Beh Sci 110 USAFA GR 2
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
unconditioned stimulus (US)
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that unconditionally—naturally and automatically—triggers a response.
unconditioned response (UR)
In classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (US), such as salivation when food is in the mouth.
neutral stimulus (NS)
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning
conditioned stimulus (CS)
in classical conditioning, an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned response.
conditioned response (CR)
in classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus (CS)
acquisition
The initial stage in classical conditioning; the phase associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a conditioned response. In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response.
Extinction
the diminishing of a conditioned response; occurs in classical conditioning when an unconditioned stimulus (US) does not follow a conditioned stimulus (CS); occurs in operant conditioning when a response is no longer reinforced.
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished conditioned response
Generalization
the tendency, once a response has been conditioned, for stimuli similar to the conditioned stimulus to elicit similar responses
Discrimination
in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimulus and stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher
positive reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli, such as food. A positive reinforcer is any stimulus that, when presented after a response, strengthens the response.
food for good
negative reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli, such as shock. A negative reinforcer is any stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens the response. (Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment.)
seatbelt ding goes away
positive punishment
the administration of a stimulus to decrease the probability of a behavior's recurring
getting a speeding ticket
negative punishment
the removal of a stimulus to decrease the probability of a behavior's recurring
taking away privileges
classical conditioning vs operant conditioning
-the first is learning reflexes to neutral stimuli and -the second is learning to make voluntary actions based on learned rewards
observational learning
learning by observing others; also called social learning
prosocial modeling
positive, constructive, helpful behavior
you see someone get a positive form 10 for volunteering for a parade
antisocial modeling
-detrimental, destructive, unhelpful behavior
-ex: someone goes on the wrong strip and gets yelled at
continuous reinforcement
reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs
interval reinforcement
A schedule of reinforcement in which the organism is reinforced after a certain time period has elapsed.
sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds
working/short term memory
a kind of workspace in which information from sensory memory and long-term memory is brought together, attended to, and processed
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences.
Encoding
the processing of information into the memory system—for example, by extracting meaning.
storage
the retention of encoded information over time
Retrival
the process of getting information out of memory storage
parallel processing
the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions, including vision. Contrasts with the step-by-step (serial) processing of most computers and of conscious problem solving.
implicit memory
retention independent of conscious recollection
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information, such as word meanings
explicit memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Chucking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically
mnemonics
memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
Hierachies
broad concepts divided and subdivided into narrower concepts and facts
distributed practice
spacing the study of material to be remembered by including breaks between study periods
spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information
deep processing
encoding semantically, based on the meaning of the words; tends to yield the best retention
shallow processing
encoding on a basic level based on the structure or appearance of words
LTP (long term potentiation)
an increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation. Believed to be a neural basis for learning and memory.
aterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories
retrograde amnesia
an inability to retrieve information from one's past
proactive interference
the forward-acting disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information
retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information
missinformation effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event
imagination effect
occurs when repeatedly imagining fake actions and events can create false memories
source amnesia (source misattribution)
attributing to the wrong source an event we have experienced, heard about, read about, or imagined
impact on memory construction
Makes us misremember events
explicit memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
hippocampus/frontal lobes
semantic/epidosic
semantic memory
a network of associated facts and concepts that make up our general knowledge of the world
episodic memory
the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at a particular time and place
impicit memory
retention independent of conscious recollection
space/time/frequency, motor & cognitive skills, classical conditioning
cerebellum & basal ganglia
memory consolidation
the gradual, physical process of converting new long-term memories to stable, enduring memory codes
primacy and recency effect
the tendency to show greater memory for information that comes first or last in a sequence
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating

how cognition increases efficiency and guides thinking
think faster
concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people

prototype
used to form concept a mental image or best example of a category
Algorithm
A methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem.
Heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than algorithms
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common

representativeness heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information
conformation bias
a tendency to search for information that confirms one's preconceptions

Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.

belief perseverance
clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
Framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments.

hindsight bias
"I knew it all along"
Perceived order in random events
When one will believe that there is a pattern where there is none.
System 1 thinking
Automatic, fast, little or no effort, no sense of voluntary control
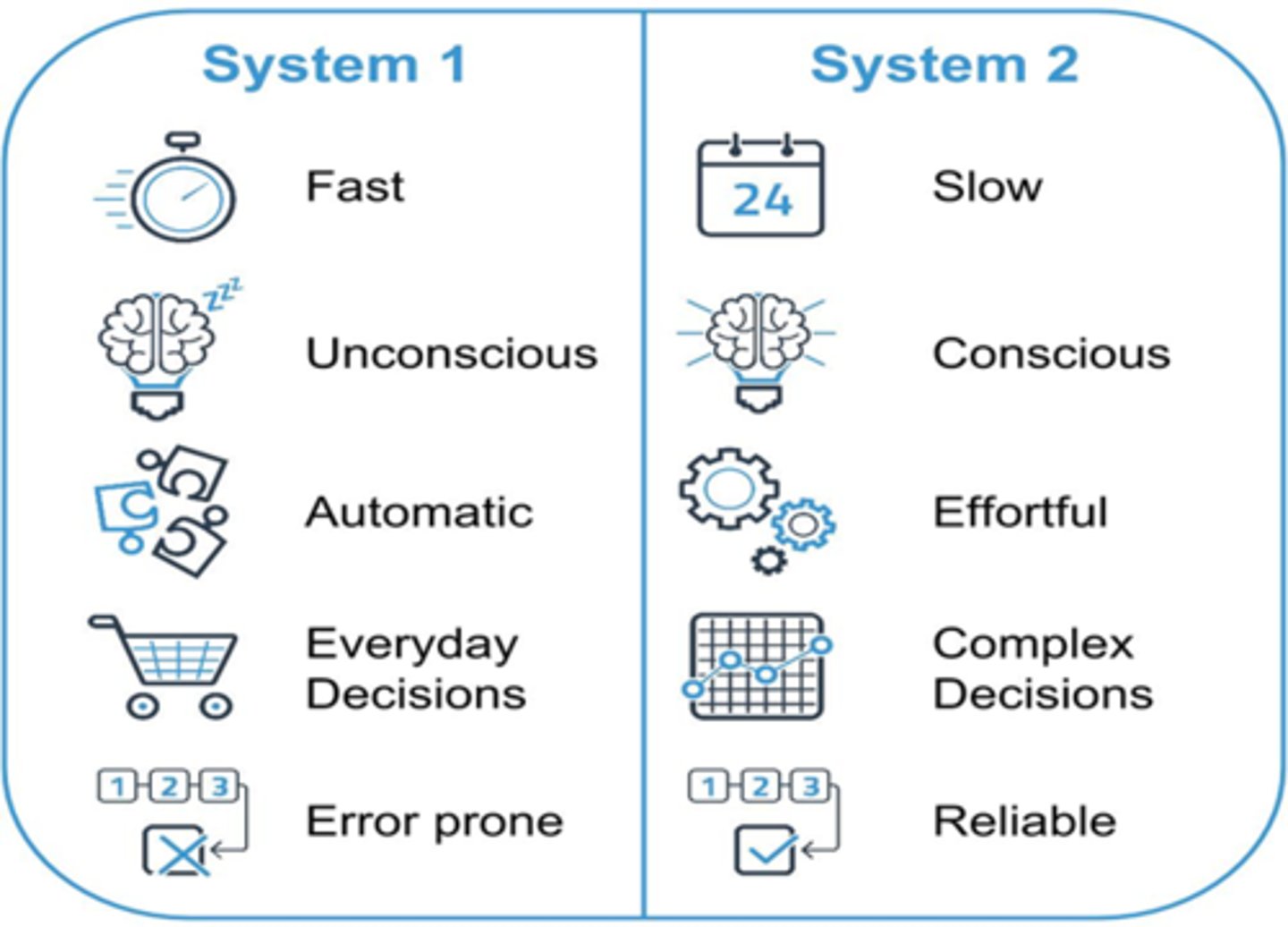
System 2 thinking
Reflective thinking that is slow, deliberate, and conscious. Often less charged with emotions.

social support
the aid gained through interacting with others
emotion-focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one's stress reaction
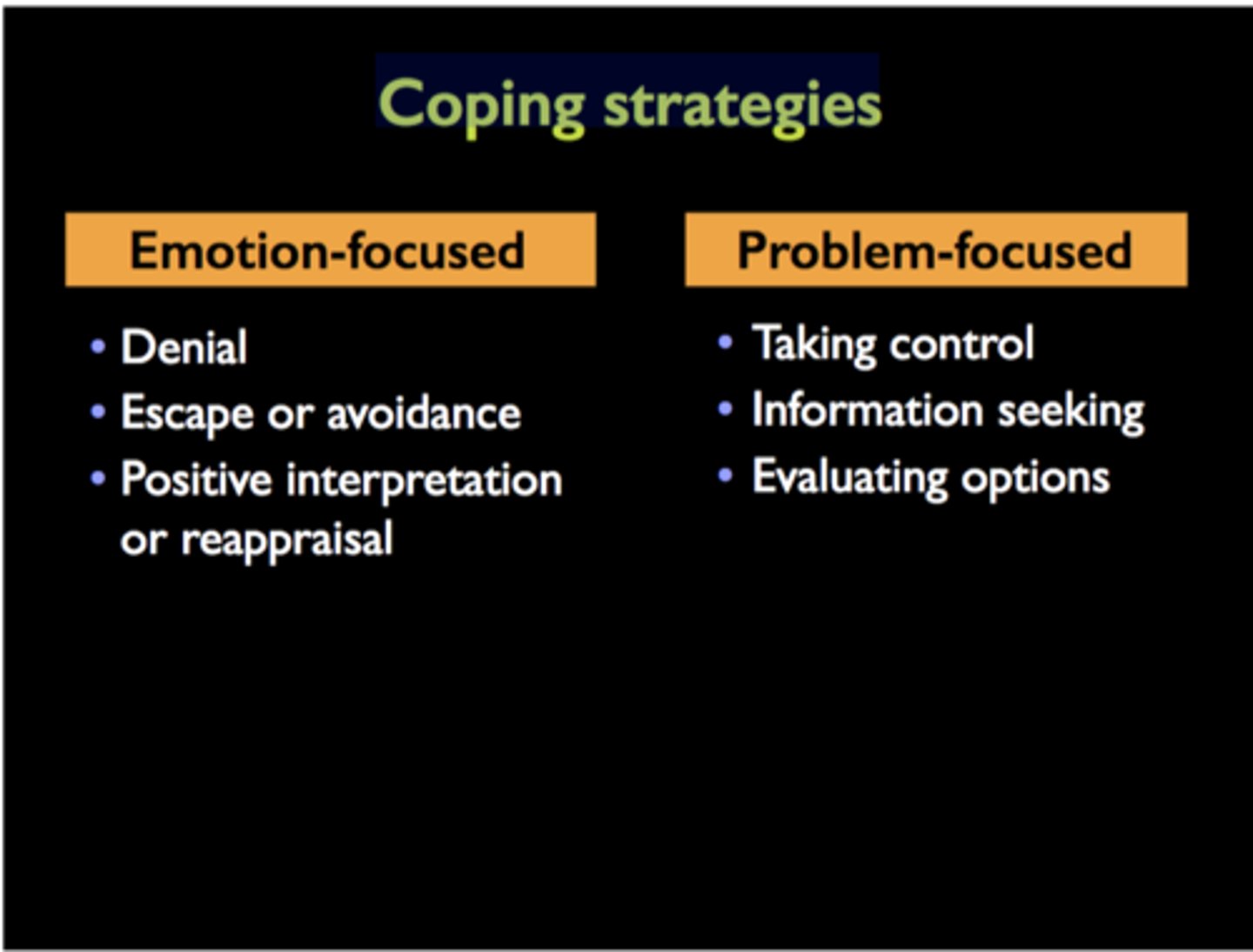
problem-focused coping
Attempting to alleviate stress directly by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor.

avoidant coping
a method of responding to a stressor by ignoring, forgetting, or hiding it
universal emotions
happiness, sadness, contempt, surprise, fear, disgust, anger
Catharsis
the process of releasing, and thereby providing relief from, strong or repressed emotions.
facial feedback hypothesis
The hypothesis that emotional expressions can cause the emotional experiences they signify
behavior feedback effect
the tendency of behavior to influence our own and others' thoughts, feelings, and actions
Biofeedback
a system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension

optimism
Hopefulness and confidence about the future or the successful outcome of something
stress appraisal
the events of our lives flow through a psychological filter. How we appraise an event influences how much stress we experience and how effectively we respond.
spontaneous remission
recovery from a disorder that occurs without formal treatment
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations