Male Reproductive System and Gametogenesis Overview
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Zygote
Cell formed by fusion of male and female gametes.
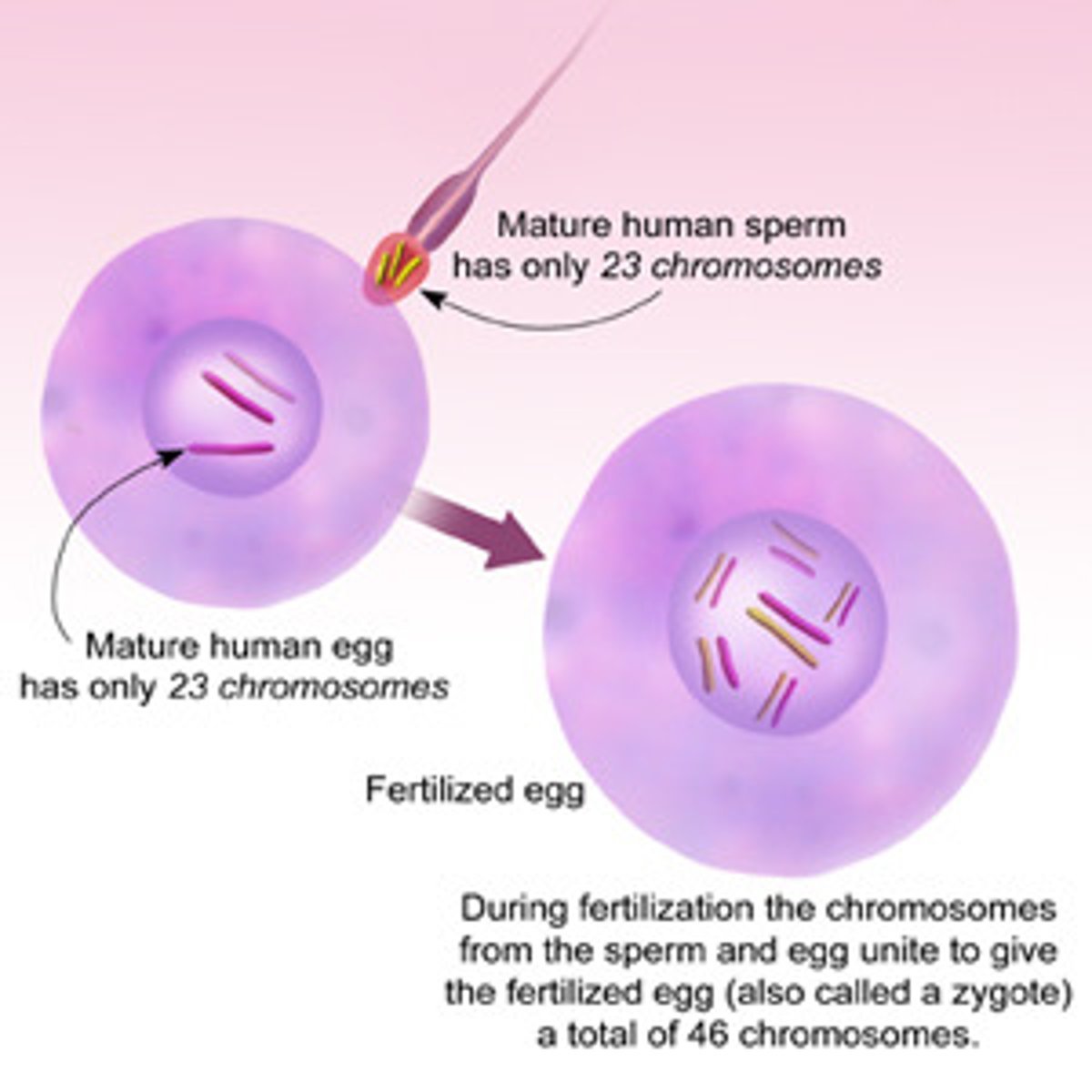
Sperm
Male gamete with motility for fertilization.
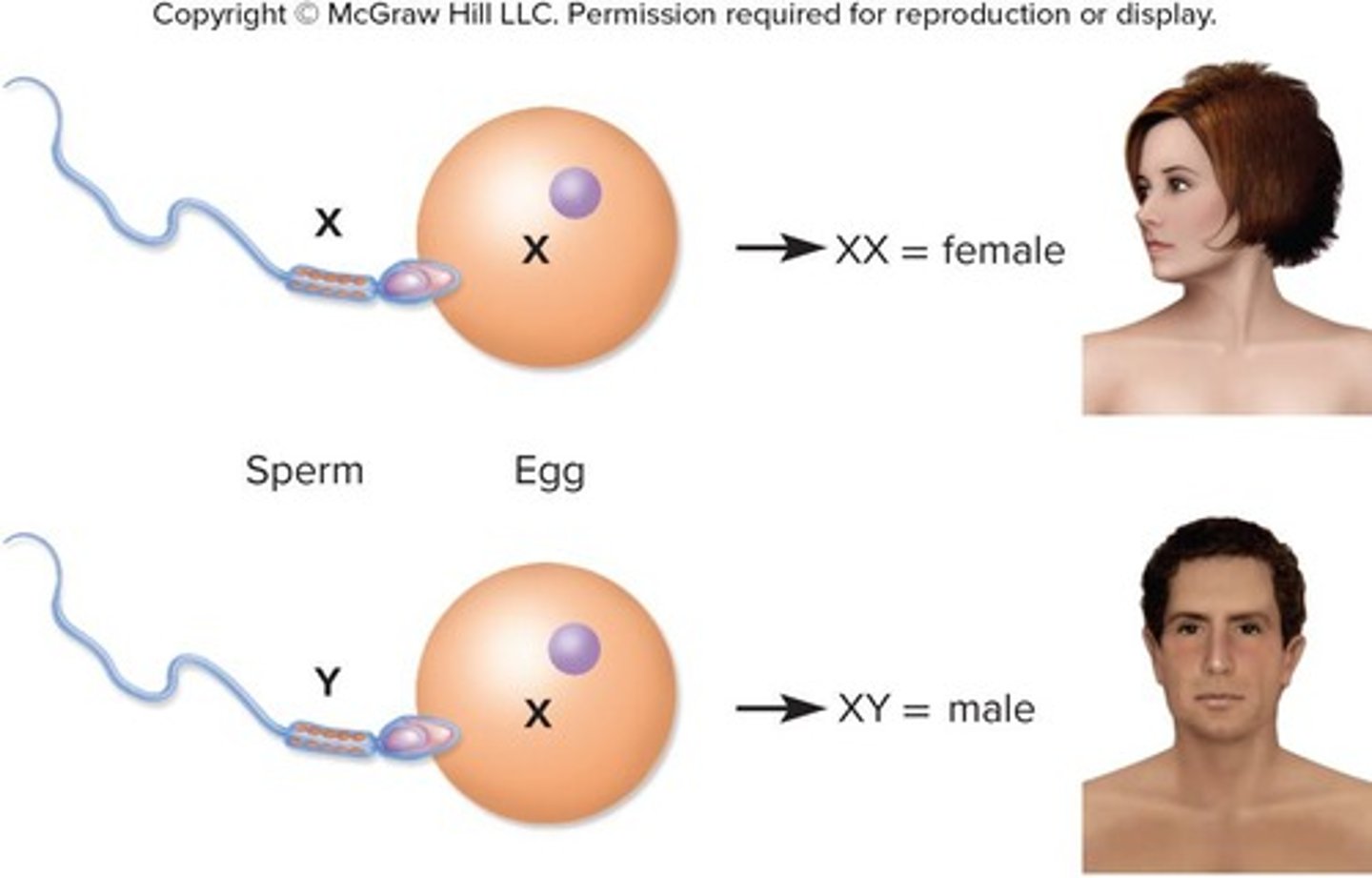
Y Chromosome
Chromosome determining male sex in mammals.
Egg (Ovum)
Female gamete providing nutrients for embryo.
Female Parent
Produces eggs and provides prenatal nutrition.
Male Parent
Produces sperm and carries Y chromosome.
Chromosomal Sex Determination
Sex determined by XX or XY chromosome pairs.
Autosomes
22 pairs of non-sex chromosomes in humans.
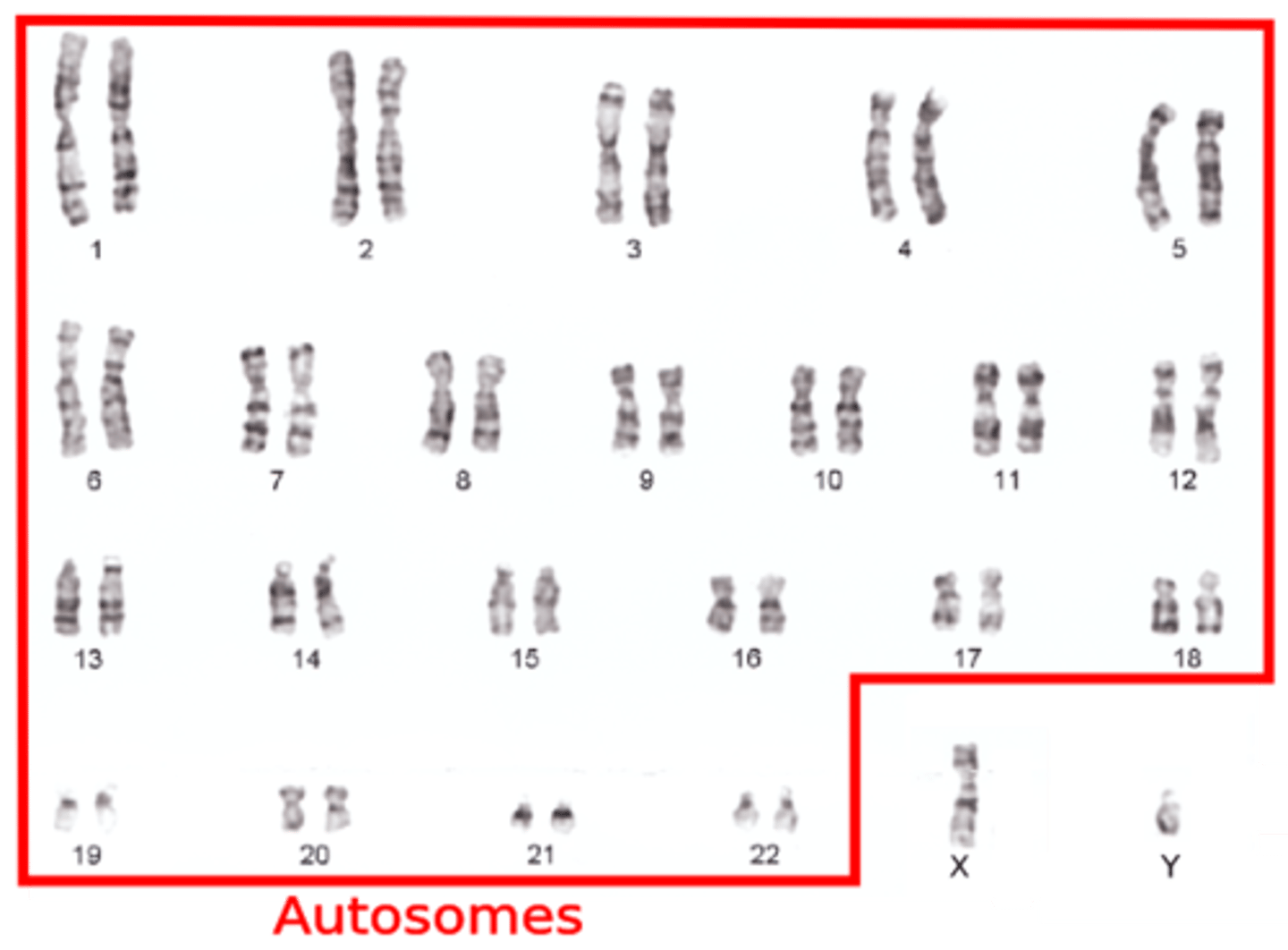
Sex Chromosomes
1 pair determining biological sex (XX or XY).
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm after mitosis or meiosis.
Interphase
Phase before cell division; cell prepares for mitosis.
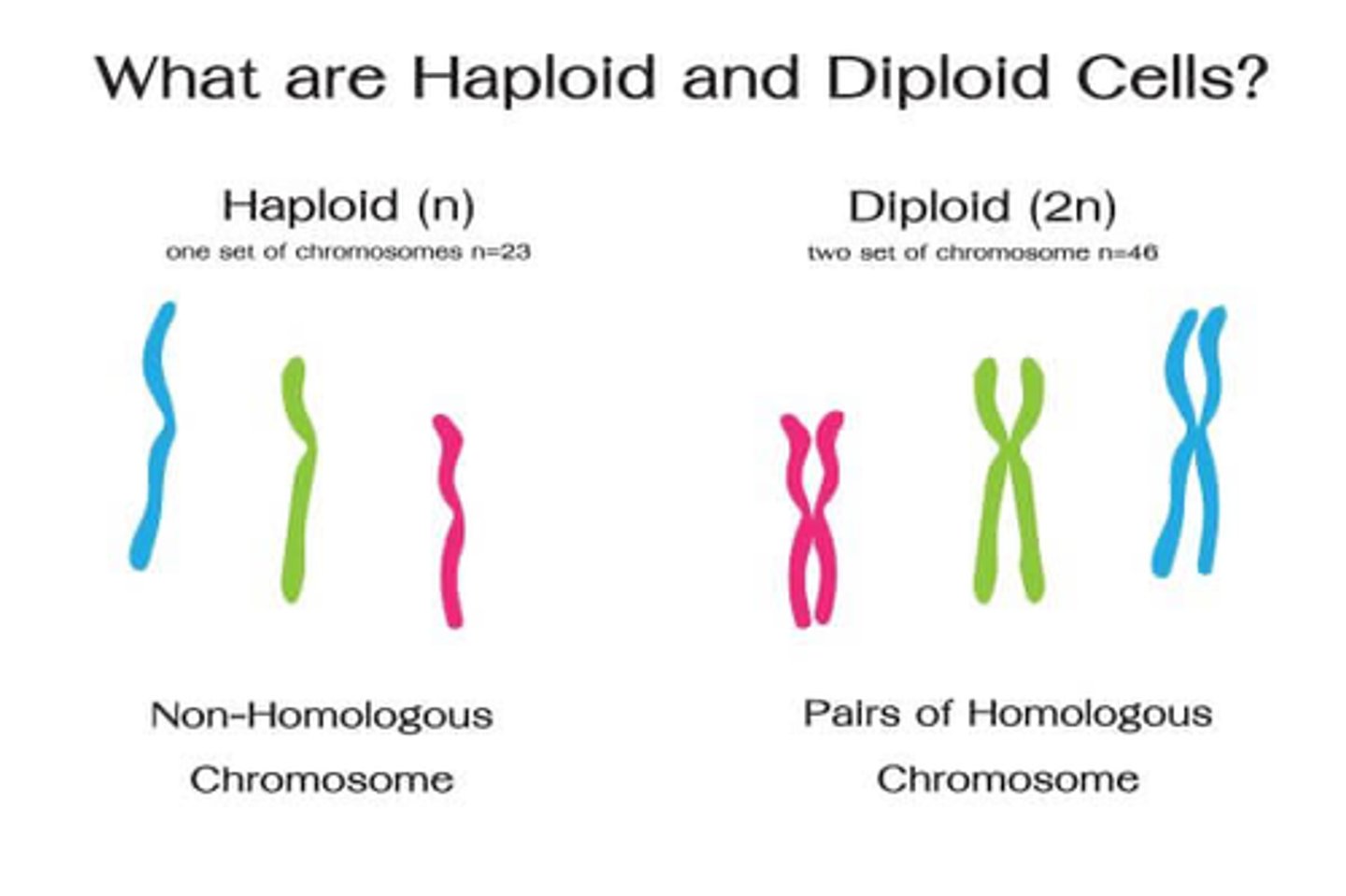
Diploid Cell
Cell with two complete sets of chromosomes.
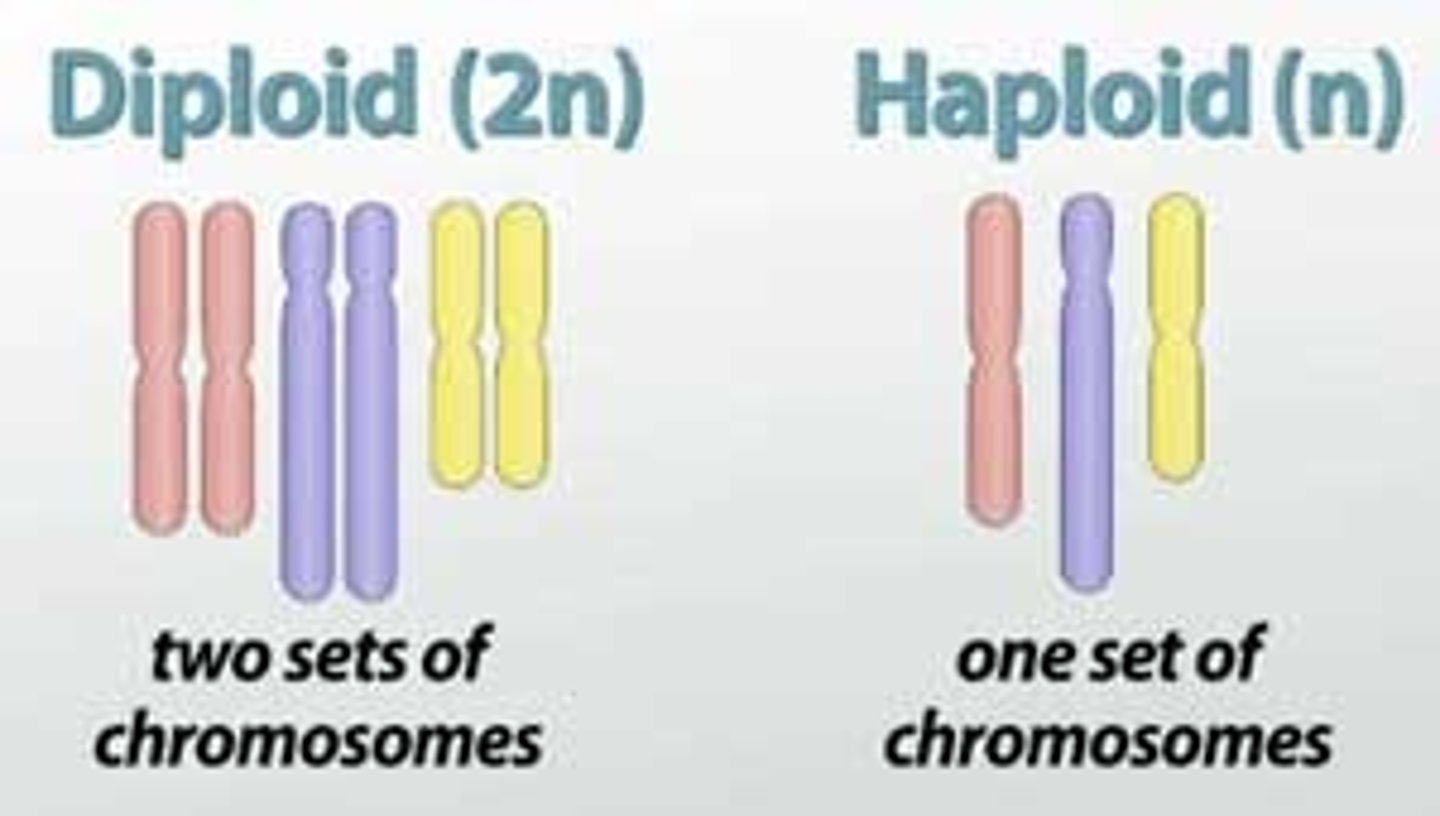
S Phase
Phase where DNA is replicated in interphase.
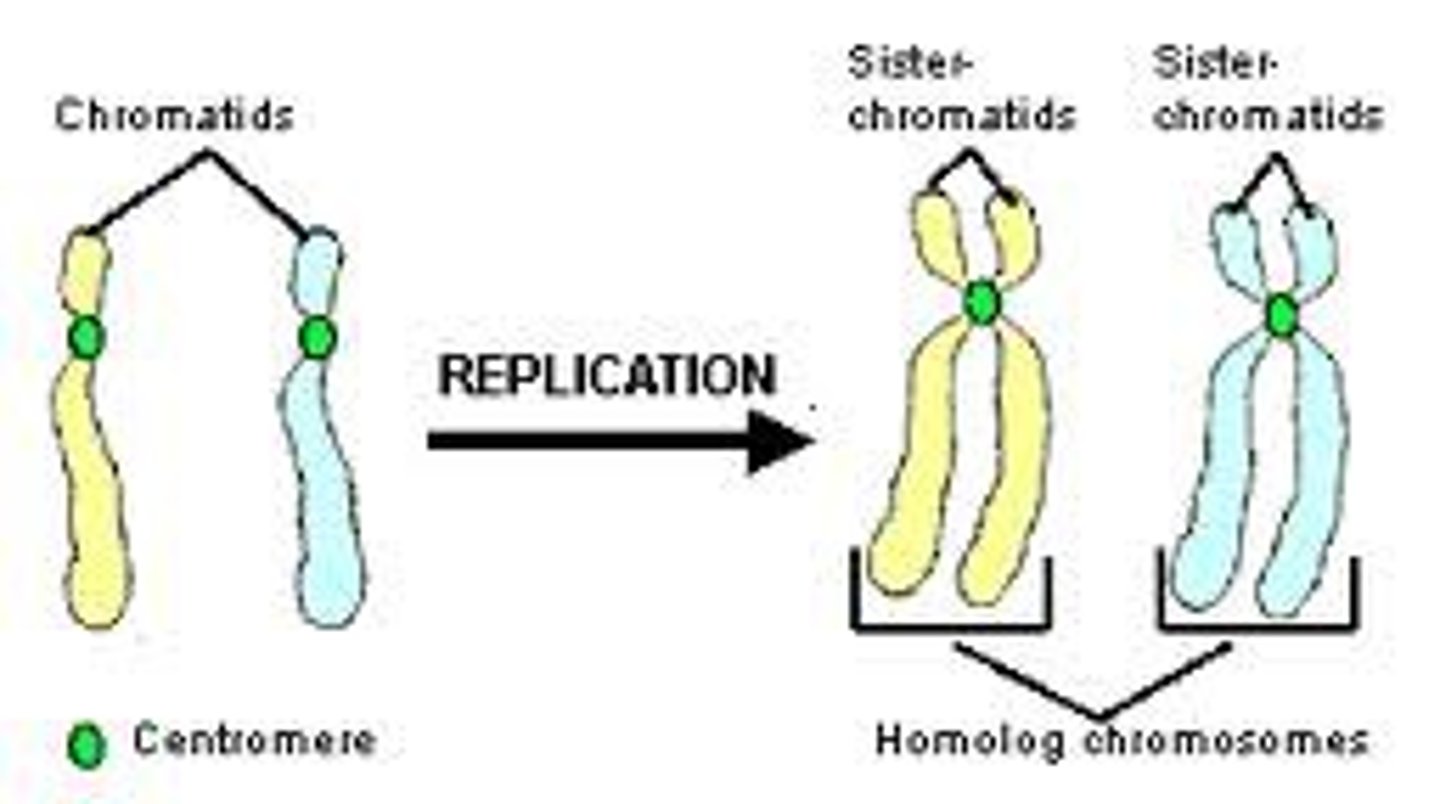
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible.

Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane.
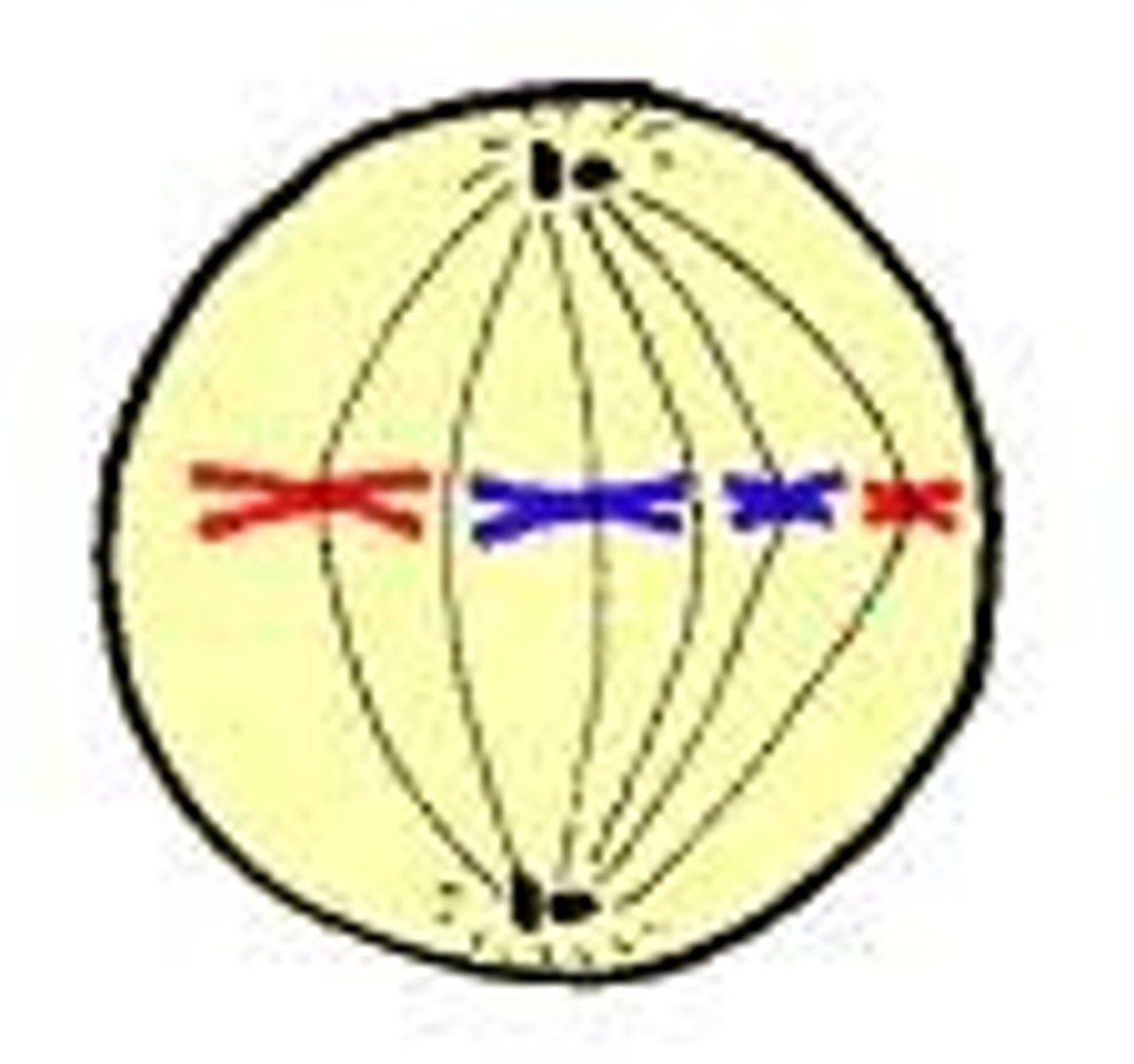
Anaphase
Homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids separate.
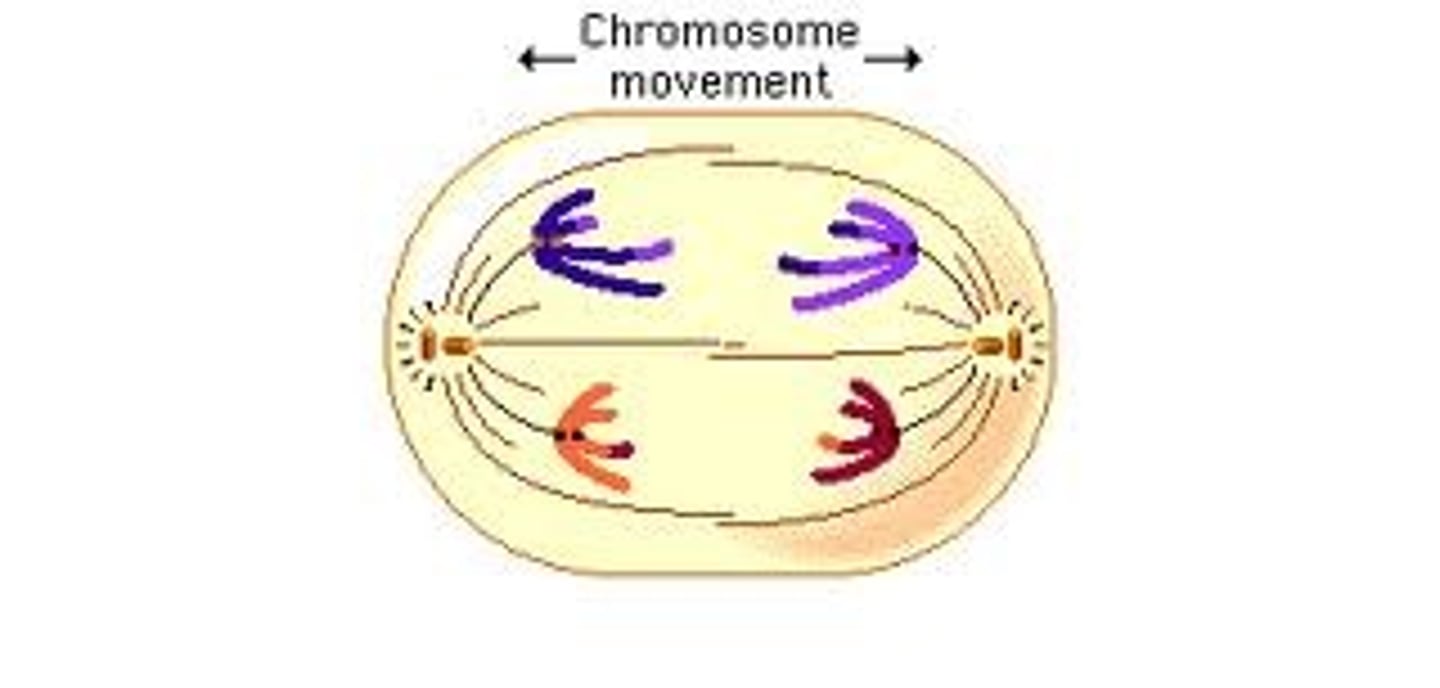
Telophase
Nuclear envelopes reform around separated chromosomes.
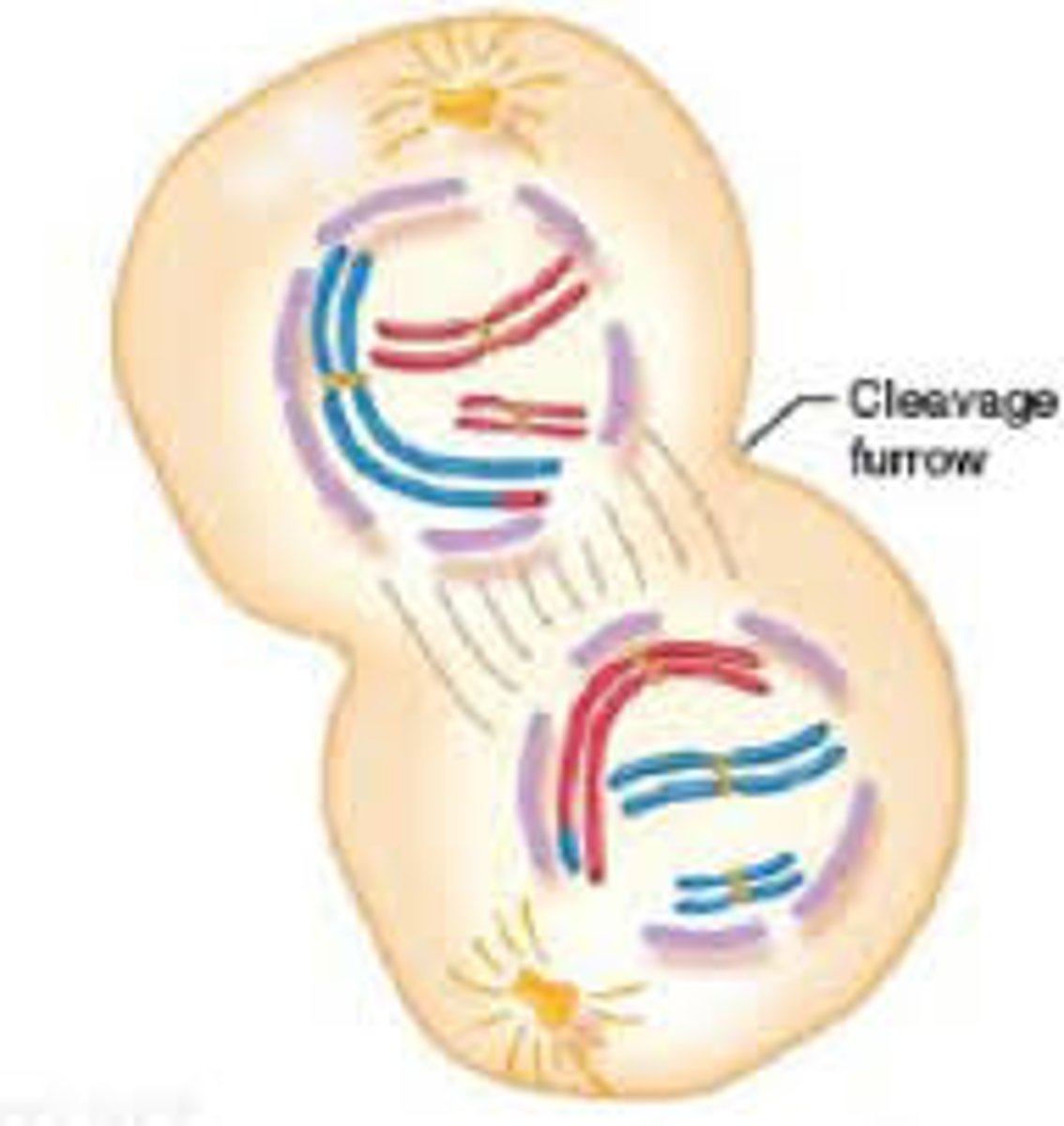
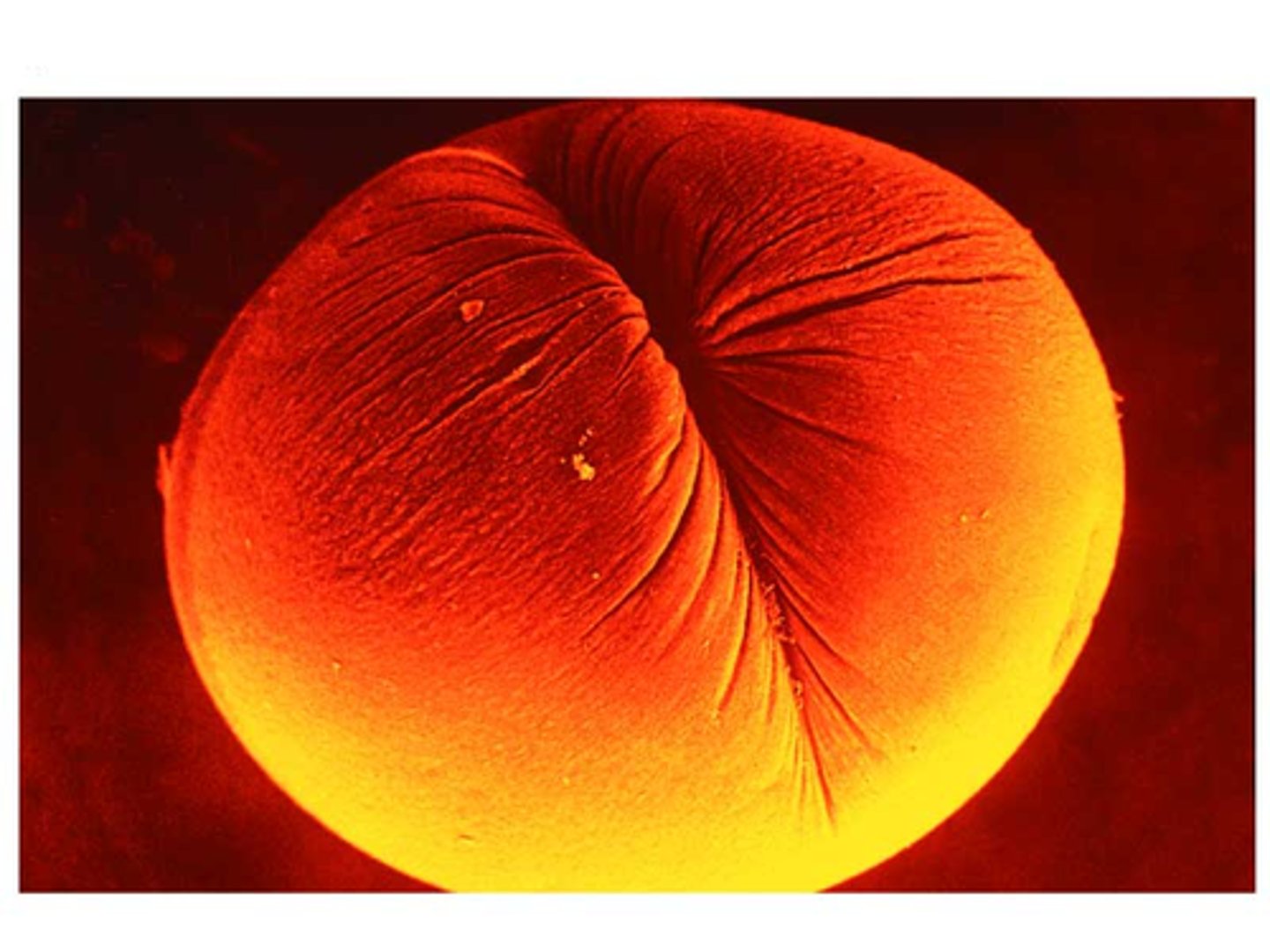
Cleavage Furrow
Indentation in the cell surface during cytokinesis.
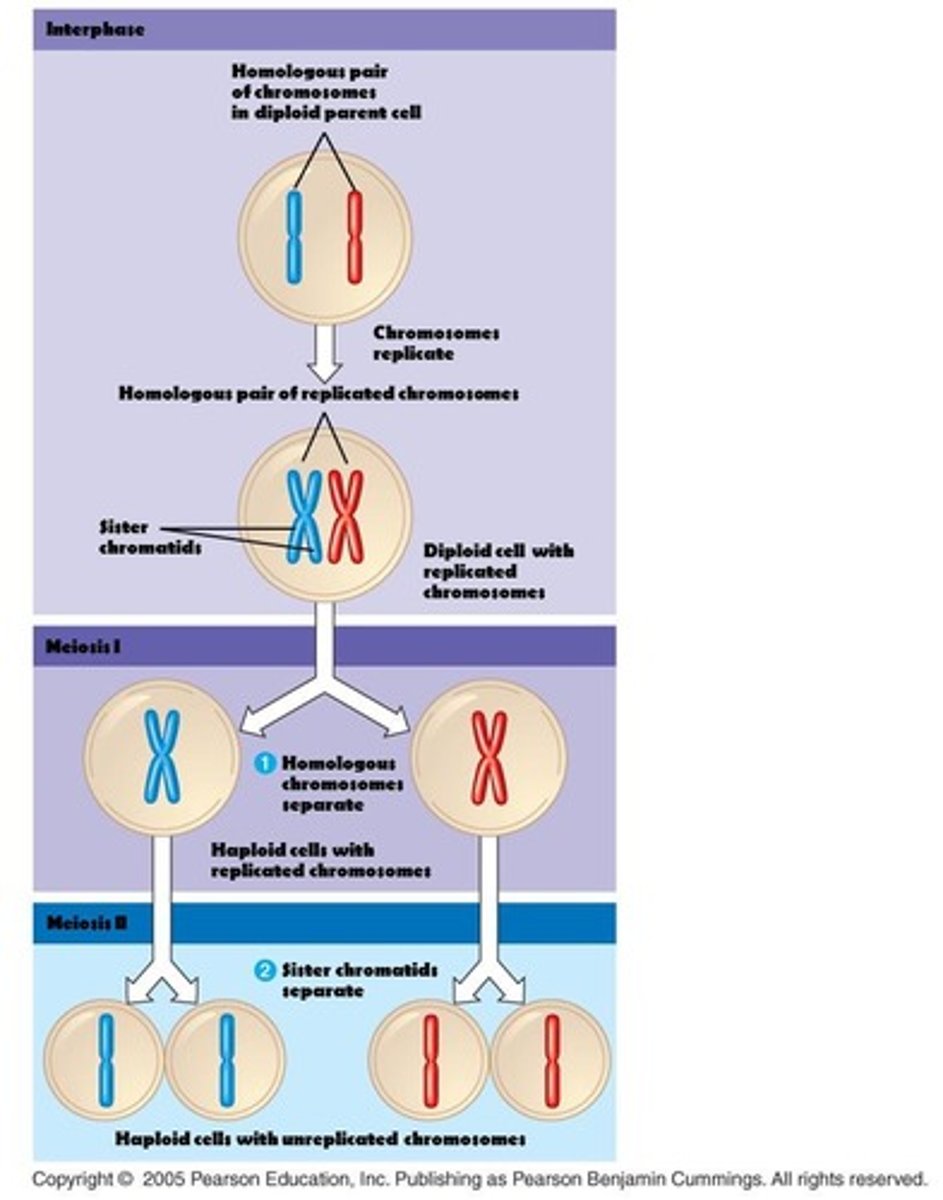
Meiosis
Two rounds of cell division producing four haploid cells.
Haploid Cell
A cell with ONE set of chromosomes, which is half of the regular (diploid) number.
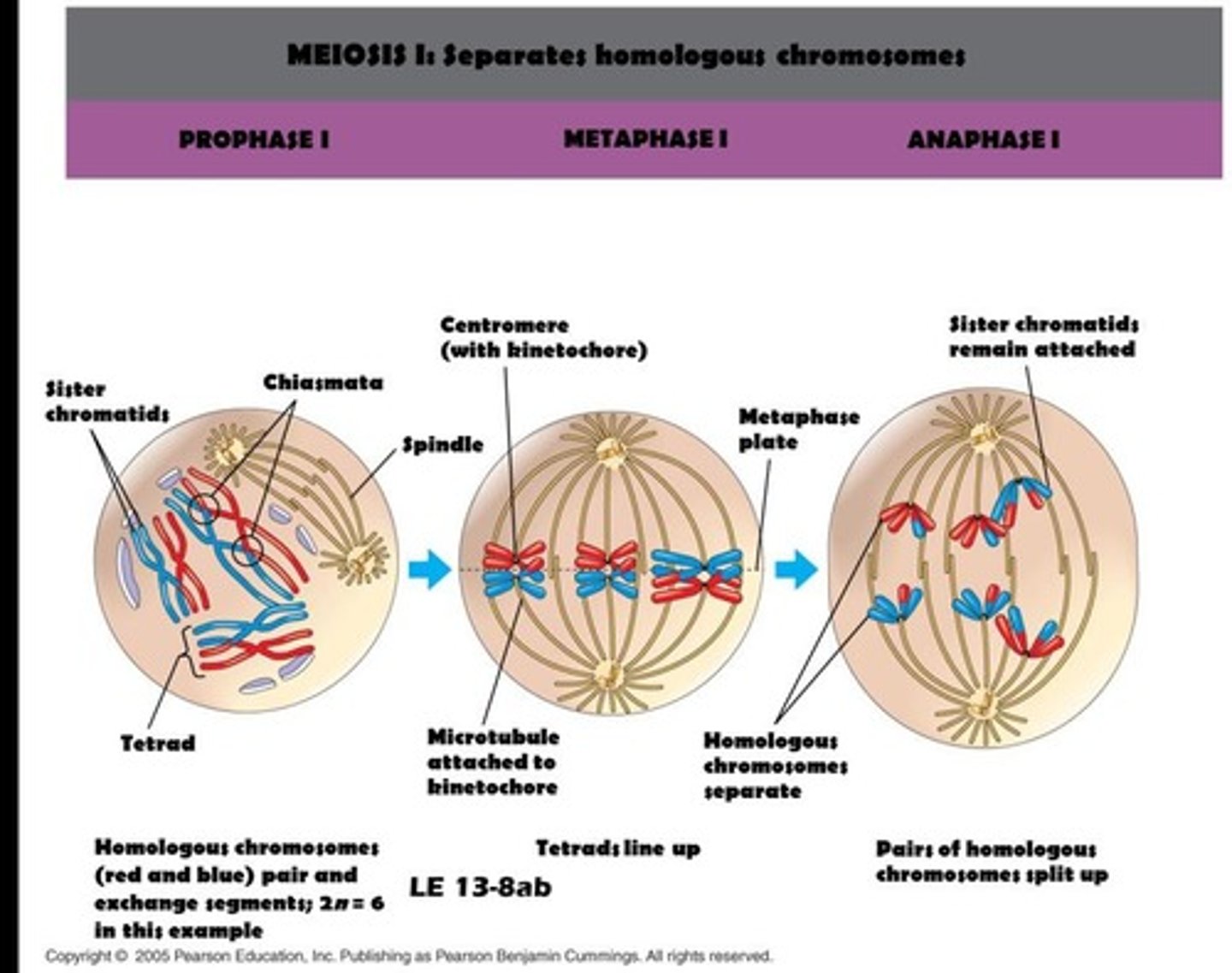
Meiosis I
First division; homologous chromosomes separate.
Meiosis II
Second division; sister chromatids separate.
Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes pair and exchange DNA segments.
Tetrad
Structure formed by homologous chromosomes during prophase I.
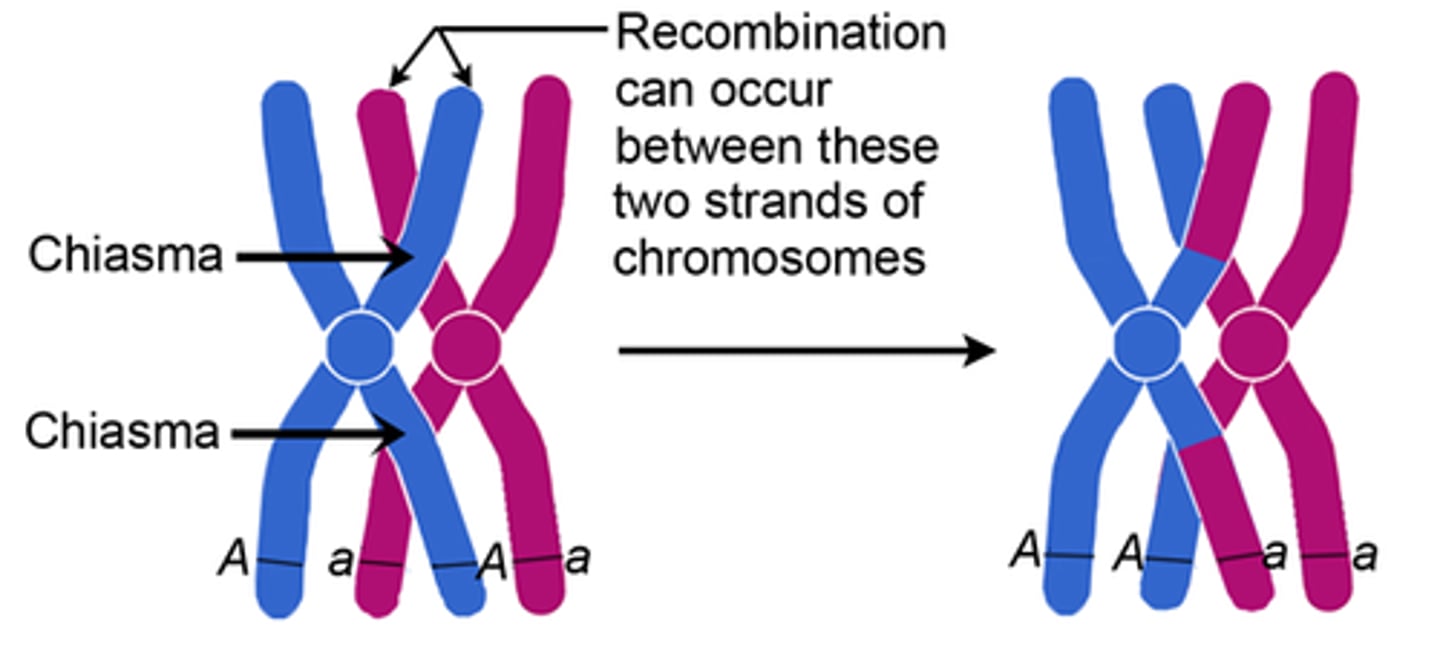
Crossover
Exchange of genetic material between nonsister chromatids.
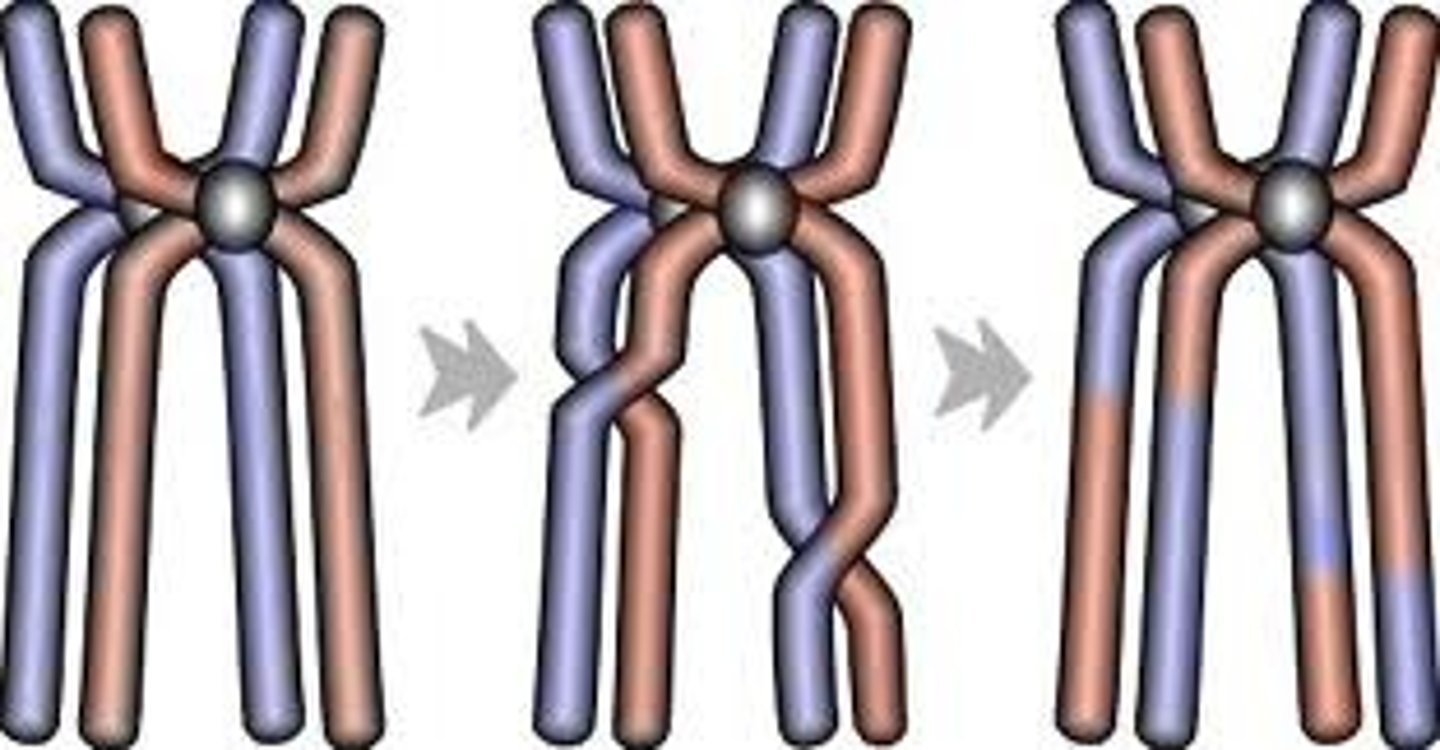
Chiasmata
X-shaped regions where crossing over occurs.
Metaphase I
Tetrads align at the metaphase plate.
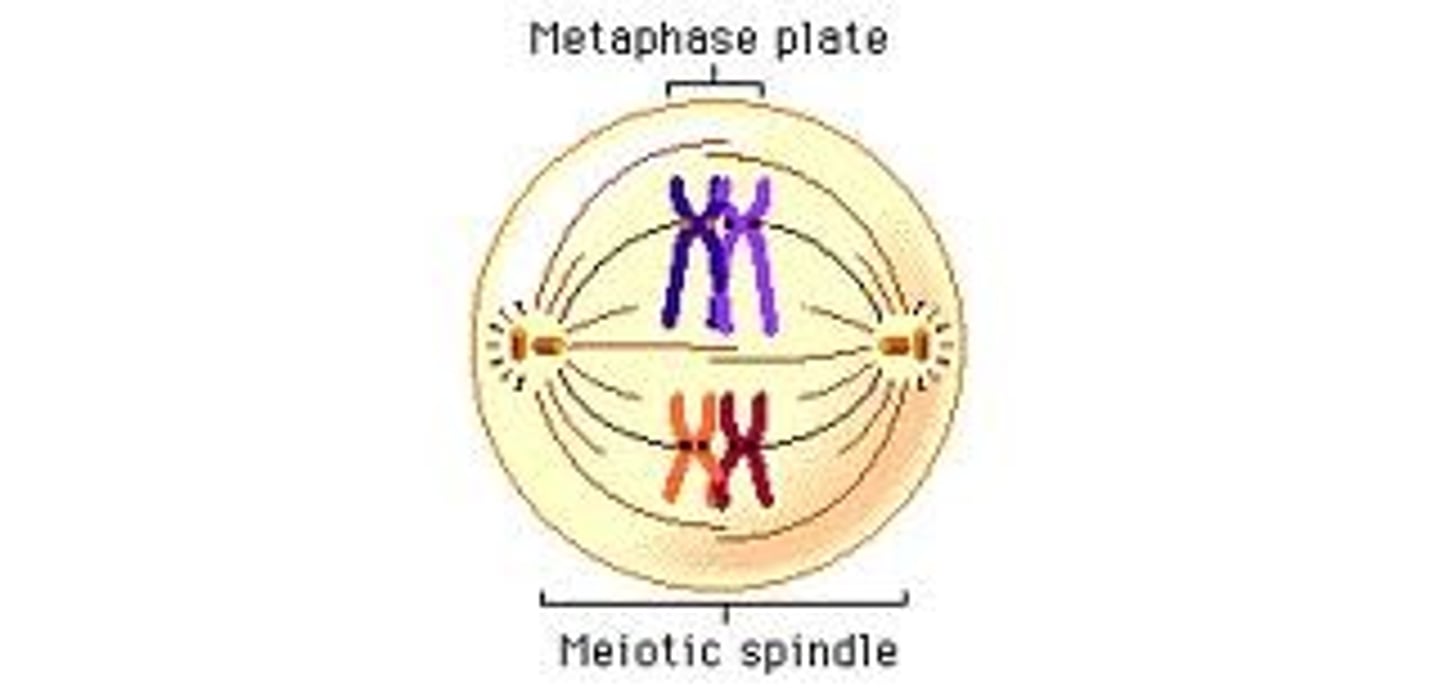
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles.
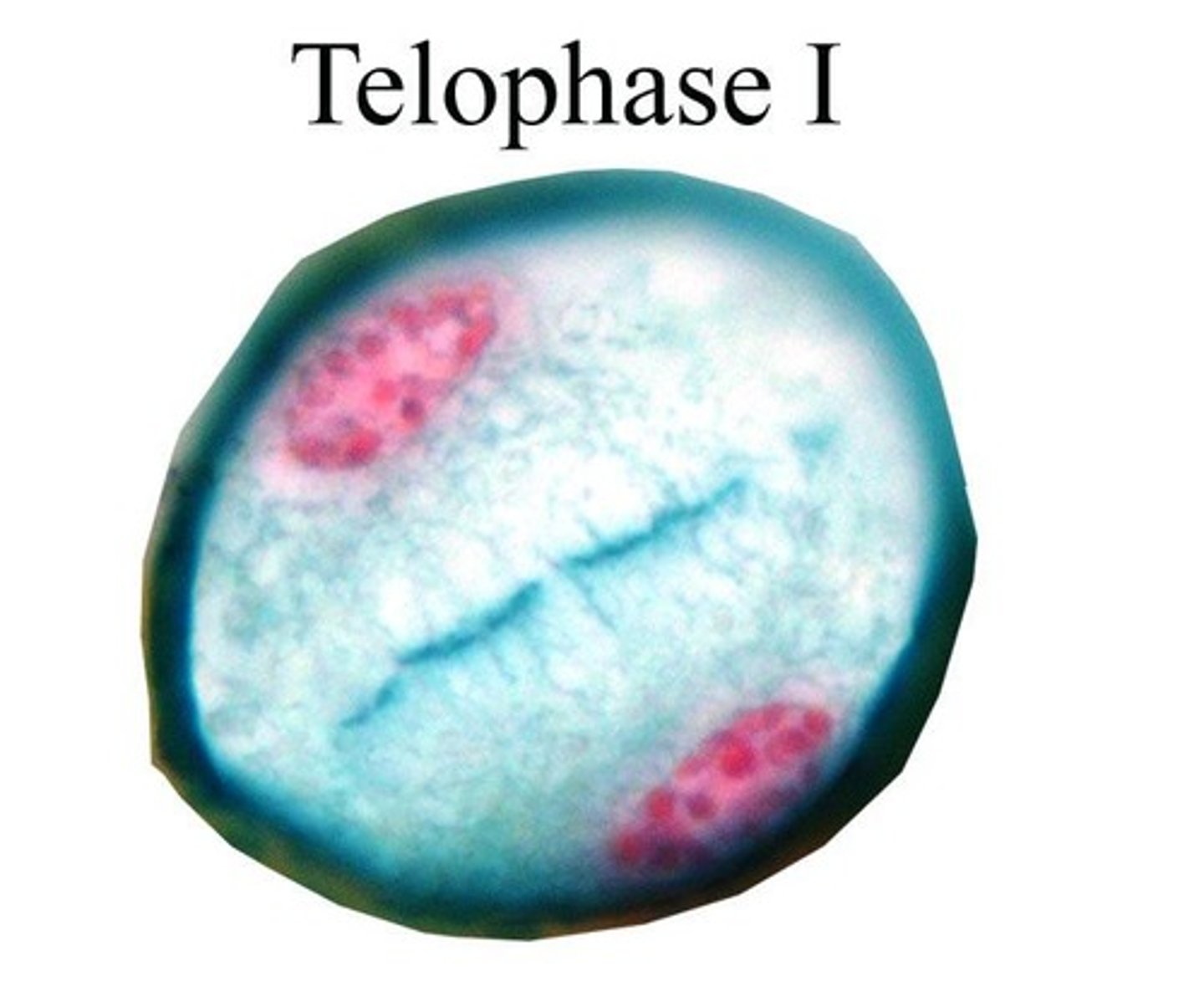
Telophase I
Nuclear envelopes form; cytokinesis produces two haploid cells.
Prophase II
Spindle apparatus forms; similar to mitosis.
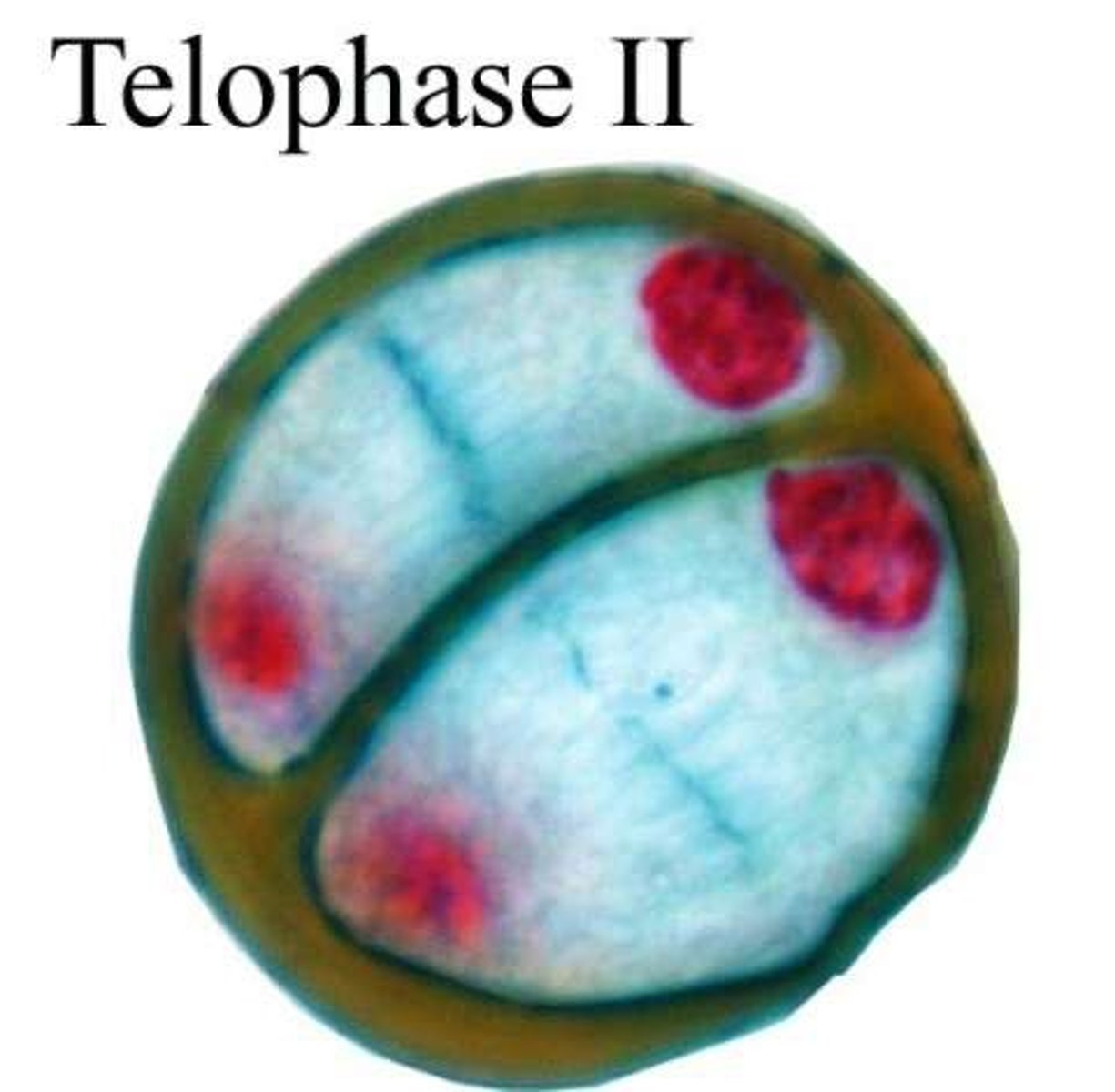
Telophase II
Nuclear envelopes reform; cytokinesis produces four distinct cells.
Gametes
Haploid cells formed from meiosis, used in reproduction.
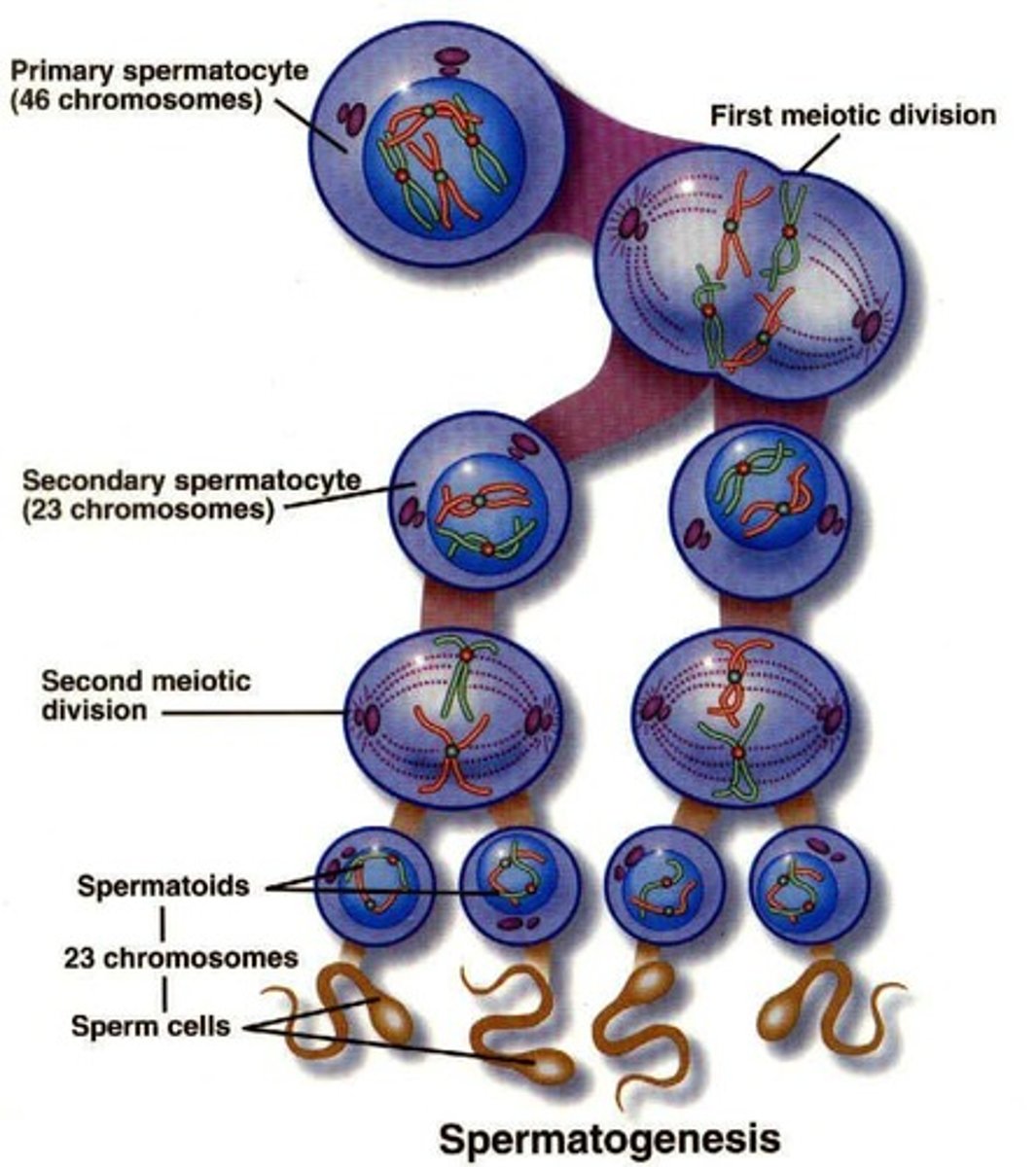
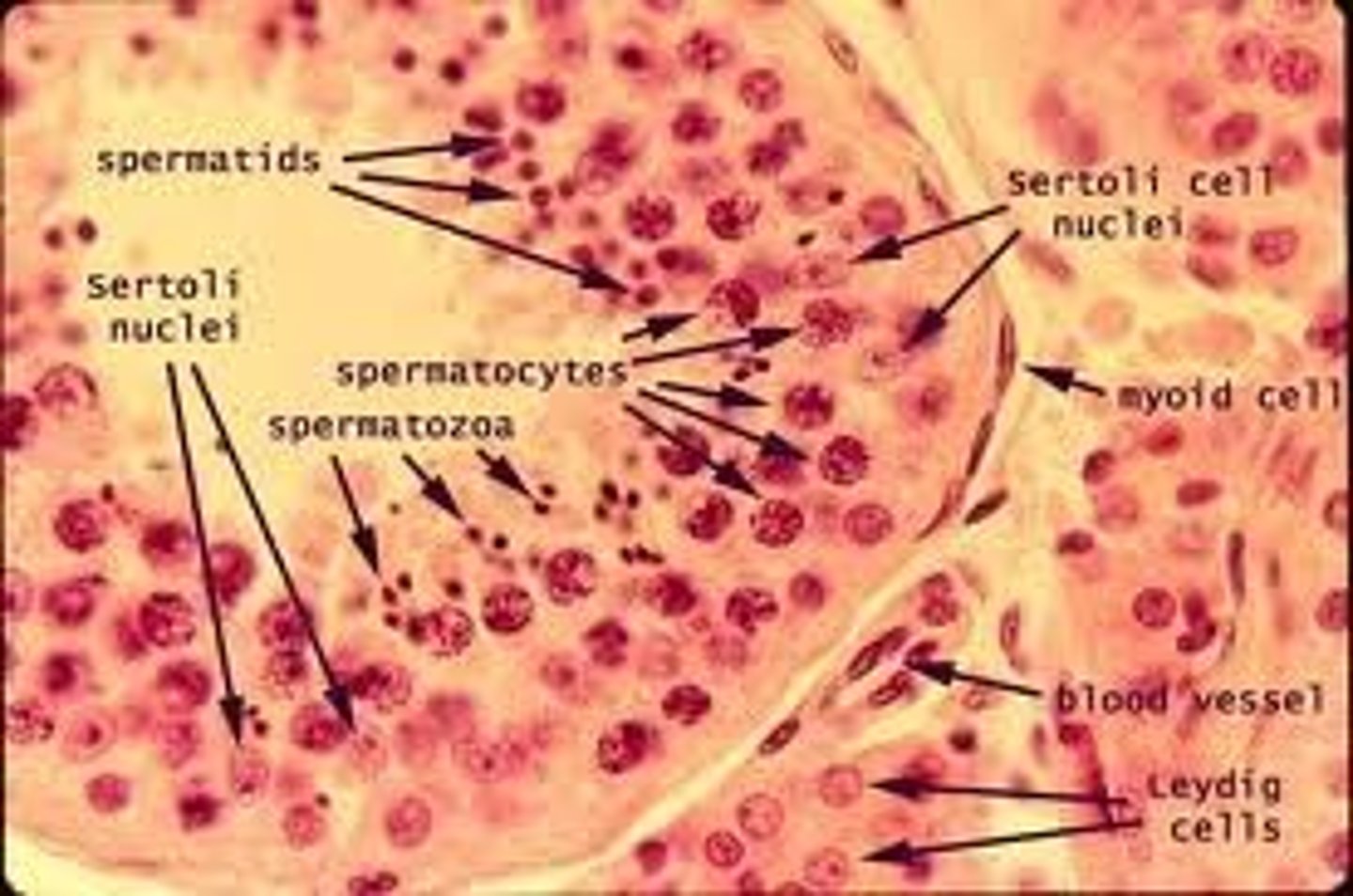
Spermatogenesis
Process of sperm cell development involving mitosis and meiosis.
Spermiogenesis
Process of sperm maturation in seminiferous tubules.
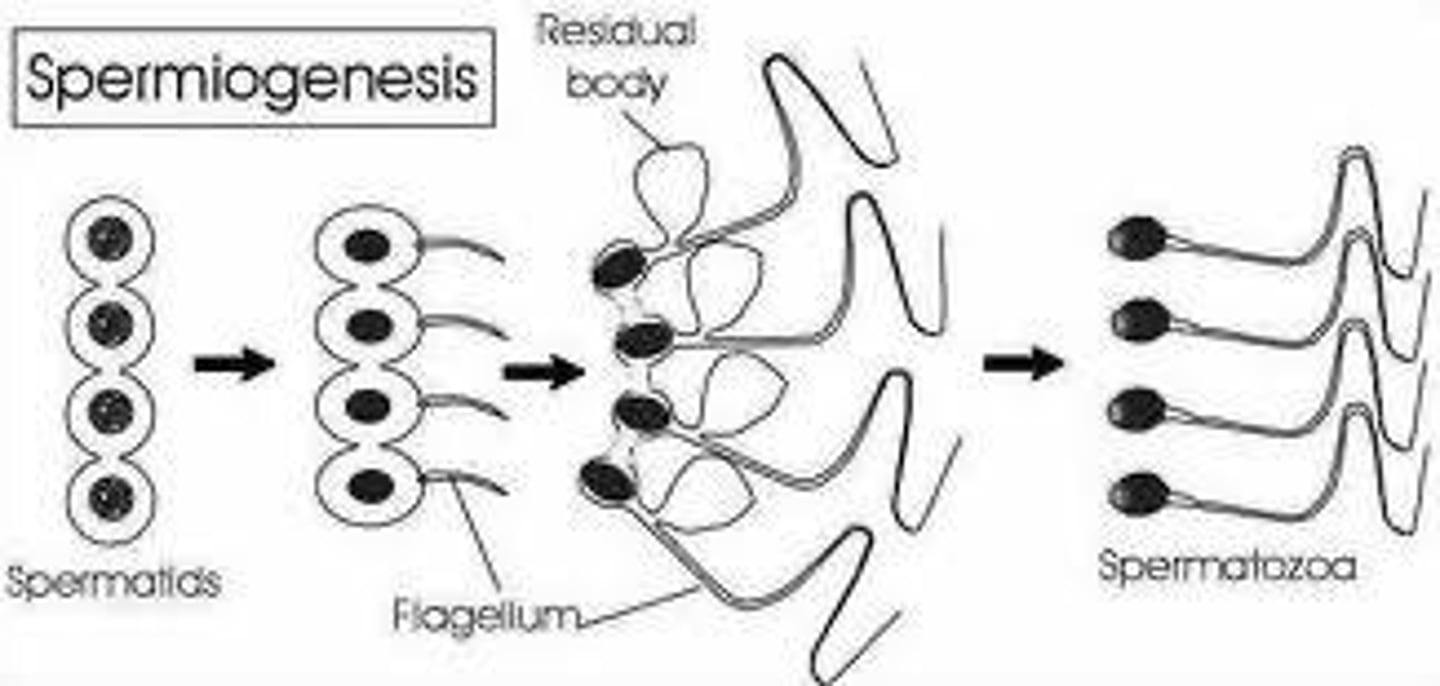
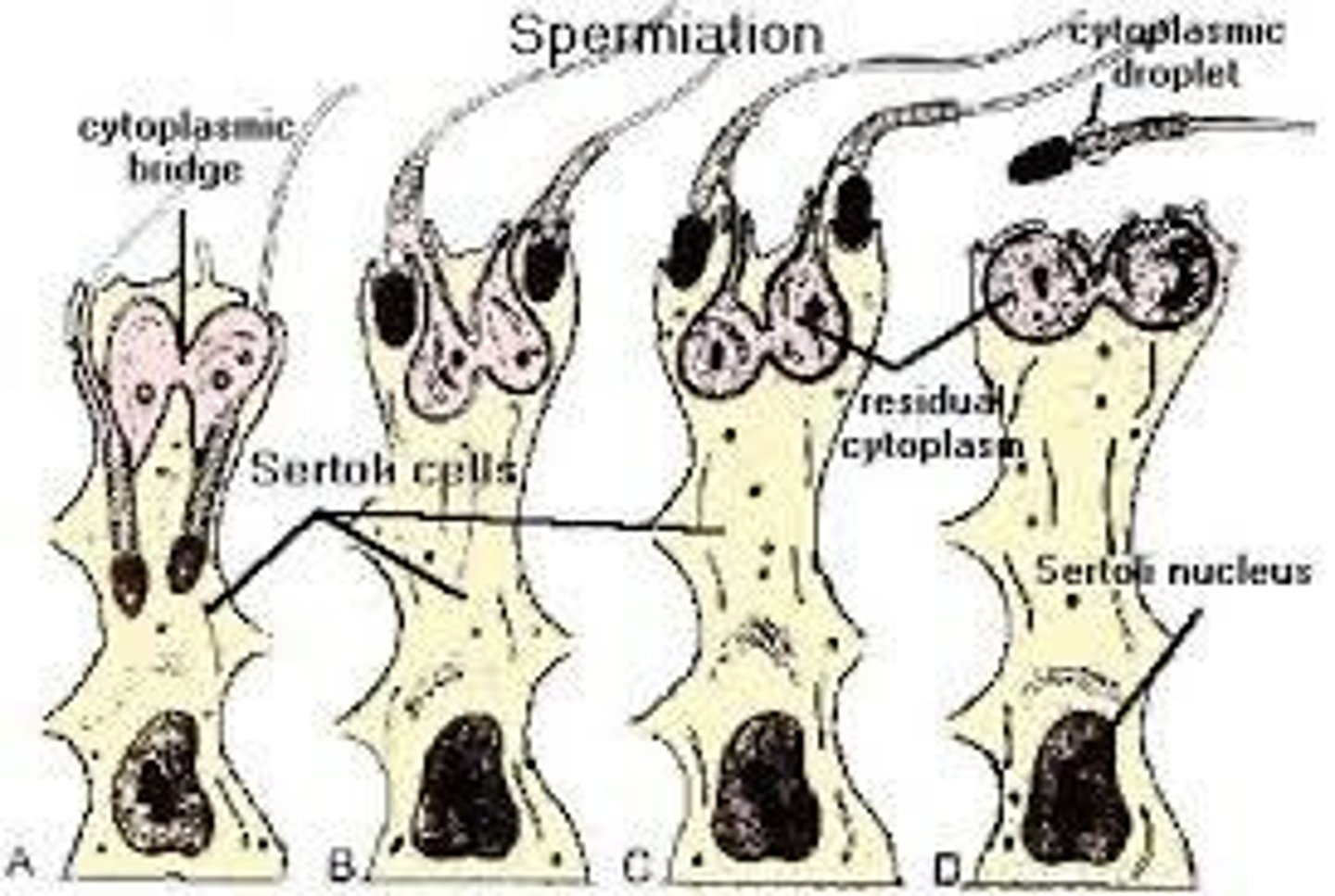
Spermiation
Release of spermatozoa into seminiferous tubule lumen.
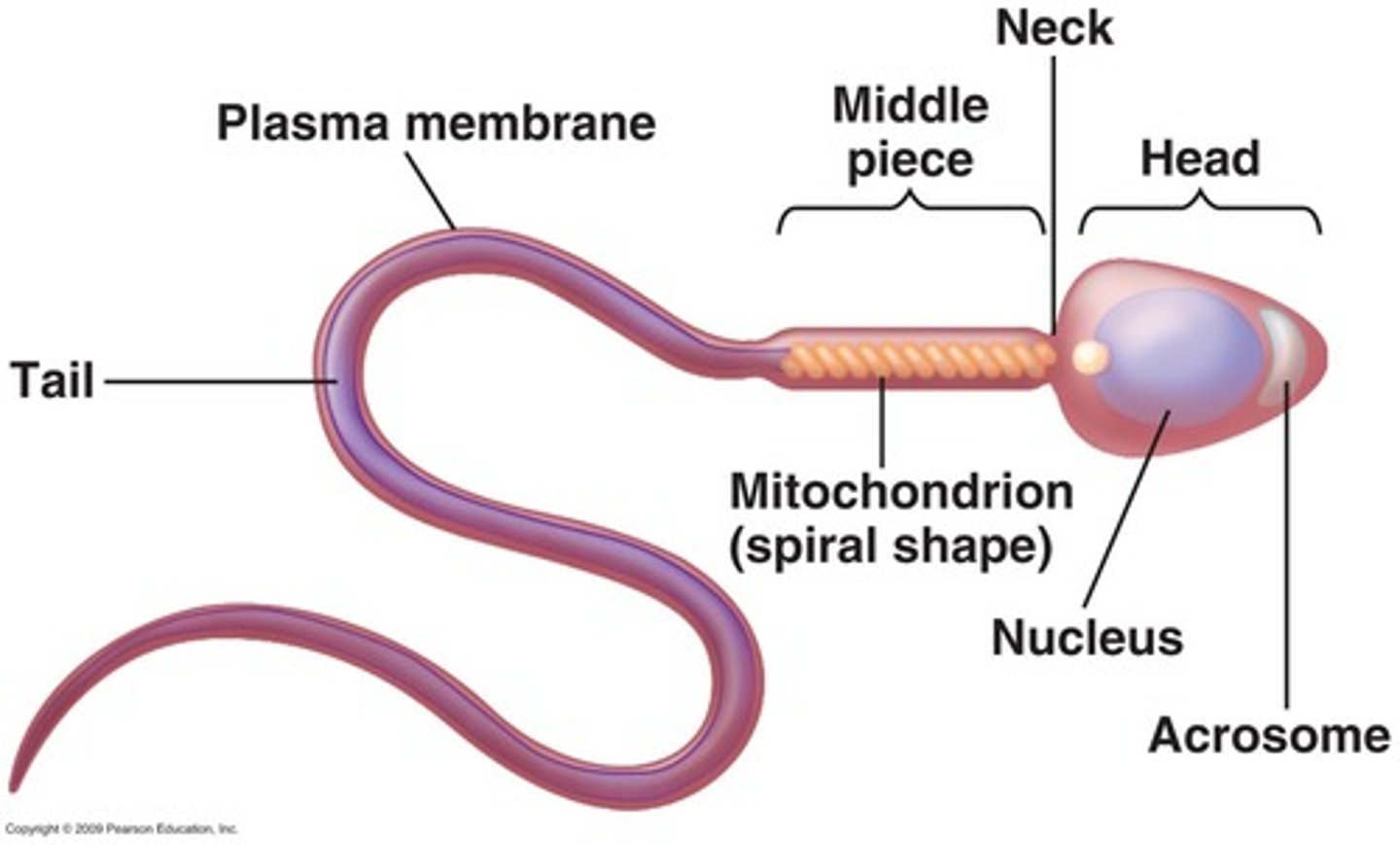
Spermatozoan
Mature male gamete involved in reproduction.
Acrosome
Cap on sperm head containing enzymes for fertilization.
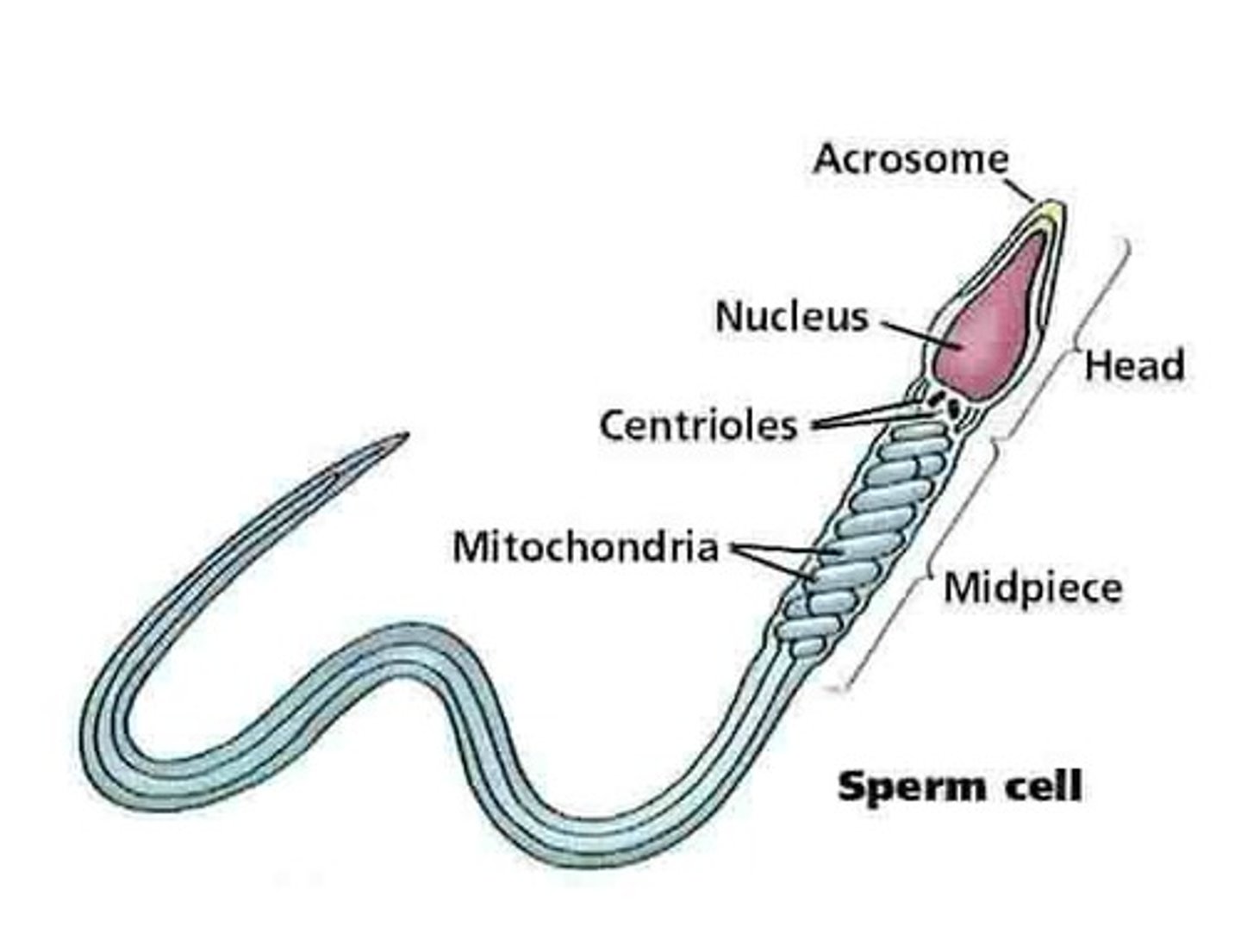
Middle piece of sperm
Contains mitochondria for ATP production.
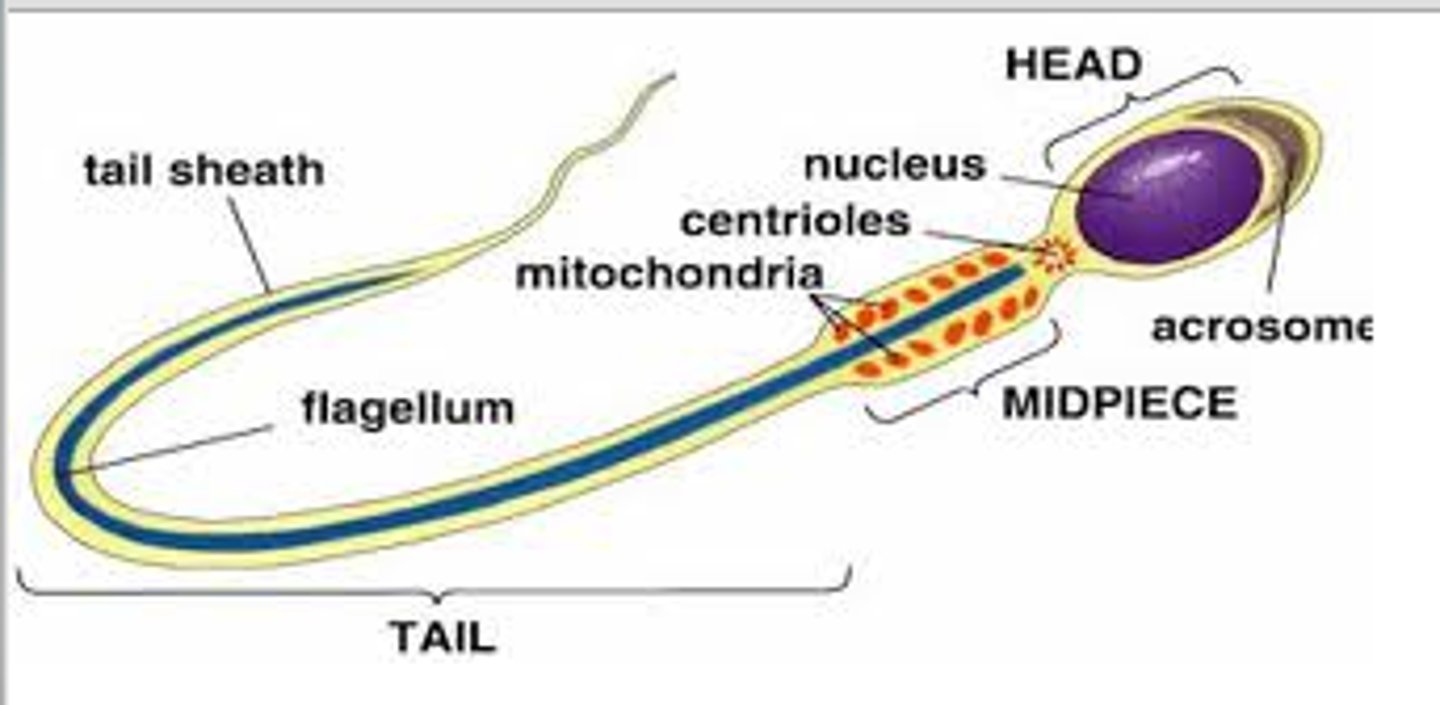
Tail of sperm
Enables motility with corkscrew motion.
Gubernaculum testis
Connective tissue guiding testis descent.
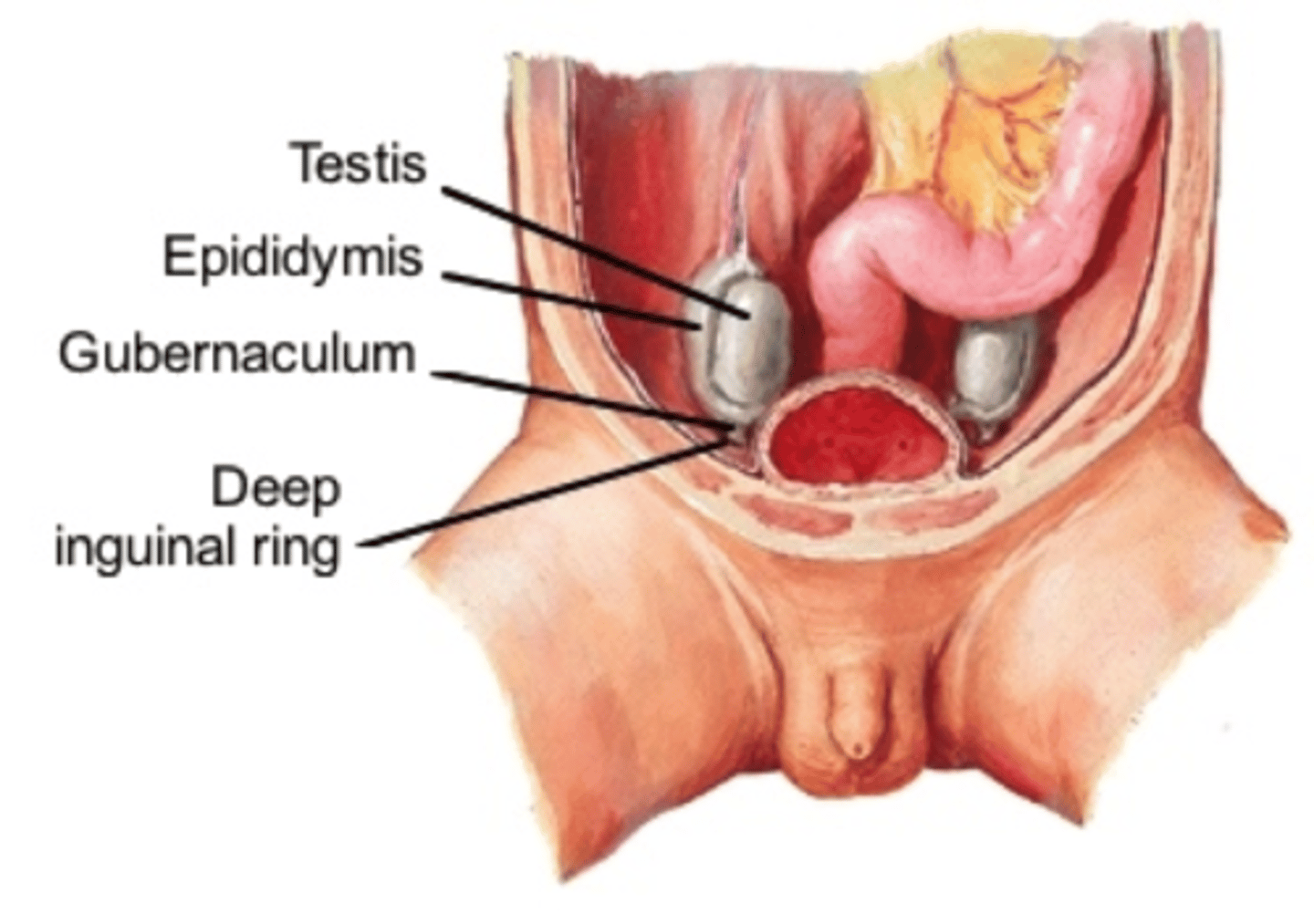
Scrotum
Pouch containing testes, regulates temperature.
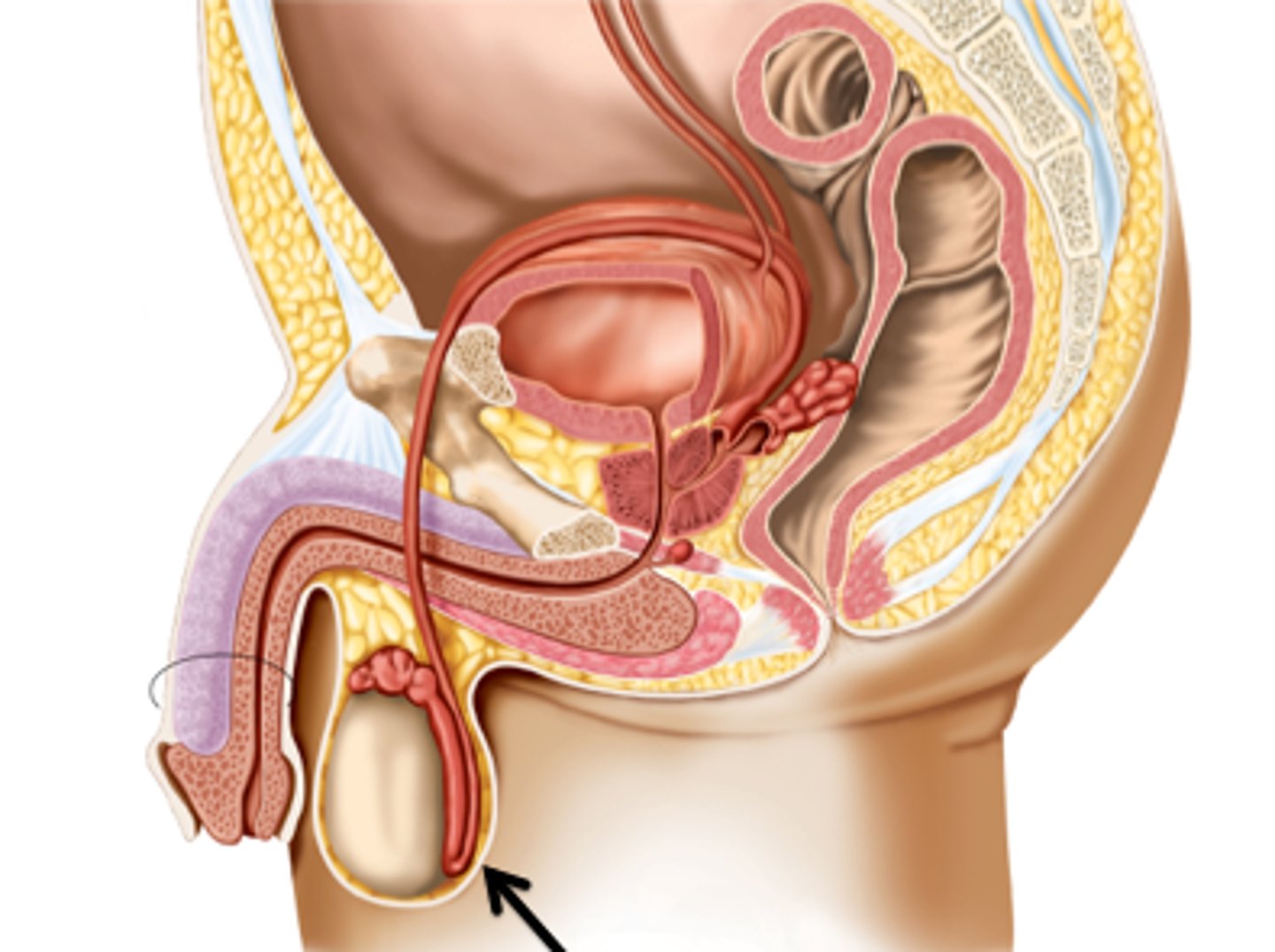
Cremaster muscle
Adjusts testis position for temperature control.
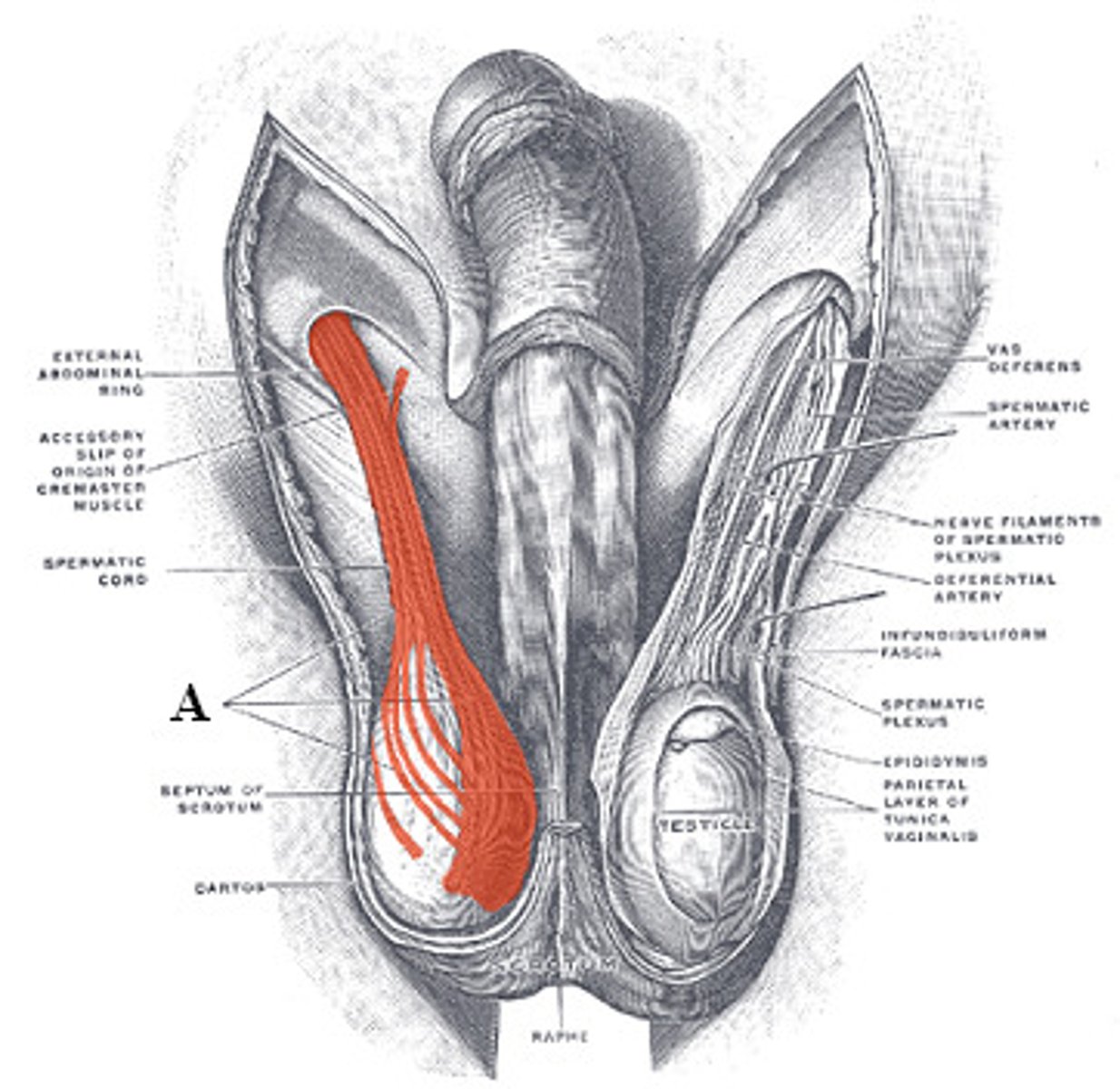
Dartos fascia
Contracts to wrinkle scrotum, reducing heat loss.
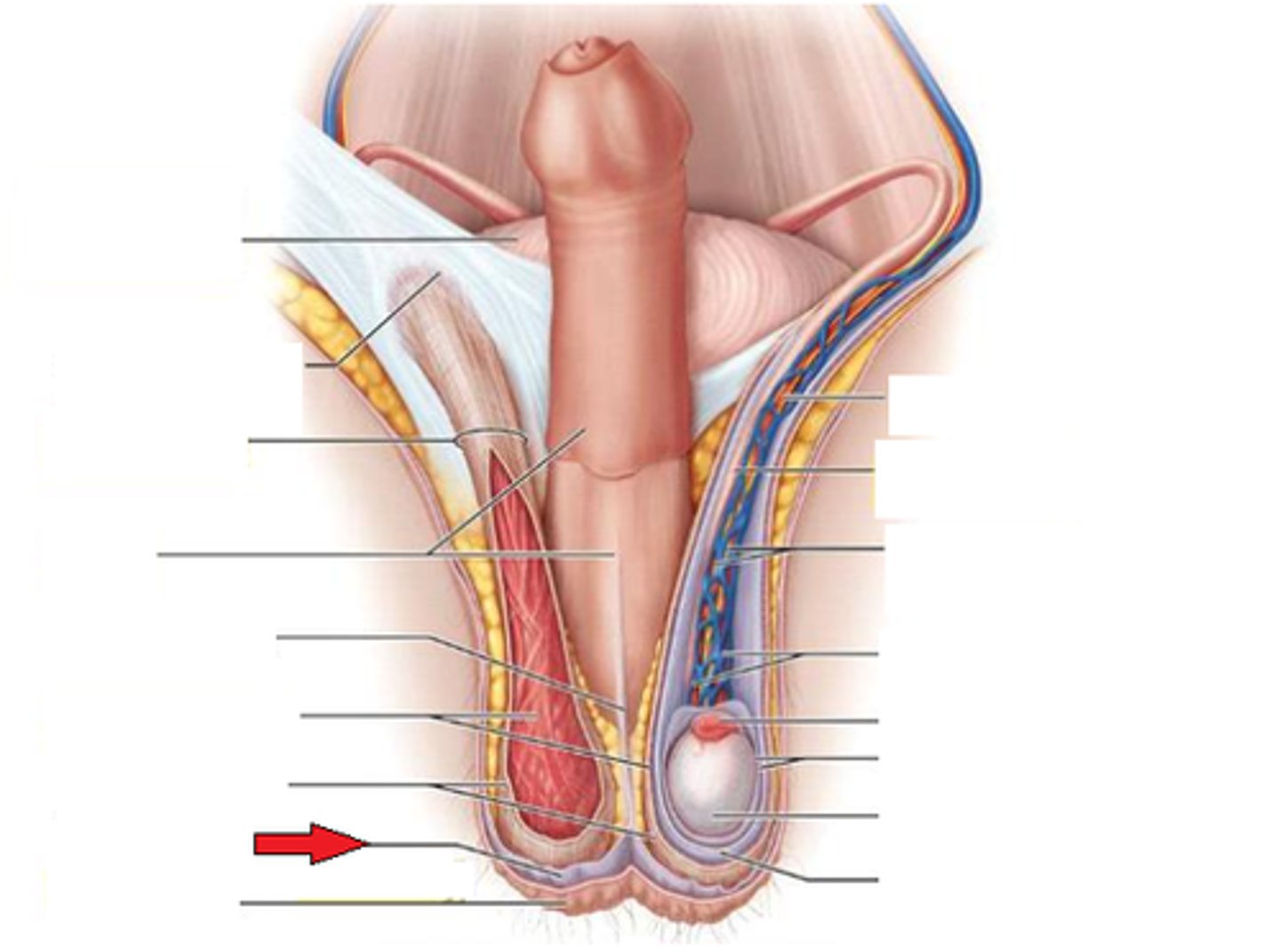
Pampiniform plexus
Venous network cooling arterial blood to testes.
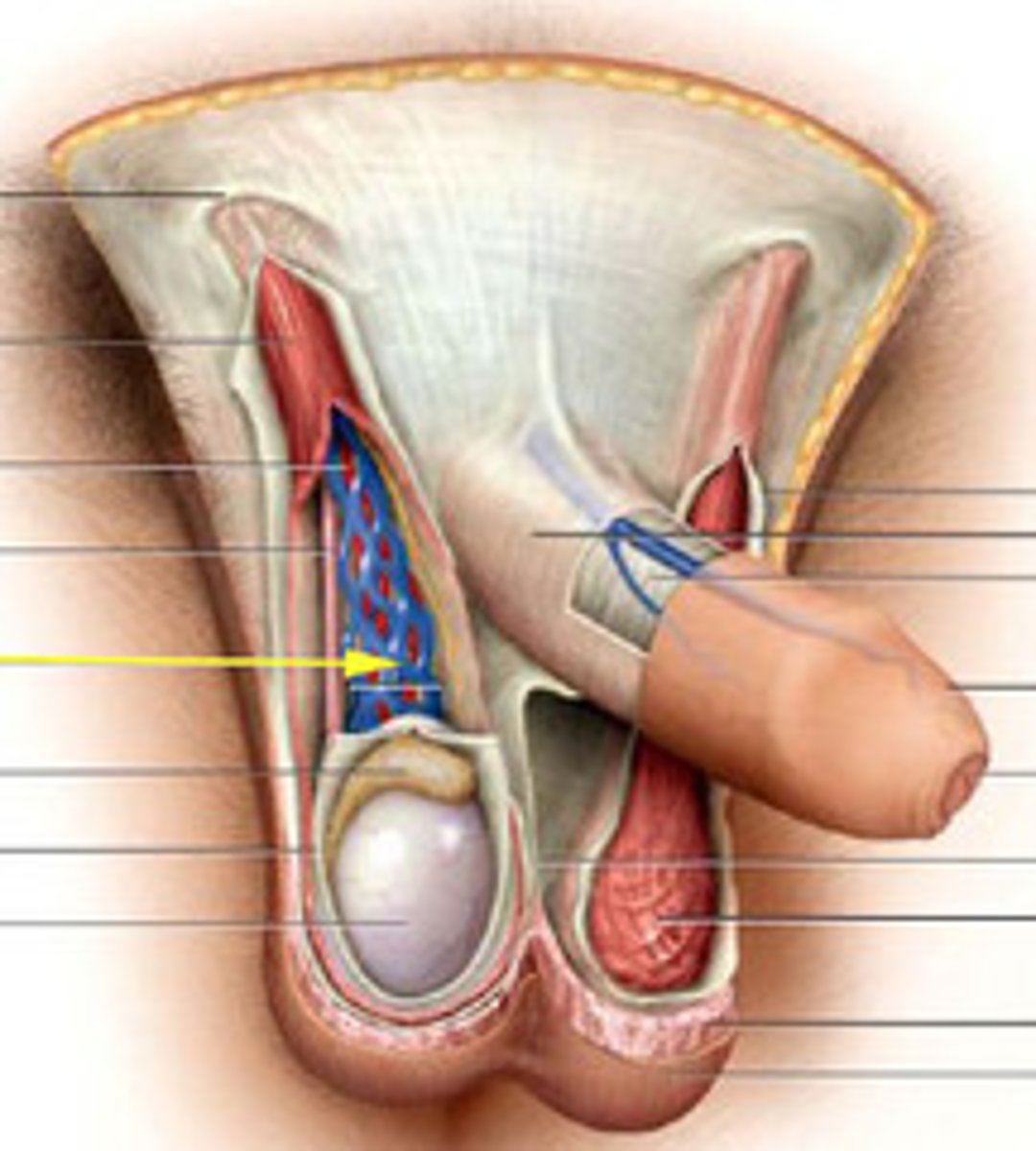
Tunica albuginea
Fibrous capsule surrounding each testis.
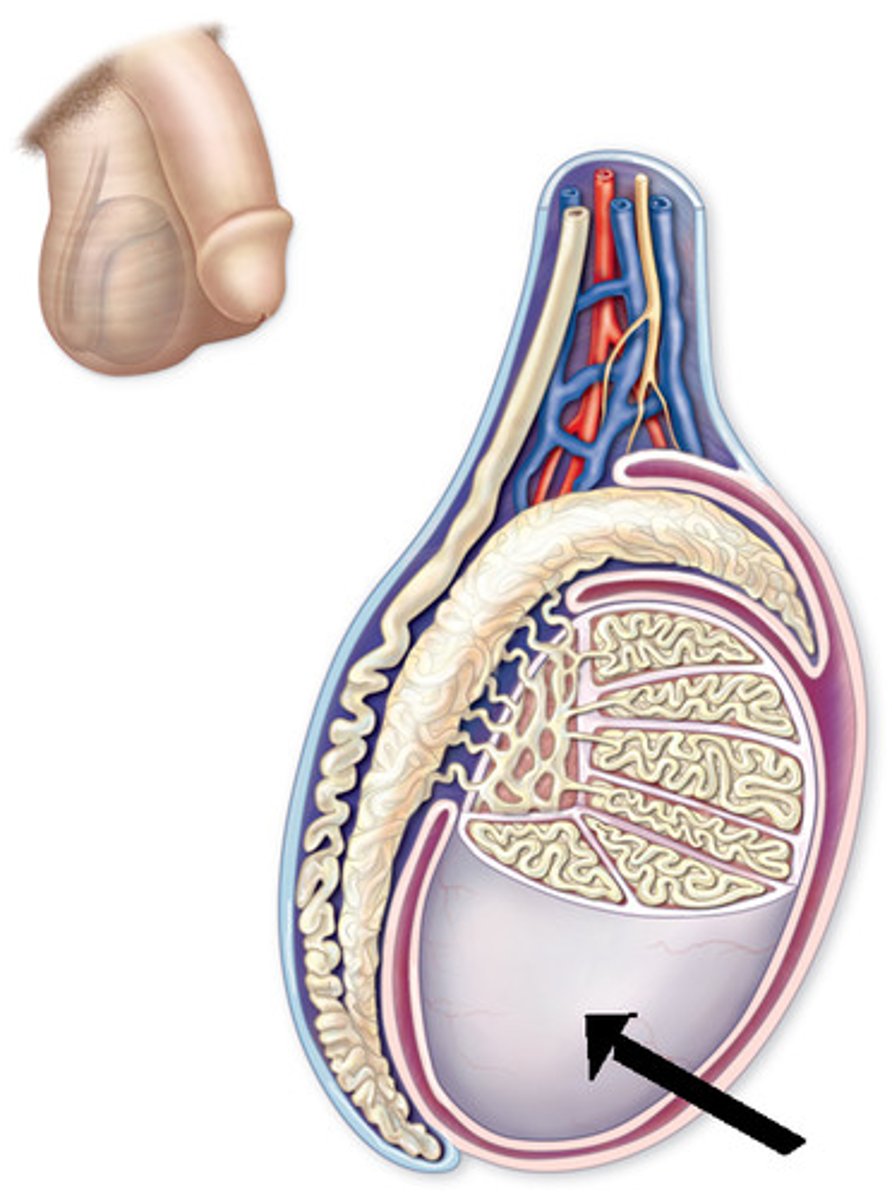
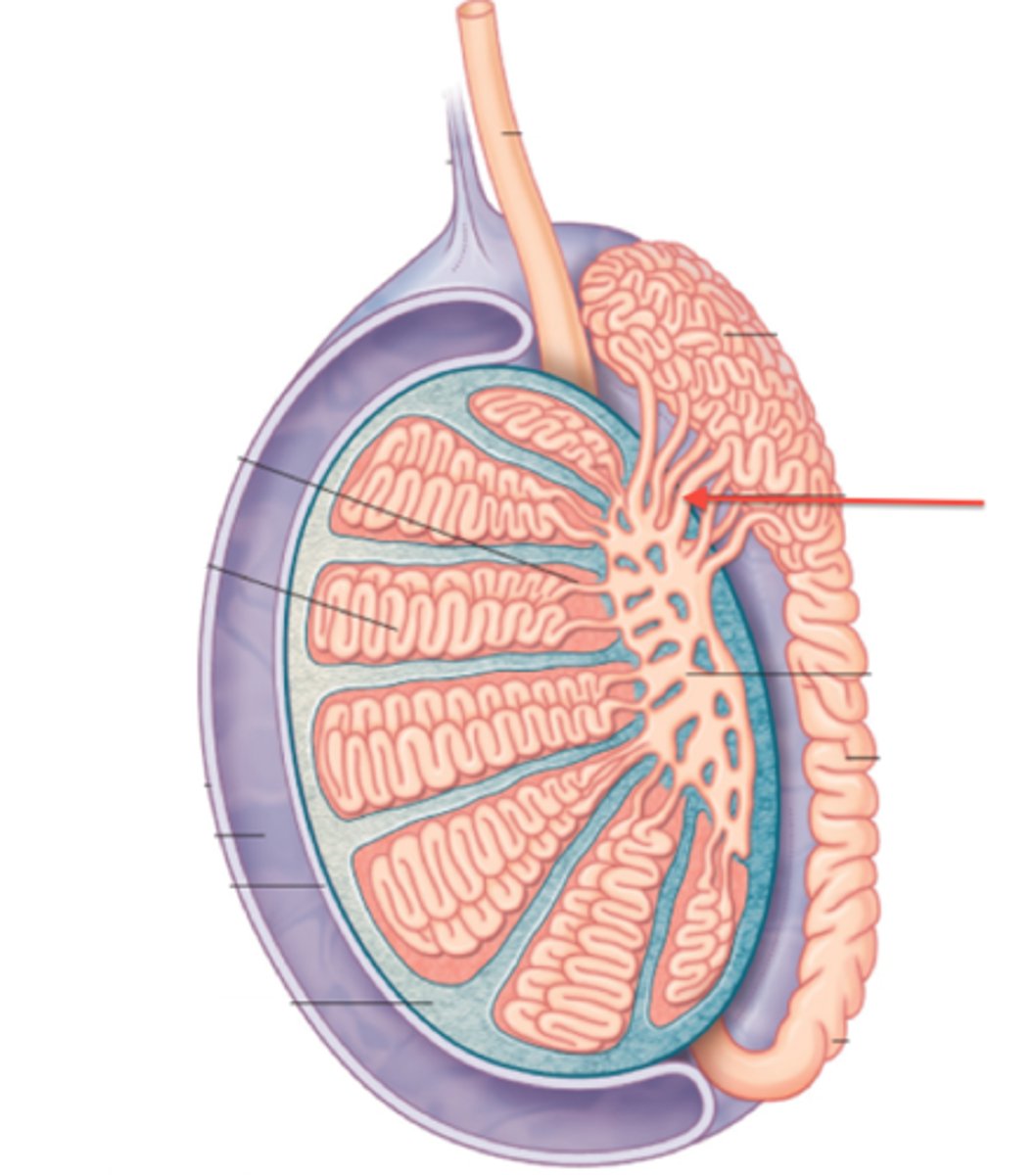
Seminiferous tubules
Site of sperm production within testis lobules.
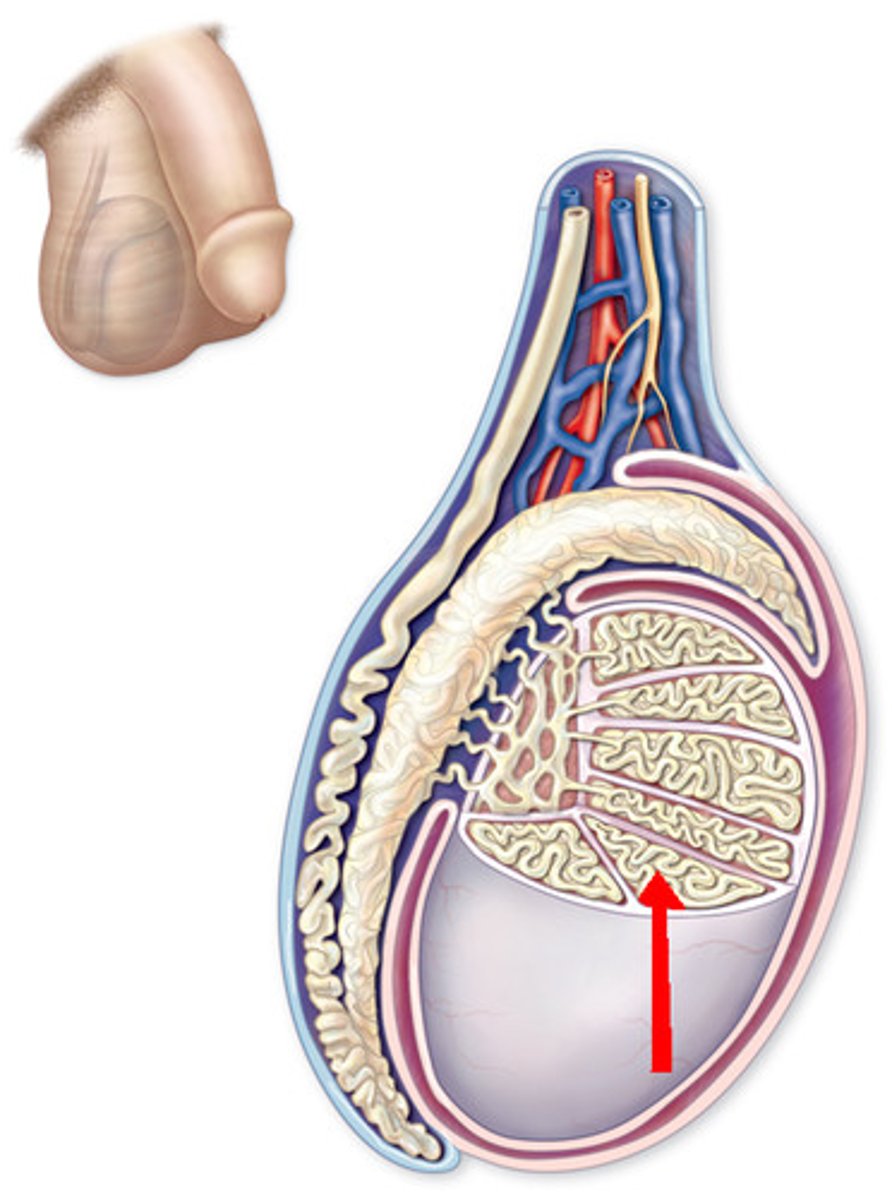
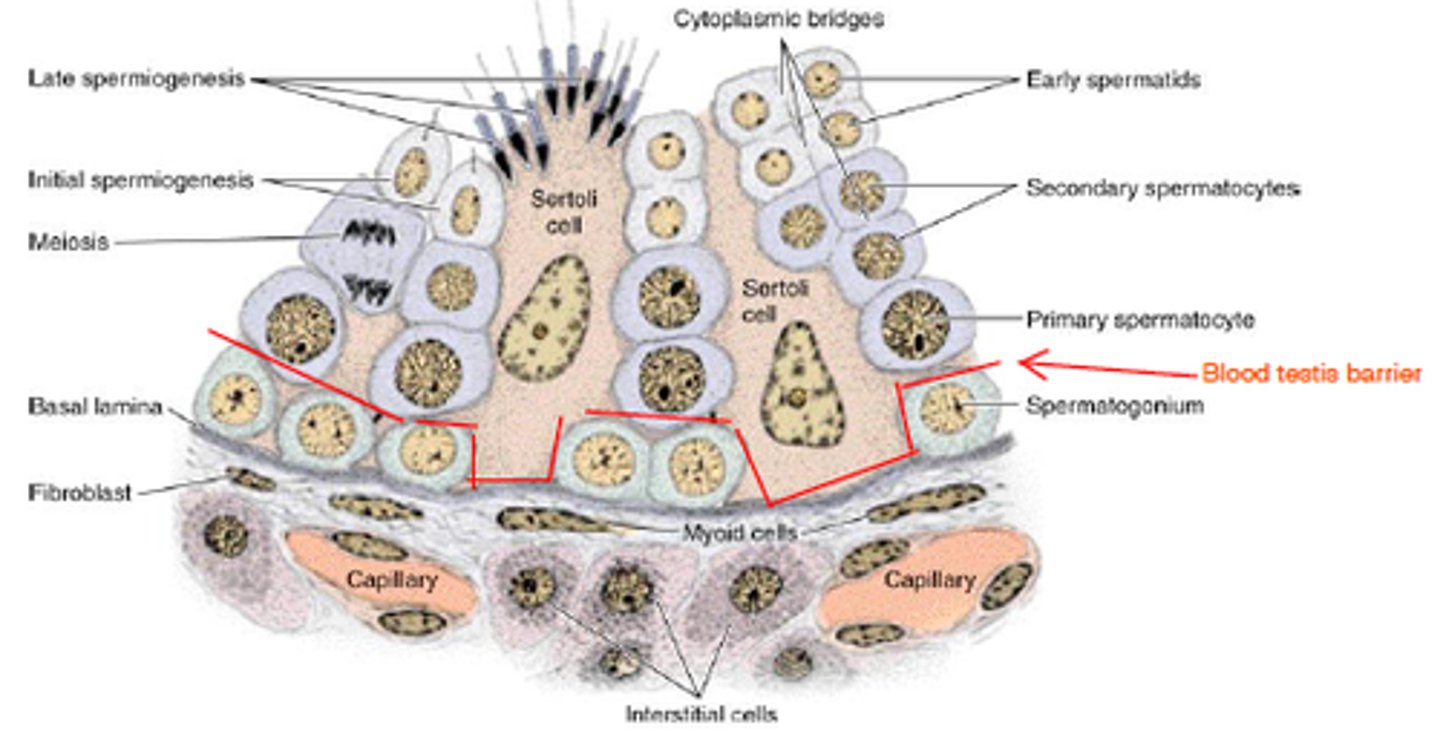
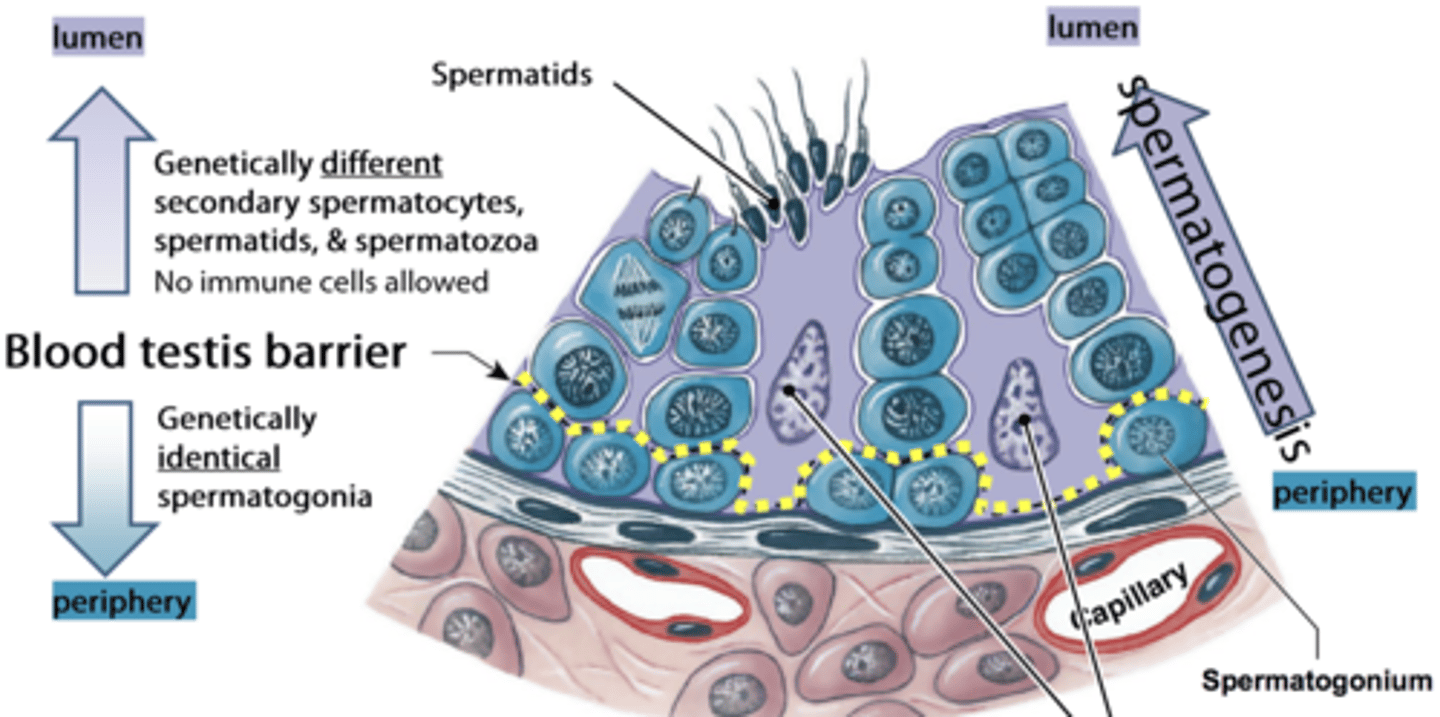
Blood-testis barrier
Prevents immune attack on developing sperm.
Efferent ductules
Transport sperm from rete testis to epididymis.
ductus deferens (vas deferens)
Tube connecting epididymis to seminal vesicle.
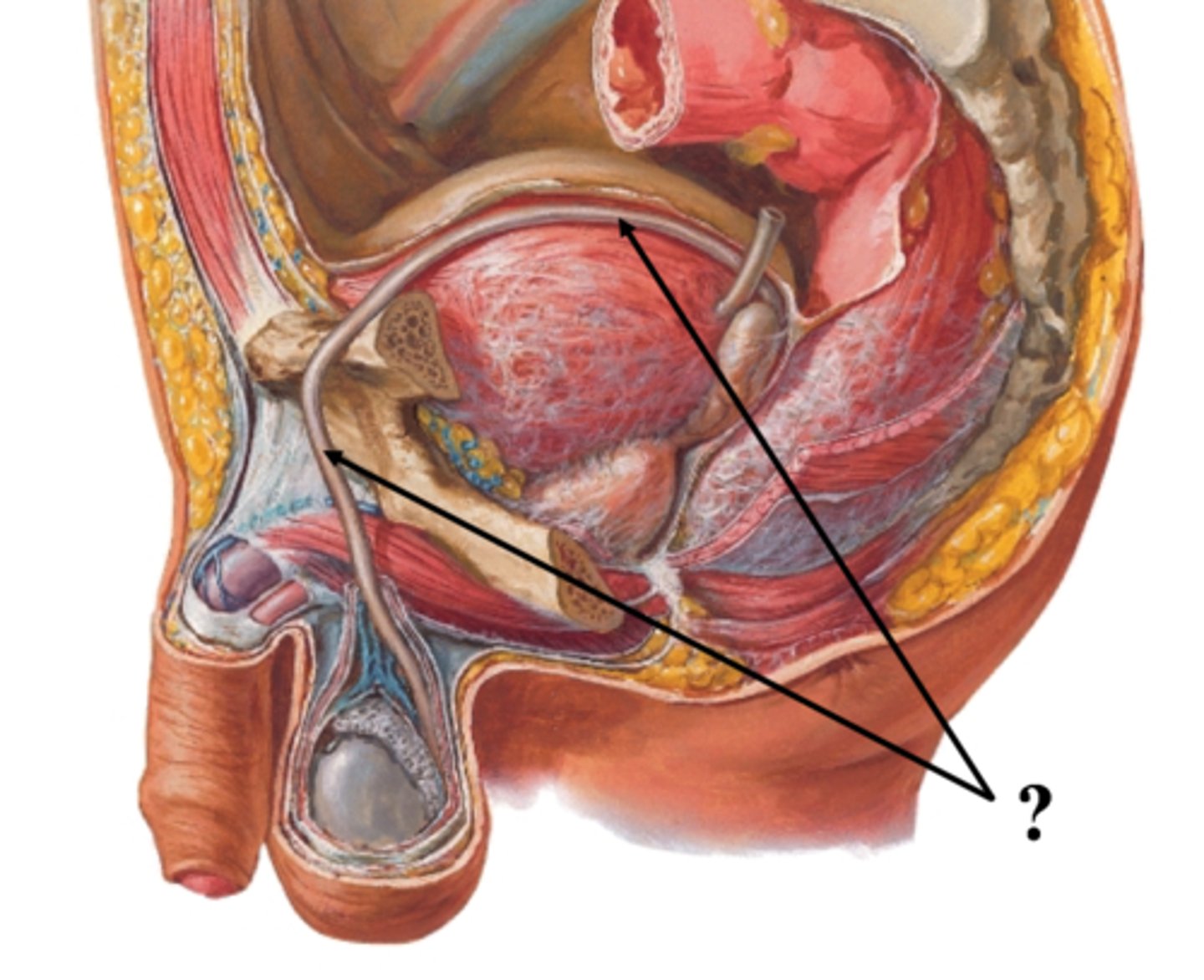
Ejaculatory duct
Formed by merging ductus deferens and seminal vesicle.
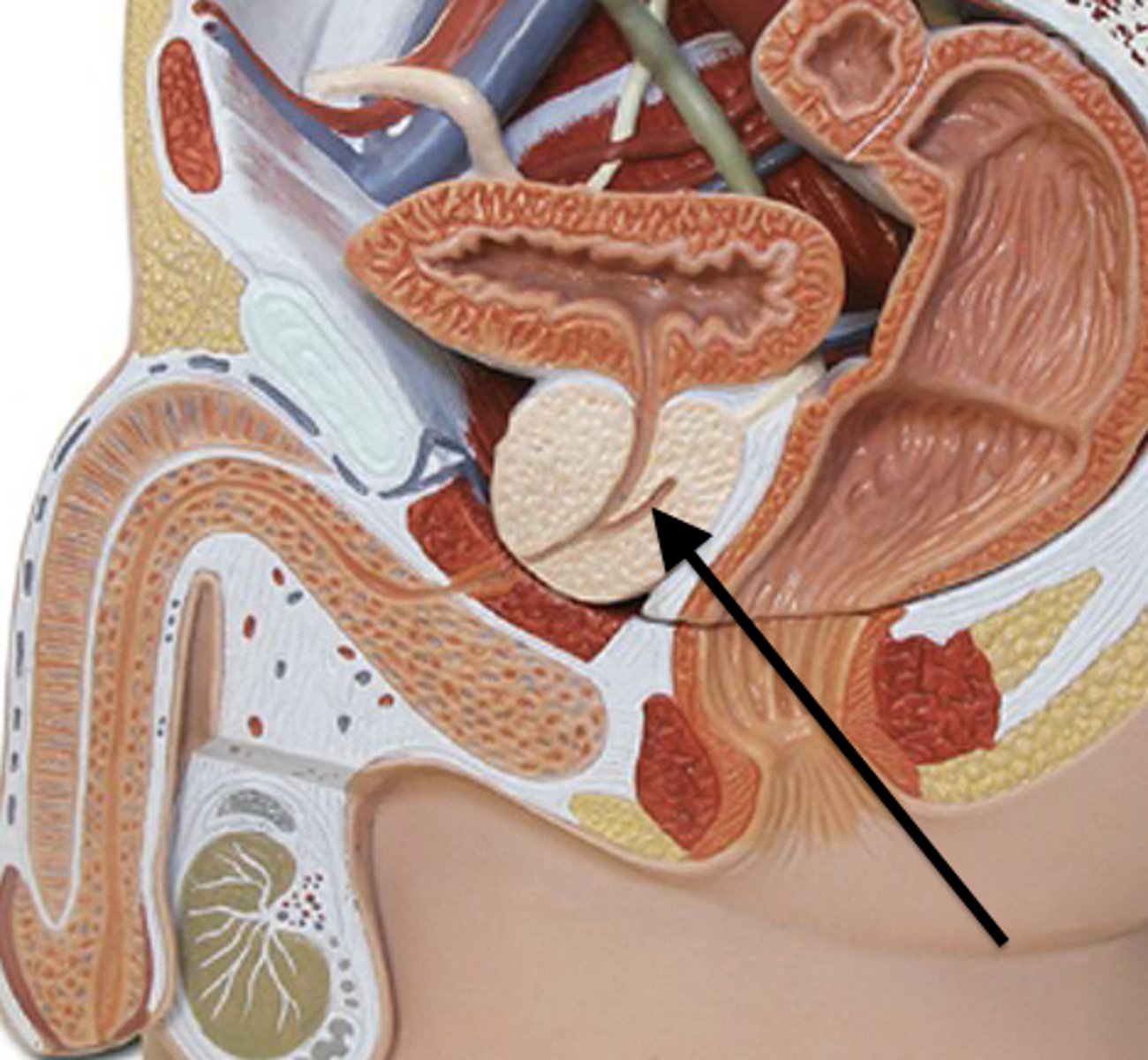
Seminal vesicles
Glands producing 60% of semen volume.
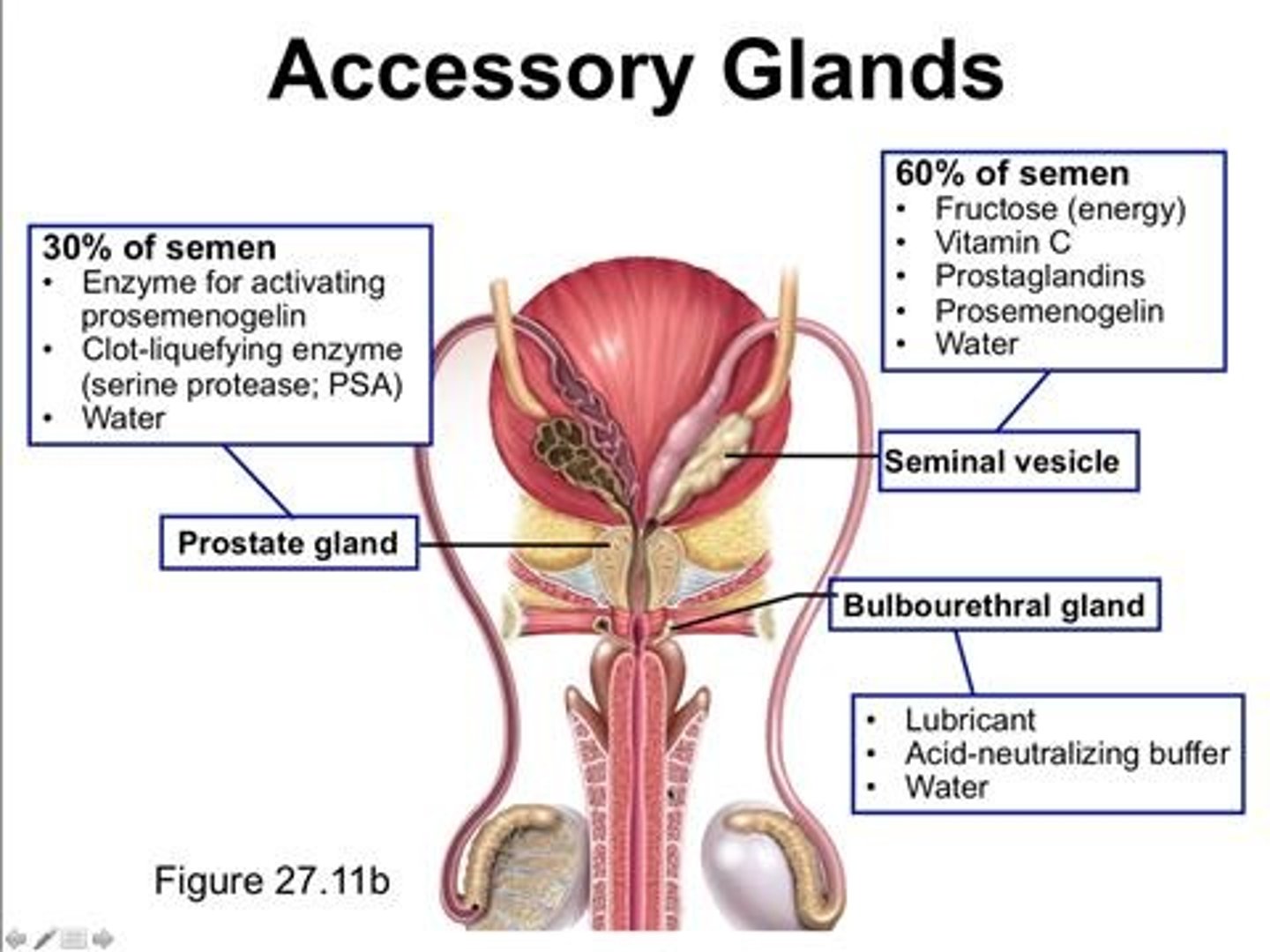
Prostate gland
Produces 30% of semen, surrounds urethra.
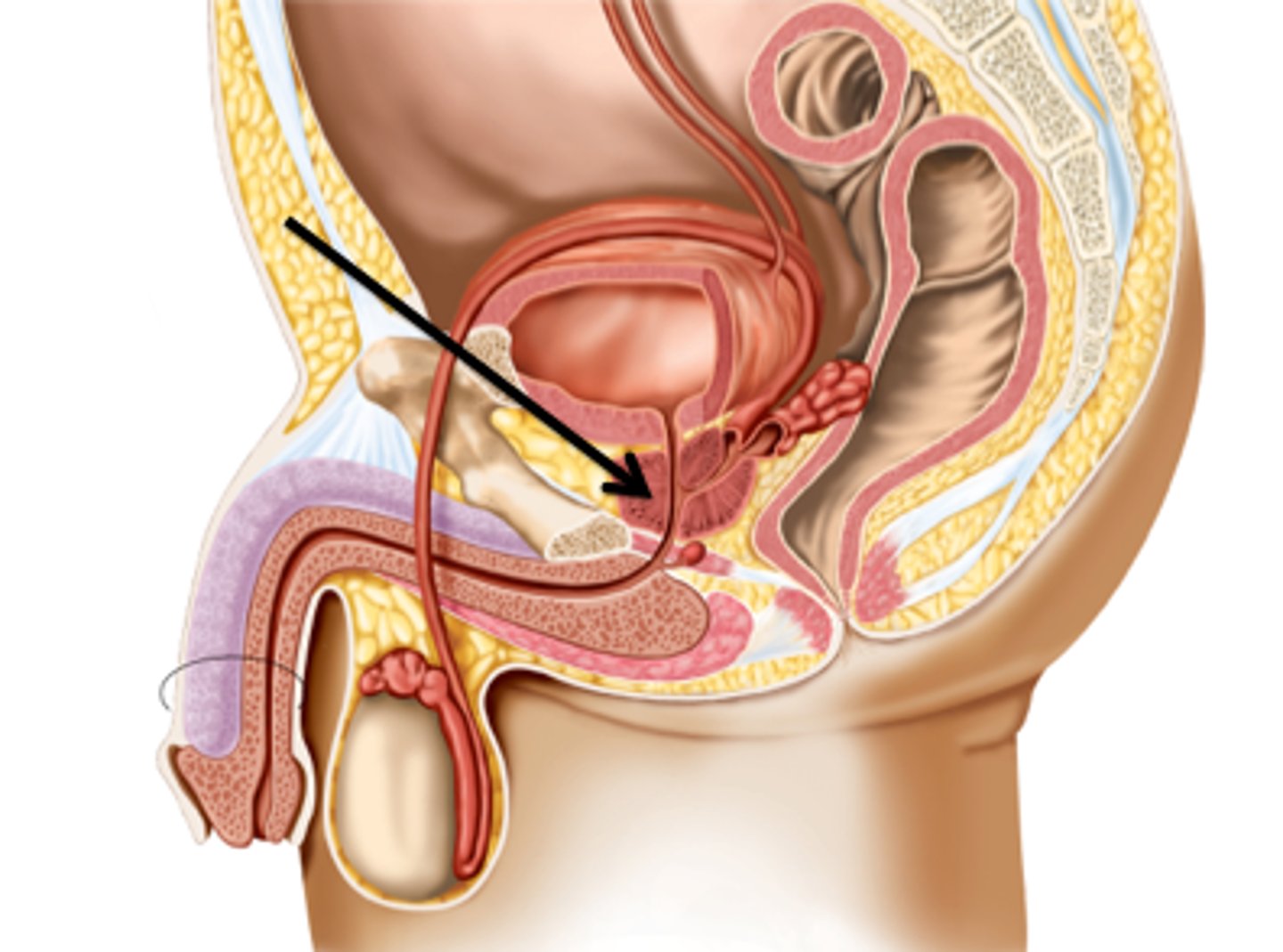
Bulbourethral glands
Secrete pre-ejaculate for lubrication.
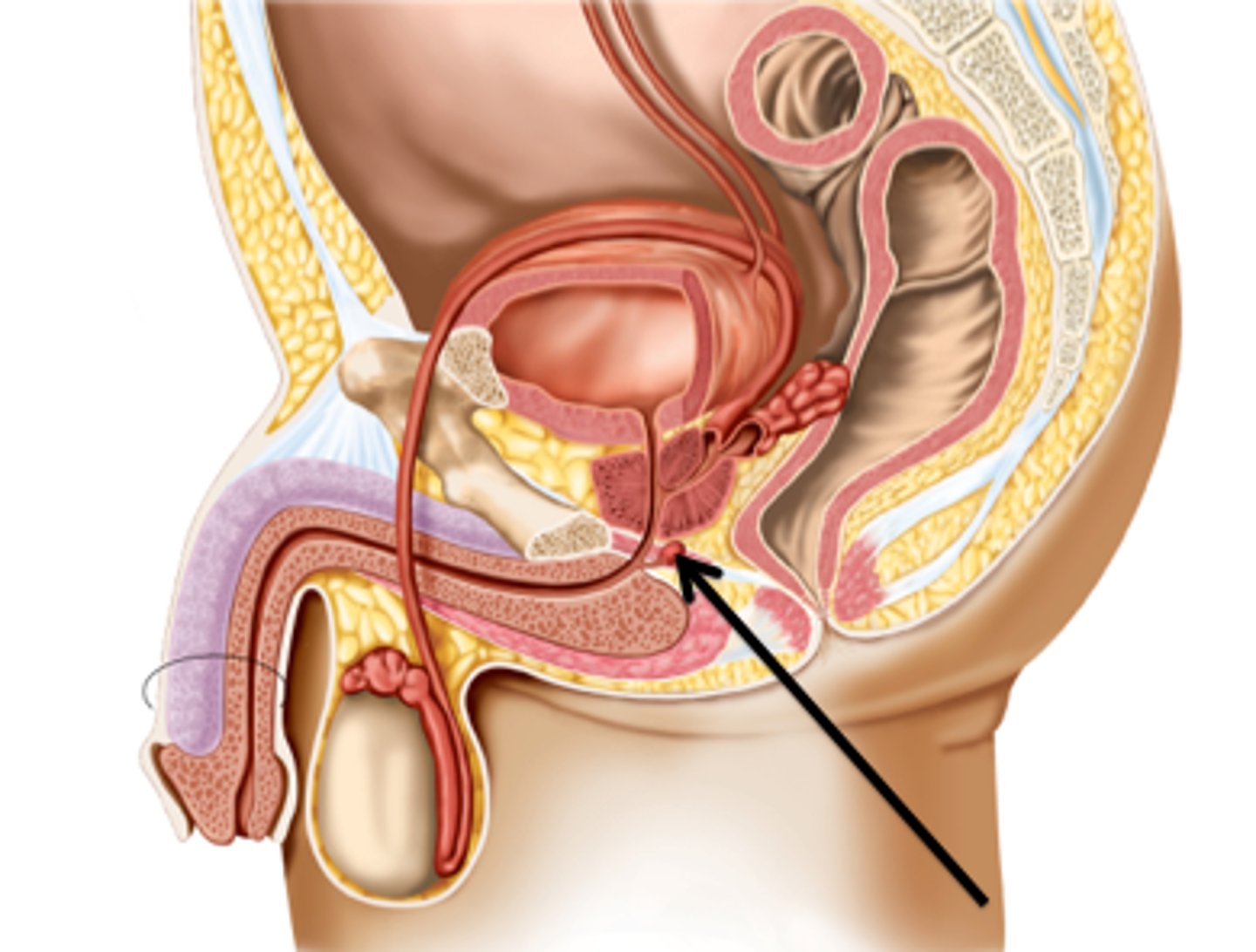
Corpus spongiosum
Erectile tissue surrounding the penile urethra.
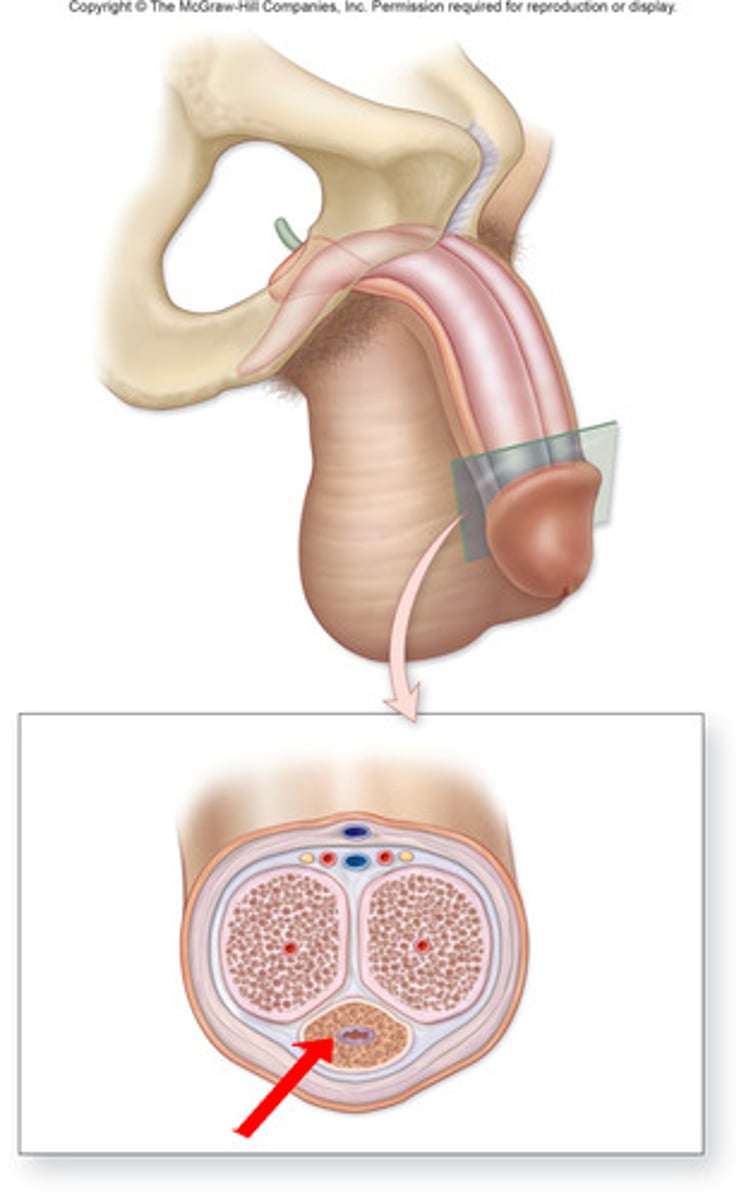
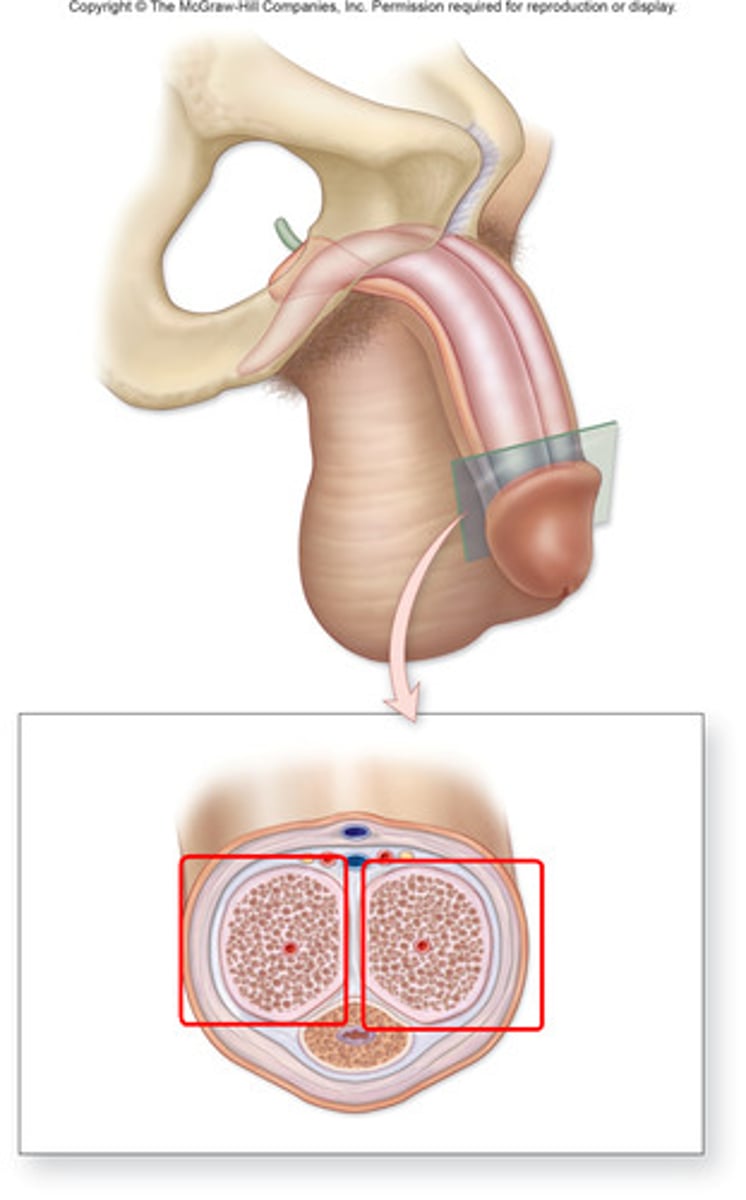
Corpora cavernosa
Two erectile tissues facilitating penile erection.
Puberty
Onset of reproductive system activity around age 12.

Androgens
Hormones responsible for male secondary sexual characteristics.

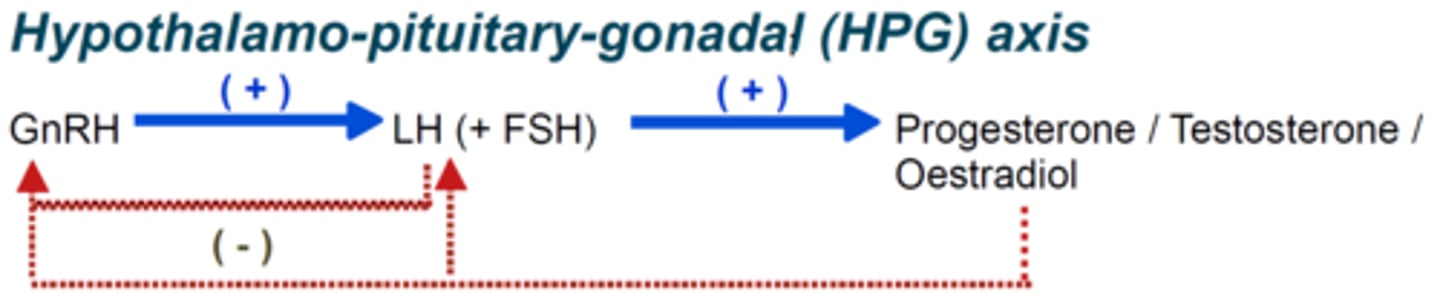
Hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis (HPG axis)
Regulatory system controlling male reproductive hormones.
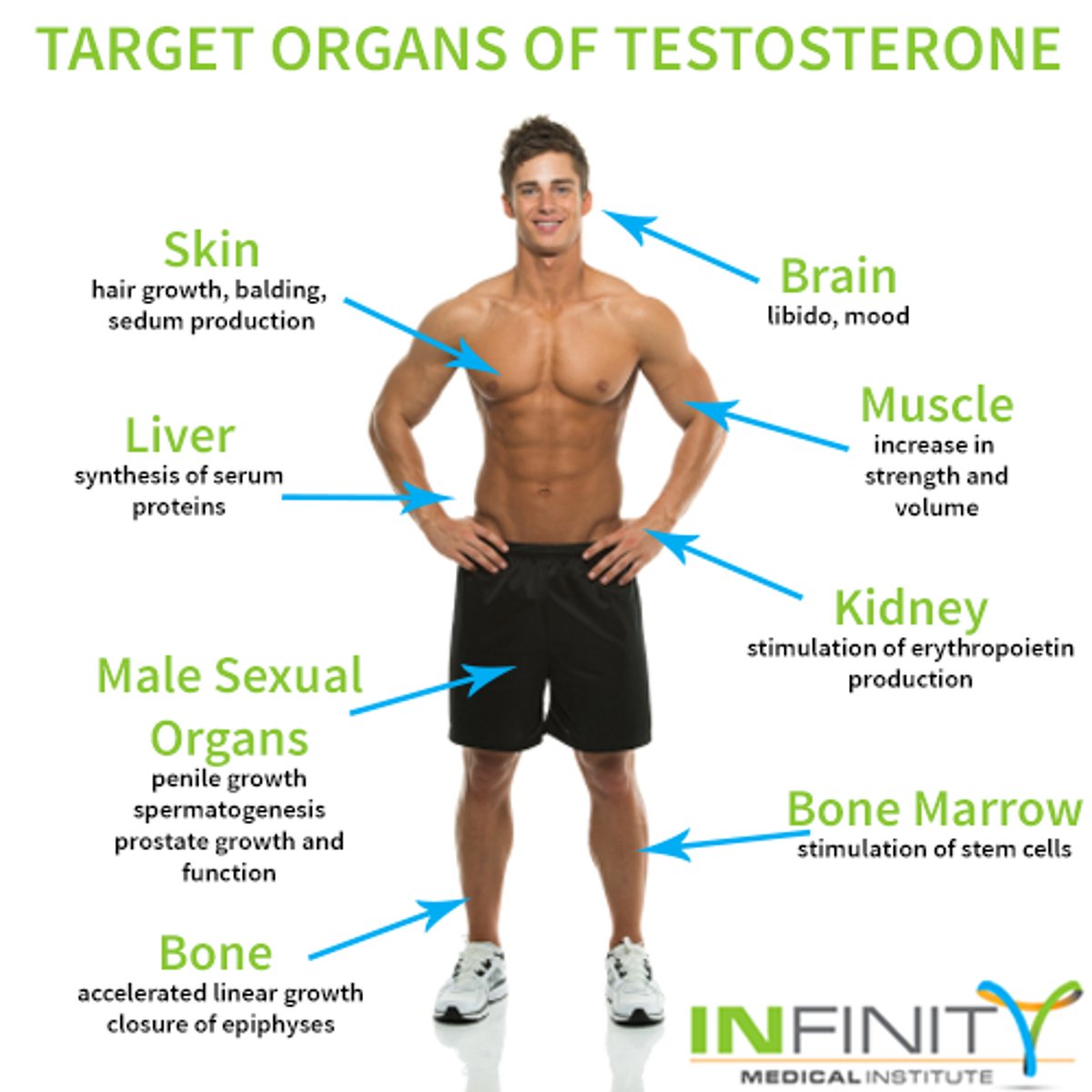
Testosterone
Primary male sex hormone, influences libido and spermatogenesis.
Erectile dysfunction
Inability to achieve or maintain an erection.

Semen
Fluid containing sperm expelled during ejaculation.
Semen composition
Includes seminal plasma from various glands.
Orgasm
Climax marked by ejaculation and intense pleasure.
Refractory period
Time post-orgasm where another erection is impossible.
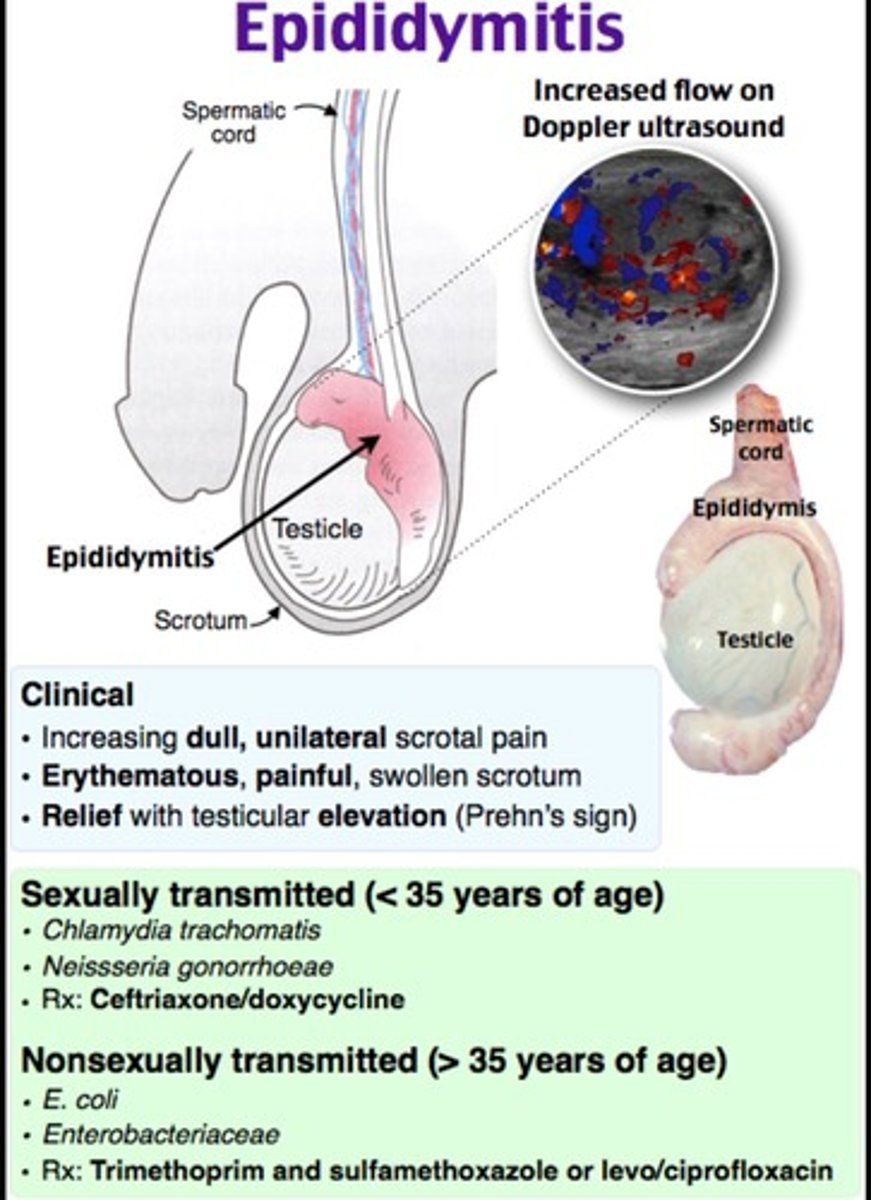
Epididymitis
Inflammation of the epididymis, often painful.
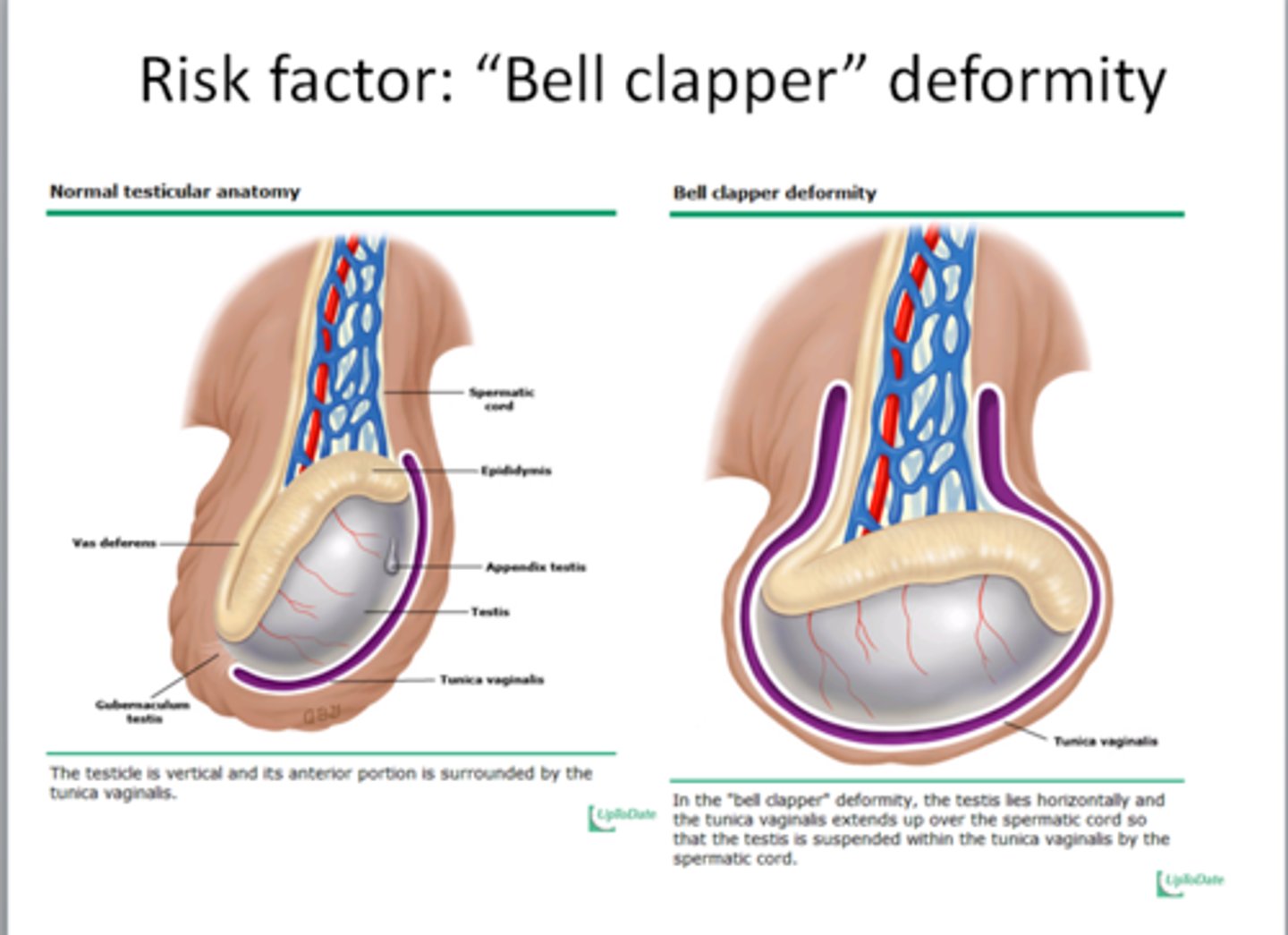
Testicular torsion
Twisting of spermatic cord, risking testicular necrosis.
Prostate cancer
Common cancer affecting older men, screening recommended.
Mitochondria
Organelles in sperm middle piece providing ATP.
Corkscrew motion
Tail movement of sperm facilitating propulsion.
Temperature control
Mechanisms maintaining testes at 35°C for sperm production.
Tunica vaginalis
Serous membrane covering the testes.
Blood-testis barrier (BTB)
Protective barrier preventing immune attack on germ cells.
Testicular cancer
Cancer primarily affecting young men, often one testicle.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
Medications enhancing erectile function by increasing cGMP.
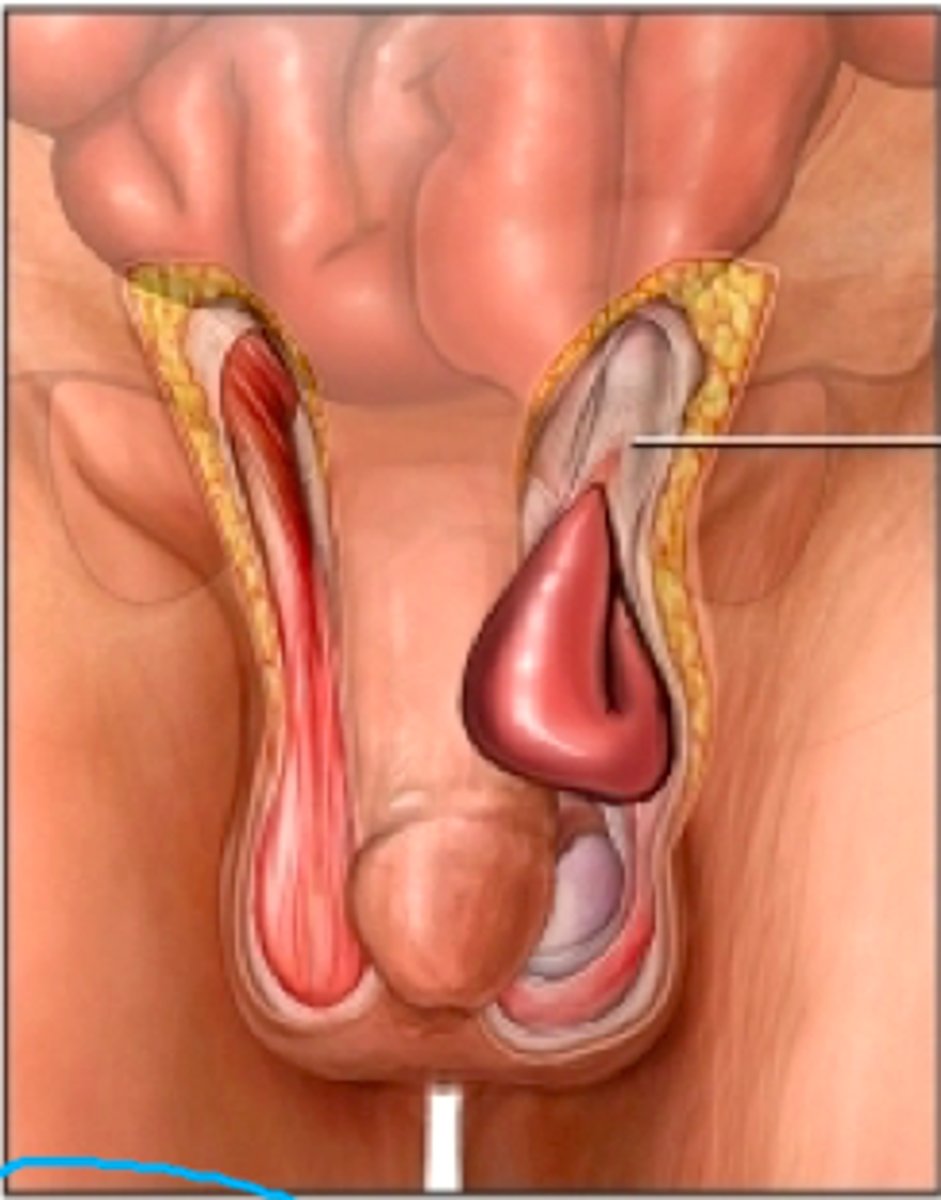
Inguinal hernia
Protrusion of tissue through abdominal wall into inguinal canal.
Peyronie's disease
Scar tissue causing painful, curved erections.