types of hormones
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
follicle stimulatiing hormone
F = follicle production
M = sperm production
anterior lobe

lutenising hormone
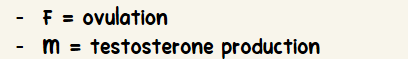
F = ovulation
M = testosterone production
anterior lobe
grwth hormone
Body grows
particularly skeleton
Maintainance of body organs
Rate of protein synthesis
anterior lobe
gh

thyroid stimulating hormone
Production and release of thyroid hormones
anterior lobe
tsh

adrenocorticotropic hormone
Production and release of adrenal gland (cortex) hormones
acth
anterior lobe

prolactin
anterior lobe
prl
Initiate and maintain breast milk secretion

oxytocin
posterior lobe
OT
F = uterine muscle contractions
Milk let down reflex
M = contractions of vas deferens

antidiuretic hormone
posterior lobe
adh
Causes kidneys to reabsorb water
Returns to bloodstream
Can constrict arterioles
Increase blood pressure

melatonin
pineal
Regulates sleep patterns
Production stimulated by the dark, inhibited by light

thyroxine
t4
thyroid gland
Controls the metabolism
Breakdown and synthesis of complex molecules -> cellular metabolism
Breakdown of molecules releases energy
Some as ATP - cell activity
Some in heat - body temp
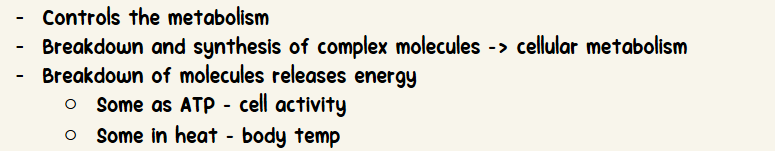
parathyroid hormone
thyroid
PTH
Release triggered by low levels of calcium in the blood
Body responds to:
Absorbing more calcium in food in the small intestine
Releasing calcium stored in bones
Releases calcium in renal tubules

thymosins
thymus
Group of hormones
Influences maturation of T lymphocytes
Type of white blood cells needed for immune response

corticosteroids
cortex of adrenal glands
aldosterone
one of main corticosteroids
Acts on kidneys to reduce sodium increases potassium in urine

cortisol
one of the main corticosteroids
Promotes normal metabolism
Helps withstand stress and repair or damadged tissue

adrenaline
one of main corticsteroids
medulla of the adrenal glands
Epinephrine
Fight or flight response

noradrenaline
medulla of the adrenal gland
Norepinephrine
Similar to adrenaline
Mainly increases rate and force of adrenaline

insulin
endocrine pancreas gland
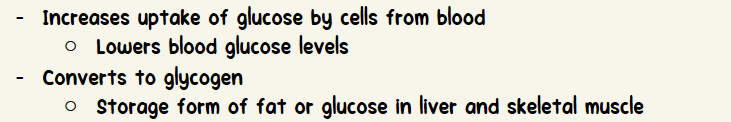
Increases uptake of glucose by cells from blood
Lowers blood glucose levels
Converts to glycogen
Storage form of fat or glucose in liver and skeletal muscle
glucagon
Opposite of insulin
Breakdown of glycogen to glucose
Or fat to glucose
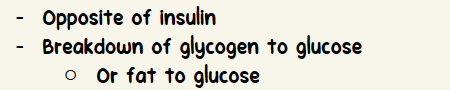
androgen
testes
Testosterone
Development and maintenance of male sex characteristics

oestrogen
Development of female sex characteristics
Regulates menstrual cycle
ovaries

progesterone
ovaries
Regulates menstrual cycle
Regulates pregnancy
