Topic 7: Electric and magnetic fields
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:01 PM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
What is an electric field?
* A region of space in which a charged particle feels a force
* The charged particle could be stationary or moving, and will feel an electric force in that field
* The charged particle could be stationary or moving, and will feel an electric force in that field
2
New cards
What creates an electric field?
* All charged particles create their own electric fiels
3
New cards
What force does the field exert on other charged particles?
* Electrostatic force
4
New cards
What happens with particles of the like charge? (+ve and +ve, -ve and -ve)
* They repel each other
* Means the force on each charge are away from the other charge
* Means the force on each charge are away from the other charge
5
New cards
What happens when particles are oppositely charged?
* They attract each other
* The force on each charge is towards the other charge
* The force on each charge is towards the other charge
6
New cards
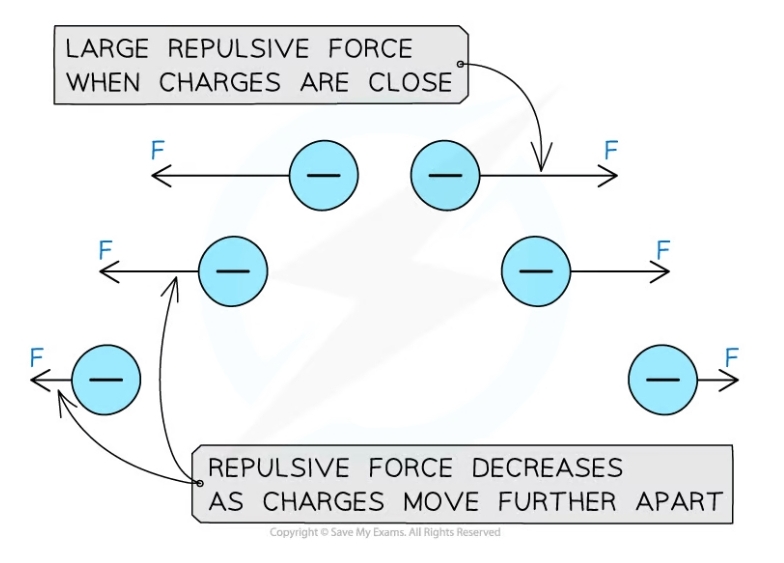
How does the size of the force change?
* It changes with distance
* The bigger the distance between the charged particles, the smaller the force
* The bigger the distance between the charged particles, the smaller the force
7
New cards
What is the electric field strength defined by?
* The force per unit charge acting on a positive test charge at a certain point
8
New cards
Equation for the electric field strength
E=F/Q
* E: Electric field strength (NC-1)
* F: electrostatic force on the charge (N)
* Q: charge (C)
* E: Electric field strength (NC-1)
* F: electrostatic force on the charge (N)
* Q: charge (C)
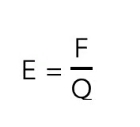
9
New cards
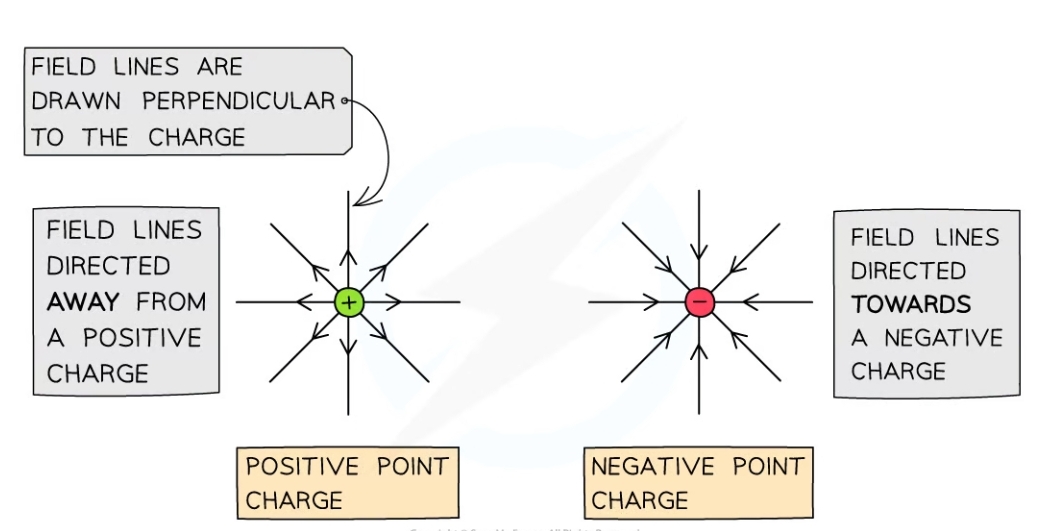
Why is a positive test charge used in the definition?
* It determines the direction of the electric field
* The electric field strength is directed away from a positive charge
* Towards a negative charged
* The electric field strength is directed away from a positive charge
* Towards a negative charged
10
New cards
What is Coulomb’s law?
* The electrostatic force between two point charges is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation
11
New cards
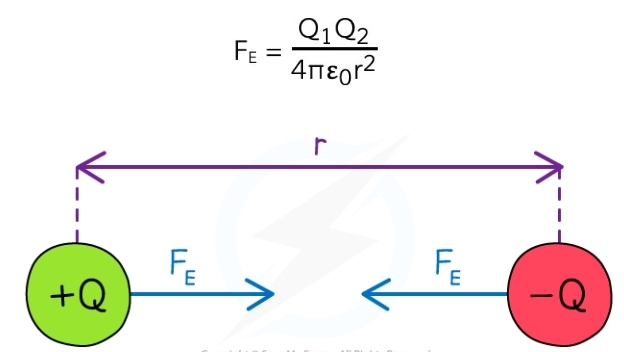
Coulomb’s Law equation
* Fe: electrostatic force between two charges (N)
* Q1 and Q2: two point charges (C)
* ε0: permittivity of free space
* r: distance between the centre of the charges (m)
* Q1 and Q2: two point charges (C)
* ε0: permittivity of free space
* r: distance between the centre of the charges (m)
12
New cards
What is permittivity of free space?
* A constant which represents the capability of an electric field to permeate a vacuum.
* 8.85\*10^-12 (Fm^-1)
* 8.85\*10^-12 (Fm^-1)
13
New cards
What is the inverse square law?
* 1/r^2
* When a separation of two charges doubles, the electrostatic force between them reduces to (½)2 = ¼ of its original size
* When a separation of two charges doubles, the electrostatic force between them reduces to (½)2 = ¼ of its original size
14
New cards
Charges of Q1 and Q2
* If they are oppositely charged
* Fe is -ve
* Attractive force
* If they have the same force
* Fe is +ve
* Repulsive force
* Fe is -ve
* Attractive force
* If they have the same force
* Fe is +ve
* Repulsive force
15
New cards
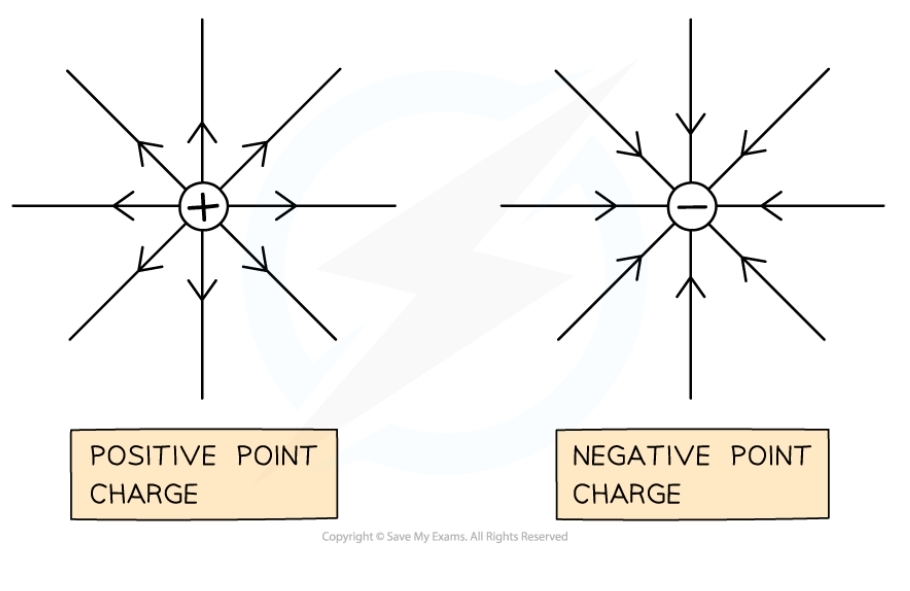
What type of electric field does a point charge produce?
* A radial field
16
New cards
What is the equation for electric field strength at distance r due to a point charge Q in free space?
(Electric field strength with only one Q)
(Electric field strength with only one Q)
* Q: the point charge producing the radial electric field (C)
* r: distance from the centre of charge (m)
* ε0: permittivity of free space (F m-1)
* r: distance from the centre of charge (m)
* ε0: permittivity of free space (F m-1)
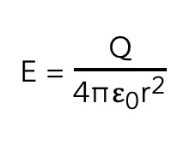
17
New cards
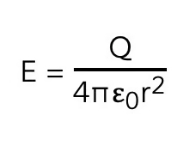
What does the equation of electric field strength of a point charge show?
* Electric field strength in a radial field is not constant
* As the distance from the charge *r* increases, *E* decreases by a factor of 1/r^2
* As the distance from the charge *r* increases, *E* decreases by a factor of 1/r^2
18
New cards
What is the direction of the electric field strength?
* If the charge is negative, the E field strength is negative and points **towards** the centre of the charge
* If the charge is positive, the E field strength is positive and points **away** from the centre of the charge
* If the charge is positive, the E field strength is positive and points **away** from the centre of the charge
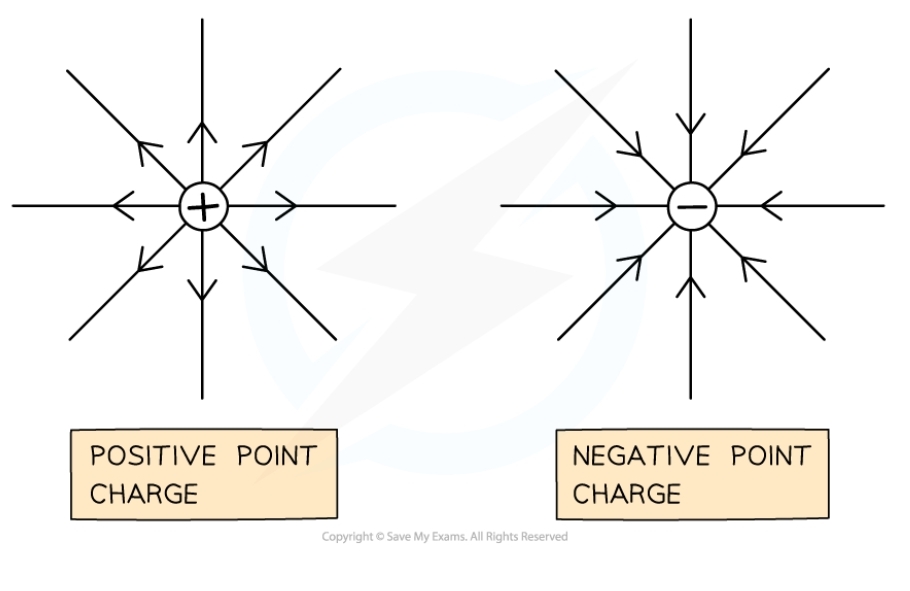
19
New cards
Comparison of electric fild strength to gravitational field strength
* Very similar
* Only difference is that gravitational field lines are always towards the mass, whilst electric field lines can be towards or away from the point charge
* Only difference is that gravitational field lines are always towards the mass, whilst electric field lines can be towards or away from the point charge
20
New cards
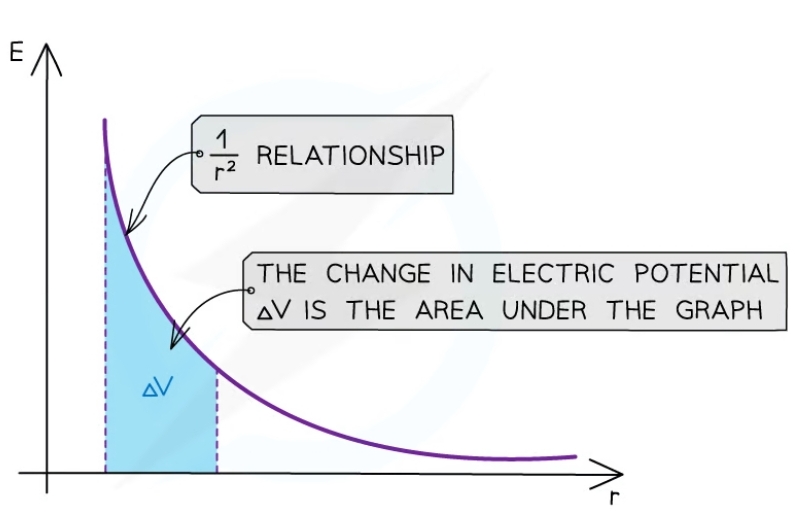
Graph of E against r for a charge
* The values for *E* are all positive
* As *r* increases, *E* against *r* follows a 1/*r2* relation (inverse square law)
* The area under this graph is the change in electric potential Δ*V*
* The graph has a steep decline as *r* increases
* As *r* increases, *E* against *r* follows a 1/*r2* relation (inverse square law)
* The area under this graph is the change in electric potential Δ*V*
* The graph has a steep decline as *r* increases