Cells & Molecules Unit 3
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What are autotrophs (self-feeders)?
photosynthetic organisms that make their own food from ions and molecules
Non-photosynthetic organisms are __________, or different-feeders.
heterotrophs
How does photosynthesis harness sunlight to make carbohydrates?
converts electromagnetic energy to chemical energy requiring sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water (with oxygen as a by-product).
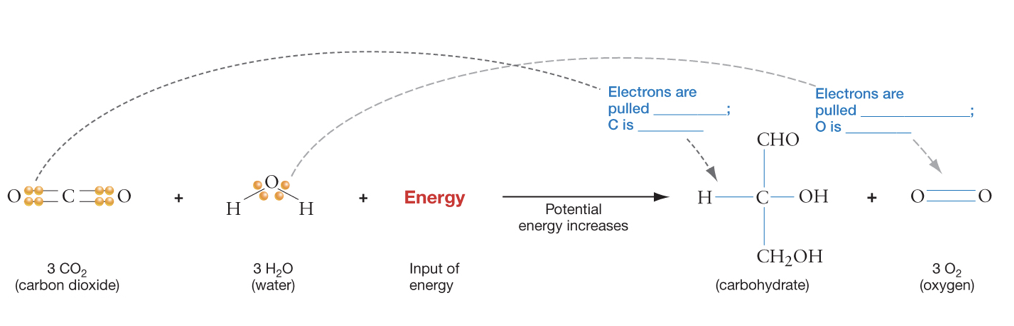
Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis.
CO2 + H2O + light energy —> (CH2O)n + O2
Photosynthesis consists of what two sets of reactions?
Calvin cycle reactions and light-capturing reactions
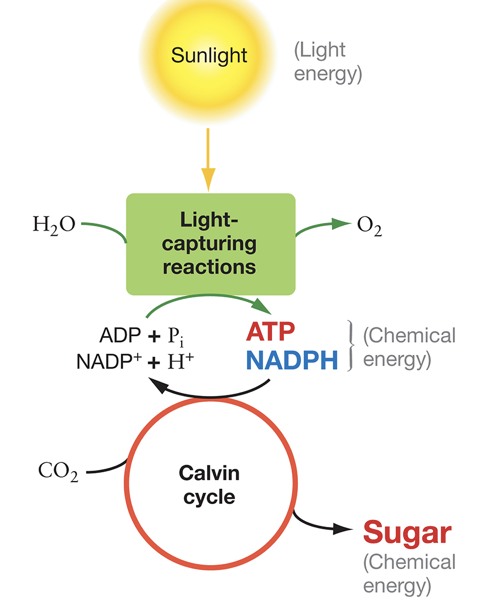
Describe the Calvin cycle reactions during photosynthesis.
reactions produce sugar from CO2, and electrons and ATP are used to reduce CO2
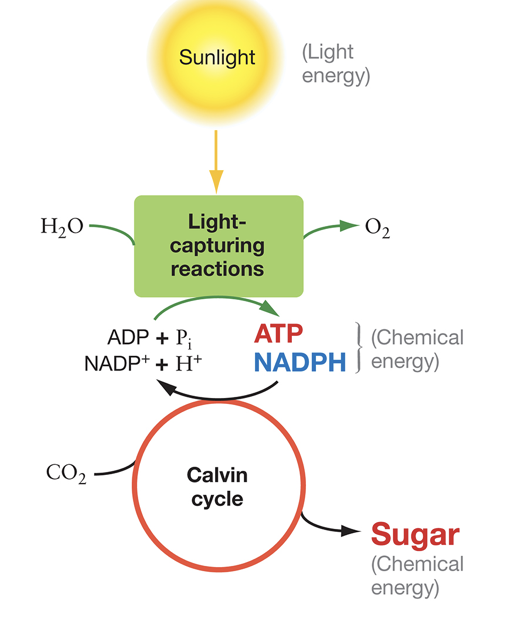
Describe the light-capturing reactions during photosynthesis.
produce O2 from H2O, water splits to form O2, excited electrons are transferred to electron carrier NADP+ to form NADPH
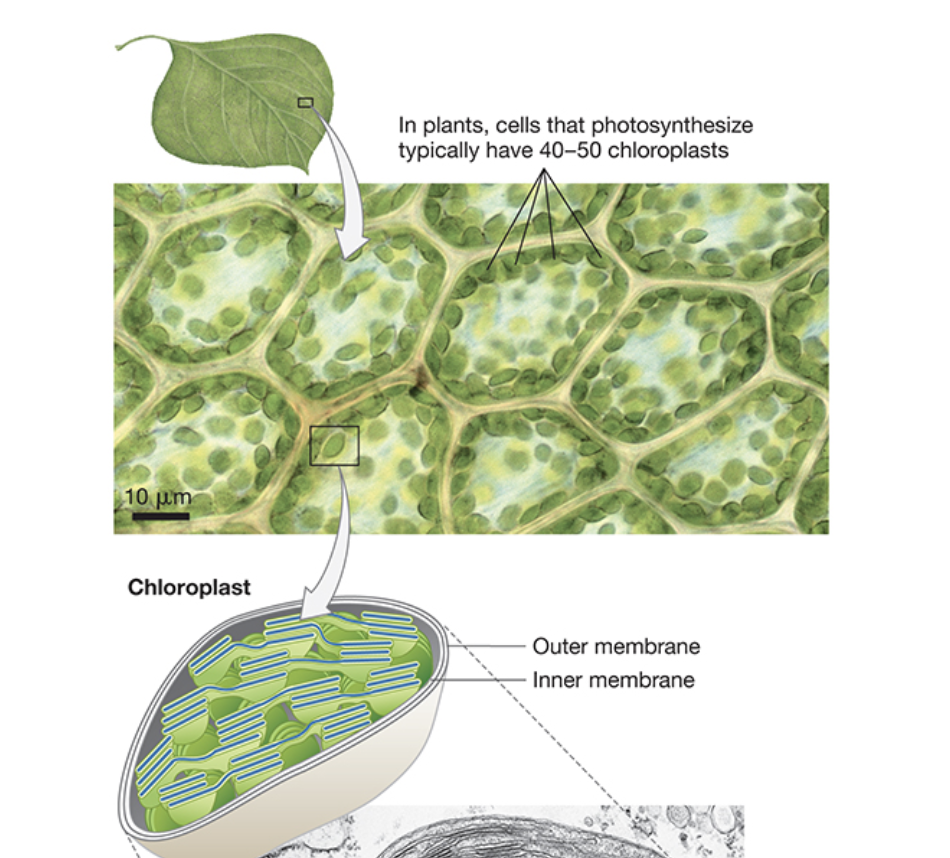
Where does photosynthesis occur?
chloroplasts
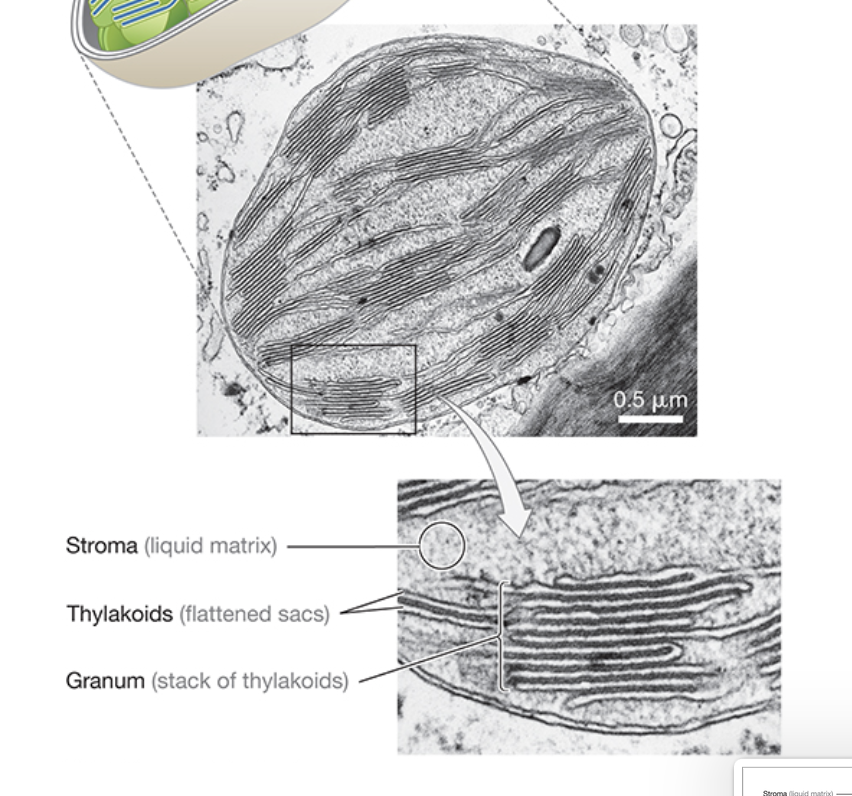
Describe the inner membrane of chloroplasts.
filled with thylakoids, stroma, and granum
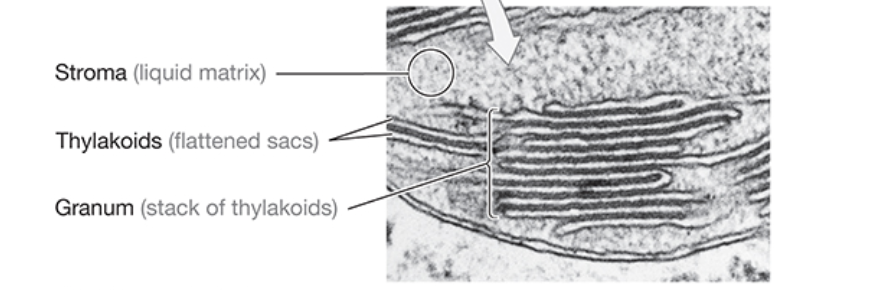
What is the stroma?
fluid-filled space between thylakoids
What is the lumen?
the space inside the thylakoid
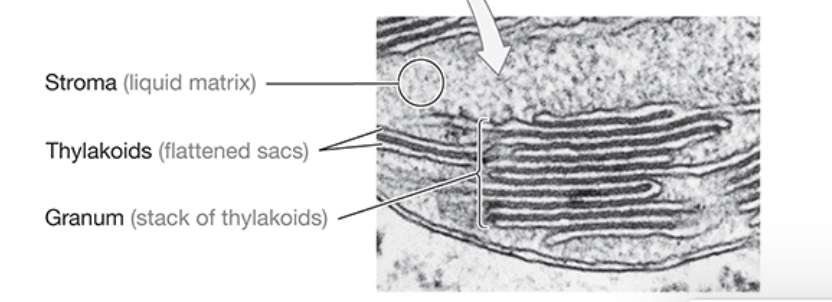
What is the name of the flattened vesicle-like structures on the interior of the chloroplast?
thylakoids
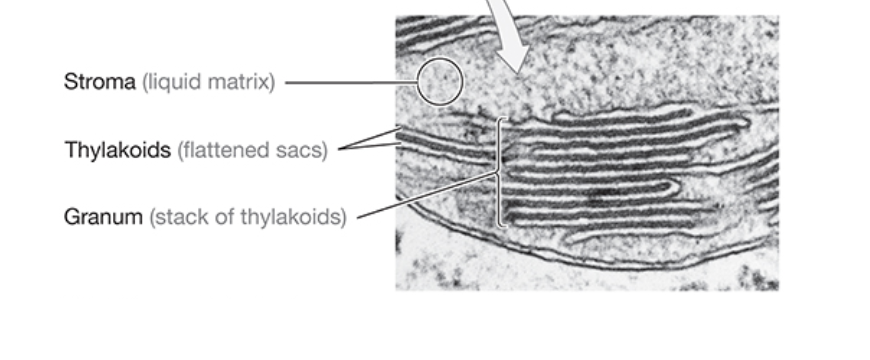
What is grana?
interconnected stacks of thylakoids within a chloroplast
Thylakoid membranes contain large quantities of pigments, which absorb only certain wavelengths of light. What is the most common pigment in chloroplasts?
chlorophyll
Describe the color and function of chlorophyll
reflects green light, responsible for green color of plants and algae
Light is a type of ______________ _________.
electromagnetic radiation
How do pigments capture light energy?
by absorbing specific wavelengths of visible light and transforming it into chemical energy through photosynthesis
Each photon and wavelength have a specific amount of energy — is the energy of photon of light proportional to its wavelength?
inversely proportional
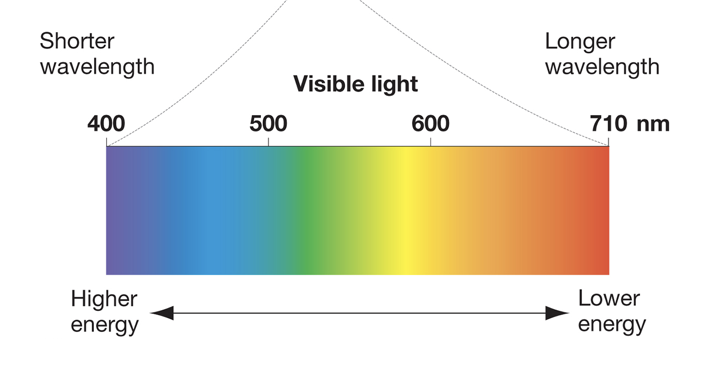
_________ wavelengths have more energy than ________ wavelengths.
shorter, longer
What do photons do when they strike an object?
can be absorbed, transmitted, or reflected
What are the two major classes of pigment and plants and what do they absorb and reflect?
chlorophylls — absorb red and blue light, reflect green
carotenoids — absorb blue and green light, reflect yellow, orange, and red
What is the action spectrum for photosynthesis?
wavelengths that drive light-capturing reactions, most effective with pigments that absorb blue and red photons

What is the absorption spectrum for pigments?
measures how wavelength of photons influence amount of light absorbed by pigment
Name the 2 fundamental parts of chlorphyll a and b.
long isoprenoid tail and head
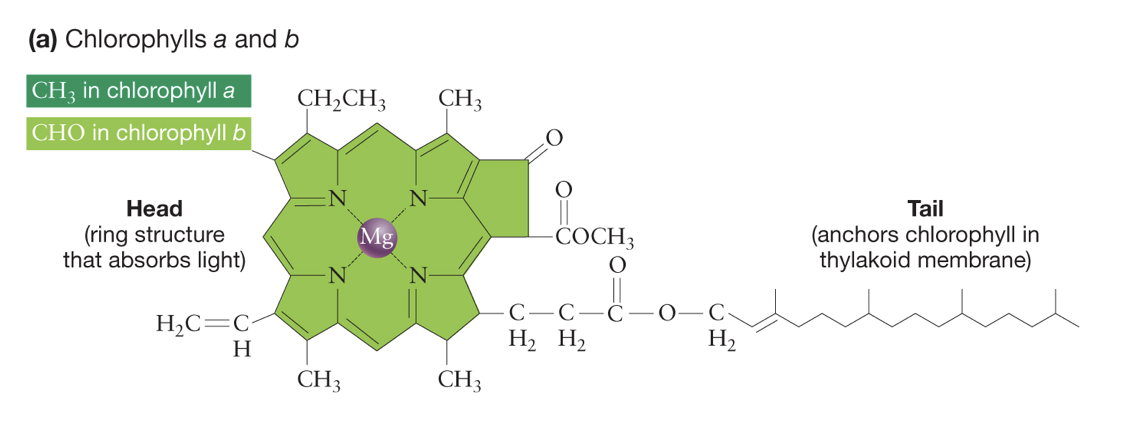
Describe the long isoprenoid tail of chlorophyll.
interacts with protein embedded in thylakoid membrane
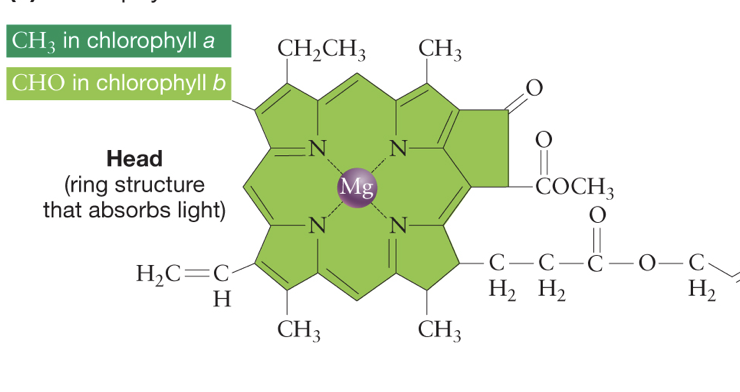
Describe the head of chlorophyll.
consists of large ring structure with magnesium atom in middle, light is absorbed here
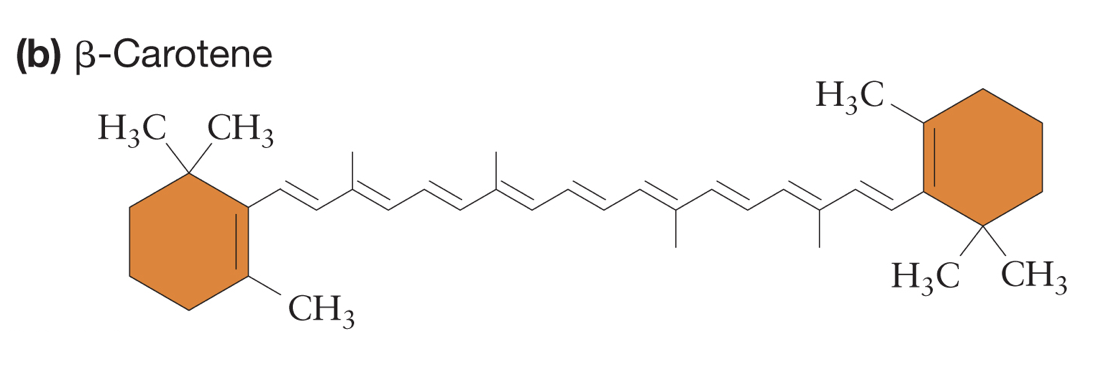
What are carotenoids?
accessory pigments found in chloroplasts that absorb light and pass energy onto chlorophyll
What happens to chlorophyll and carotenoids when trees begin to die?
their chlorophyll degrades and carotenoids absorb wavelengths of light
Name 2 benefits that carotenoids provide for chlorophyll.
extends range of wavelengths that drive photosynthesis and protects chlorophylls from damage by stabilizing free radicals
What happens when a chlorophyll absorbs a photon?
photon’s energy is transferred in bonds in chlorophyll’s head ragion, electrons become excited
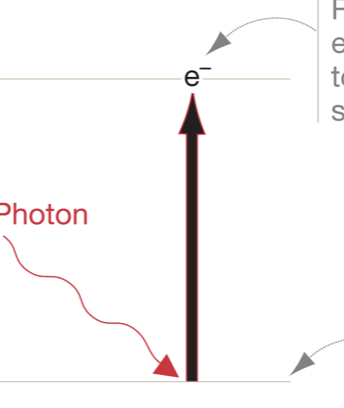
Red photons bump an electron up ___ energy level.
one
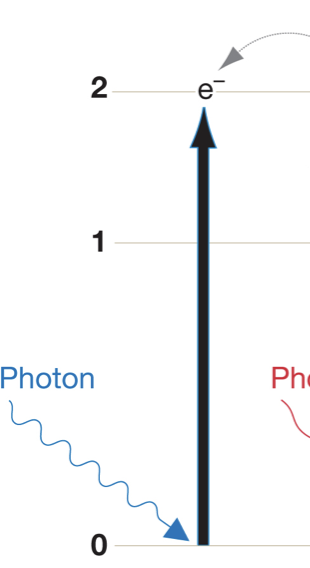
Blue photons bump an electron up ___ energy levels.
two
Green photons are _________.
intermediate — are not absorbed
Describe what happens when excited electrons fall back to ground state.
absorbed energy is released as heat and/or light
When does fluorescence occur?
when electron emits light as it falls back to ground state
How do chlorophyll molecules work together in groups?
thylakoid membrane is composed of 200-300 chlorophyll and accessory pigment molecules (photosystem)
Pigment molecules in photosystems serve as…
light-gathering antenna pigments which guide energy towards central reaction center
Describe what happens when pigments in antenna complex absorb photons.
energy (not electron) is passed to nearby chlorophyll molecules (resonance energy transfer) proteins organize and tune absorbtion potential of antenna pigments. electron falls back to ground state and energy is transferred inside photosystem
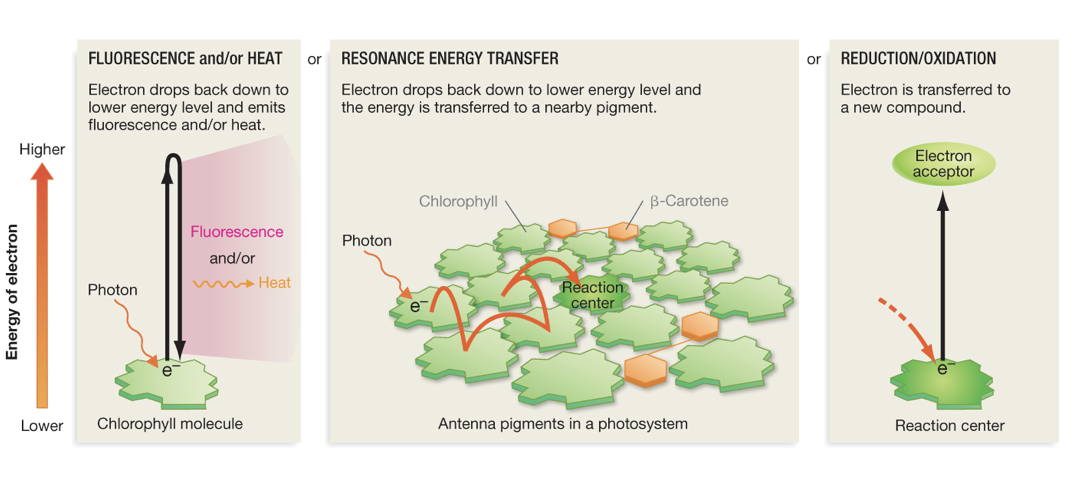
List the 4 things that energy released from electrons can do
be emitted as light (fluorescence), be given off as heat, excite electron in nearby pigment and induce resonance, or be transferred to electron acceptor in redox reaction
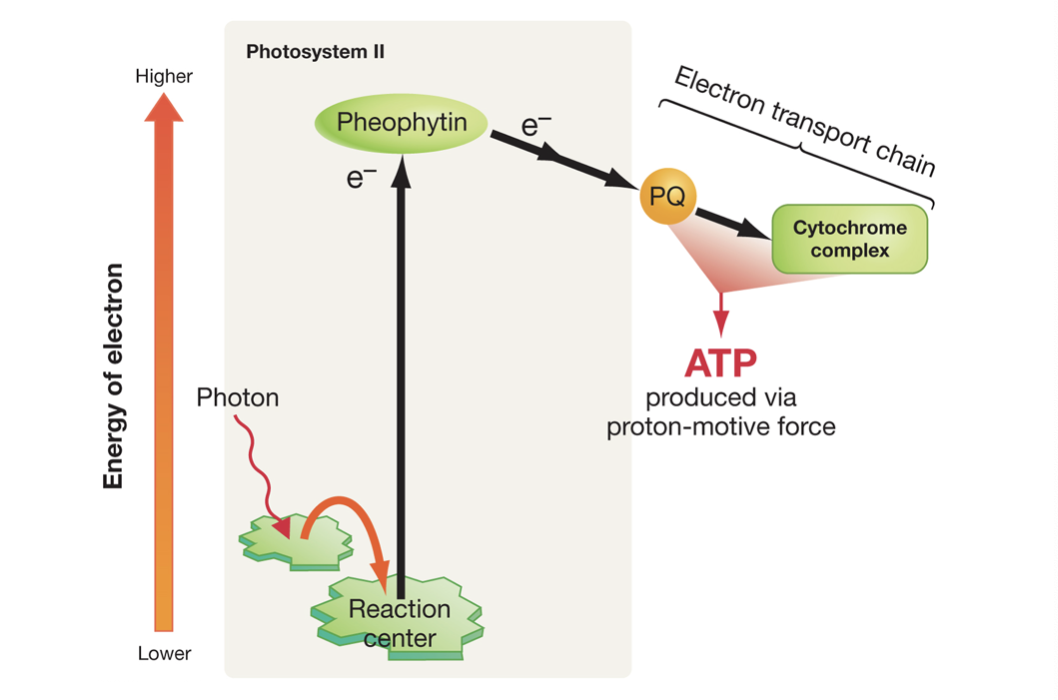
Describe the chemical process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
photon moves into reaction center and transmits resonance energy to antenna pigment, pheophytin (pigment molecule) is reduced with high energy electron, electron is passed down to electron transport chain in thylakoid membrane which produces ATP.
The electron transport center (ETC) includes plastoquinone (PQ) which is what?
electron carrier that shuttles electrons from photosystem II across thylakoid membrane to cytochrome complex, drops off protons in thylakoid lumen
How does the proton concentration inside thylakoid change when the PQ drops them off?
increases 1000-fold
Photophosphorylation is…
energy from light used to initiate synthesis of ATP in chloroplast
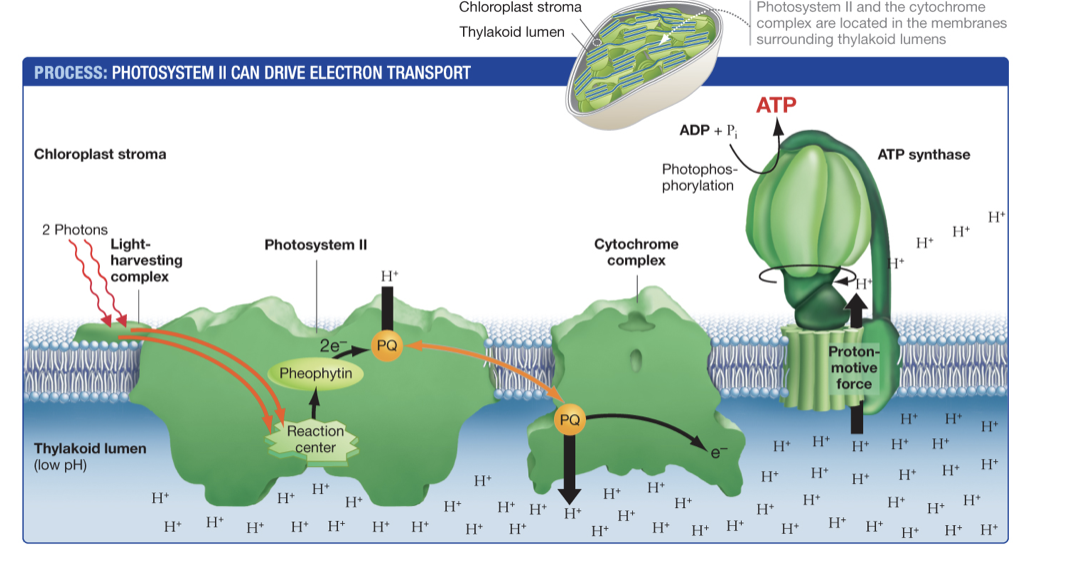
What happens after electrons travel through the ETC when converting light to energy into chemical energy?
protons travel into cytochrome complex before diffusing through ATP synthase causing conformation changes in enzyme driving synthesis before photophosphorylation.
How does photosystem II obtain electrons?
by oxidizing water
What is the process called in which water is oxidized and its low energy electrons are used to reduce the reaction center, where photosystem II splits water and produces oxygen
oxygenic photosynthesis
Other organisms have only a single photosystem, meaning what?
they do not oxidize water, they do not produce oxygen, and perform anoxygenic photosynthesis
Photosystem I passes excited electrons to what electron carrier?
NADP+
Describe the process photosystem I uses to pass excited electrons.
antenna pigments absorb photons and pass energy to photosystem I reaction center, electrons are excited, reaction center pigments are oxidized, excited electrons passed to NADP+ which reduces to NADPH
How does photosystem I work?
electrons from photosystem I produce NADPH, electrons from photosystem II produce proton-motive force that drives ATP synthesis, photosystems I and II produce chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH