1.3.2b - negative externalities
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
negative externality meaning
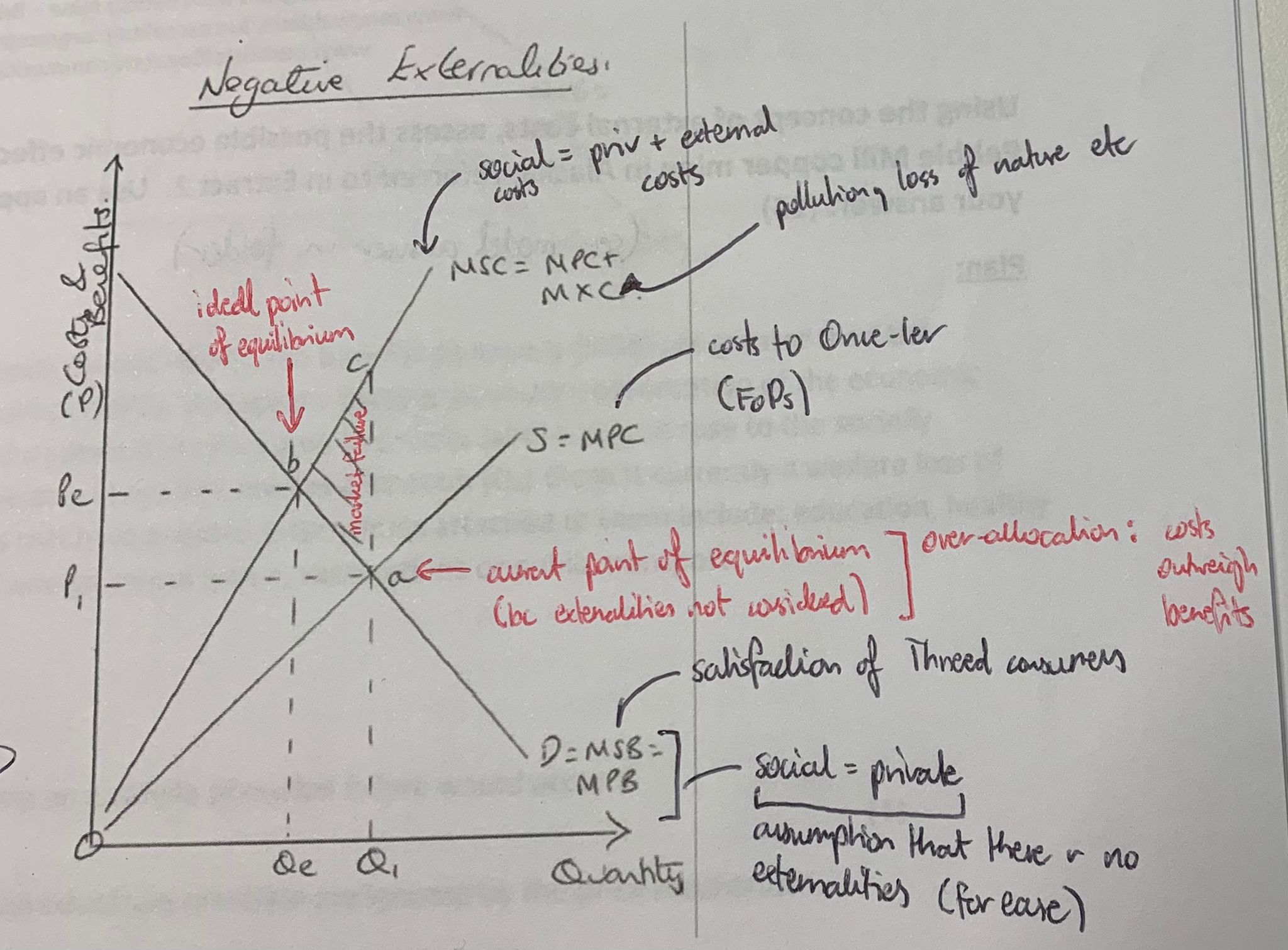
the costs to society are greater than the private costs of production
which curve does negative externality always affect
the supply curve
examples of external costs [of production]
pollution, loss of nature, litter, etc
when we have a graph showing negative externalities, what do we do with the demand curve
for ease, we assume there are no externalitites (only one line, social = private)
what is on the x and y axis of an externalities graph
y = costs and benefits (valued as price)
x = quantity
show a negative externalities graph
over-allocation means social costs outweigh social benefits, since the market failed to consider externalities
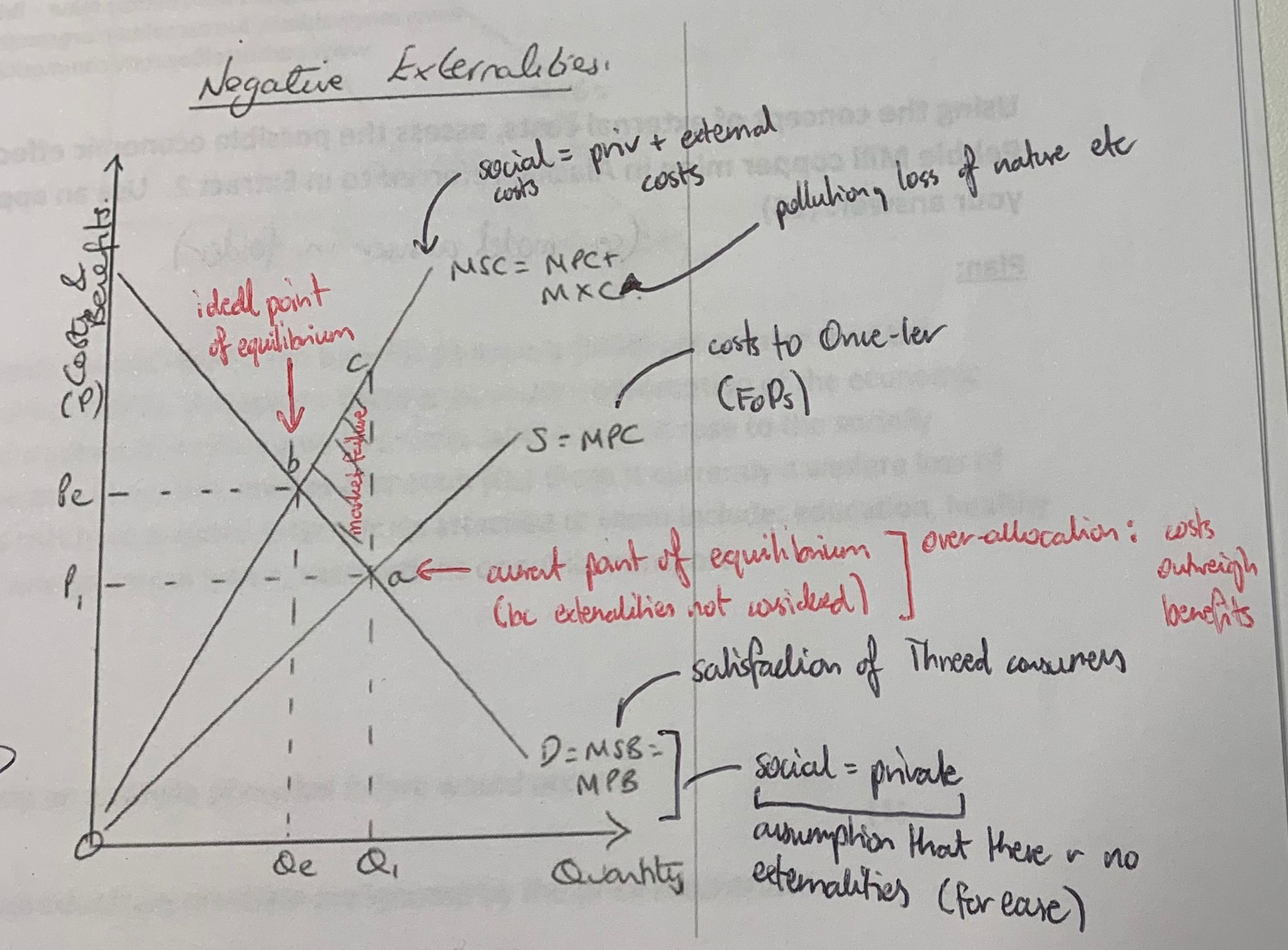
what does a negative externality mean
because social costs outweigh social benefits, there is a loss of welfare to society
represented by the triangle in the middle of the graph