unit 1 part 2: introduction to public health
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Last updated 4:30 PM on 2/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
10 **Essential** Public Health Services
1. Monitor Health
2. Diagnose and Investigate
3. Inform, Educate, Empower
4. Mobilize Community Partnership
5. Develop Policies
6. Enforce Laws
7. Link to/Provide Care
8. Assure a Competent Workforce
9. Evaluate
10. Research
2
New cards
The Public Health System
“all public, private, and voluntary entities that **contribute to the delivery of essential public health services** within a jurisdiction.”
3
New cards
* **Public health agencies** at state and local levels
* Healthcare **providers**
* **Public safety** agencies
* **Human service and charity** organizations
* **Education and youth development** organizations
* **Recreation and arts-related** organizations
* **Economic and philanthropic** organizations
* **Environmental** agencies and organizations
* Healthcare **providers**
* **Public safety** agencies
* **Human service and charity** organizations
* **Education and youth development** organizations
* **Recreation and arts-related** organizations
* **Economic and philanthropic** organizations
* **Environmental** agencies and organizations
public health system includes:
4
New cards
**multidisciplinary** and **interdisciplinary**
Public Health requires ___ actions
5
New cards
partnership
Public health does not exist in a vacuum, it involves ___.
6
New cards
protect health
If the primary intent of any measure is to ___, then **that is public health.**
7
New cards
cost jobs = price products = tax increase = cut companies’ profit
**Public Health & Economic Impact:**
Public health regulation
Public health regulation
8
New cards
resist pasteurization
**Public Health & Economic Impact:**
Resisting change in more milk production
Resisting change in more milk production
9
New cards
resist building codes
**Public Health & Economic Impact:**
Landlords
Landlords
10
New cards
resist design changes to improve safet
**Public Health & Economic Impact:**
Automobile manufacturers
Automobile manufacturers
11
New cards
harmful to health = causing thousands of deaths = million of dollar healthcare cost annually
**Public Health & Economic Impact:**
Tobacco Industry
Tobacco Industry
12
New cards
**short term** - Preserve fishing and tourism
**long term** - Stable climate
**long term** - Stable climate
**Public Health & Economic Impact:** *Trade Off*
Restrictions on timber
Restrictions on timber
13
New cards
**short term** - Require expensive equipment
**long term** - Add up cost to consumer
**long term** - Add up cost to consumer
**Public Health & Economic Impact:** *Trade Off*
Safety of workers
Safety of workers
14
New cards
**short term** - Competitiveness in international market
**long term** - Good environmen
**long term** - Good environmen
**Public Health & Economic Impact:** *Trade Off*
Pollution control in the industry
Pollution control in the industry
15
New cards
**short term** - Lost market share & profits
**long term** - Less use of cars, less pollution
**long term** - Less use of cars, less pollution
**Public Health & Economic Impact:** *Trade Off*
High gas price
High gas price
16
New cards
**short term** - Expensive screening of cows
**long term** - Prevention of spread of disease
**long term** - Prevention of spread of disease
**Public Health & Economic Impact:** *Trade Off*
Mad cow disease
Mad cow disease
17
New cards
**short term** - Less harvest and production, increase price
**long term** - Prevention of chronic diseases (cancer)
**long term** - Prevention of chronic diseases (cancer)
**Public Health & Economic Impact:** *Trade Off*
Use of pesticides
Use of pesticides
18
New cards
**cost** of public health measures
**Public Health & Economic Impact:**
much **easier** to calculate than the benefits.
much **easier** to calculate than the benefits.
19
New cards
difficult
**Public Health & Economic Impact:**
It is often ___ to **quantify what the risk really is and how to balance it against the other risk.**
It is often ___ to **quantify what the risk really is and how to balance it against the other risk.**
20
New cards
Sensitive issues on sexual practices and family planning, abortion
**Moral & Religious Beliefs:**
Sexual and reproductive health, unwanted pregnancy
Sexual and reproductive health, unwanted pregnancy
21
New cards
Use of protective methods for safe sex, (condom use),sex education among minors. Promoting immoral grounds
**Moral & Religious Beliefs:**
AIDS, STDs and Blood borne STIs
AIDS, STDs and Blood borne STIs
22
New cards
Private behavior and does not directly harm others
**Moral & Religious Beliefs:**
Drugs and alcohol abuse, use of safe needles
Drugs and alcohol abuse, use of safe needles
23
New cards
ineffective, and self-defeating
**Moral & Religious Beliefs:**
While __regulation for the common good is valid__, **legislating morality** has often proven to be ___ because **people differ in views as moral.**
While __regulation for the common good is valid__, **legislating morality** has often proven to be ___ because **people differ in views as moral.**
24
New cards
unhealthy behaviors
**Moral & Religious Beliefs:**
Moral and religious concerns may **interfere with scientists** cause many of these problems are due to ___.
Moral and religious concerns may **interfere with scientists** cause many of these problems are due to ___.
25
New cards
Scientific Integrity in Policy Making
**Political Interference with Science:**
* Formed by the **Union of Concerned Scientists**, composed of 60 leading scientists including 20 Nobel prize winners in 2004 during the George Bush Administration.
* Documented many instances of the **misrepresentation or suppression of scientific information of stacking of scientific advisories** to __obscure__ the fact that **policy decisions were based on its political agenda**, which __favored right-wing constituents and large corporations.__
* Formed by the **Union of Concerned Scientists**, composed of 60 leading scientists including 20 Nobel prize winners in 2004 during the George Bush Administration.
* Documented many instances of the **misrepresentation or suppression of scientific information of stacking of scientific advisories** to __obscure__ the fact that **policy decisions were based on its political agenda**, which __favored right-wing constituents and large corporations.__
26
New cards
preventing teenage pregnancy versus condom use
**Political Interference with Science:** *Issues involve policy making in public health and political agenda*
* Sexual Abstinence-only program
* Sexual Abstinence-only program
27
New cards
sex education program versus abstinence
**Political Interference with Science:** *Issues involve policy making in public health and political agenda*
* Condom use on HIV/AIDS prevention program
* Condom use on HIV/AIDS prevention program
28
New cards
Abortion
**Political Interference with Science:** *Issues involve policy making in public health and political agenda*
* **causes breast cancer was discredited and removed from inaccurate information** despite reported by the National Cancer Institute in US
* **causes breast cancer was discredited and removed from inaccurate information** despite reported by the National Cancer Institute in US
29
New cards
Conflict of interest
**Political Interference with Science:** *Issues involve policy making in public health and political agenda*
* those who hold position in the committee and who have ties to the industry
* those who hold position in the committee and who have ties to the industry
30
New cards
suppressed information and discredited scientific evidence
**Political Interference with Science:** *Issues involve policy making in public health and political agenda*
* Global warming versus Global Climate Change
* Global warming versus Global Climate Change
31
New cards
ideologues and industry representatives
**Political Interference with Science:** *Issues involve policy making in public health and political agenda*
* scientific advisory committee
* scientific advisory committee
32
New cards
Health Economics
**discipline of economics** applied to the topic of health care.
33
New cards
**Broadly defined**, economics
**Health Economics:**
concerns how society allocates its resources among alternative uses
concerns how society allocates its resources among alternative uses
34
New cards
**Scarcity** of these resources
**Health Economics:**
provides the **foundation** of economic theory
provides the **foundation** of economic theory
35
New cards
* **What** goods and services shall we produce?
* **How** shall we produce them?
* **Who** shall receive them?
* **How** shall we produce them?
* **Who** shall receive them?
**foundation** of economic theory questions
36
New cards
Economic evaluation
**What Do Health Economists Do?**
relating the costs and benefits of alternative ways of delivering health care
relating the costs and benefits of alternative ways of delivering health care
37
New cards
Roots of health economics
Emerged as a **sub discipline of economics** in the1960s
38
New cards
“Uncertainty and Welfare Economics of Medical Care”
**Roots of health economics:**
Kenneth Arrow (1963)
Kenneth Arrow (1963)
39
New cards
“The Economics of Moral Hazard: Comment”
**Roots of health economics:**
Mark Pauly (1968)
Mark Pauly (1968)
40
New cards
(scarce) resources are **allocated to and within** the health economy
**Health Economics:**
Health economics is the study of how ___
Health economics is the study of how ___
41
New cards
magnitude and importance
**Health Economics:**
Demonstrates the ___ of the health sector
Demonstrates the ___ of the health sector
42
New cards
different
**Health Economics:**
What makes it ___ from other markets and how our analysis may need to adjust
What makes it ___ from other markets and how our analysis may need to adjust
43
New cards
improve health status
**Health Economics:**
Models the determinants of health status and looks and how government policy might ___ in short and long run
Models the determinants of health status and looks and how government policy might ___ in short and long run
44
New cards
1. The size of the health economy is **large and
growing**
2. **Role of government** in the health care
markets
3. Health care market is **different from other markets**
4. **Externalities**
**Health Economics Importance**
45
New cards
**Public** Healthcare Facilities
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
* National Health Services (Primary)
* Regional District & Rural Health Services (Secondary)
* RHU & Barangay Health Centers (Primary care)
* National Health Services (Primary)
* Regional District & Rural Health Services (Secondary)
* RHU & Barangay Health Centers (Primary care)
46
New cards
**Private** Healthcare Facilities
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
* Specialty Private Hospital
* General Private Hospital
* Private Clinic
* Specialty Private Hospital
* General Private Hospital
* Private Clinic
47
New cards
Government
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
* bears the **major responsibility** for public health
* when **alone, cannot achieve the objectives** of public health
* bears the **major responsibility** for public health
* when **alone, cannot achieve the objectives** of public health
48
New cards
organized community efforts
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *Government*
* to prevent disease and prolong life **must involve all sector of the community**, including healthcare services, local business, community organizations, the media, and general public
* to prevent disease and prolong life **must involve all sector of the community**, including healthcare services, local business, community organizations, the media, and general public
49
New cards
**Non-government** organizations
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
* play important roles, especially in education, lobbying and research focuses on specific diseases
* American Heart Association
* American Cancer Society, Philippine
Cancer Society
* American Diabetes Association
* Philippine Coalition Against TB (PhilCAT)
* AIDS Society of the Philippines
* Association of Diabetes Nurse Educators
in the Philippines
* ASEAN Society for Pediatric Infectious
Diseases.
* Philippine Public Health Association
* play important roles, especially in education, lobbying and research focuses on specific diseases
* American Heart Association
* American Cancer Society, Philippine
Cancer Society
* American Diabetes Association
* Philippine Coalition Against TB (PhilCAT)
* AIDS Society of the Philippines
* Association of Diabetes Nurse Educators
in the Philippines
* ASEAN Society for Pediatric Infectious
Diseases.
* Philippine Public Health Association
50
New cards
Rockerfeller Foundation
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *Other Philanthropic Foundation*
focuses on **world population** issues
focuses on **world population** issues
51
New cards
Robert Wood Johnson Foundation
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *Other Philanthropic Foundation*
providing health care to the **poor as well as on AIDS, alcoholism, drug abuse.**
providing health care to the **poor as well as on AIDS, alcoholism, drug abuse.**
52
New cards
Kaiser Family Foundation
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *Other Philanthropic Foundation*
health and public policy especially on **minorities, children and elderly people**
health and public policy especially on **minorities, children and elderly people**
53
New cards
Melida Gates Foundation
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *Other Philanthropic Foundation*
the mission is to **improve global health.**
the mission is to **improve global health.**
54
New cards
ability to obtain the participation of other agencies
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *Other Philanthropic Foundation:* __*Rationale*__
Public health is **dependent** on its ___ __to solve health problems__
Public health is **dependent** on its ___ __to solve health problems__
55
New cards
adept
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *Other Philanthropic Foundation:* __*Rationale*__
Public health leaders must be ___ at n**egotiation and coalition building and develop a framework** for public health planning and action that involves all sectors of the community at the local state and national levels
Public health leaders must be ___ at n**egotiation and coalition building and develop a framework** for public health planning and action that involves all sectors of the community at the local state and national levels
56
New cards
National Government level
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
The DOH acts as the national lead agency in health.
The DOH acts as the national lead agency in health.
57
New cards
18 bureaus and services
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *The DOH*
The DOH central office consists of ___ responsible for __policy development, programme planning, standards setting and regulation, and related management support services.__
The DOH central office consists of ___ responsible for __policy development, programme planning, standards setting and regulation, and related management support services.__
58
New cards
17 regional health offices
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *The DOH*
To __provide technical assistance to LGUs and monitor field operations__, the DOH has ___, one for each of the 28 17 administrative regions of the country
To __provide technical assistance to LGUs and monitor field operations__, the DOH has ___, one for each of the 28 17 administrative regions of the country
59
New cards
Health Facilities and Services Regulatory Bureau
**The role of public and private sector in public health:** *The DOH*
MedTechs’ bureau
MedTechs’ bureau
60
New cards
**Executive Order No. 366 signed 29** by President Gloria Arroyo on 4 October 2004
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
reflects the **major organizational changes** brought about by the __strategic review and rationalization of Government agencies and functions__
reflects the **major organizational changes** brought about by the __strategic review and rationalization of Government agencies and functions__
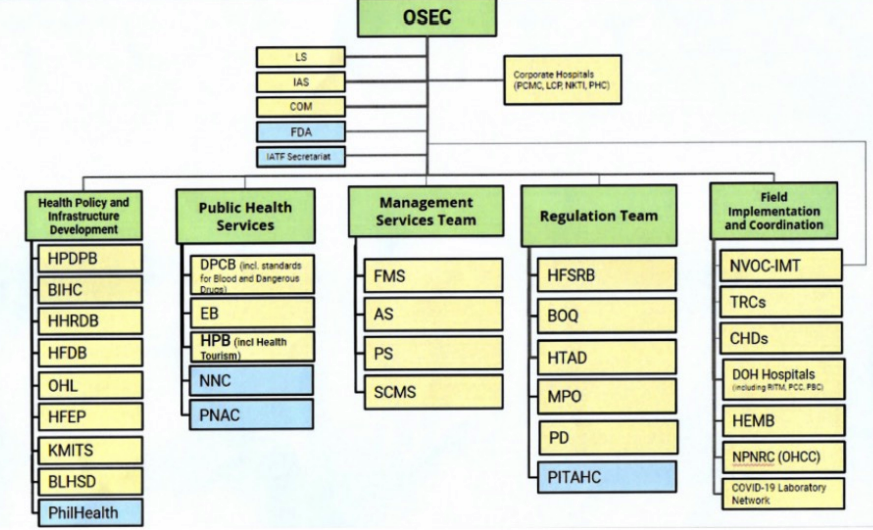
61
New cards
the **nomenclature** of bureaus, services and regional offices
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
Effected by the DOH in 2013 with the final approval of its rationalization plan, this organizational change standardized ___
Effected by the DOH in 2013 with the final approval of its rationalization plan, this organizational change standardized ___
62
New cards
The **enactment of the Local Government Code of 1991** (Republic Act No. **7160**)
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
mandated the **devolution of health** **services** from the National Government to the LGUs.
mandated the **devolution of health** **services** from the National Government to the LGUs.
63
New cards
a fragmented system
**The role of public and private sector in public health:**
What used to be a **highly centralized health system** run by the DOH became ___ consisting of **more than a thousand** autonomous local health systems
What used to be a **highly centralized health system** run by the DOH became ___ consisting of **more than a thousand** autonomous local health systems
64
New cards
Dual health system
**PH Health System:**
Organization and Governance
Organization and Governance
65
New cards
No Balance Billing (NBB)
**PH Health System:**
this means that __if you do not have the capability to pay__, **the state will pay** for you
this means that __if you do not have the capability to pay__, **the state will pay** for you
66
New cards
Universal Healthcare Bill (UHC)
**PH Health System:**
**shows equity in health**. If there will be a payment, they are provided at a cost which means that it will generate no income
**shows equity in health**. If there will be a payment, they are provided at a cost which means that it will generate no income
67
New cards
**Public** Sector
**PH Health System:**
Health services are **provided by health facilities** run by the National and local governments and are largely **financed through a tax-based budgeting system**
Health services are **provided by health facilities** run by the National and local governments and are largely **financed through a tax-based budgeting system**
68
New cards
**Private** sector
**PH Health System:**
Largely **market-oriented**, where HS are generally **paid for through user fees** at the point of service
Largely **market-oriented**, where HS are generally **paid for through user fees** at the point of service
69
New cards
**Public** Sector
**PH Health System:**
typically **funded through the government** and managed by national healthcare organizations
* organizations receive their funding exclusively **from government agencies**
* **Taxpayers** will put money toward salaries, equipment, facility operations, medical procedures, and prescriptions
* **limited number of services** due to funding restrictions
typically **funded through the government** and managed by national healthcare organizations
* organizations receive their funding exclusively **from government agencies**
* **Taxpayers** will put money toward salaries, equipment, facility operations, medical procedures, and prescriptions
* **limited number of services** due to funding restrictions
70
New cards
**Private** sector
**PH Health System:**
created for **profit** and can be **funded through self-employed practitioners** and nongovernment organizations
* An **owner or board members** will be responsible for **setting a budget** __to manage the organization__
* The business owner will draw up **contracts** with employees **to set salaries**
* the private sector may have the potential to **offer more services** to patients
* The private sector health care facility could also make **higher investments in new equipment** pieces and workspaces.
created for **profit** and can be **funded through self-employed practitioners** and nongovernment organizations
* An **owner or board members** will be responsible for **setting a budget** __to manage the organization__
* The business owner will draw up **contracts** with employees **to set salaries**
* the private sector may have the potential to **offer more services** to patients
* The private sector health care facility could also make **higher investments in new equipment** pieces and workspaces.
71
New cards
**Public** Sector
**PH Health System:**
* Typically offer **higher base pay** guaranteed by the state
* **Plantilla** positions are **limited**
* Hiring based on **exigency** depending on **available public funds**
* Salaries determined by **established salary grades**
* Typically offer **higher base pay** guaranteed by the state
* **Plantilla** positions are **limited**
* Hiring based on **exigency** depending on **available public funds**
* Salaries determined by **established salary grades**
72
New cards
**Private** sector
**PH Health System:**
* Typically offer __**less competitive**__ **base pay**
* Job positions **based on services offered and available funds**
* May offer **more** **lucrative salaries** for __higher managerial positions__
* Typically offer __**less competitive**__ **base pay**
* Job positions **based on services offered and available funds**
* May offer **more** **lucrative salaries** for __higher managerial positions__
73
New cards
**Public** Sector
**PH Health System:**
* Typically **longer** waiting time
* **Lower** personnel to patient ratio
* Targets **population segments** with limited capacity for out-of-pocket payments
* **Affordable** rates
* Typically **longer** waiting time
* **Lower** personnel to patient ratio
* Targets **population segments** with limited capacity for out-of-pocket payments
* **Affordable** rates
74
New cards
**Private** sector
**PH Health System:**
* Has **shorter** waiting time
* **Higher** personnel to patient ratio
* Targets **affluent patients** with **higher** capacity **to pay**
* More **expensive** rates
* Has **shorter** waiting time
* **Higher** personnel to patient ratio
* Targets **affluent patients** with **higher** capacity **to pay**
* More **expensive** rates
75
New cards
private providers
**PH Health System:**
relies heavily on ___
relies heavily on ___
76
New cards
**30%** of the Philippine population
**PH Health System:**
uses the private healthcare system as their **main source of care**
uses the private healthcare system as their **main source of care**
77
New cards
60%
**PH Health System:**
are also **privately owned**
are also **privately owned**
78
New cards
Medical tourism
**PH Health System:**
important part of the **economy**, which explains why there are so many private hospitals and specialty clinics
important part of the **economy**, which explains why there are so many private hospitals and specialty clinics
79
New cards
**Public** Health
* focus on the health of the **population of a specific country or community**
80
New cards
**International** Health
* focuses on the **health issues**, especially __infectious diseases, and maternal and child health__ in **low-income countries**
81
New cards
**Global** Health
* an area for study, research, and practice that places a **priority on improving health and achieving health equity** for all people **worldwide**
* health issues that **transcend national boundaries** and governments and call for actions on the global forces that determine the health of people
* collaborative trans-national research and action for promoting **health for all**
* health issues that **transcend national boundaries** and governments and call for actions on the global forces that determine the health of people
* collaborative trans-national research and action for promoting **health for all**
82
New cards
* Immunization
* Malaria and Parasitic Diseases
* Malaria and Parasitic Diseases
**CDC Global Health Issues:**
* Global Health **Security**
* Global Health **Security**
83
New cards
* Traveler’s Health
* Other Disease and Threats
* Other Disease and Threats
**CDC Global Health Issues:**
* Global Health **Protection**
* Global Health **Protection**
84
New cards
* HIV and Tuberculosis
* Food & Water
* Food & Water
**CDC Global Health Issues:**
* Global Health **Equity**
* Global Health **Equity**
85
New cards
* **environmental** health
* **human** health
* **animal** health
* **human** health
* **animal** health
**WHO One Health Approach:**
what makes one health
what makes one health
86
New cards
interdependence
**WHO One Health Approach:** *We Need to:*
Recognize the ___ of human, animal and environmental health
Recognize the ___ of human, animal and environmental health
87
New cards
systems thinking
**WHO One Health Approach:** *We Need to:*
Approach **health issues and opportunities** holistically using ___
Approach **health issues and opportunities** holistically using ___
88
New cards
**interdisciplinary/transdisciplinary** teams
**WHO One Health Approach:** *We Need to:*
Form ___ across human, animal and environmental health practitioners
Form ___ across human, animal and environmental health practitioners
89
New cards
communication and collaboration
**WHO One Health Approach:** *We Need to:*
Promote ___ among representatives of diverse constituencies across human, animal, environmental health and other relevant disciplines
Promote ___ among representatives of diverse constituencies across human, animal, environmental health and other relevant disciplines
90
New cards
human health is **inextricably linked** with animal and environmental health.
concept of one health
91
New cards
* Increasing global population pressures
* Deforestation and environmental destruction
* Intensive agriculture
* Global trade and travel
* Climate change
* Deforestation and environmental destruction
* Intensive agriculture
* Global trade and travel
* Climate change
Why are these infectious diseases emerging in the 20th century?
92
New cards
* food safety
* control of zoonotic diseases
* laboratory services
* neglected tropical diseases
* environmental health
* antimicrobial resistance
* control of zoonotic diseases
* laboratory services
* neglected tropical diseases
* environmental health
* antimicrobial resistance
areas of work in One Health approach
93
New cards
Roemer 1991
**Health Delivery Systems: WHO Framework:** *Health System*
**combination** of resources, organization, financing and management that **culminate in the delivery of health services** to the population.
**combination** of resources, organization, financing and management that **culminate in the delivery of health services** to the population.
94
New cards
World Health Organization (2000)
**Health Delivery Systems: WHO Framework:** *Health System*
* all the activities whose **primary purpose** is to **promote, restore, and maintain** health.
* includes efforts to **influence determinants of health** as well as more direct health improving activities
* all the activities whose **primary purpose** is to **promote, restore, and maintain** health.
* includes efforts to **influence determinants of health** as well as more direct health improving activities
95
New cards
* To **improve health** of the population
* To **improve responsiveness of health system** to people’s health expectations
* Providing **financial risk protection**
* To **improve responsiveness of health system** to people’s health expectations
* Providing **financial risk protection**
**Main Goals** of Health Systems
96
New cards
Health Service **Provision**
**4 main health system functions:**
* Direct **provision of services** to patients
* **Public and private** health services
* the approaches can either be **preventive, curative or diagnostic**
* Direct **provision of services** to patients
* **Public and private** health services
* the approaches can either be **preventive, curative or diagnostic**
97
New cards
Health Service **Inputs**
**4 main health system functions:**
* health **products and supply** chain
* manufacturing, sales, and distribution of key assets, including facilities, drugs, and devices
* **resource generation**: investing in people, facilities, and equipment
* health **products and supply** chain
* manufacturing, sales, and distribution of key assets, including facilities, drugs, and devices
* **resource generation**: investing in people, facilities, and equipment
98
New cards
Stewardship
**4 main health system functions:**
* **process of setting the strategic goals** of a health system
* sets the **context and policy framework** for the overall health system
* **overall stewards** of the resources, powers and expectations
* HS function in **generating appropriate data for policy making**
* dependent on **financing**
* **process of setting the strategic goals** of a health system
* sets the **context and policy framework** for the overall health system
* **overall stewards** of the resources, powers and expectations
* HS function in **generating appropriate data for policy making**
* dependent on **financing**
99
New cards
priorities
**4 main health system functions:** *Stewardship*
* What are the health ___ to which public resources should be targeted?
* What are the health ___ to which public resources should be targeted?
100
New cards
* institutional framework
**4 main health system functions:** *Stewardship*
* What is the ___ in which the system and its many actors should function?
* What is the ___ in which the system and its many actors should function?