ECON 3330 Test 1
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
David Bowes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Barter
The alternative to money
Trading goods for goods
Double-Coincidence of Wants
Barter requires _______
Makes it difficult to compare values of things; some goods are not easily divisible. are not durable, and/or are difficult to transfer
Money
Any item agreed upon to be acceptable for trade as an alternative to barter
Commodity Money
Early Money
Made of material that was valuable itself
Representative money
Made of material that is not intrinsically valuable, but can be exchanged for some item of value that exists somewhere
Fiat Money
Today’s money – not made of material that is intrinsically valuable
Value comes from faith, trust, and confidence that it will continue to be accepted
Evolution of Money
commodity → representative → fiat → electronic money, making transactions easier but relying more on faith
Factors of deciding which form of money to use
Ease of transport
Durability
Divisibility
Source of value
Easier transactions = more transactions
When transactions are easter their are more of them
3 Functions money serves
Medium of exchange
Store of value
Unit of account
Money Supply
A measure of the quantity of money available in an economy
M1
currency in circulation + demand deposits + other liquid assets
Most important part of M1 for our class
Currency in circulation + demand deposits
M2
M1 + more savings accounts
M2 adds
Adds assets that are less LIQUID
Financial market importance to economy
Moves money from savers (non-productive uses) to borrowers (productive uses)
Liquidity, information, and risk sharing
Good financial markets provide
Financial Market Diagram
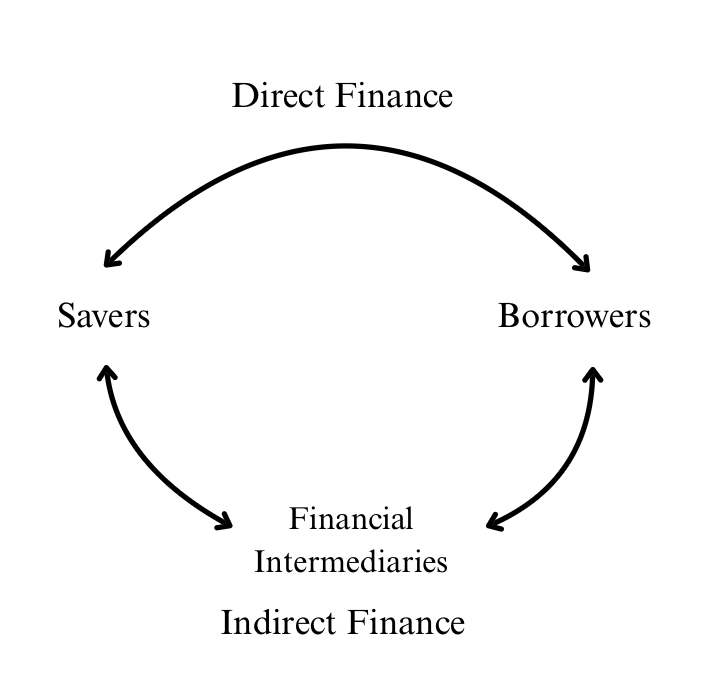
Financial Intermediaries examples
Depository (commercial banks) and Securities firms (investment banks)
Basic function in the Economy
Move money from savers to borrowers
Savers/Lenders
Have extra money and no productive uses
Borrowers/investors
Have productive uses and not enough money
Financial instruments
Bank CDs, Bank Loans, Bonds, Stock
Why is indirect finance more common?
Indirect finance
Savers → Intermediary → Borrowers
Financial Intermediaries exist and add value because they:
SPREAD RISK among savers
Reduce transaction Costs (time & trouble)
Provide Economies of Scale
Provide Liquidity
Information Services: Reduce problems of asymmetric information, moral hazard, and adverse selection between saver and borrower
Interest rate represents payment to:
Savers for risk
Cost to borrowers
Time value of money
Future value of money lent today:
Amount lent x (1+i)n
Money lent today
More valuable in the future at higher rates
Present value of money received in the future:
Amountn/ (1+i)n
Money received in the future
Less valuable today at higher rates
Discount factor
(1+i)n
money received in the future must be discounted by time (n) and risk of non-payment (i)
Discount bond
Buy the bond for less than its face value
Discount bond easy calculation
[(face value - price)/price]/maturity
![<p>[(face value - price)/price]/maturity</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3111b298-dad1-4bd7-91f8-15b929f264bb.png)
Discount bond correct calculation
Price = Face Value/ (1+i)n
More than
You will never pay ___ ___ face value for a discount bond
Coupon bond
Use of present value bond to determine interest rate
Coupon rate
% of face value as periodic payment
Bond price
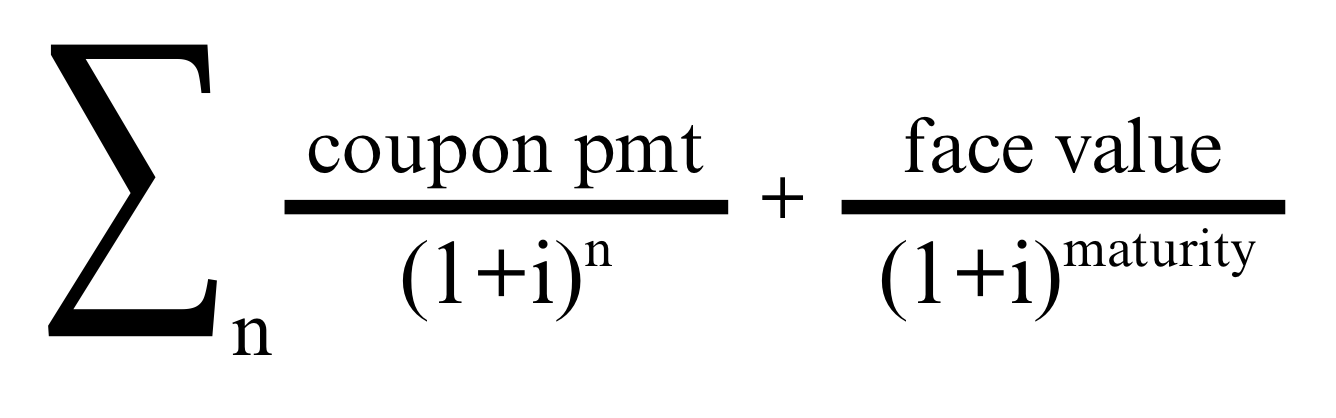
i = coupon rate
If you buy a coupon bond at face value
i < coupon rate
If you pay more than face value
i > coupon rate
If you pay less than face value
Fisher equation
Nominal rate = real rate + expected inflation
Real rate = nominal rate - inflation
Borrowers
Inflation is good for
Savers
Inflation is bad for