Human Factors
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Similar packaging
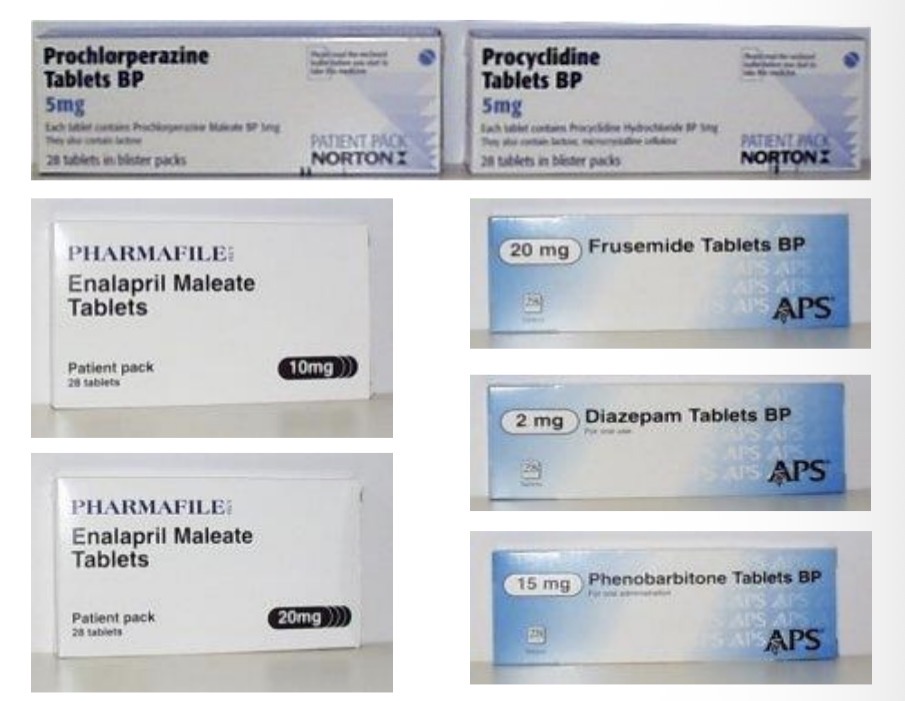
Human factors definition
The study of all the factors that make it easier to do the work right away, sometimes known as ergonomics
Applies wherever humans work
What do human factors acknowledge?
The universal nature of human fallibility
The inevitability of error
Assumes errors will occur
Designs things in the workplace to try to minimise the likelihood of error or its consequences
It should be made impossible (or near impossible) to make mistakes
HCP working with complexity
HCP are quite good at compensating for some of the complex and unclear design of some aspects of the workplace
Equipment
Physical layouts
High resilience
2 views on human error - old view
Old view: person approach
Human error is a cause of accidents
To explain failure, you must seek human failure
Find people’s incorrect assessments, wrong decisions & bad judgements
Get rid of ‘bad apples’ replace with new personnel
2 views on human error - new view
New view: system approach
Error is a symptom of deeper trouble
To explain failure, look for the system failure
Explore how actions and assessments made sense at time
Replacing people leaves problems in place
Systems-based approach - 2 types of failure
“The system approach isn’t about changing the human condition but rather the conditions under which humans work”
Active failure (immediate cause)
Acts or omissions committed by individuals at the sharp end
Latent failures (underlying causes)
Contributory factors that may lie dormant for days, months, years
Often stem from fallible decisions
Resident ‘pathogens’ within a system
Provide the conditions in which unsafe acts occur
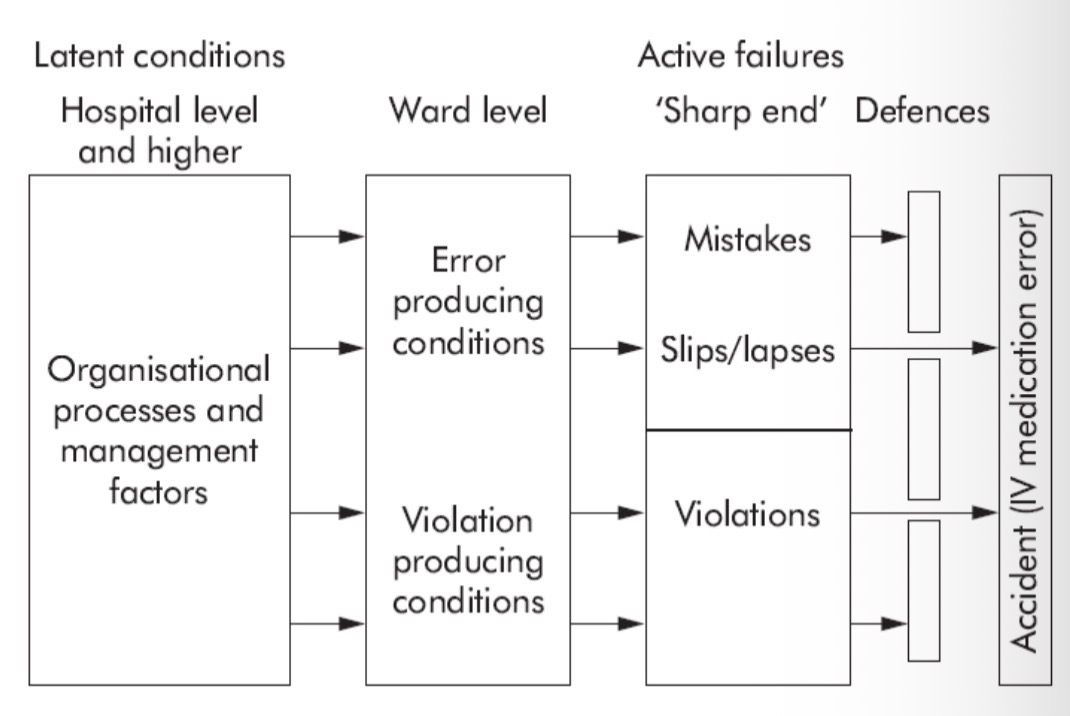
Slips & lapses: errors of action
Active failures (immediate causes)
When one or more step is executed incorrectly (a slip) or because one or more step is omitted (a lapse)
Skill-based
Not amendable to threats or training
Capture slips
Loss of activation slips
Description slips
Mistakes: errors of intention
A planning failure, where actions go as planned but the plan was bad
Stems from cognitive breakdowns
Rule-based or knowledge-based
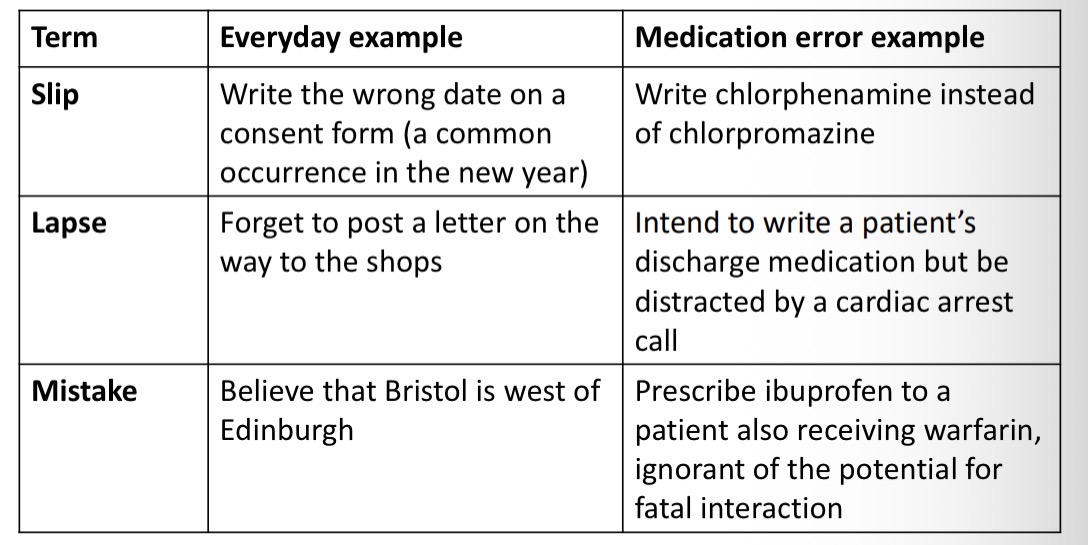
Example of slip, lapse and mistake
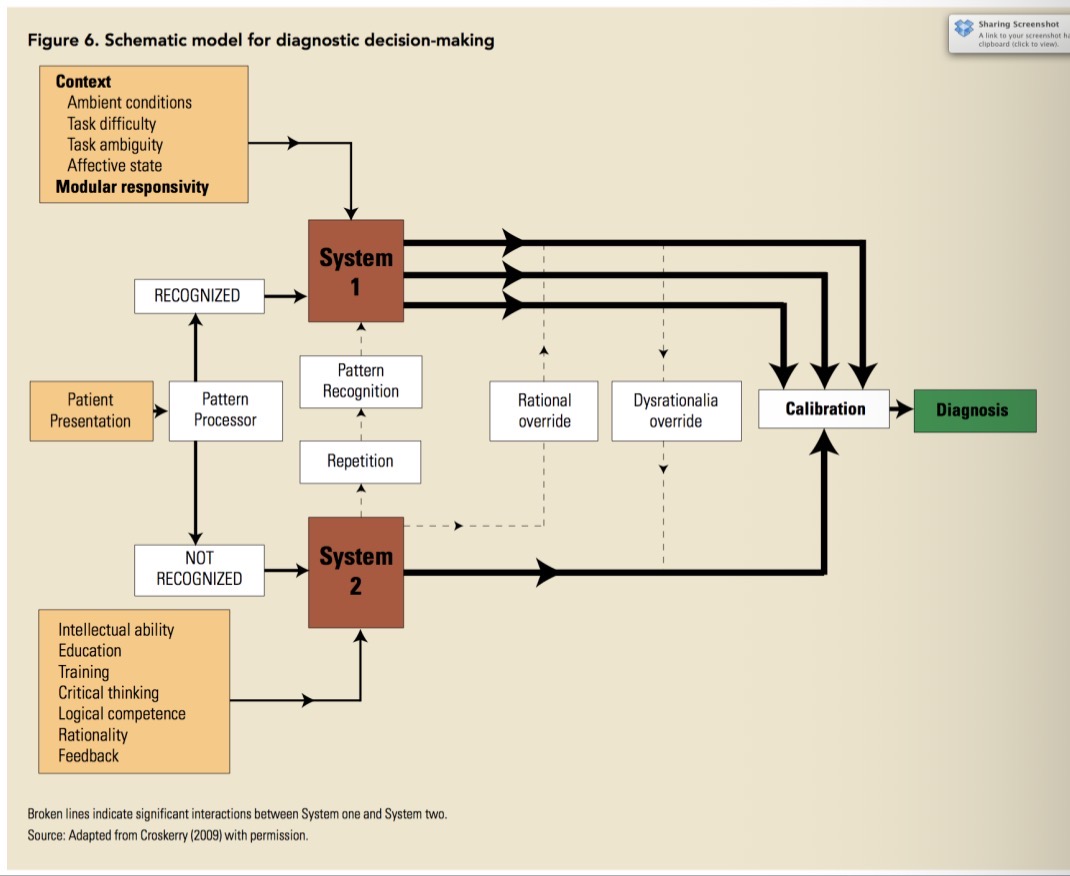
Dual process theory
2 decision making modes:
System 1 - intuitive, automatic, fast, effortless
System 2 - analytical, deliberate, slower, effortful
System 1 - contextual cues important
Cognitive biases
We rely on shortcuts and rules of thumb - known as ‘heuristics’
Mental shortcuts that are likely to generate acceptable solutions
Specific biases in decision making include:
Insensitivity biases in decision making include:
Overconfidence
Failure to consider alternative options
Availability heuristic
Managing error
Slips are inherent to the human condition
Slips can only be minimised when the processes and systems are made safer
Mistakes often reflect lack of knowledge and experience
Improved training and supervision
Inferior design of a system may predispose to error
Human failure needs to be engineered out of the systems
Automate, standardise, use checklists, decrease number of steps and handoffs, add redundancy (double checks) for high-risk processes
Human errors: facts (inevitable)
All of use make dumb errors everyday
No one makes an error on purpose
Fear of punishment isn’t irrational
No one admits an error if you punish them for it
An error isn’t misconduct
Errors are made for reasons
Summary
Errors are inevitable
Medical errors and frequent and significant threats to safe and quality of healthcare
Be aware of errors that can increase the likelihood of errors
Attention to human factor principles can lead to a reduction in error or its consequences