NS 1150 Prelim 2(Credits to KCK)
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can change forms but is neither created nor destoryed
Glycolysis
Breaking down of glucose into (2) pyruvate
Catabolic
B-Oxidation
Breakdown of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA
Catabolic
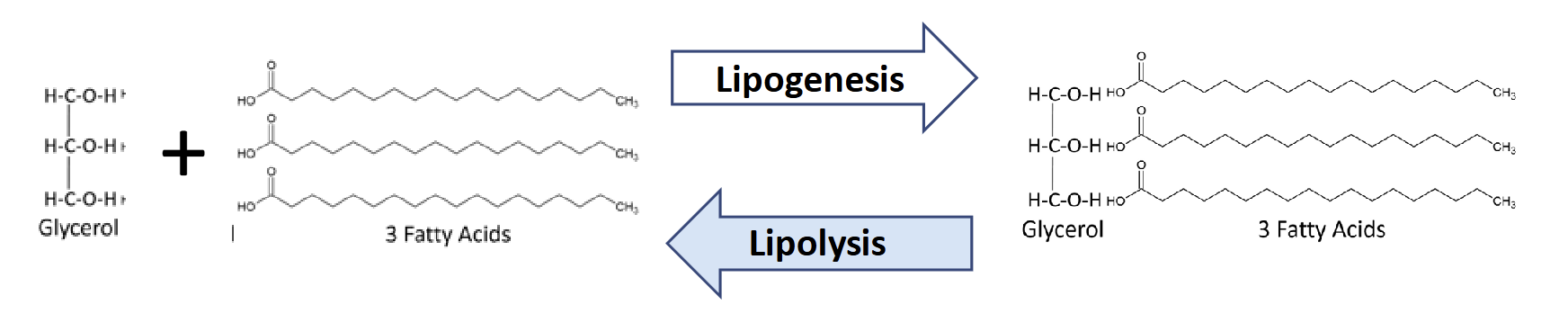
Lipolysis
Breakdown of triglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol
Catabolic
Proteolysis
Breakdown of protein to amino acids
Catabolic
Gluconeogensis
Glucose synthesis from noncarbohydrate sources
Anabolic
Glycogenesis
Formation of glycogen
Anabolic
Lipogenesis
Synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides
Anabolic
How are metabolic pathways used to be able to do work: moving muscles, synthesize, & transport
Catabolic reactions(favorable) are coupled with anabolic reactions(unfavorable standalone)
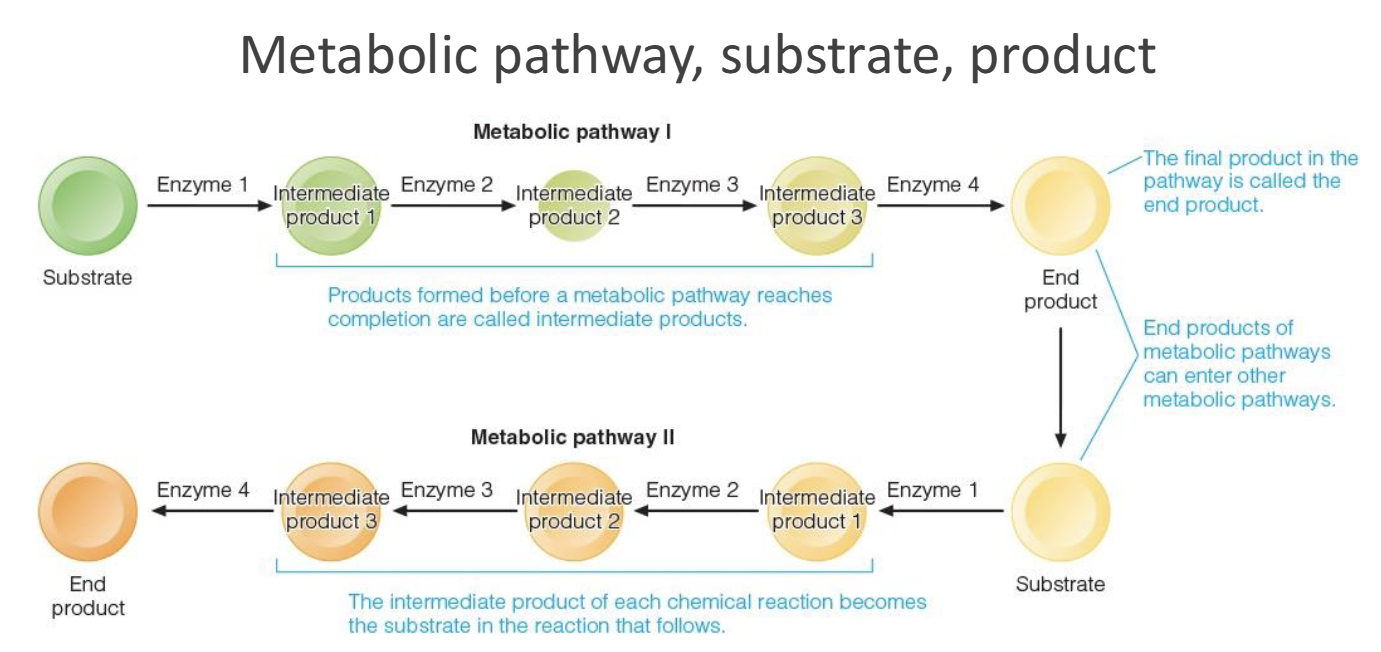
Catabolic Pathway or Catabolism
Breaking down compounds(Thermodynamically Favorable)
Anabolic Pathway
Needs energy, putting together macromolecules(Thermodynamiccaly Unfavorable)
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate or the high energy compound released during breakdown
2 ways that Acetyl CoA proceed
Synthesis of fats for storage (lipogenesis, anabolic pathway)
Oxidative phosphorylation (generates ATP)
Stores of energy(macronutrient - simple form - stored form - primary store site)
CHO - glucose - glycogen - liver > muscle
Lipids/Fat - free fatty acid - triglycerides - adipose tissue>muscle>serum
Proteins - amino acids -(CANNOT BE STORED) - Muscle
Under very extreme metabolic condition (starvation) will muscle be broken down
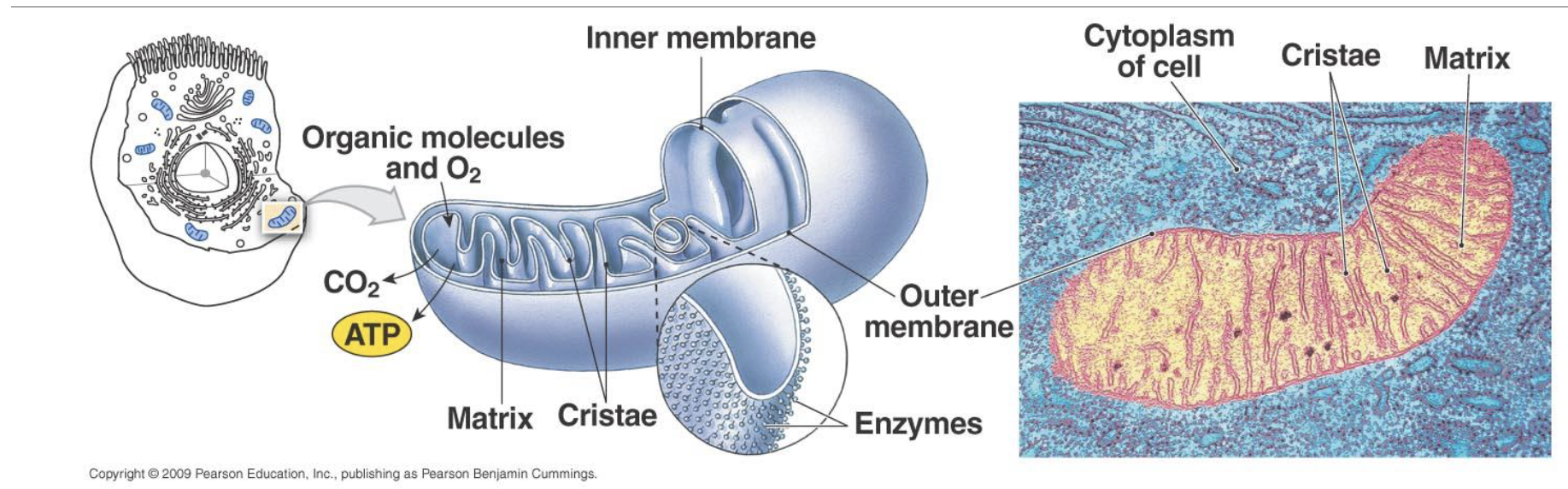
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Primary Source of ATP at rest & steady state exercise lating >3min
Primarily uses Carbs & Fat as substrates
Occurs when O2 supply is sufficient
Takes place in Mitochondria
Mitochondrion Regions
Inner compartment(contains the matrix) - site of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, fatty acid oxidation, and TCA cycle
Inner membrane - site of the electron transport chain reaction
Subsystem of Oxidative Phosphorylation
Aerobic glycolysis (CHO-Glucose-Pyruvate-Acetyl CoA)
Aerobic lipolysis (Fatty Acid - Acetyl CoA)
Oxidation of CHO: Aerobic glycolysis
Glycolysis (glucose to pyrivate) - occurs in cytosol
Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle - mitochondria
Electron Transport chain (ETC) - mitochondria
What macronutrients can make acetyl-CoA
All macronutrients can be used
Glucose - Pyruvate - Acetyl CoA
Fatty Acids - Acetyl CoA
Amino acids - Pyruvate - Acetyl CoA
What are the high energy electron carriers produced in TCA cycle
NADH and FADH2 are coenzymes that supply electrons to the oxidative phosphorylation system
What is the Oxidative System(ETC) comprised of
A series of electron carriers mounted in the mitochondrial intermembrane space(IMS)
Complexes I through IV & protein complex F1F0 ATP Synthase(Complex V)
Function of Oxidative System(ETC)
Coenzymes NADH and FADH2 supply electrons, which are carried through protein complexes (and the redox centers inside them) to pump H+ across the membrane to outer, therby powering ATP synthase (spinner!)
Oxygen accepts the electrons and combines w/hydrogen to form H2O
Net ATP 36-38 per glucose
Oxidation of Fat: Aerobic lipolysis
Fatty acid is activated with CoA group to form Fatty acyl-CoA entering the innermembrane space and reacts with carnitine yielding acyl carnitine that enters the matrix and B-oxidation removes 2 carbon units to generate NADH and FADH2 and acetyl-CoA
*B-Oxidationn process repeats until entire chain is broken down
What is Stored Triglyceride(TG) broken down into
1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids
What are the 3 type of energy expenditure
Basal(resting) metabolic rate - energy needed to perform normal body functions (respiration, circulation, digestion)
Thermogenesis - the energy cost of food processing (ingestion, digestion, absorption, transport, & storage)
Physical Activity - Body movement determining activity induced
Factors influencing Basal Metabolic Rate(BMR)
Genetics - determine how body utilizes
Age - BMR decreases with age
Sex - Male have higher BMR than females of equal size and weight
Growth - BMR higher during periods of growth
Body weight - BMR increases as weight body increase
Body Composition - More muscle higher BMR than more adpipose tissue
Energy Restriction - Fasting
How is heat measured
Calorimetry - The science that studies the change in energy of a system by measuring heat exchange
Calorimeter - An instrument to measure the transfer of heat
What are calories
1 cal is the unit of E required to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 C
1000 cal = 1kcal = 1 dietary calorie(USA)
1kcal = 4148 Joules
Bomb calorimeter
Determine the energy content of nutrients(boom)
Carbohydrates = 4.3kcal = 4kcal
Protein = 5.65 kcal = 4 kcal
Fat = 9.45 kcal = 9 kcal
Alcohol = 7.0 kcal = 7 kcal
Calorimetry rooms
Measures body heat production, not practical or accurate
Indirect Calorimetry
Measures respiratory gas exchange —> O2 consumed and CO2 produced per min
estimates energy expenditure
Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
RER = Co2Made / O2 Used
Measurement of how many CHO or fat we are using for energy
Classification of Carbohydrates (Simple vs Complex)
Simple Sugars = Monosaccharides & Disaccharides
Complex Carbohydrates = Oligosaccharides & Polysaccharides
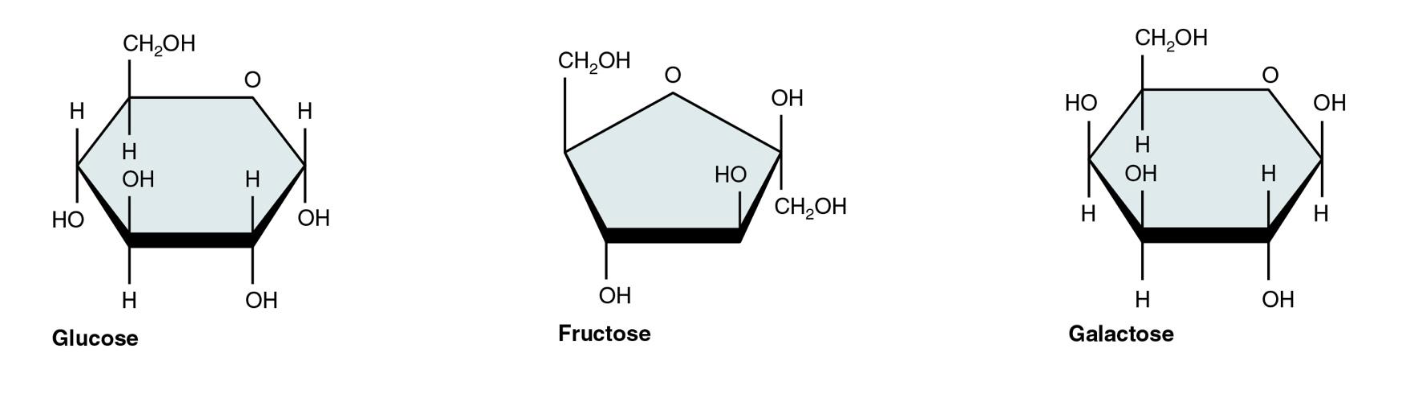
What are monosaccharides
Single unit sugar that differ in arragement of atoms (glucose serve as an essential energy source)
i.e Glucose, Fructose, and Galactose
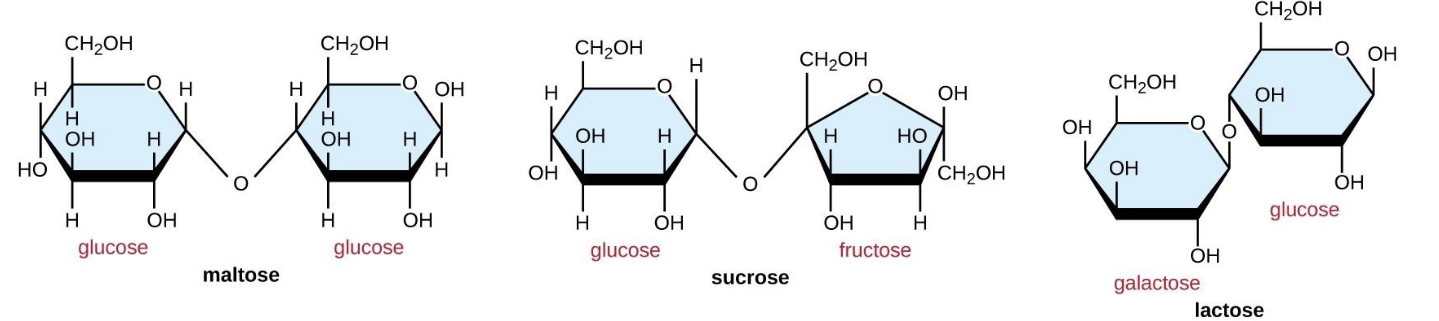
What are Disaccharides
Pairs of monosaccharides
Put together by condensation & apart by Hydrolysis
Glucose + Glucose = Maltose
Glucose + Fructose = Sucrose
Glucose + Galactose = Lactose
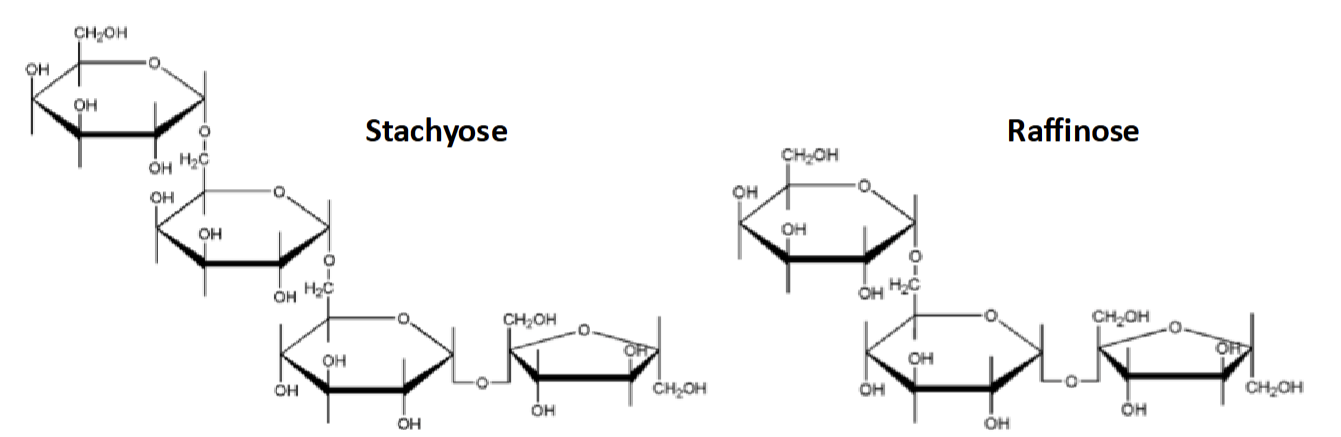
What are oligosaccharides
Made of 3-10 monosaccharides
Human lack the enzyme to digest some dietary oligosaccharides, pass into large intestine where gut bacteria break them down
i.e Stachyose & Raffinose
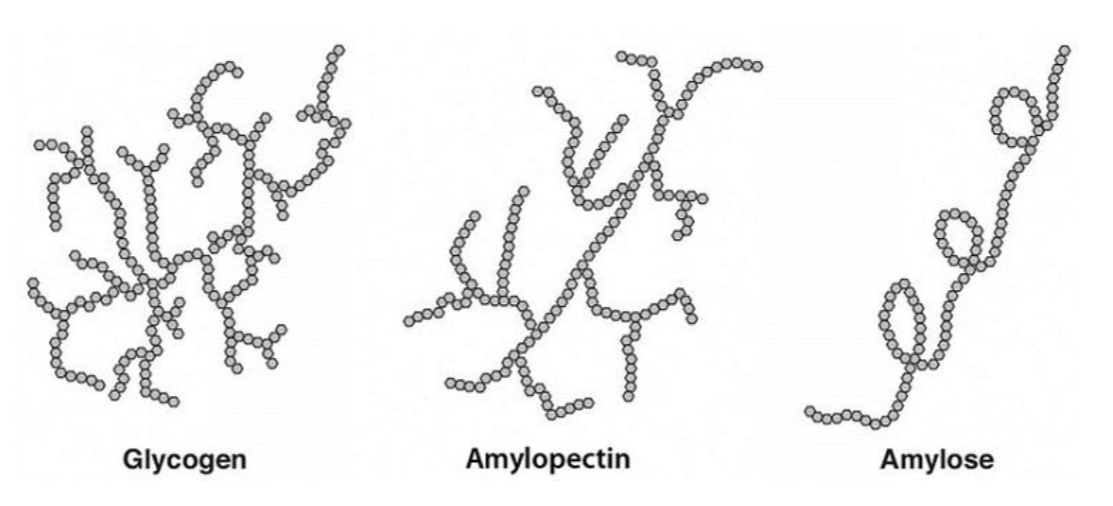
What are polysaccharides
Chains of monosaccharide
Made almost exclusively by glucose
i.e Glycogen, Starch, Fiber, Amylopectin, & Amylose
Exmples of CHO
Sugar, Starches, & Fiber
Where can CHO be found
All plants food, & milk
Not in animal-source food or fats
Monosaccharides Sources
Glucose = consumed as a component of disaccharides & polysaccharides (dextrose)
Galactose = milk
Fructose = naturally in fruits & honey (soft drinks, ready to eat cereal, high frcutose corn syrup)
Where can Disaccharides food source be found
Sucrose = Fruits, vegetables, and gains(table sugar)
Lactose = Milk
Maltose = Barley
What is lactose intolerance
inability to digest lactose due to deficiency in lactase
25% of US adults are lactose intolerant
Where is Complex CHOs food source found in
Starch = Plant product like grains(wheat, rice), root crops, tubers(yams & potatos), and legums(beans & peas)
Glycogen(storage of glucose for animals) = limited extend in meats
Not a significant contributor of CHO
Fiber(dietary fiber/non-starch polysaccharides) = structural component of platns(stems, cell wall) & indigestable by humans
Branch vs Linear Polysacchrides
Branch is more easily digested than linear
Whole Grains vs Refined Grains
Whole grain = Endosperm(starchy potion w/some protein), Germ(fiber filled w/vitamin B), Bran(Vitamin B & E, phytochemicals)
Refined Grain = Only Endosperm(no nutrient left)
Difference between whole grain stamps
100% Stamp = All of the grain is whole grain (min = 16gram of whole grain per serving)
50% Stamp = At least 50% of grain is whole (min = 8gram of whole grain per serving)
Basic Stamp = Significant whole grain primarily of refined grain (min = 8g of whole grain per serving)
What is High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS)
Made from corn
Enzyme convert starch into individual glucose molecules
Additional enzyme convert some of the glucose into fructose
Most HFCS is 55% furctose & 45% glucose
Sucrose is 50% furctose & 50% glucose
What are the affect of HFCS consumption
Fructose is converted to glucose, glycogen, or fatty acid and stored in the liver
Excessive fructose lead to metabolic dyfunction associated steatotic liver disease(MASLD) previously known as non-alcohol fatty liver disease(NAFLD)
Increase TG
Increase LDL-C
Increase Visceral Fat
Which part of the GI Tract is CHO halted
Stomach
Enzyme involved in Digestion of Carbohydrates
Mouth = Salivary amylase
Pancreas = Pancreatic amylase
Small Intestine = Maltase, Sucrase, & Lactase
Absorption of CHO
Only monosaccharides can be absorbed by enterocytes, then enter bloodstream and sent to liver via hepatic portal vein
What happens in the liver for CHO absorption
Fructose and Galactose are converted to glucose and glycogen
What are the 3 metabolic fate of glucose
Cellular Respiration - ATP production (FUEL)
Stored as Glycogen - Glycogenesis
Converted to Fatty Acid & Stored as Adipose Tissue - Lipogenesis
Excessive fructose consumption increases lipogenesis
Body Functions of Glucose
Brain/Central Nervous System - Primary source of energy for brian and CNS
Muscle - Muscle glycogen is the primary energy source for the body(exercise)
Red Blood Cells - Glucose is the primary source of RBC (90% catabolized anaerobically)
Functions of Carbohydrates
Energy Reserves
Glucose levels high = Liver uses glucose to make glycogen
Glycogen stores are key in maintaining steady levels of glucose
Prevents protein catabolism in body
Decrease gluconeogenesis
(amino acid/lactate/glycerol —>glucose)
Spares muscle tissue
Functions of Starch & Fiber
Slows breakdown of starch into glucose
Soluble fiber traps nutrients & delays GI tract transit, promoting slower glucose absorption
Enhance Health of LI
Block absorption of unwanted constituents
Increase stool weight, ease passage, reduce transit time
Promote Healthy gut bacteria
RDA intake for CHO & %Added Sugar
130g/day for adults & children(minimum glucose used by brain)
Higher during pregnancy & lactation
No UL for total CHO intake
Added Sugar no more than 25% of total kcal or <10% of total kcal
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range(AMDR) for CHO
DRI for CHO 45-65% of daily E intake
Daily Value for a 2000kcal: 900 to 1300kcal = 225g - 325g of CHO
DRI recommendation for fiber
No established RDA or UL
Adequate Intake:
21-25g/day for women
30-38g/day for men
What are the 3 health effects of excess sugar
Dental cavities
Nutrient Deficiencies
Obesity
Dental Cavities
Naturally occuring & added sugar contribute to tooth decay
Bacteria ferment sugar from food
Drinks(w/sugar & low pH) erode tooth enamel
Nutrient Deficiencies
Added sugar contribute to nutrient deficiencies by displacing nutrient(donut for breakfast)
Faactors of Obesity
Biological Factor
Genetic & Metabolic
Social/Environmental
Cultural, Behavioral, Socioeconomic
What role does genetics play in obesity
Causative role in only a few cases of obesity
What are the Genetics of Obesity
Syndromic Form(affects broader)
Chromosomal rearrangements(large scale change in gene)
Pleiotropic(one gene affect multiple organ)
Non-Syndromic Form
Polygenetic(multiple gene)
Monogentic(one gene)
What is Monogenic Obesity
related to mutation in genes that are vital for the regulation of appetite and satiety
POMC,NPY,LEP,LEPR,MC3R
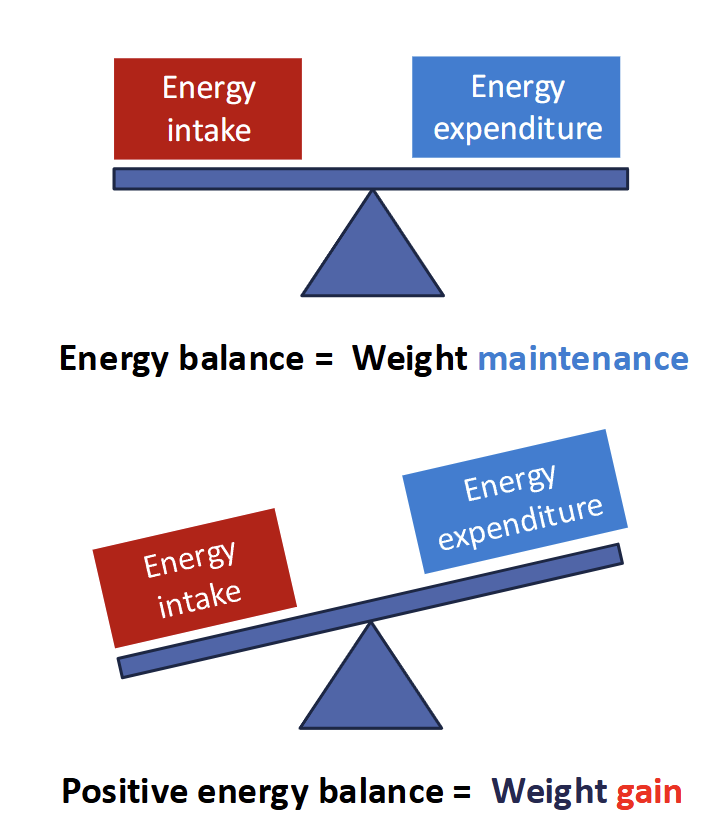
Energy Balance
Related to obesity and overweight by calories consumed and calories expended
increase energy dense food (high fat & sugar)
increase in physical inactivity (work,transportation,urban)
What chronic noncommunicable diseases(4) does obesity contribute to
Cardiovascular diseases, Chronic Respiratory Disease, Diabetes, & Cancer
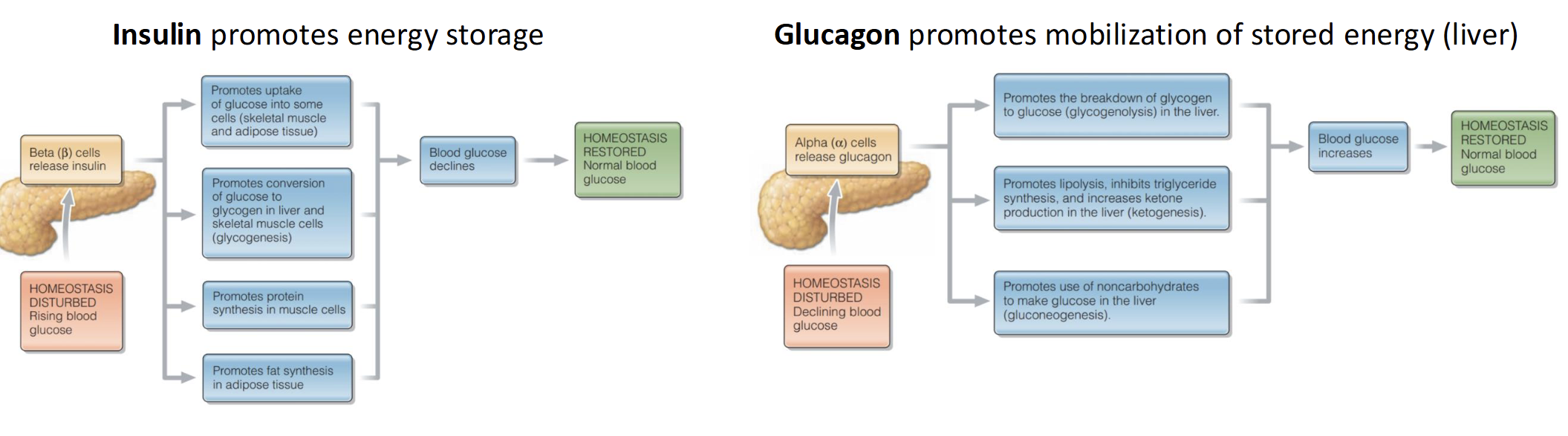
What is Glucose Homeostasis
Hormonal and Neural mechanism that the body uitlizes to maintain blood glucose levels at relatively steady level
What does the uptake of plasma glucose into cells require
GLUT or Glucose Transportors
What are the different types of GLUT
14 GLUT isoforms throughout the body
GLUT1
blood, blood brain barrier, heart(lesser extent)
GLUT2
Liver, Pancreas, SI
GLUT 3
Brain, Neurons, Sperm
GLUT 4(most abundant receptor)
Skeletal Muscle, Adipose Tissue, Heart
What Transportor is required for glucose uptake in enterocytes
Mainly driven by sodium dependent active transport mechanism of SGLT1(Sodium linked Glucose Transportor)
Pancreas(15 cm in length) function in glucose homeostasis
Produce key hormones
B-Cells release Insulin (high sugar level released)
A-Cells release Glucagon (low sugar level released)
Liver function in glucose homeostasis
Stores and release energy
glycogen(stored sugar)
Acinar cells
exocrine; pancreatic jucie 95% of cells
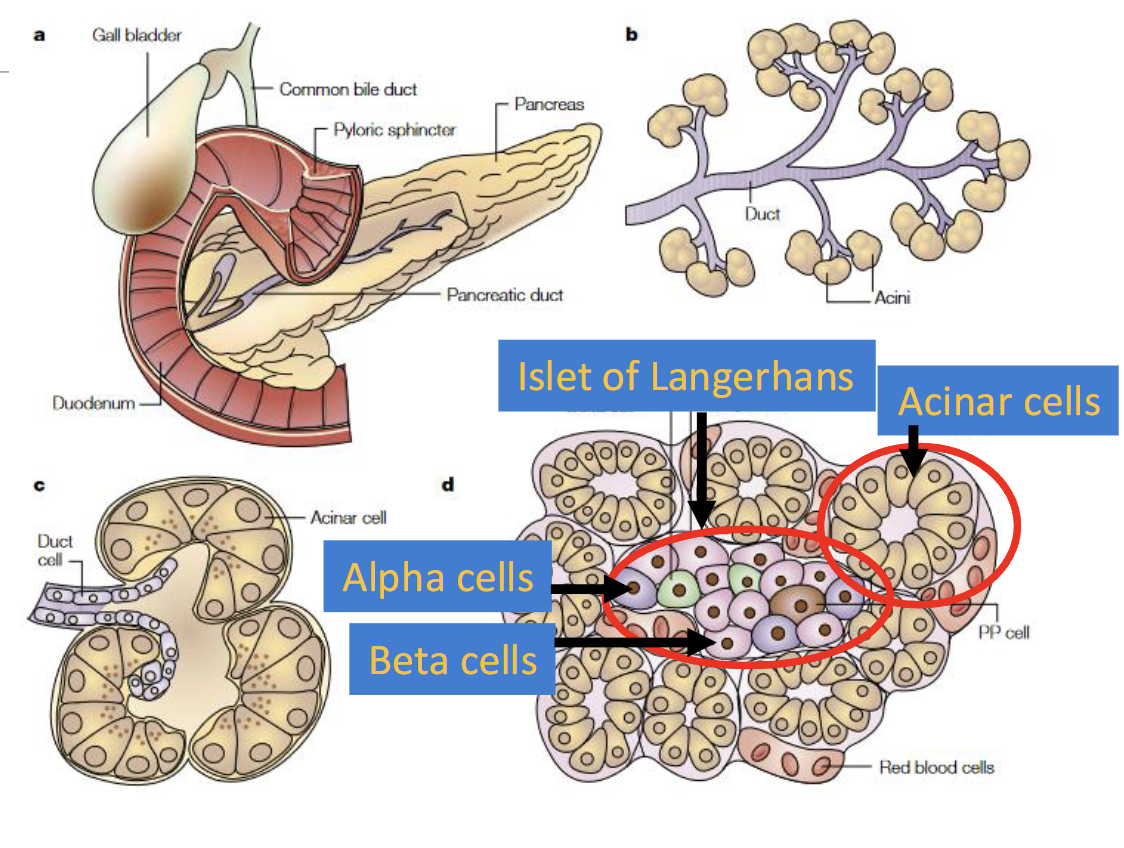
Islet of Langerhans
Hormone producing cells(endocrine); 2-5% of cells
Beta Cells - insulin
Alpha Cells - Glucagon
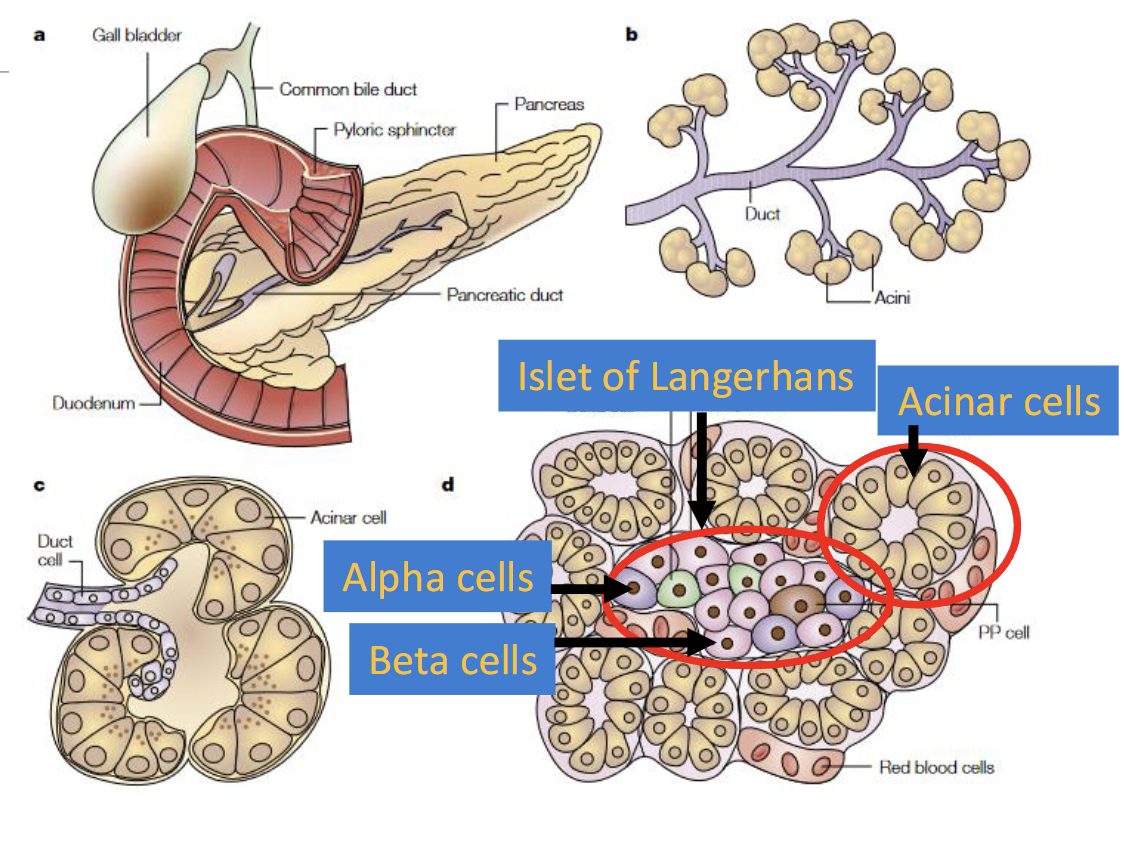
Insulin & GLUT 4 Relationship
Insulin serves as signal for rapid transfer of GLUT 4 into cell membraneof muscle & adipose cells, increasing transport of glucose
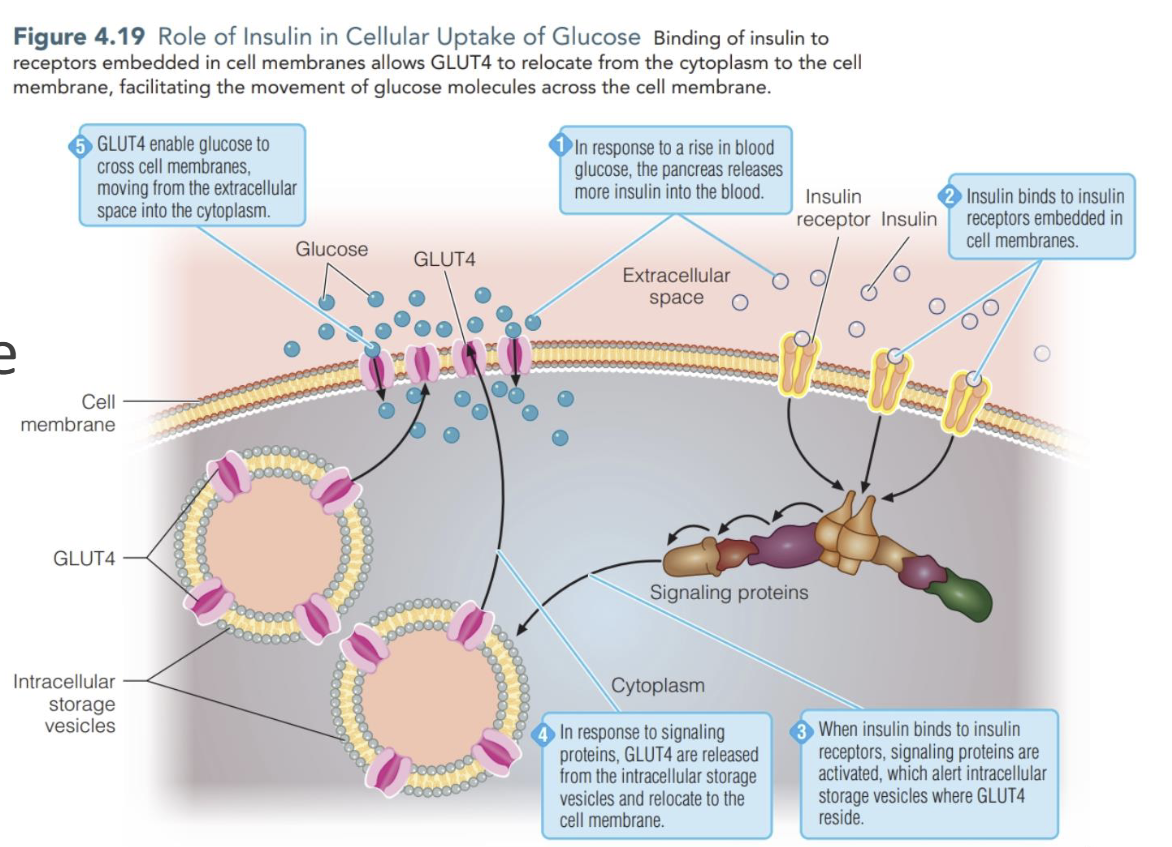
Are all tissues insulin dependent
No
Brain is always permeable to glucsoe (GLUT 1 & GLUT 3)
Skeletal muscle are insulin dependent at rest but not during exercise
Glucose Homeostasis: After a Meal
Blood Glucose increase, stimulate release of insulin allowing insulin dependent glucose transporters to take up glucose into cells; promotes formation of glycogen in liver & conversion of excess glucose into fat .
Glucose Homeostasis: In between meals
Low blood glucose stimulate release of glucagon allowing breakdown of glycogen in the liver and released into blood
Epinephrine(hormone from fight/flight) also raises blood glucose
What happens if regulation of glucose fails
Hypoglycemia (low sugar) <70mg/dL
Hyperglycemia (high sugar)
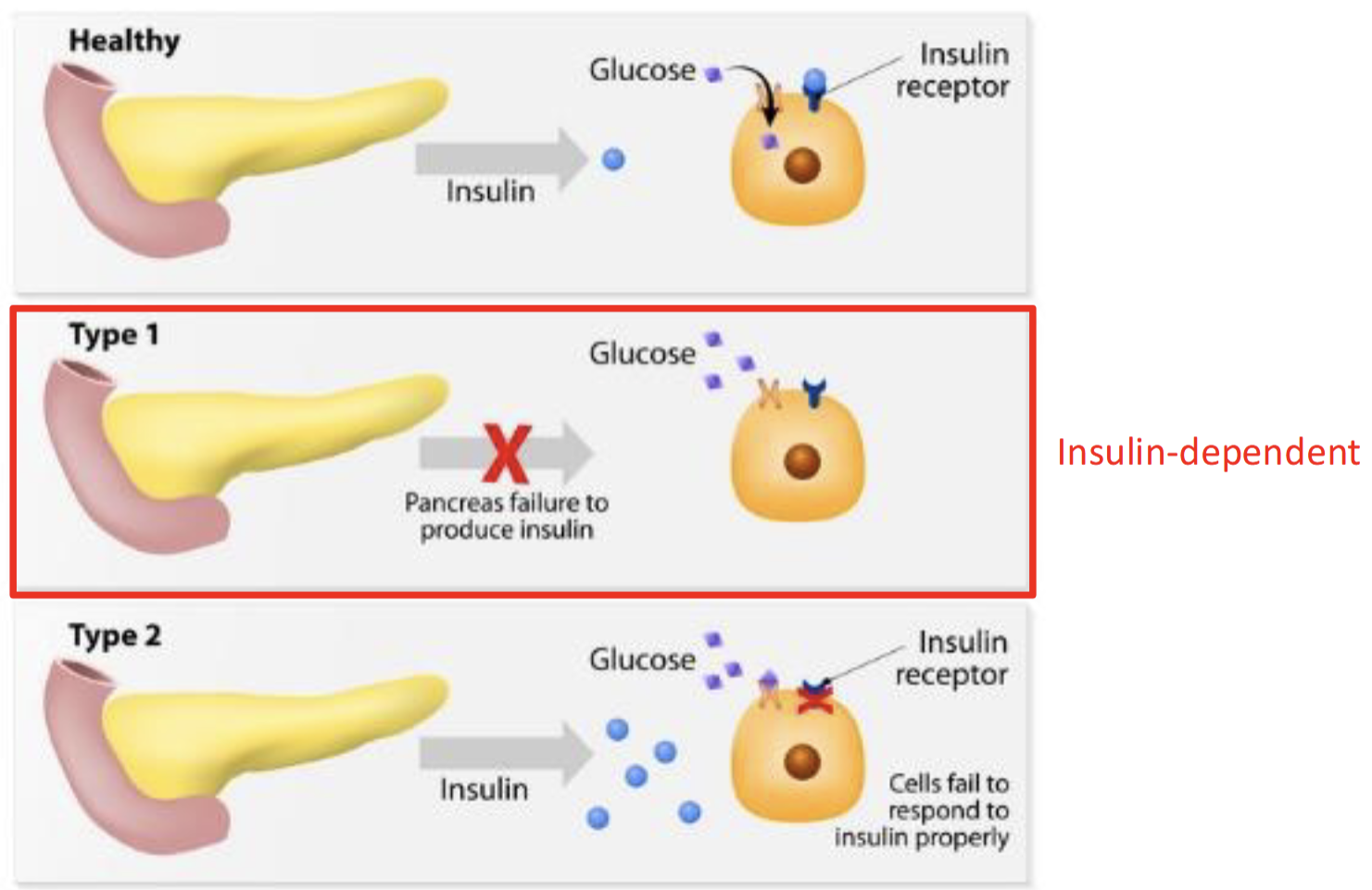
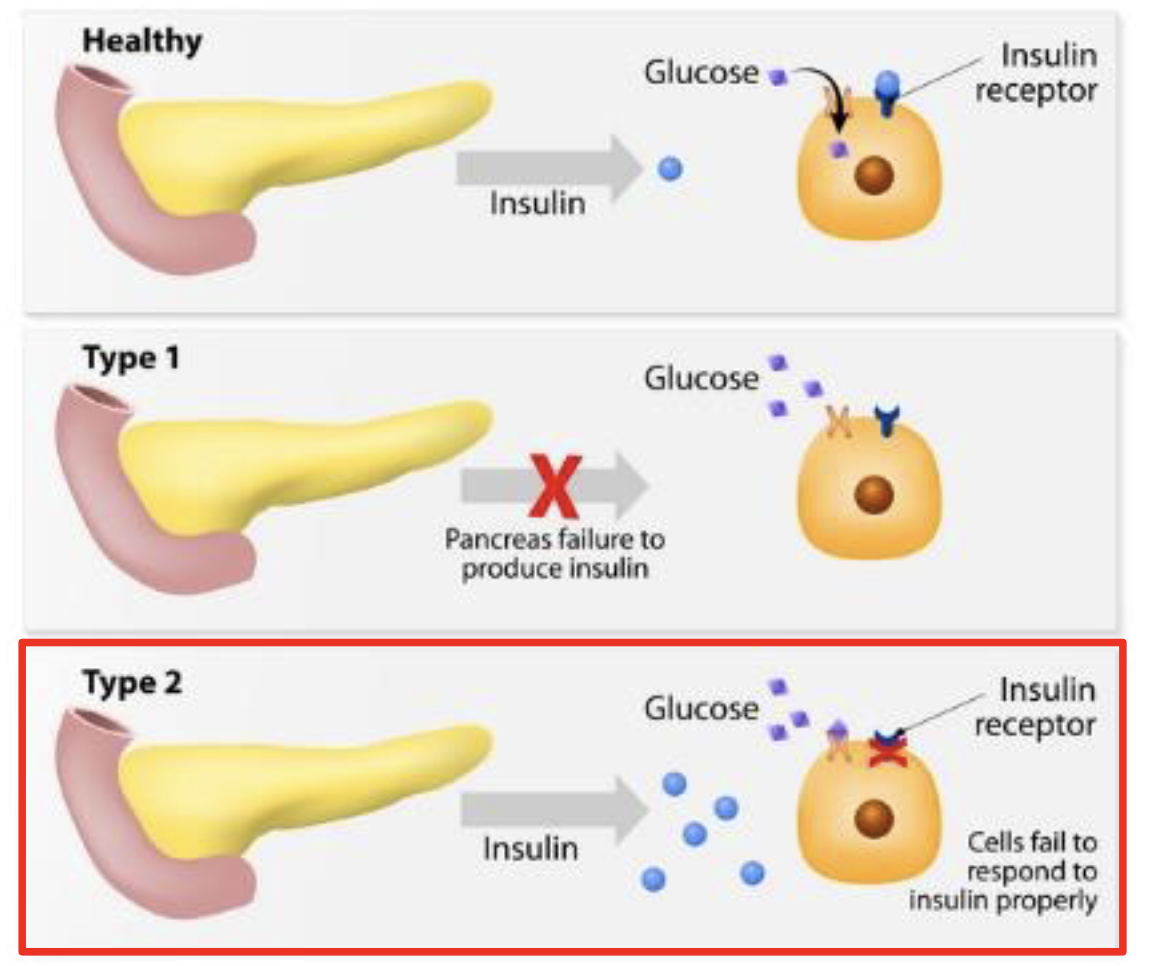
What is Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
Group of metabolic disease characterized by elevated level of glucose blood (hyperglycemia)
T1DM - 5% diabetes cases(childhood,gene, lack of insulin)
no known way to prevent
T2DM - 90-95% diabetes cases(middle-age, insulin resistance)
preventable
Risk Factors of T2DM
Family History
history of gestational diabetes
Sedentary lifestyle
exercise <3x per week
Overweight or obese
vascular disease history
What causes T1DM
Autoimmune disease - destruction of pancreatic B-cells, failure to produce insulin
What causes T2DM
Chronic elevated level of blood glucose increasing insulin but receptors are not responsive
Chronic complication of DM
Cell produce sugar alcohols - toxicity & distention(bloating)
Cell produce glycoproteins - loss of protein function
loss of circulation & nerve function
infection - poor circulation
What are the loss of circulation & nerve function in DM complication
Disease of large blood vessels(Macrovascular)
Diabetic cardiomypopathy
Disease of small blood vessels(Microvascular)
diabetic retinopathy
diabetic nephropathy
Disease of the nerves
diabetic neuropathy(affect legs before hand)
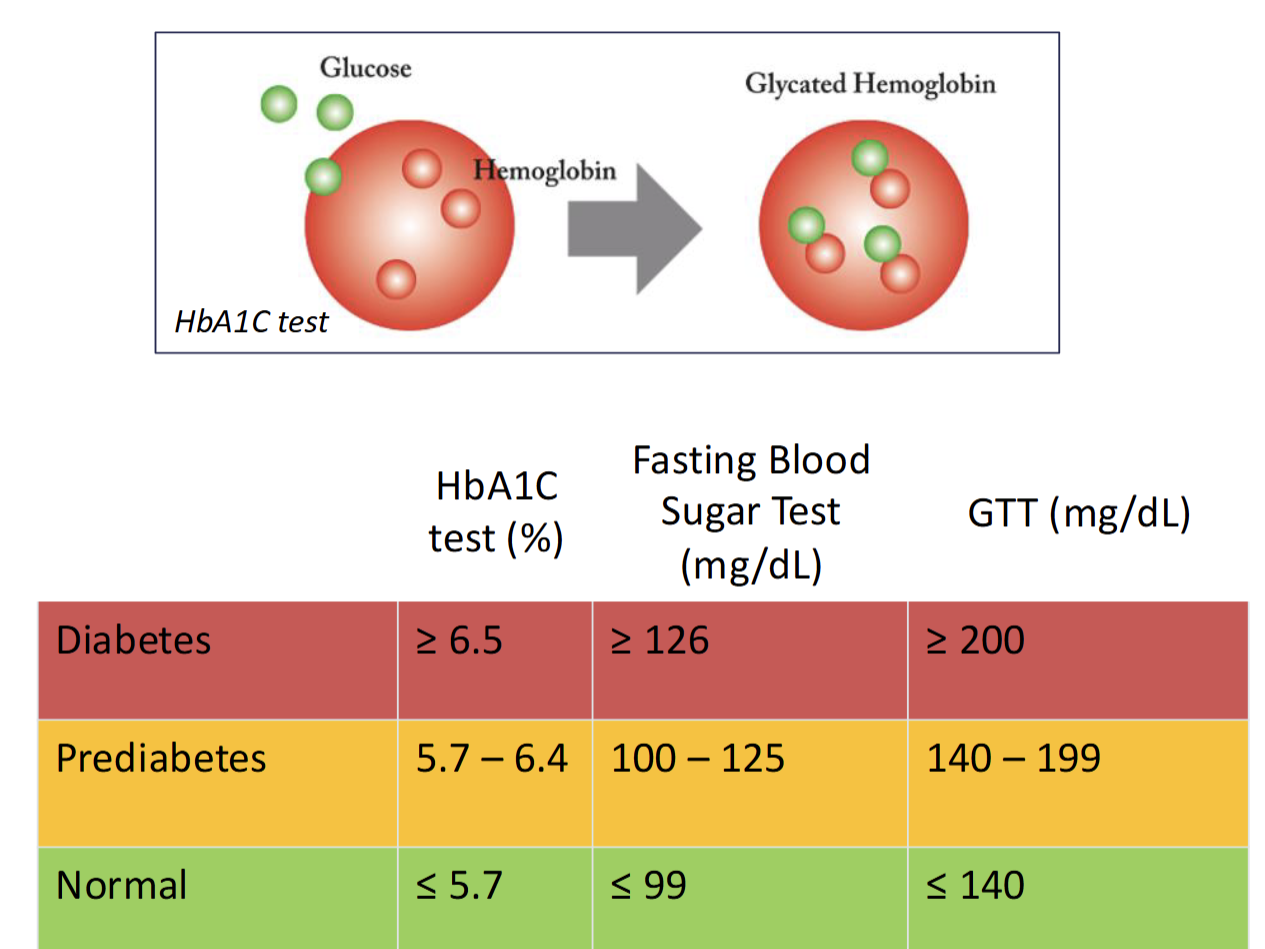
How is diabetes diagnosed
Hemoglobin A1C(HbA1C) - represents average blood sugar levels over past 3-4 months (life span of RBC)
Glucose tolerance test(GTT) - measure blood sugar before and after a drink containing glucose
What is the most abundant lipid in the human body and food
Fatty acids
What are fatty acids(FA) comprised of(elements)
Carbon, Hydrogen, & Oxygen atoms
What are the 2 carbon backbone of fatty acids
Alpha end - with a carboxylic group (COOH)
Omega end - with a metyhyl group (CH3)
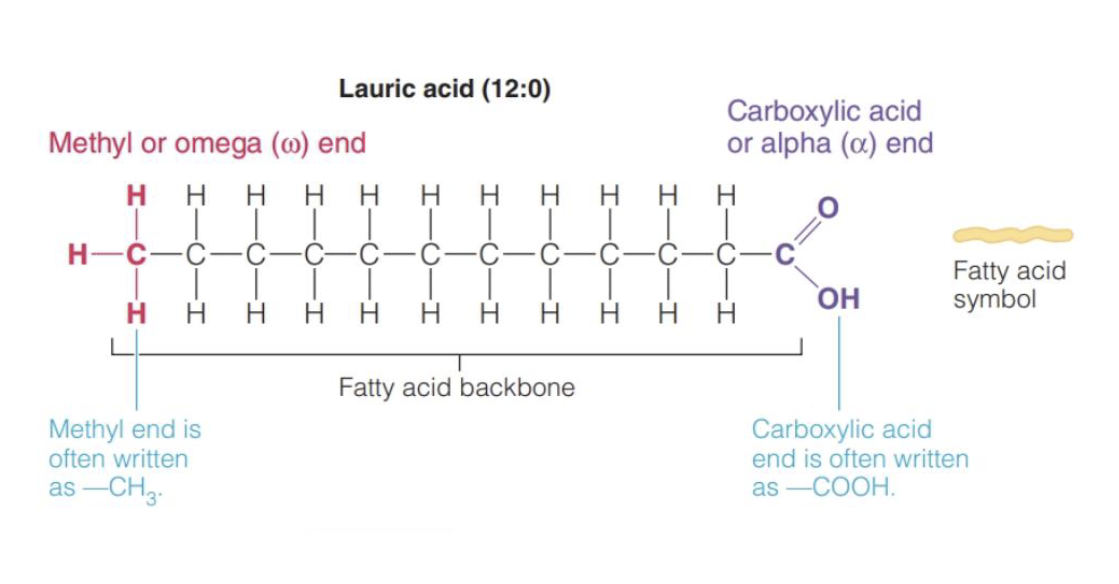
What are the different Chain Length of Fatty Acids(affects chemical & physical function)
Short Chain FA
2-5 carbon, predominant
Medium Chain FA
6-12 carbons
Large Chain FA
>12 carbons
Type of saturation of Fatty Acids
Saturated (Solid at RT)
Maximum possible number of H atom bound to e/carbon
Unsaturated (liquid at RT)
Mono-unsaturated(MUFAs) - one double bond
Poly-unsaturated(PUFAs) - many double bonds
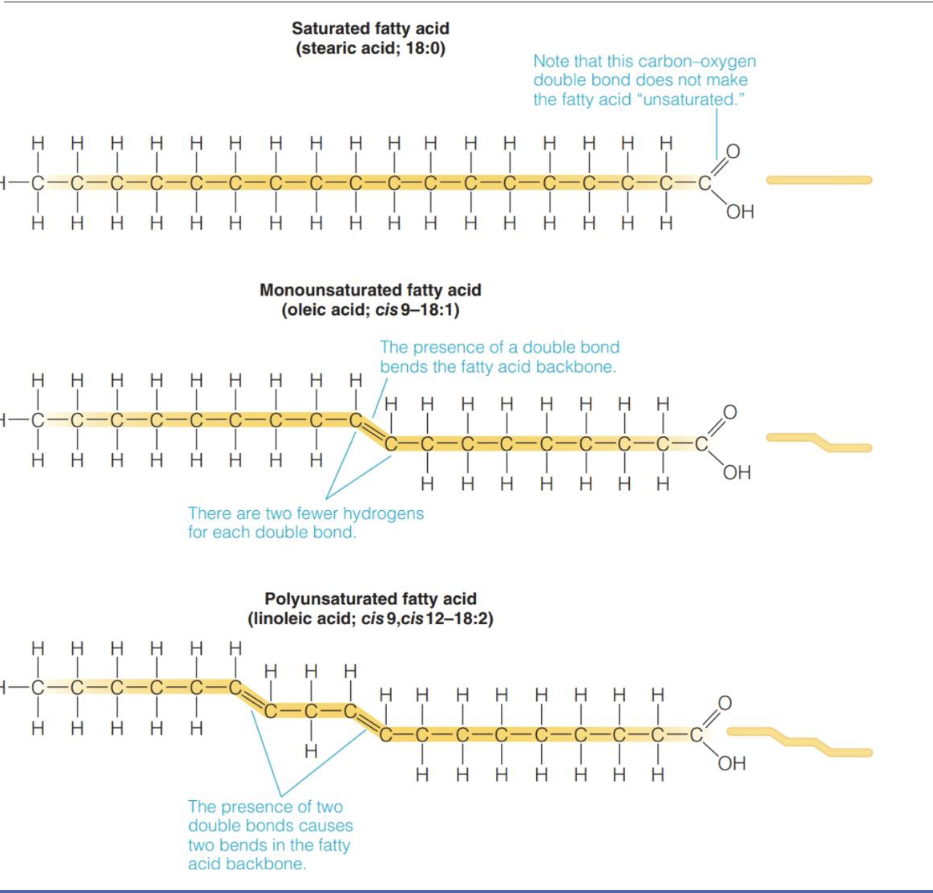
Unsaturated FA classification
Cis Unsaturated FA
H atoms are positioned on the same side of the double bond
Bending of FA, liquid at RT
Contain Omega 3 & Omega 6 FA
Trans Unsaturated FA
H atoms are positioned on opposite sites of double bond
No bending of FA, Solid at RT
Associated with Increased CDV
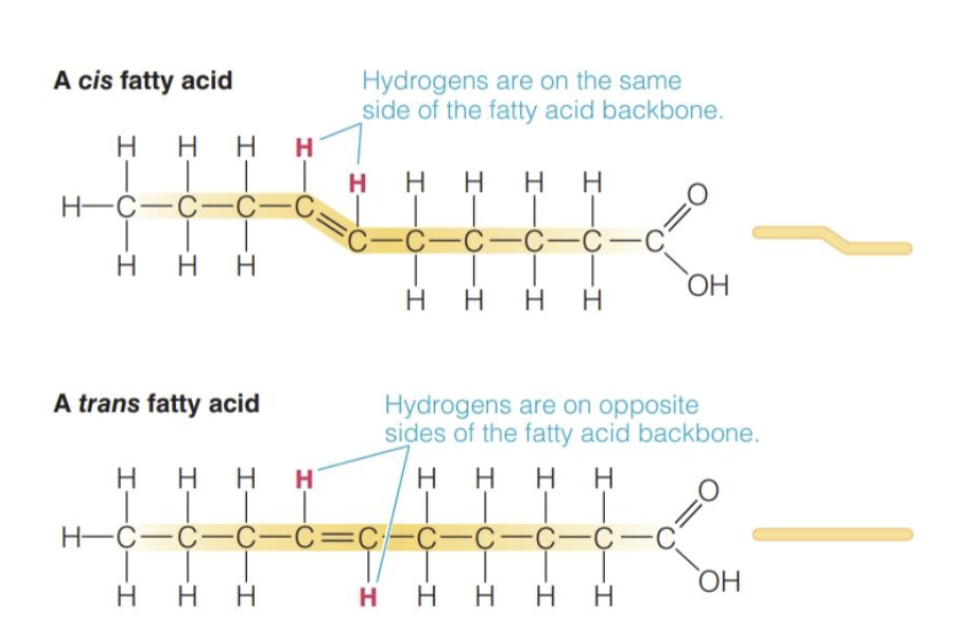
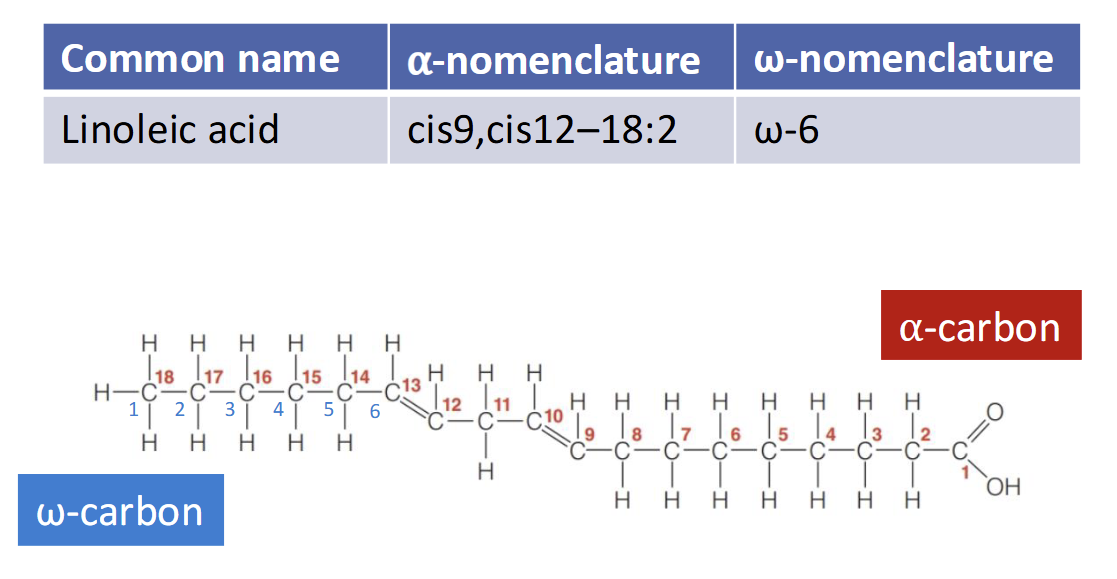
Systematic naming of Unsaturated FA
Alpha naming system
Position of the double bond relative to alpha carbon
Omega naming system
Position of the double bond relative to omega carbon
Does not identify whether the double bond is cis or trans
Food source of where lipids are found
Fats, Milk, Starch, animal Source
(No Furits/vegatables)
What are the 3 complex fatty acid molecules
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Sterols
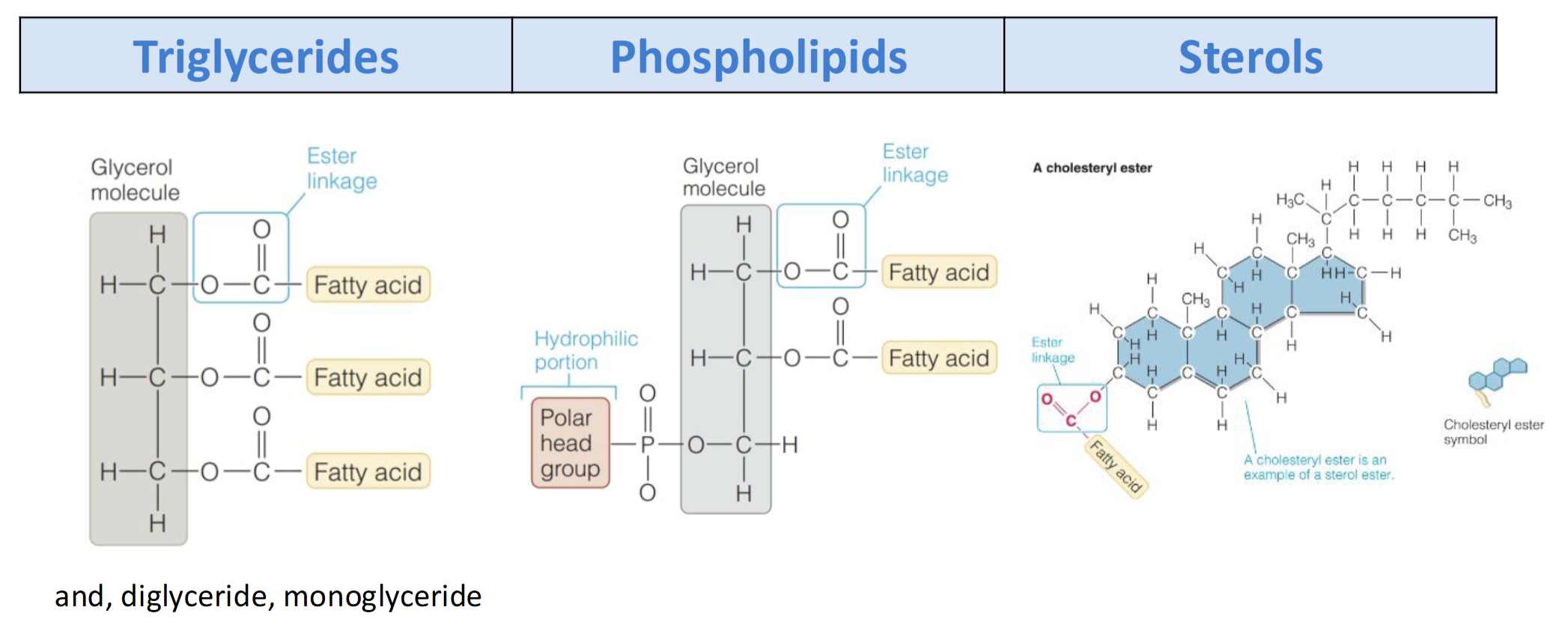
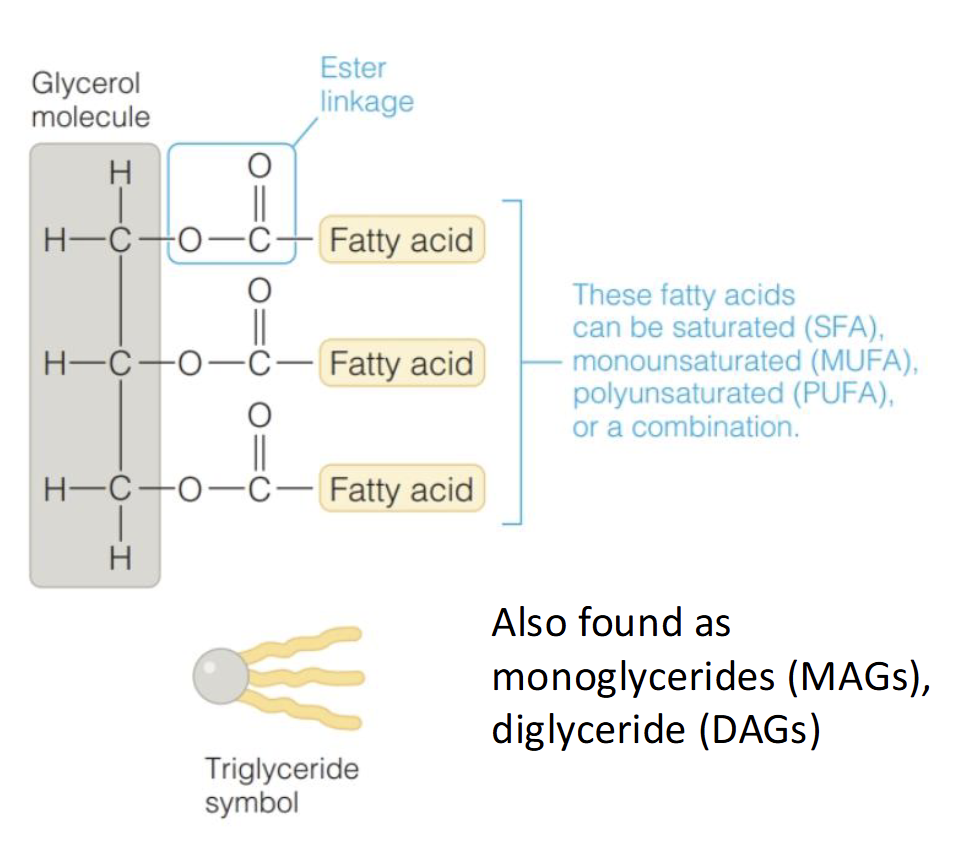
What are triglycerides(TG) or Triacylglycerol(TAG)
Primary dietary lipid & major source of energy
Composed of 1 glycerol + 3 FA bounded by ester linkages
What are Phopholipids(PL)
Found Naturally in most foods
Composed of 1 glycerol + 2 FA bounded by ester linkages
PL have a phophate containing polar head group
Amphipathic(Hydrophilic & Hydrophobic)

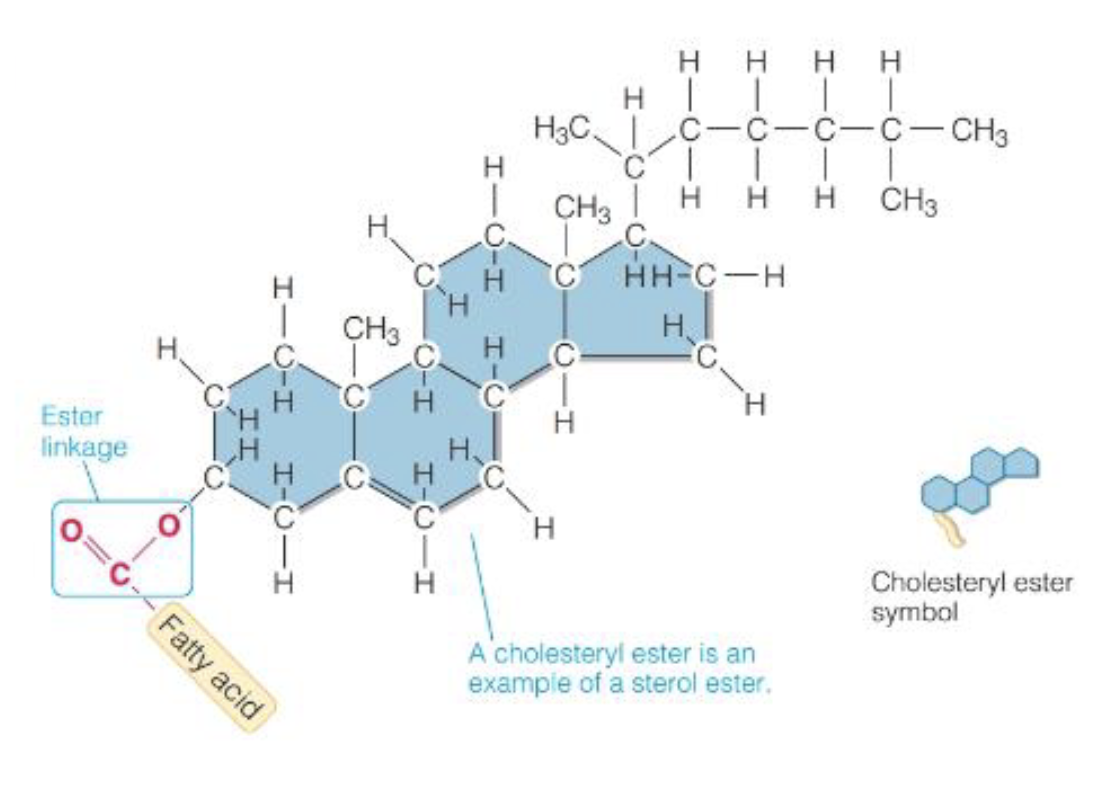
What are Sterols & Sterol esters
Lipids w/multi-ring structure
Composed of 1 chloestrol + 1 FA bonded by ester linkage
Can be synthesized endogenously
Needed to synthesize bile acid & steriod hormone(membrane fludiy)