Disorders of the Gallbladder
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are some RFs associated with cholelithiasis?
Age, female, Pregnancy (hormones) obesity, genetics, diet, family history
**FAT, FEMALE, FERTILE, 40s
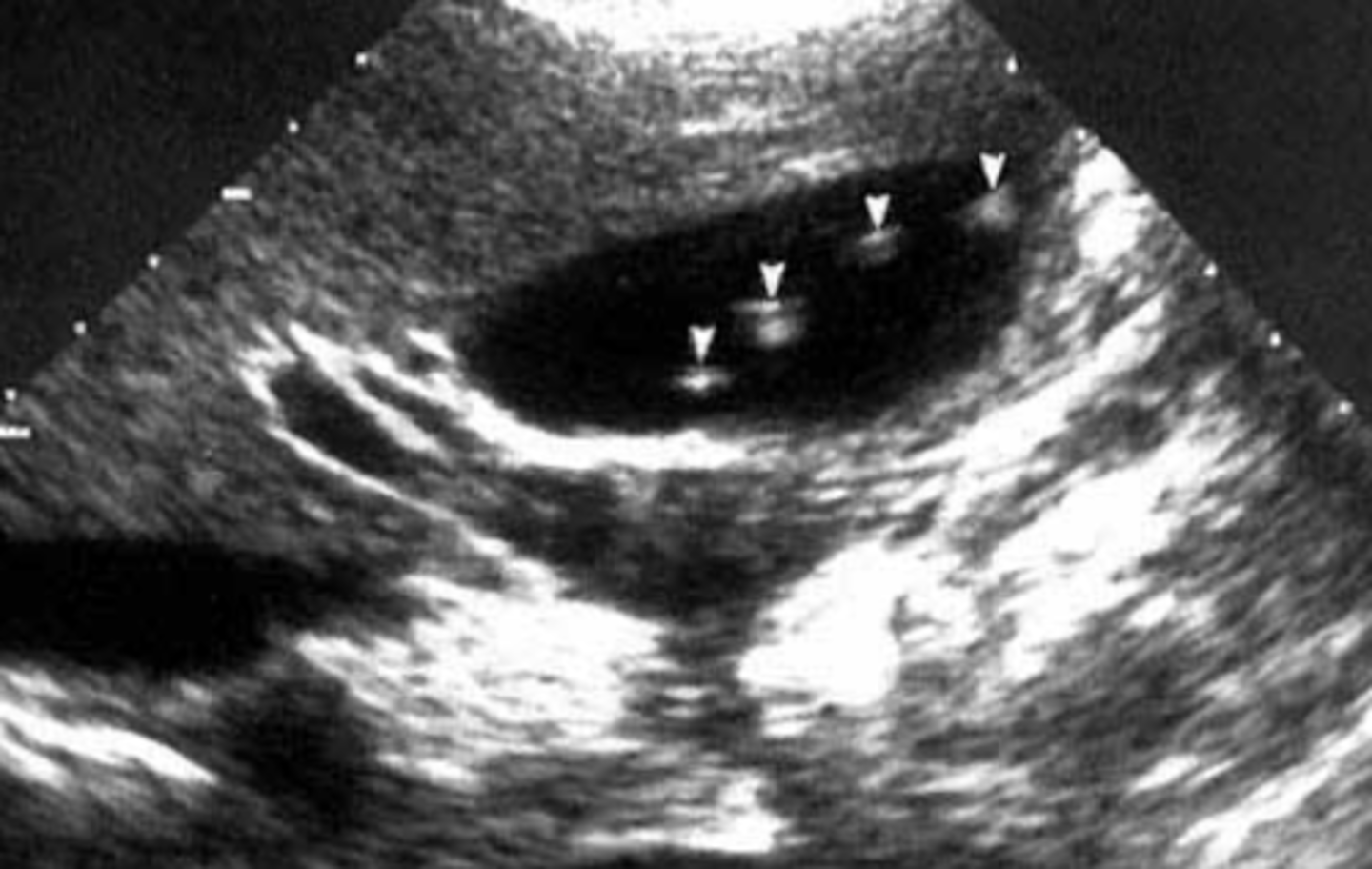
A pt presents with episodic epigastric RUQ pain and nausea. She states that it began abruptly after eating a large fatty meal and is continuous and resolves slowly 20ms. he findings on the US are attached. ---- what is the likely dx?
cholelithiasis
For an asymptomatic pt with cholelithiasis what is the tx?
observe
For an symptomatic pt with cholelithiasis what is the tx?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy – surgical intervention of choice
What is the diagnostic imaging of choice for cholelithiasis?
ultrasound TOC
What is 90% of the time associated with gallstones bc of impaction of the cystic duct?
acute cholecystitis
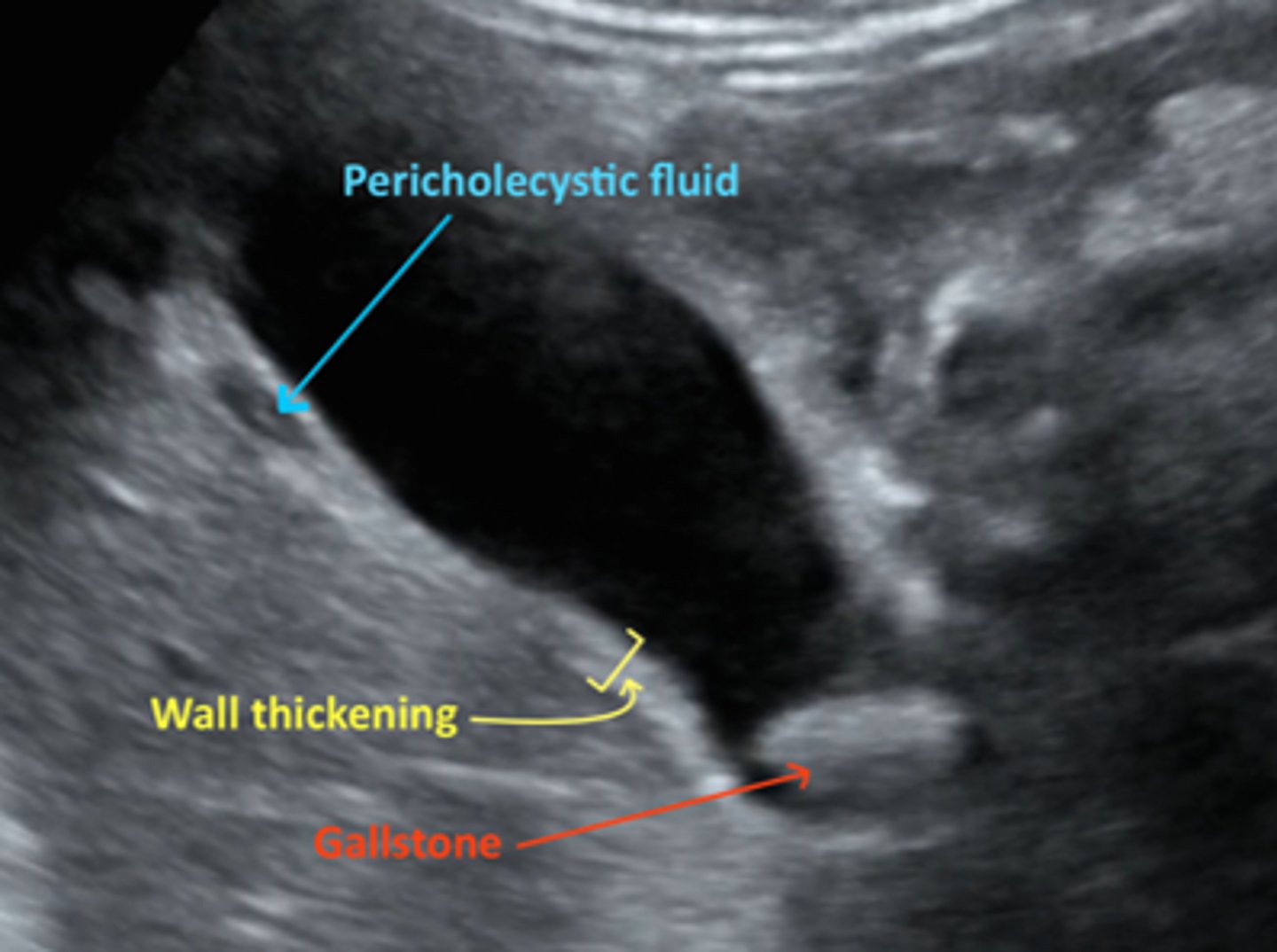
A pt presents with fever, N/V, and complaints of steady severe pain in the epigastric RUQ area. Upon PE you see some jaundice and obtain a + murphy's sign. An US (attached) shows GB wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid, and sonographic murphys. --- what is the likely dx?
cholecystitis
What will an US show for suspected acute cholysititis?
GB wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid, sonographic Murphy's
What are some complications associated with acute cholysititis?
◦Gangrene of the gallbladder
◦Chronic cholecystitis → strawberry GB
◦ porcelain GB
◦Mirizzi syndrome
What is the tx for acute cholecystitis?
◦NPO, IVF, analgesics, IV abx- Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 1-2g Qdaily + metronidazole (Flagyl) 500mg QID
◦Laparoscopic cholecystectomy usually recommended
What occurs due to gallstones in the common bile duct and the risk increases with age?
choledocholithiasis and cholangitis
A pt presents with biliary colic pain. Upon PE you note jaundice-- what is the likely dx?
choledocholithiasis and cholangitis
What is the tx for choledocholithiasis and cholangitis?
Stone extraction with ERCP
Surgery: cholecystectomy with IOC
What is a biliary infection that can occur secondary to obstruction CBD by gallstones and is an EMERGENCY?
acute cholangitis
A pt presents with fever/chills, RUQ pain, and AMS. PE notes jaundice. --- what is the likely dx?
acute cholangitis
What composes charcots triad that is associated with acute cholangitis?
fever/chills, RUQ pain, jaundice
What composes Reynolds pentad that is associated with acute cholangitis?
fever/chills, RUQ pain, jaundice + shock and AMS
What are the diagnostic tools associated with acute cholangitis?
CBC
CMP
Prolonged PT
US, CT
ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) *Urgent: allows procedure
For a pt with community acquired acute cholangitis--- what is the tx?
IV Ciprofloxacin + metronidazole (Flagyl)
◦Surgery once stable: cholecystectomy
For a pt with hospital acquired acute cholangitis--- what is the tx?
Piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn) or Meropenem
◦Surgery once stable: cholecystectomy
What can occur due to surgical anastomosis or injury to the biliary tree?
biliary stricture
What is a complication associated with biliary stricture?
Cholangitis
What are the diagnostics for biliary stricture?
◦ERCP>MRCP
◦CT
What is the tx for biliary stricture?
◦ERCP
◦Dilation and/or stent via EUS- Metal stents generally only used if life expectancy <2 years
◦Surgical intervention- Choledochojejunostomy or hepaticojejunostomy
What is MC in males, strongly associated with UC (90%), and occurs due to:
DIFFUSE inflammation of the biliary tract → fibrosis → strictures
primary sclerosing cholangitis
What diagnostics are used in the diagnosis of primary sclerosing cholangitis?
MRCP, ERCP
+ P-ANCA
ALK, GGT also elevated
PBCIW
PBCIW → Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (Cholangitis) “Intrahepatic” “Women”
helps remember PBC is Idiopathic autoimmune disease of intrahepatic small bile ducts
MC in middle aged women
PSC is the opposite, doesn’t involve intrahepatic and typically occurs more in males
A pt presents with complaints of fatigue and pruritis. Upon PE you note jaundice, RUQ pain, hepatomegaly, and some signs of portal HTN. The diagnostics show + anti-mitochondrial Ab. --- what is the likely dx?
primary biliary cirrhosis (cholangitis)
What are the diagnostic tools for primary biliary cholangitis?
+ anti-mitochondrial antibody = hallmark*
↑ ALP w/ ↑ GGT, GGT often strikingly elevated, ↑ ALT, AST, bilirubin
Elevated IgM
Liver bx
What is the tx for primary biliary cholangitis?
Ursodeoxycholic acid 1st line