behsci gr 1 review
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
survey
way to obtain the self reported attitudes and behaviors of individuals by questioning a representative, random sample/ part of a group
correlation v causation
Correlation DOES NOT EQUAL causation - the only way to determine causation is through the experimental method
hindsight bias
I knew it all along phenomenon; the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it. (i knew it all along. oh yeah i knew they would break up [said after said event occurred])
social cultural psych perspective
how INDIVIDUAL behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures. *differing social settings —> how can x environmental stimuli impact one's thinking, reasoning, accustomed norms, etc. think nature v nurture
cognitive psych perspective
how we encode, process, store, and retrieve information. studies our interpretations v. reality
Behavioral psych perspective
how we learn observable responses. determining what triggers certain responses. analyzing stimulus-response relationships and the effects of conditioning on observable behaviors. Key topics in behavioral psychology include classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and the role of reinforcement in shaping behavior. differs from social cultural as it studies individual learned behaviors in response to environmental stimuli.
psychodynamic perspective
how behavior springs from unconscious drives and conflicts. (clinical, counseling, personality). outbursts=outlet for unconscious hostility. a theory of personality that focuses on the importance of unconscious mental processes and childhood experiences in the development of adult personality. example: wishes and fears that we're not fully aware. takeaway: internal drives create human personality
Evolutionary Psych Perspective
how the natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes. biological, developmental, social
Behavior Genetics Perspective
how genes and environment influence individual differences such as personality, developmentally, legal/ forensic.
neuroscience psych perspective
how the body and brain enable emotions, memories, and sensory experiences. studies brain circuts
psychology sub fields
ex: counseling, clinical psych, psychiatry, community psych
what are the psych perspectives?
neuroscience, evolutionary, behavioral genetics, psychodynamic, behavioral, cognitive, social cultural
biopsychological perspective
interdisciplinary branch of psychology that analyzes how the brain, neurotransmitters, and other aspects of our biology influence our behaviors, thoughts, and feelings. incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis. all of the levels of analysis
levels of analysis/ 3 main parts
bio, psychological, social/cultural. all effect/ compose/ impact behavior
LoA(level of analysis): social
presence of others
cultural, societal, family expectations
peer and other group influences
compelling models
LoA: psychological
learned fears and others learned expectations
emotional responses
cognitive processing and perceptual interpretations
LoA: biological
genetically influenced traits, genetic mutations, natural selection, genes response to environment. aka how do biological levels of analysis impact
mental processing def
informal, subjective experience inferred from behavior. (flash second thinking. ex: split second thinking of pulling out a gun(violent i know) and shooting that bastard)
behavior(def)
any action or pattern an organism displays
psychology def
the science of behavior and mental processes
critical thinking attributes
CEPE:
-source credibility
-evidence(look at it)
-inclusive of multiple perspectives(aka minimized bias)
-exposure to more sources (even those that contradict)
scientific attitude
1. Curiosity
2. Skepticism
3. Humility
CSH
emperical approach
evidence based approach that draws on observations and experimentation
the blind men and the elephant
emphasizes value in utilizing multiple perspectives when overcoming complex tasks. more viewpoints= more understanding
SQ3R
Scan
Question
Read
Retrieve(testing effect)
Review
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information. recalling strengthens retention
evidence based suggestions to be an academic weapon
#locked
-get full/ beneficial sleep
-exercise
-long term goal setting w daily aims
-growth mindset
-prioritize relationships
descriptive design attributes/ observing methods
describes characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. It does not answer questions about how/when/why the characteristics occurred. addresses the "what" question (what are the characteristics of the population or situation being studied?).
ex: case studies, natural observations, surveys
overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.
aka we think we know more than we do.
perceiving order in random events
Humans want to see a whole rather than parts
we tend to connect the parts to create one logical line of thinking.
tendency to see patterns or connections in events that are actually unrelated or coincidental. This is a cognitive error that reflects our desire to impose order and meaning on the chaotic and unpredictable world. Some examples of perceiving order in random events are seeing faces or images in clouds, believing in lucky numbers or superstitions, or attributing a winning streak to a hot hand
inhibitions to critical thinking
overconfidence, hindsight bias, order within random events
elements of scientific method
theory, hypothesis, operational definition, replication
theory
explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
hypothesis
testable prediction, often implied by:
-theory
-observation
-research
operational definition
a carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study. aka methodology/ how experiment is designed/ intended to test variables
replication (scientific method)
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in a different setting to see if basic conclusions drawn are consistent
case study
people are studied in depth in hopes of finding a universal principle
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without manipulating or interfering with the situation
3 parts of brainstem
(thalamus)
top
midbrain
pons
medulla oblongata
bottom
2 main functions of brain stem
1. maintain automatic functions such as breathing, digestion, heart rate
2. sort information coming from spinal cord and out of brain. first responder for bottom up processing and sends top bottom processing out
independent v dependent variable
independent= intentionally changed
dependent= being changed/ observed
(aka independent= what is changed so we can study the impact on the dependent variable. ex: adding plant fertilizer. independent= plant fertilizer and dependent= plant growth)
confounding variables
factors that is not being directly studied that may influence the result of a study
informed consent& debriefing
psychological safeguards put in place by researchers
define:
mean
median
mode
stan dev
mean: average
median: middle
mode: most common
stan dev: measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its mean. spread of data (from middle of graph)
3 cognitive principles associated w enhanced learning
1. distribution of material/ practice
2. test-enhanced learning
3. explanatory questioning
parts of neuron
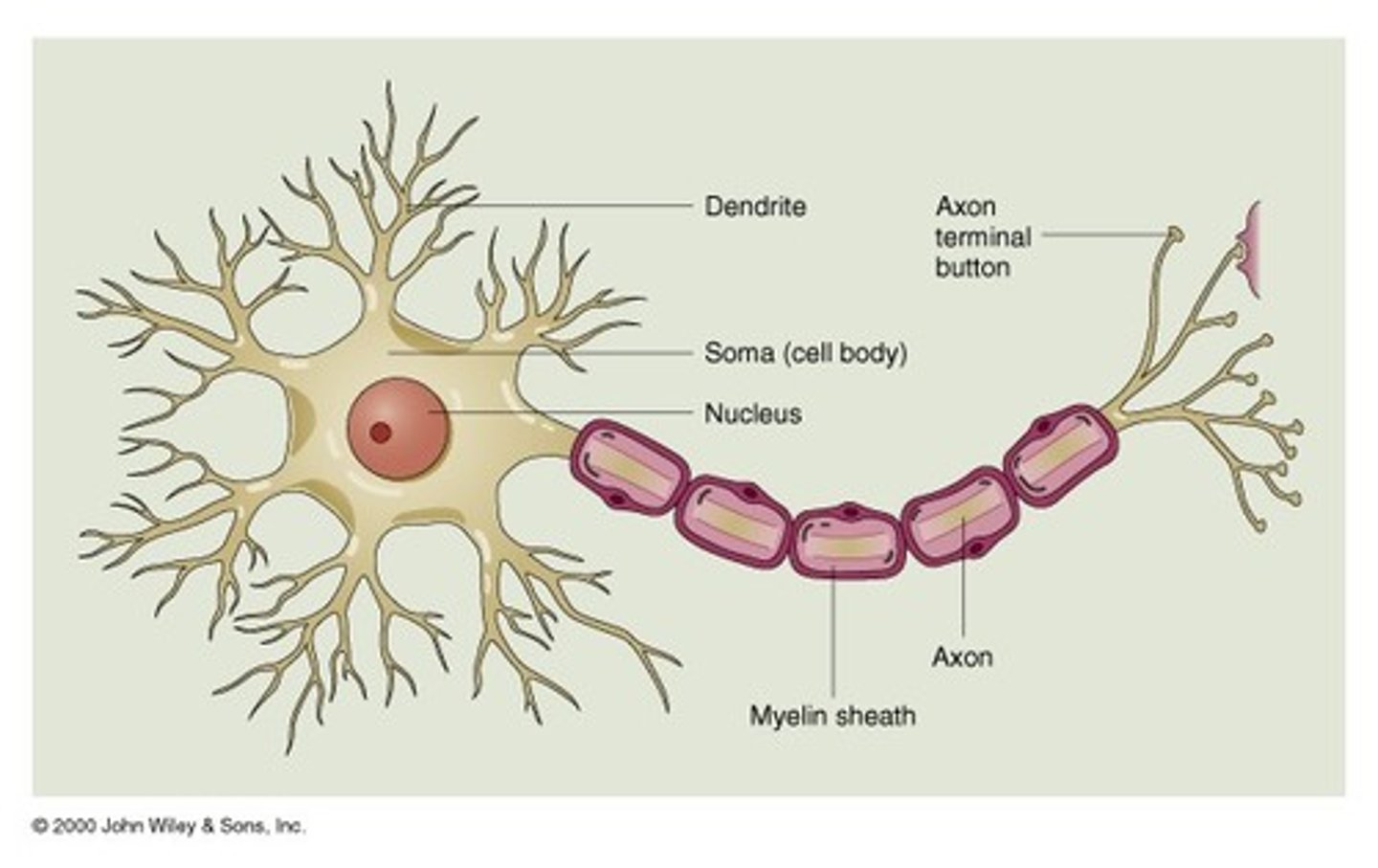
dendrites function
receive messages from other cells
axon function function
passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
terminal axon branches function
form junctions w other cells
myelin sheath function
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulsesnc
neural impulse def/function
electrical signal traveling down the axon (action potential)
cell body of neuron function
DNA here, where neurotransmitters are manufactured. input integrates through here from dendrites. aka life support.
process of neural transmission
1. dendrite receives messages in form of neurotransmitters
2. through temporal and spatial summation, message is passed
3. depolarization of cell body begins
4. if depolarization is sufficient to reach threshold, action potential occurs
5. action potential travels down axon (propagation)
--> Threshold(all or nothing response. must pass certain threshold to trigger neural impulse)
(if threshold passed-->)
6. At synapse, action potential is converted to neurotransmitter which is released into synaptic cleft
7.NT binds to receptors on dendrites of next neuron (process starts over in new neuron)
8.Hyperpolarization occurs in original neuron and refractory period is entered
propagation
The spread of the action potential down an axon, caused by successive changes in electrical charge along the length of the axon's membrane.
action potential
the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
major neural transmitters
Acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, GABA, glutamate, endorphins
Ace the Dog served Nora, gabby, glen, & ender
Acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning, and memory. people w lower levels of acetylcholine have Alzheimer's disease
serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. undersupply=Anxiety, Depressed mood, Aggression, Impulsive behavior, Insomnia
dopamine
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. Oversupply linked to schizophrenia. Undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson's disease.
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal; undersupply can cause Anxiety, Depression, ADHD
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. keeps activity levels of brain in check, preventing overstimulation. CLAMS Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia. GABA is known as the "calming" neurotransmitter. It's involved in sleep, relaxation, anxiety regulation and muscle function
glutamate
opposite of GABA. major neurotransmitter EXCITES. oversupply= seizers, migraines, overstimulation. Glutamate is also needed for making another neurotransmitter in your brain called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Glutamate is your body's most abundant amino acid. Glutamate in your body is made and stored in muscle tissue.
endorphins
Neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure.
nervous system
the network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body. consists of central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
CNS
brain and spinal cord
PNS
Peripheral Nervous System. 2 parts: automatic and somatic nervous system
What is the composition of the PNS?
Sensory and motor neurons that connect CNS w rest of body
What are the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system within the PNS?
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
automatic nervous system
controls self regulating glands and organs.
sympathetic: helps your body activate its "fight-or-flight" response. This system's activity increases when you're stressed, in danger or physically active. Its effects include increasing your heart rate and breathing ability, improving your eyesight and slowing down processes like digestion.
parasympathetic: calms you down
somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Enables voluntary actions to be undertaken due to its control of skeletal muscles
corpus callosum function
large band of neural fibers that connect that right and left brain hemispheres and allow your brain's left and right hemispheres to communicate.
temporal lobe
An area on each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex near the temples that is the primary receiving area for auditory information. (hearing/ language). located above ears, receive info from opposite ear.
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. back of head. receives info from vesical fields
cerebral cortex components
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
temporal lobe
occipital lobe
corpus callosum
parietal lobe
receives sensory input for touch and body position. located at top of head and rear. (above occipital lobe). includes somatosensory cortex.
Somatosensory cortex
an area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. (receiver)
frontal lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving/planning. includes prefrontal cortex, aka motor cortex (controls voluntary movement)
limbic system
amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
-neural center
-Hippos have great memories!
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
label parts of brain
you dont know it do you. think again. think once more. go study and LOCK IN
(brainstem, pons, midbrain, medulla, pituitary, thalamus, cerebellum, limbic system, lobes of brain, corpus callosum, cerebral cortex)
Amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; regulate emotion
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions (bc everything evolved from it). automatic survival functions
reticular formation
a nerve network that travels through the brainstem --> thalamus and plays an important role in controlling arousal
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla (traffic hub)
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance. coordinates movements, output and balance, enables nonverbal learning/memory.
-movements, judges time, emotional , texture, and sound regulation
cerebral cortex parts
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, somatosensory cortex, motor cortex
endocrine system impact on nervous system
impacts interest in sex, food, aggression
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, to reach tissues/ organs to regulate various bodily functions:
growth, metabolism, mood, reproduction.
hormone= homeostasis
feedback system
brain -> pituitary -> other glands -> hormones -> body and brain
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Conciousness
subjective awareness of ourselves and environment
cognitive neuroscience
the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language)
define awareness in context of consciousness
allows to assemble information, focuses attention on complex subjects, and flit(move swiftly/ easily) between different states of consciousness
-spontaneous: dreaming, drowsiness
-physiological: hallucination, starving
-psychological: sensory deprivation, hypnosis
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
limitations of selective awareness
inattentional blindness and change blindness
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness
dual processing
the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks
high road: conscious/ deliberate
low road: unconscious/ automatic
stages of sleep
1. Lightest Sleep (NREM1)
2. Slightly Deeper Sleep (NREM2)
3. Deeper Sleep (NREM3)
4. Delta Waves are omitted but there is not much difference between this stage and stage 3 (NREM4)
5. REM