Infrared spectroscopy
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Atoms in molecules are joined by covalent bonds which possess energy and vibrate naturally about a central point. What affects the amount of vibration?
Temperature
How does infrared (IR) radiation affect molecules?
Each bond vibrates at its own frequency
All molecules absorb IR radiation, making them bend or stretch more
Name the 2 types of vibration
Stretch
Bend
Describe the stretch of a bond
Stretch - rhythmic movement along the line between atoms so that the distance between the two atomic centres increases and decreases
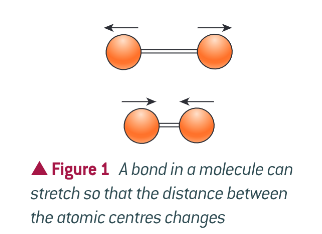
Describe the bend of a bond
Bend - change in bond angle
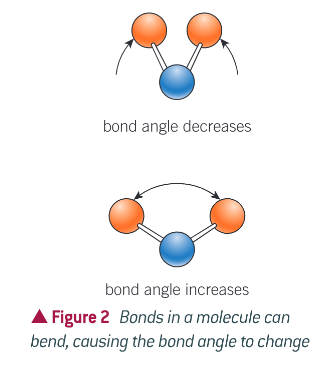
What does the amount of vibration depend on?
Bond strength - stronger bonds vibrate faster than weaker bonds
Mass of each atom in the bond - heavier atoms vibrate more slowly than lighter atoms
Bond length - shorter bonds usually vibrate faster than longer bonds
What kinds of radiation frequencies can a bond absorb?
The bond can only absorb radiation with the same frequency as the natural frequency of the bond
Why is the scale of wavenumber used by chemists?
The frequency values are very large
What range are most of the vibrations of bonds observed in?
IR wavenumber range of 200cm-1 to 4000cm-1
How does the Sun’s visible and IR radiation work?
The radiation passes through the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface, where most of it is absorbed
Some is re-emitted from the Earth’s surface in the form of longer-wavelength IR radiation
Name the 3 most abundant greenhouse gases
Water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane
How do greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Greenhouse gases absorb the longer-wavelength IR radiation re-emitted from the Earth’s surface, because it has the same frequency as the natural frequency of their bonds
The vibrating bonds in these molecules re-emit this energy as radiation which increases the temperature of the atmosphere
What is infared spectroscopy used for?
Identifying the functional groups present in organic molecules
How does infrared spectroscopy work?
The sample under investigation is placed inside an __________
A beam of ____________ in the range __________ cm-1 is passed through the sample
The molecule _______ some of the ____ frequencies, and the emerging beam of radiation is _______ to identify the frequencies that have been ______ by the sample
The IR spectrometer is usually connected to a computer that plots a ______ of _______ against ______
The sample under investigation is placed inside an IR spectrometer
A beam of IR radiation in the range 200-400 cm-1 is passed through the sample
The molecule absorbs some of the IR frequencies, and the emerging beam of radiation is analysed to identify the frequencies that have been absorbed by the sample
The IR spectrometer is usually connected to a computer that plots a graph of transmittance against wavenumber
What are the ‘peaks’ on an IR spectrum?
Peaks - dips in the graph
Each peak is observed at a wavenumber that can be related to a particular bond in the molecule
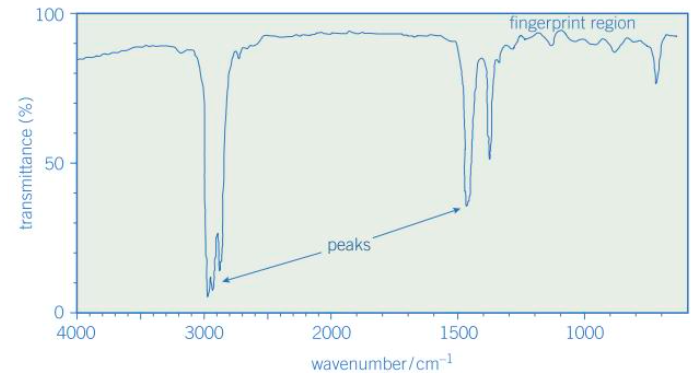
Below 1500cm-1 there are a number of peaks known as the fingerprint region. What does this contain?
The unique peaks which can be used to identify the particular molecule under investigation, either using computer software or by physically comparing to published spectra
When interpreting IR spectra what do you need to remember when identifying the bond?
Identify both the bond and the functional group it belongs to
E.g. OH bond in an alcohol
What should be remembered when looking at peaks between 2850 and 3100 cm-1?
All organic compounds produce a characteristic peak between 2850 and 3100
This is not to be confused with O-H peak in alcohols
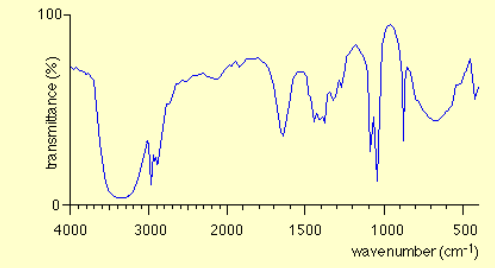
State the most likely type of compound of this infrared spectrum
Alcohol
Absorbance peak within the range 3200-3600cm-1, indicating O-H bond in alcohol
Peak between 1000-1300cm-1, indicating C-O bond
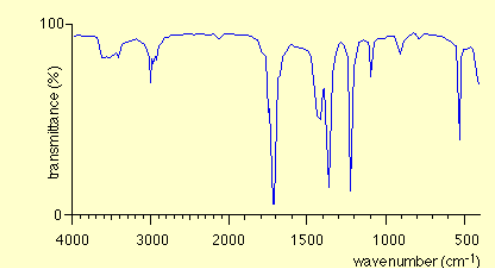
State the type of compound of the infrared spectrum
Aldehyde / ketone
Key absorbance between 1630-1820 caused by the C=O bond
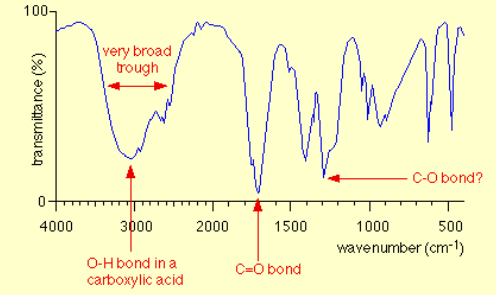
Show what an infrared spectrum for a carboxylic acid would look like
Give some applications of IR spectroscopy
Identifying functional groups present in unknown substances
Monitoring pollution by analysing IR spectra of vehicle emissions
IR-based breathalysers to measure alcohols
Quality control in perfume manufacture
Drug analysis - screening and identification of drugs
Forensics - identification of fibres and paint chips in forensic analysis
When determining the structure of an organic molecule, what is a typical sequence for identification?
______ _______
Use of _____ composition data to determine the ______ data
_____ spectrometry
Use of the _______________ from a _____ spectrum to determine the molecular _____; use of ___________ to identify _____ of a molecule
______ spectroscopy
Use of ___________ from an infrared spectrum to identify ______ and ________ present in a molecule
Once you have the _____ formula and the __________ of a compound, you can determine the molecular ______ of your unknown compound. By using evidence from the ____________, it may be possible to identify an unknown compound
Elemental analysis
Use of percentage composition data to determine the empirical data
Mass spectrometry
Use of the molecular ion peak from a mass spectrum to determine the molecular mass; use of fragment ions to identify sections of a molecule
Infrared spectroscopy
Use of absorption peaks from an infrared spectrum to identify bonds and functional groups present in a molecule
Once you have the empirical formula and the molecular mass of a compound, you can determine the molecular formula of your unknown compound. By using evidence from the infrared spectrum, it may be possible to identify an unknown compound