SP 133: Module 2: Cortical And Subcortical Structures: SUPPLEMENTARY
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Speech
complex process of human communication through spoken language; How we say words and sounds using the different systems in the body
Speech Production
is fueled by the systematic coordination of five systems: respiratory, phonatory, resonance, articulatory, and nervous systems.
Cortex
Surface of the brain is made up of neuron cell bodies and has abundance of gray matter (integration of info = control of movement, memory, and emotions), has 4 lobes
Broca's Area, Premotor Cortex, Supramarginal Gyrus, Wernicke's Area, Inferior Temporal Area
Anatomy of the Cortex
BA 44, 45
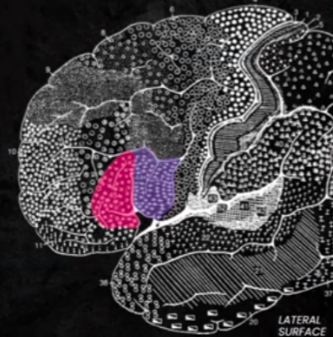
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: Broca's Area's BA
BROCA’S AREA
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: FRONTAL: posterior: (lid portion = purple), anterior: (triangular portion = pink); comprehension and production of language: (45): interpretation of language; syntax, planning and programming of verbal responses; (44): works with speech organs during the speech production process
BA 6
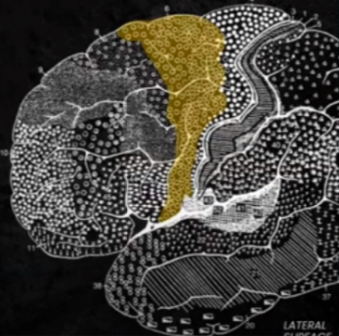
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: Premotor Cortex BA
PREMOTOR CORTEX
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: FRONTAL: Involved with BA 44: similar function in speech production: contribute to motor planninG
SUPRAMARGINAL GYRUS
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: PARIETAL: Helps in the organization of auditory image of the word in the brain, Creates a representation/tells us how the word “sounds”
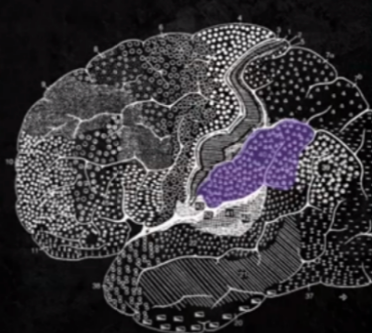
BA 40
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: Supramarginal Gyrus
ANGULAR GYRUS
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: PARIETAL: Horse-shoe-like shape; Deals with auditory, visual, and sensory language-related abilities; Has a role in connecting recognized words with existing mental pictures, ideas, or sensations
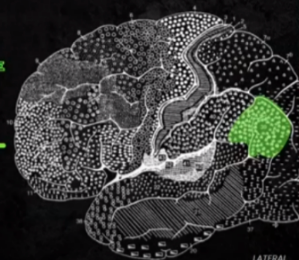
BA 39
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: ANGULAR GYRUS
WERNICKE’S AREA
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: TEMPORAL: storing auditory information as well as integration of meaning; Helps us comprehend and decode speech
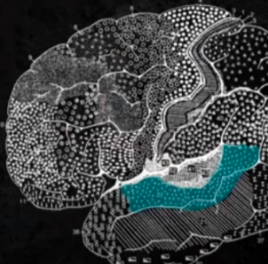
BA 22
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: WERNICKE’S AREA
INFERIOR TEMPORAL AREA
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: TEMPORAL: similar function with the Werknicke’s Area given their proximity; Has a role in deciphering speech apart from its role in visual perception.
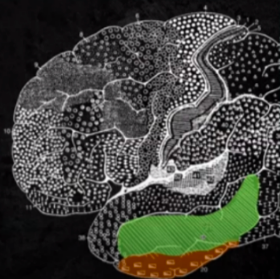
BA 20, 21
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: INFERIOR TEMPORAL AREA
CINGULATE CORTEX
CORTICAL STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN: MEDIAL SURFACE: cognitive control, Emphasized in both speech production and comprehension, Retrieves and encodes memories/prior knowledge and bridges it with perceived speech, Engages in semantic processing.
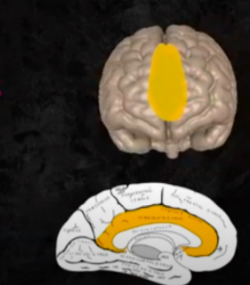
Subcortex
Structures located beneath the cortex; Mainly involved in sensory processing and motor function, among others; Also called the “information hubs” of the brain as these structures are responsible for relaying information to its different areas.
BASAL GANGLIA
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: indirect role in language processing, Sequence processing affects syntax
Caudate Nucleus
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: BASAL GANGLIA: C-shaped structures, Responsible for speech planning and speech sequencing
Putamen
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: BASAL GANGLIA: grouped W caudate nuclei = striatum, Receives information from different cortical and subcortical areas to send to other basal nuclei, Involved in speech articulation, language function, and cognitive functioning.
Globus Pallidus
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: BASAL GANGLIA: Contains 2 nuclei: internal (GPi) and external (GPe); Send information to the thalamus -> processed in the motor portion of the cerebral cortex, Related to conscious and voluntary movement.
Subthalamic Nucleus
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: BASAL GANGLIA FUNC: Helps in inhibiting in unwanted movement by sending excitatory signals to the GPi
Substantia Nigra
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: BASAL GANGLIA FUNC: Helps the GPi in sending information to the thalamus
Pars compacta
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: BASAL GANGLIA FUNC: Substantia Nigra: 2 parts: produces dopamine for the corpus striatum = Dopamine = important in initiating motor movement; Less dopamine = inhibit movement
Pars reticulata
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: BASAL GANGLIA FUNC: Substantia Nigra: 2 parts: produces GAB
Thalamus
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: gray matter, largest diencephalon component, passageway of all sensory information, important in the integration of language functions
Visual Cortex, Auditory Cortex, Language Function
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES: Thalamus: Lateral geniculate body, Medial geniculate body, Pulvinar nucleus
Hippocampus
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES:Means “seahorse” due to its compact S shape like a seahorse, long-term/declarative memory, restoring and retrieving memories
Cerebellum
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES:AKA the little brain, Associated with movement, For speech: “predicts” the final linguistic result, Identifying possible mistakes in speech before utterance occurs
Brainstem
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES:Composed of the pons, the midbrain, and the medulla oblongata, AKA mesencephalon, Regulates bodily functions like breathing, Plays a part in respiration, medulla oblongata houses the cranial nerves relevant to speech
Corpus Callosum
SUBCORTICAL STRUCTURES:Largest white matter structure in the body; Divided into 4 parts: rostrum, genu, body, and splenium; In charge of relaying information between the two hemispheres of the brain
Limbic System -> Prefrontal Cortex -> Broca's Area -> Supplementary Motor Area -> Primary Motor Cortex
HOW THE STRUCTURES WORK TOGETHER
Broca’s and Wernicke’s Areas
PRIMARY VS. ASSOCIATION CORTICES OF SPEECH: examples of association cortices
corpus callosum or the arcuate fasciculus.
PRIMARY VS. ASSOCIATION CORTICES OF SPEECH: Unlike primary cortices, they are joined by the
Feedforward
FEEDFORWARD AND FEEDBACK SYSTEMS: responsible for muscle movements in syllable and word production.
Feedback
FEEDFORWARD AND FEEDBACK SYSTEMS: in charge of providing commands to improve the words produced in the feedforward system to the point that improvement is no longer needed
connects to BA 22 to BA 6
DUAL STREAMS OF FRONTAL AND TEMPORAL CONNECTIONS: DORSAL PATHWAYS: Pathway 1: Distinguishing syllables, and other sublexical tasks as well as auditory-motor integration also occurs here.
Wernicke’s Area to Broca’s Area (BA 44)
DUAL STREAMS OF FRONTAL AND TEMPORAL CONNECTIONS: DORSAL PATHWAYS: Pathway 2: Where acoustics of speech are stored, Allows a person to compare one’s utterance with those properly pronounced.
Connects superior temporal gyrus (PAC: BA 41, 42) to Broca’s Area (BA 45)
DUAL STREAMS OF FRONTAL AND TEMPORAL CONNECTIONS: VENTRAL PATHWAYS: Pathway 1: Attach meanings to sounds and sound combinations
connects anterior-superior temporal gyrus to the frontal operculum
DUAL STREAMS OF FRONTAL AND TEMPORAL CONNECTIONS: VENTRAL PATHWAYS: Pathway 2: Attach meanings to sounds and sound combinations