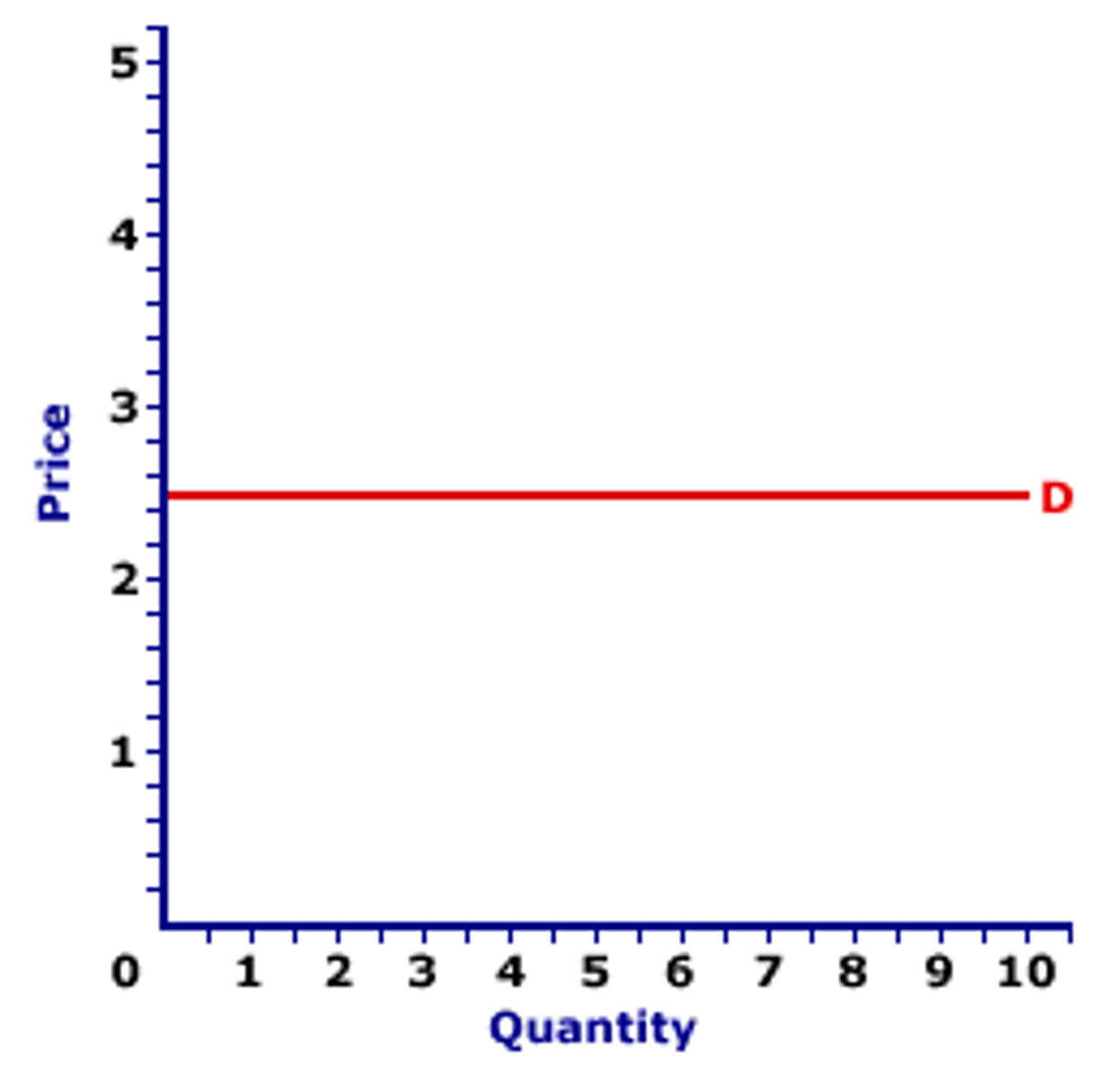
elastic
refers to a market for a product or service that is price sensitive; relatively small changes in price will generate fairly large changes in the quantity demanded
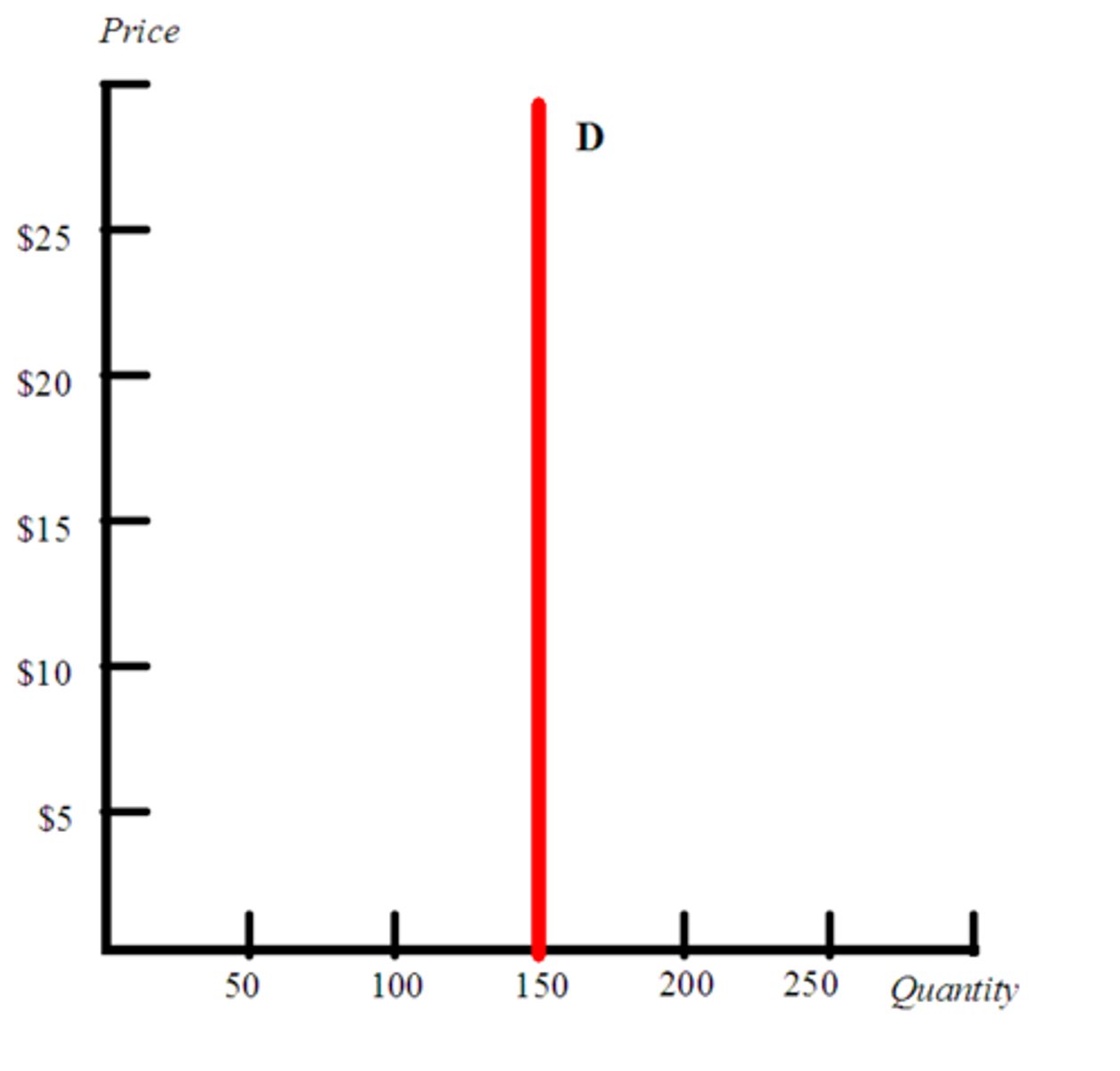
inelastic
describes demand that is not very sensitive to price changes
total revenue
Price x Quantity, the total amount of money a firm receives by selling goods or services
elastic
decrease price, increase total revenue or increase price, decrease TR (moving opposite ways)
inelastic
decrease price, decrease total revenue or increase both
total revenue test
A test to determine elasticity of demand between any two prices: Demand is elastic if total revenue moves in the opposite direction from price; it is inelastic when it moves in the same direction as price; and it is of unitary elasticity when it does not change when price changes.
unit elastic
no change in price
marginal revenue
the change in total revenue from an additional unit sold
percent change
(new-old)/old x 100
elasticity coefficient
% change in quantity / % change in price
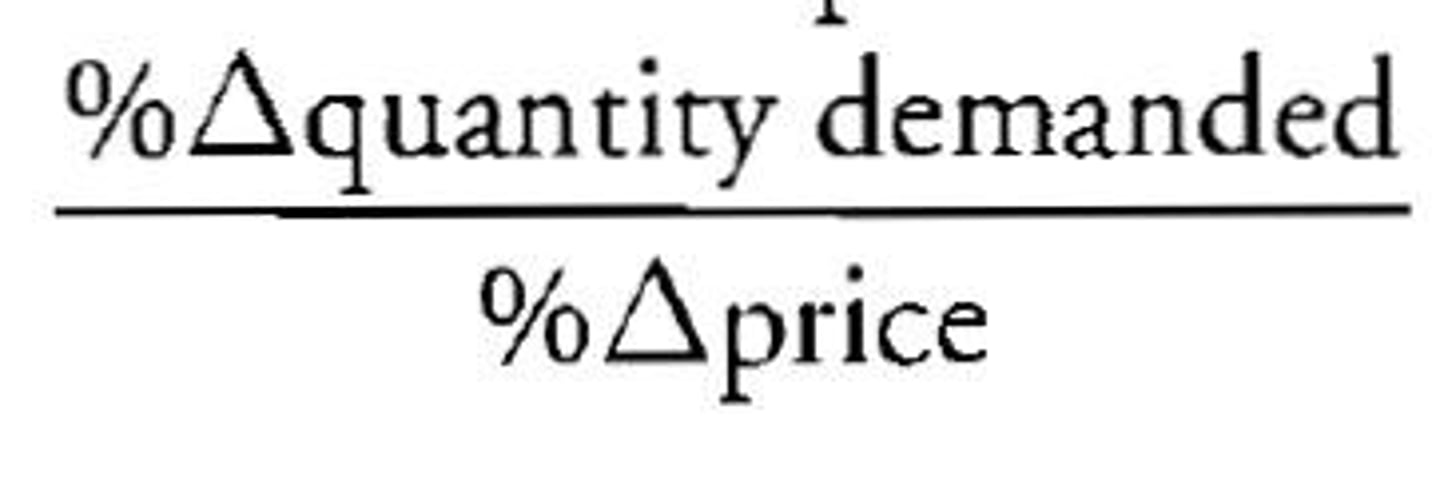
relatively elastic
If the absolute value of the elasticity coefficient is greater than 1 then it is
unit elastic
If the absolute value of the elasticity coefficient is equal to 1 then it is
relatively inelastic
If the absolute value of the elasticity coefficient is less than 1 then it is
income elasticity
% change in quantity demanded / % change in income
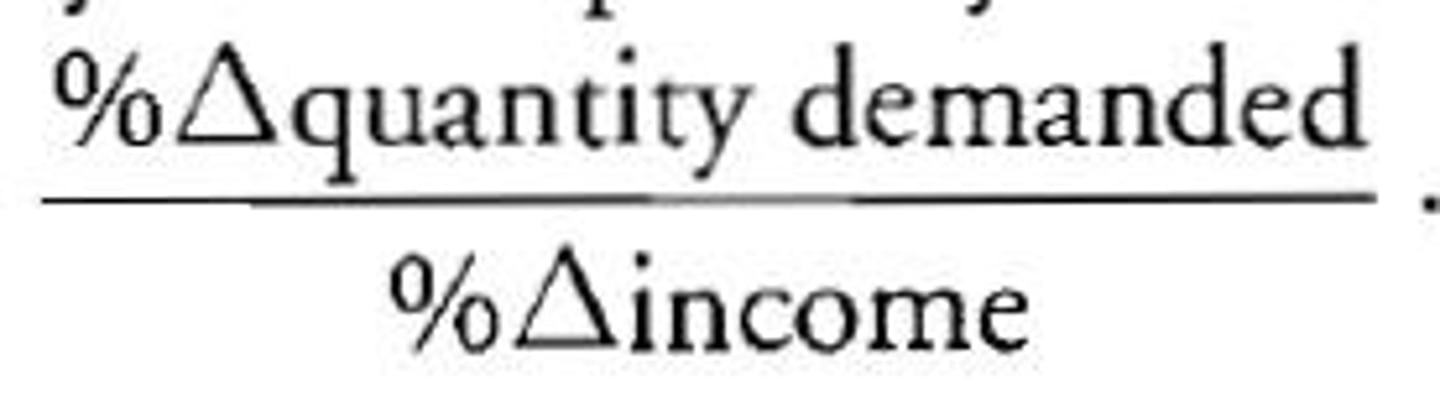
normal good
A positive income elasticity coefficient means _______ ______
inferior good
A negative income elasticity coefficient means _______ ______
cross price elasticity
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good
cross price elasticity
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price of related good
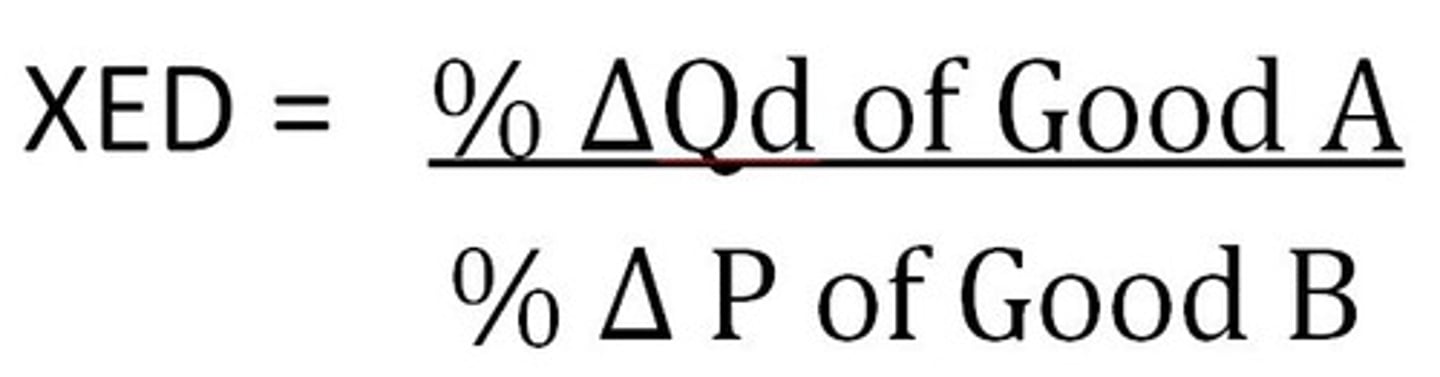
substitutes
positive cross price elasticity
complements
negative cross price elasticity
market equilibrium
Point where supply equals demand.
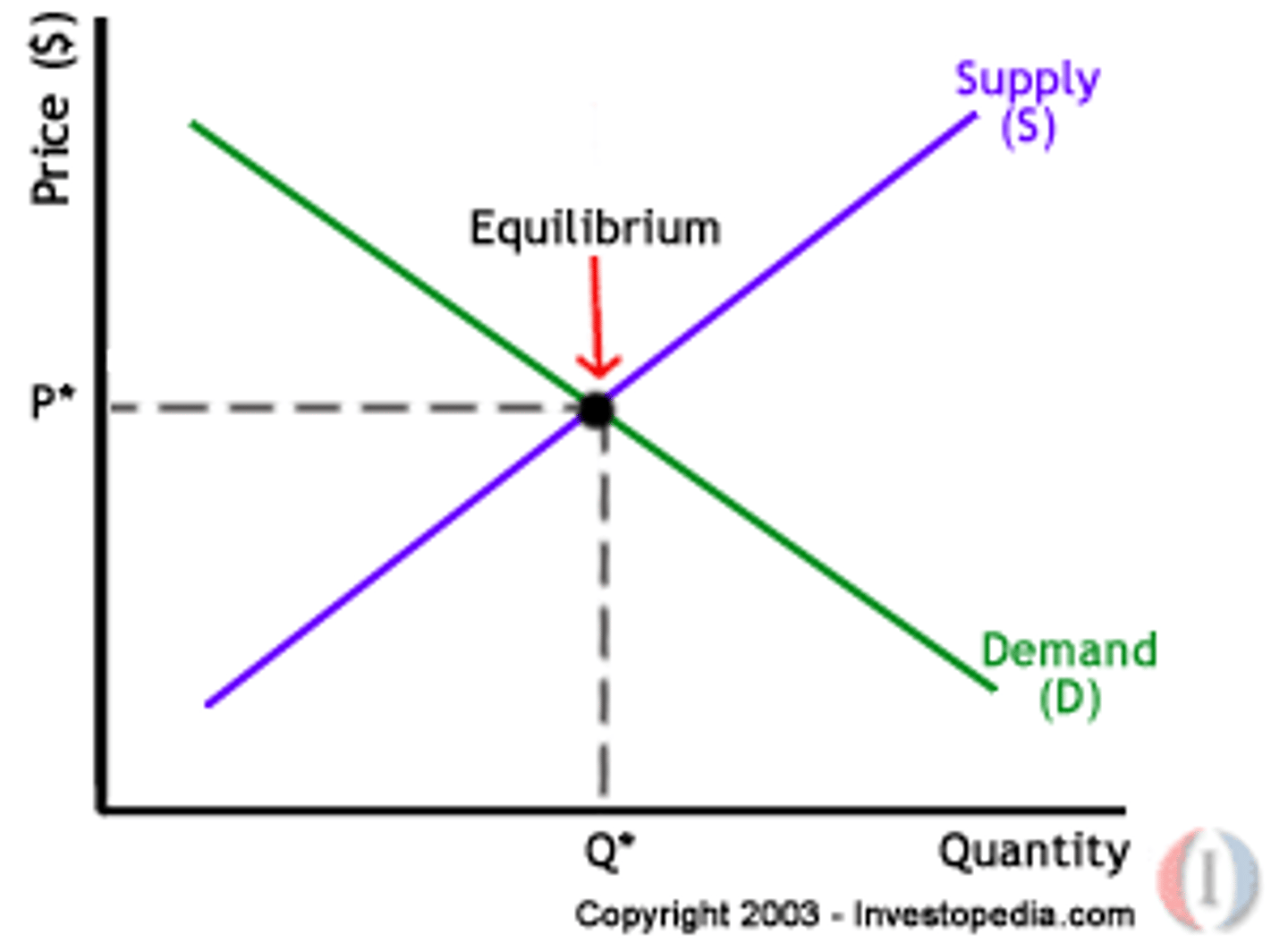
surplus
When the price is above market equilibrium, a situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
shortage
Price is below equilibrium; A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
consumer surplus
the difference between the value to the consumer and the price
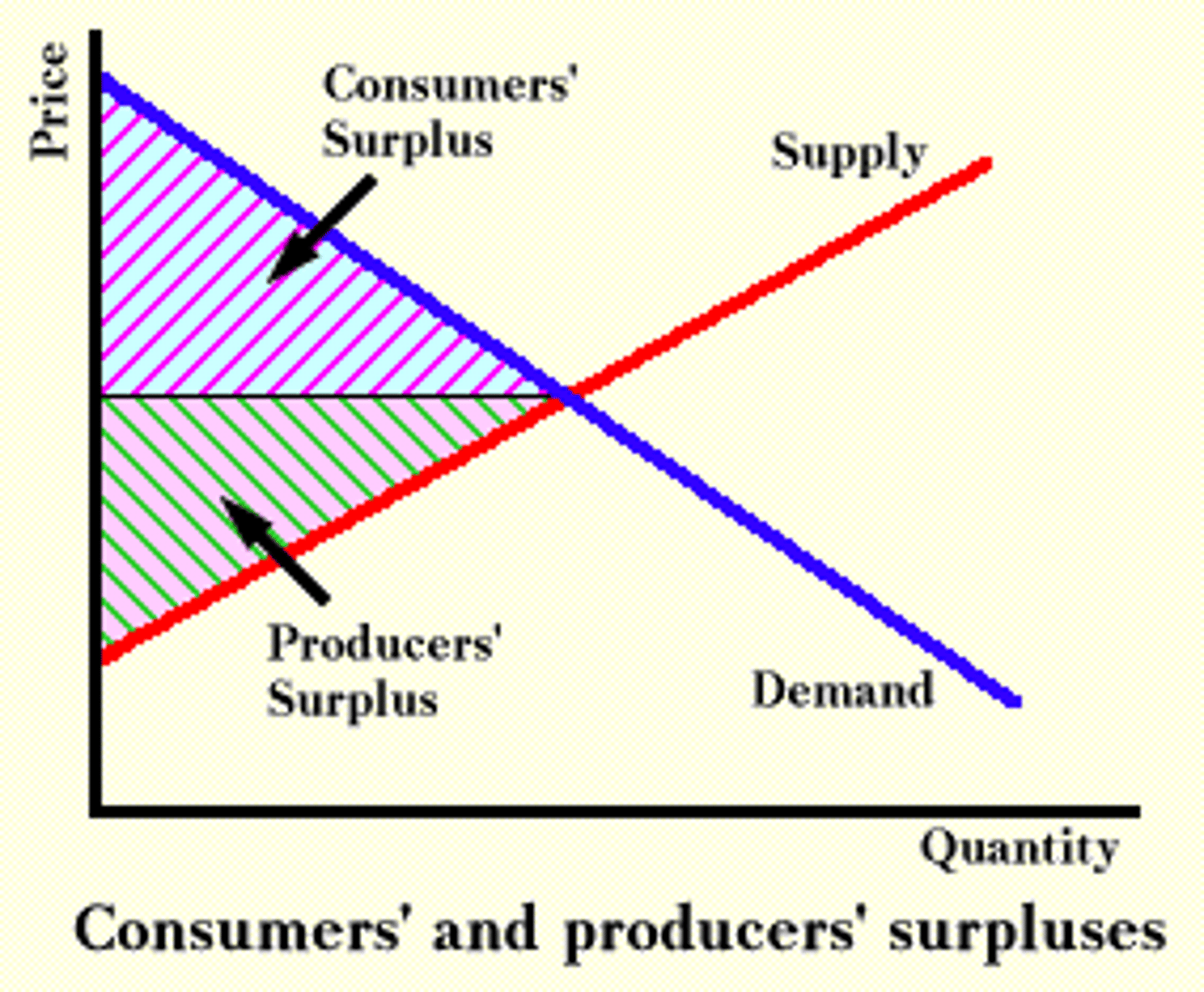
producer surplus
the amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller's cost of providing it
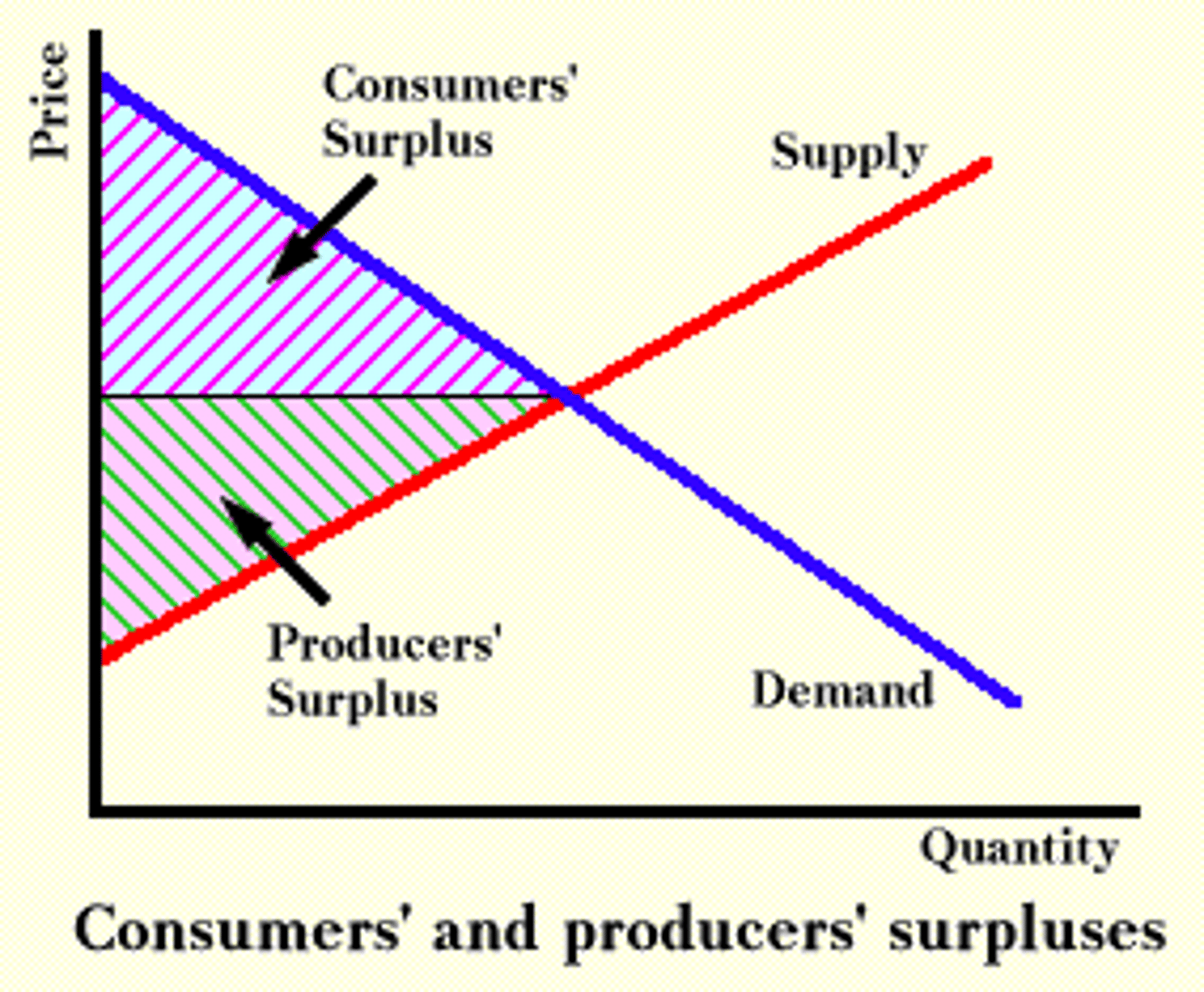
economic surplus
consumer surplus + producer surplus
allocative efficiency
when the mix of goods being produced represents the mix that society most desires, when economic surplus is maximized (@ equilibrium)
deadweight loss
the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium
price floor
A government intervention that places a legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold, (but on the graph it's actually high)
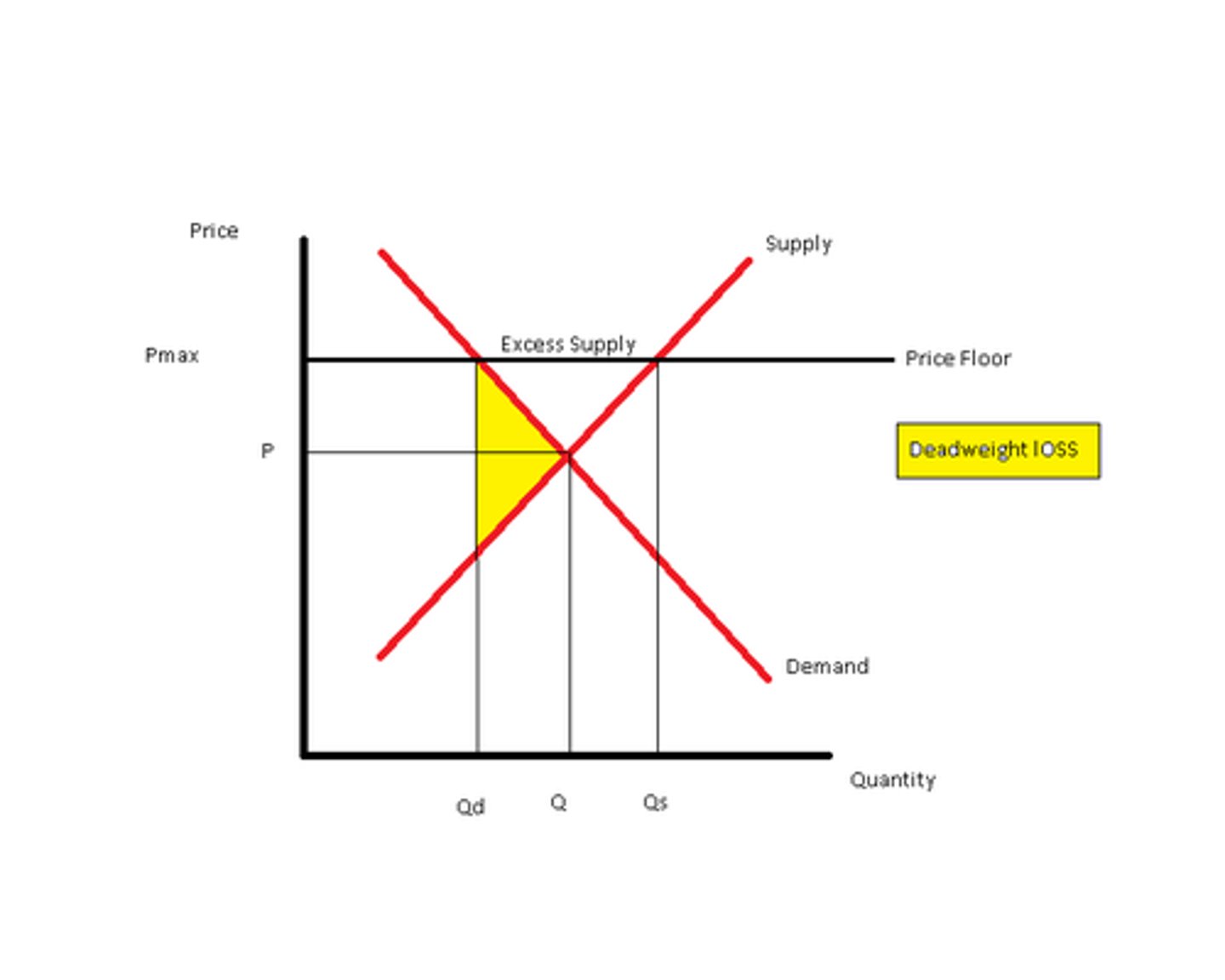
above
a price floor must be _______ the equilibrium to be binding
price ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold
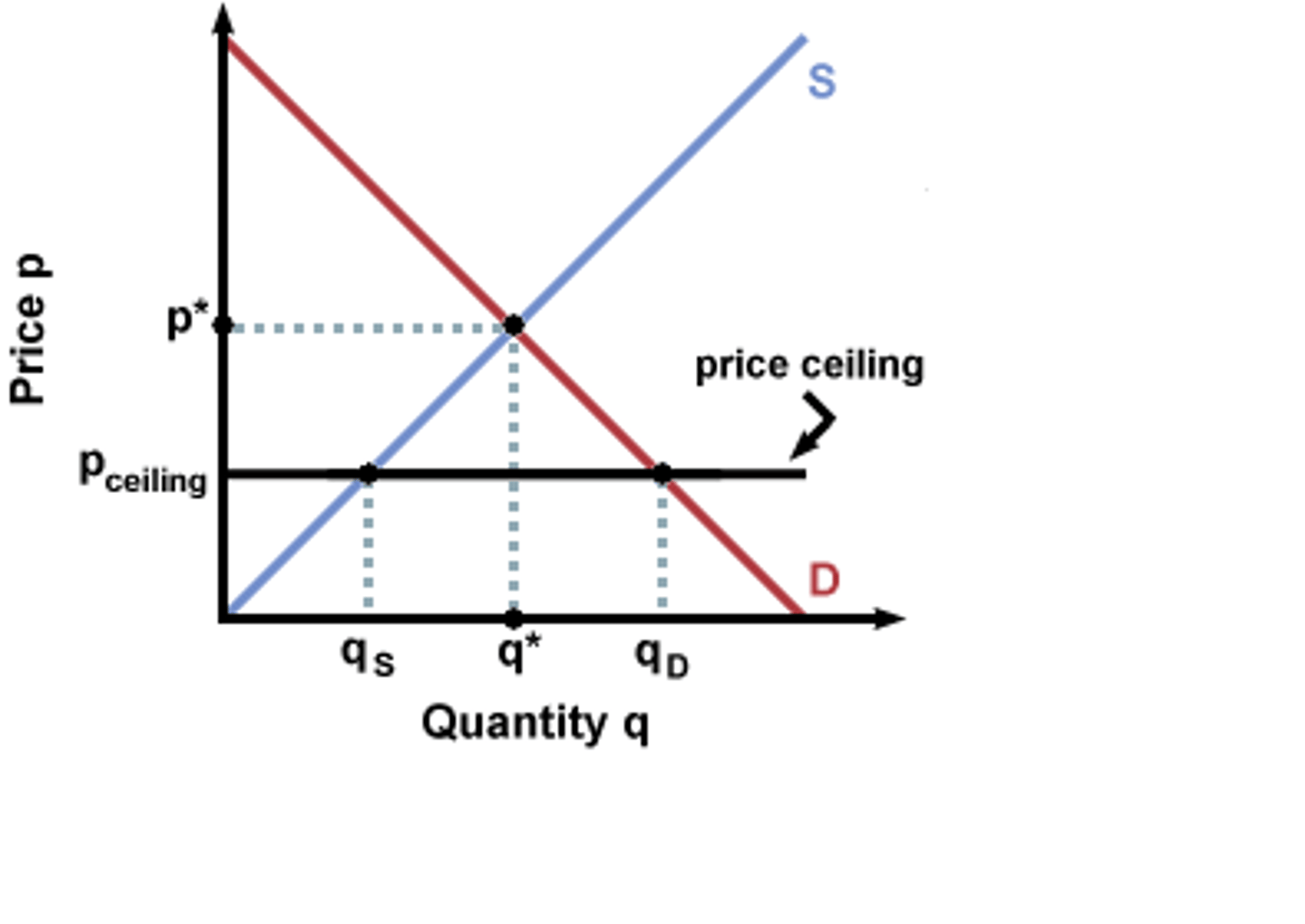
below
a price ceiling must be _______ the equilibrium to be binding
tax revenue
the money a government gains from the collection of taxes
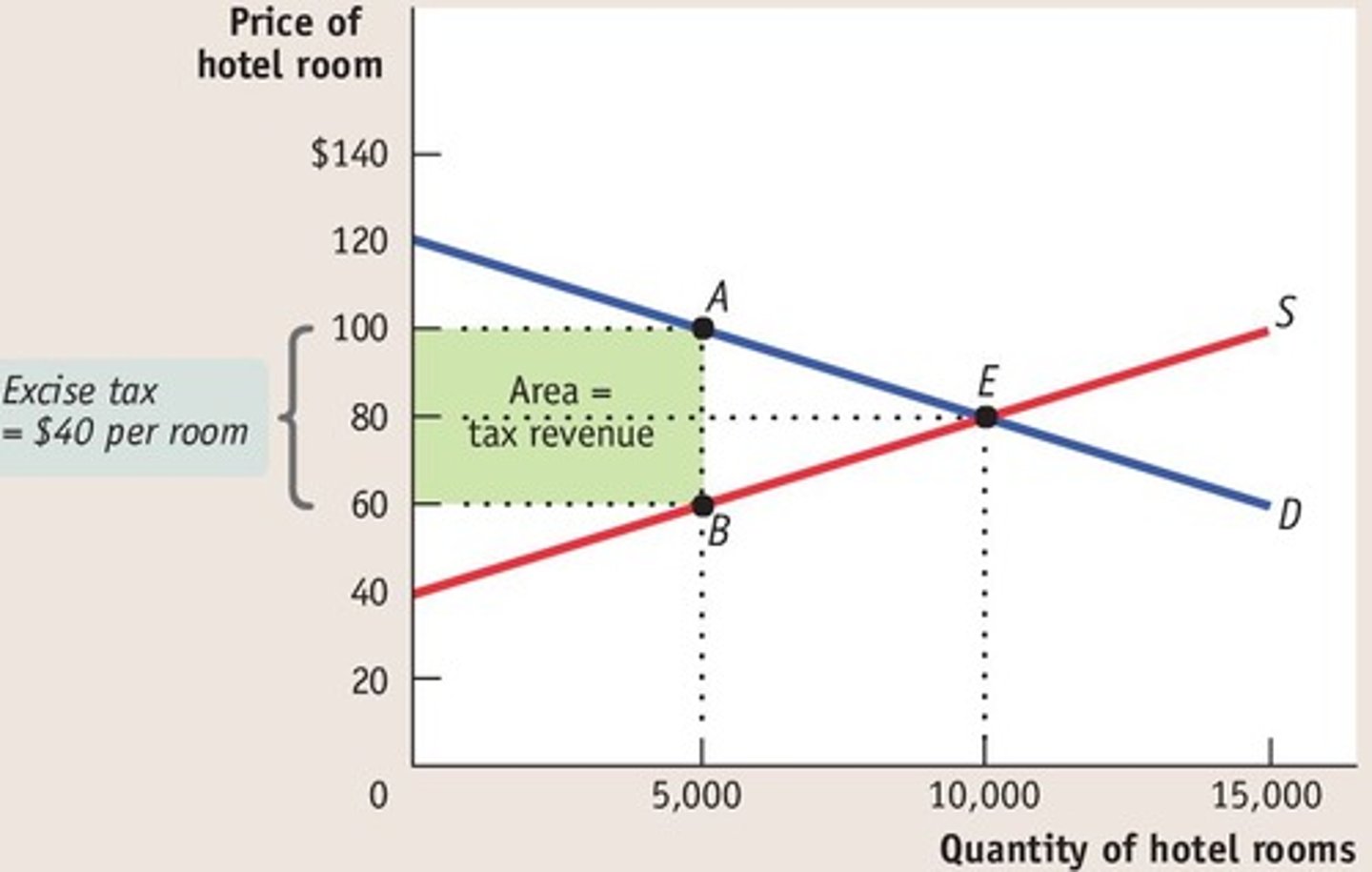
tax incidence
the actual division of the burden of a tax between buyers and sellers in a market
buyers
If the demand curve is less elastic than the supply curve, than the ________ have a bigger loss on the tax
sellers
If the supply curve is less elastic than the demand curve, than the ________ have a bigger loss on the tax
no tax
If the demand is perfectly elastic, this means there is ___ _____ and all the tax would fall on the buyers
producer
If you add a tariff, then _________ surplus increases
consumer
If you add a tariff, then _________ surplus decreases
0
Coefficient for perfectly inelastic demand
infinity
Coefficient for perfectly elastic demand
entire
A change in demand is when the _______ demand curve shifts.
movement
A change in quantity demanded is __________ along the curve.
double shift rule
If two curves shift at the same time, EITHER price or quantity will be indeterminate