simple molecular substances
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is a simple molecular substance?
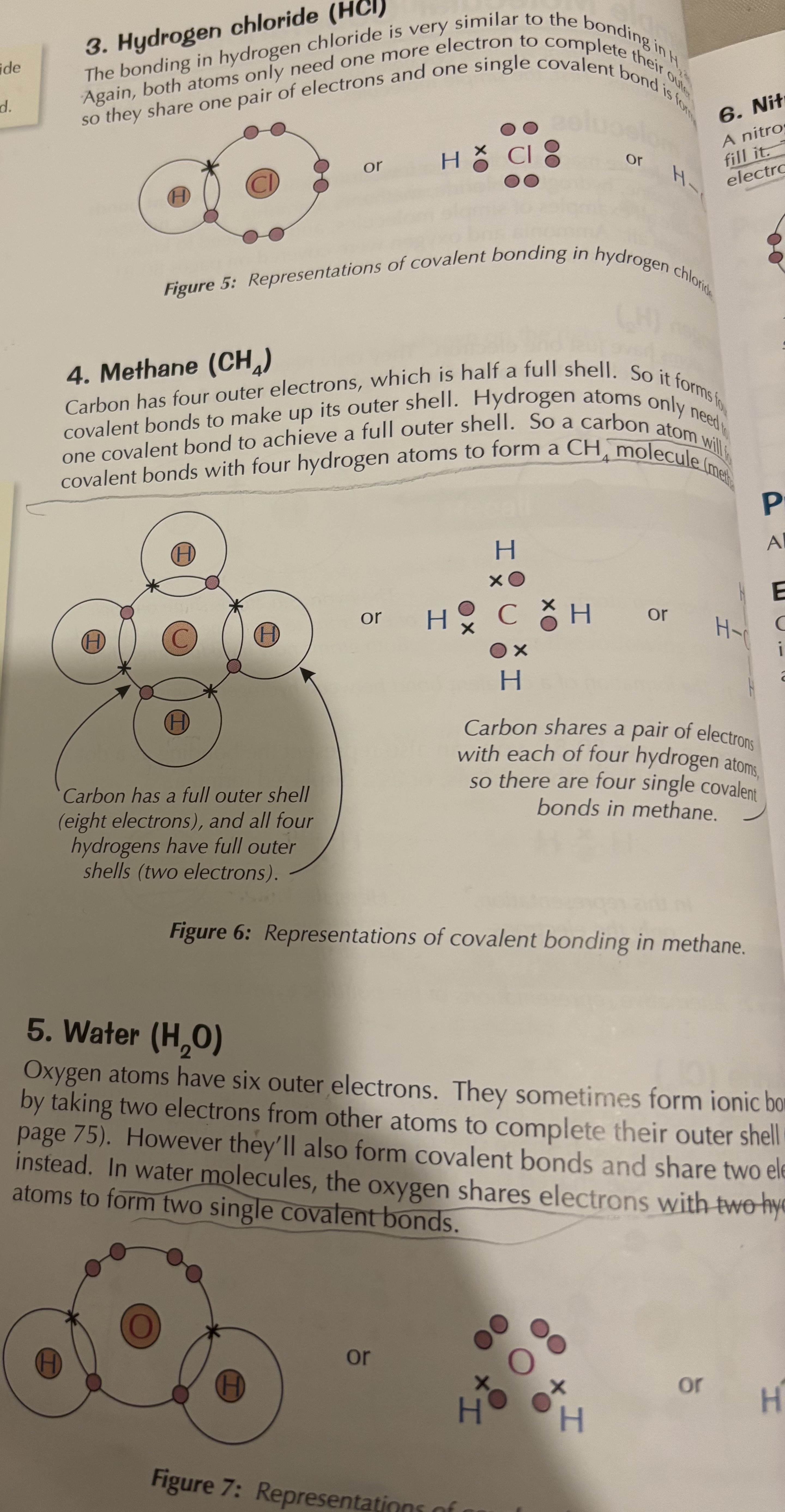
A simple molecular substance contains a few atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Examples include hydrogen (H₂), chlorine (Cl₂), hydrogen chloride (HCl), methane (CH₄), and water (H₂O).
How is a hydrogen molecule (H₂) formed?
Each hydrogen atom has one electron. They share their electrons to form a single covalent bond, giving both atoms a full outer shell.
How is a chlorine molecule (Cl₂) formed?
Each chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outer shell. They share one electron each to form a single covalent bond, completing their outer shells.
How is a hydrogen chloride molecule (HCl) formed?
Hydrogen shares its one electron with chlorine, and chlorine shares one of its seven outer electrons with hydrogen, forming a single covalent bond.
How is a methane molecule (CH₄) formed?
Carbon has four outer electrons and forms four covalent bonds by sharing electrons with four hydrogen atoms, giving all atoms full outer shells.
How is a water molecule (H₂O) formed?
Oxygen has six outer electrons and forms two covalent bonds by sharing electrons with two hydrogen atoms, completing the outer shells of all atoms.
Why do simple molecules have low melting and boiling points?
Because they have weak intermolecular forces that require only a small amount of energy to overcome.
Why don’t simple molecular substances conduct electricity?
They do not have free electrons or an overall electric charge.
What is a hydrogen bond?
A hydrogen bond is a strong dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is bonded to a highly electronegative atom like fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen.
Why does ice float on water?
In ice, water molecules form a regular pattern held by hydrogen bonds, making ice less dense than liquid water.
What trend is shown in the melting and boiling points of simple covalent molecules?
As the size of the molecule increases, the melting and boiling points also increase due to stronger intermolecular forces.
Why is hydrogen a gas at room temperature?
It has very weak intermolecular forces and a very low boiling point of −253°C.
Why does chlorine have a higher boiling point than hydrogen?
Chlorine molecules are larger and have stronger intermolecular forces than hydrogen, requiring more energy to boil.
Why do diamond and graphite have high melting points?
They are giant covalent structures with strong covalent bonds throughout the lattice, requiring a lot of energy to break.