BICD 110 midterm 1
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
LECA
hypothetical last common ancestor of all eukaryotes (around 1.5-2 billion years ago)
biological scales
mammalian cells: 10-100um
prokaryotic cells: 1-10um
organelles: 2-20um
micromolecular complexes: 200nm-2um
proteins/ ribosomes: 20nm
Hooke
invented compound microscope
discovered plant cells, named “cells” after cork micrograph drawing
Leeuwenhoek
invented single lens microscope
discovered microorganisms “animacules”S
Schleiden
“every part of a plant is made of cells”
Schwann
“plants, animals, and their products are made of cells”
Virchow
created cell theory
Palade
used diamond knife + electron microscopy to visualize many structures
invented pulse-change, SDS-PAGE
cell theory
all living organisms are 1+ cells
the cell is the most basic unit of life
all cells arise from pre-existing cells
visible light spectrum
450nm: blue
500nm: green
600nm: orange
650nm: red
fluorophores
fluorescent chemicals that can re-emit light by dropping down from an excited state to ground state
SEM (scanning electron microscopy)
samples are processed w/ metals and electrons scan surface
allows surface features to be visualized/ topographical map to be made
TEM (transmission electron microscopy)
samples are heavily processed w/ metals (thick and thin samples can be prepared); electrons pass everywhere but metal areas to visualize structures w/in cells
cryo-EM
visualizes samples more naturally; samples frozen rapidly to form non-crystalline ice
immunolabeling
antibodies respond to a protein of interest and have covalently attached labels (fluorescent dyes or gold particles)
primary antibodies + secondary antibodies to amplify signal
fixation
required for electron microscopy/ immunolabeling
freezes cell structures in place/ prevents damage during processing for visualization
permeabilization
makes plasma membrane permeable to reagents for labeling/ staining for visualizaion
four concepts for the chemistry of life
molecular complementarity: complementary interactions (shape, polarities, etc.)
polymerization: combination of subunits to create emergent properties
chemical equilibrium: rxn equilibriums can shift based on diff. environments
energy: most common source of energy is ATP
bond strengths/ energy listed in order
thermal energy < van der waals < h-bonds < ATP bond < C-C < C=C
covalent bonds x10-100 strength over noncovalent
hydrophobic effect
hydrophobic molecules group together in water to decrease entropy
Tm of lipids
melting temp of lipids; the temp at which 50% of lipids in a membrane are fluid
types of phospholipids
glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids
glycerophospholipids
phosphoatidylcholine (PC)
phosphatidylserine (PS)
phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
phosphatidylinositol (PI)
phosphatidylglycerol (PG)
cardiolipin (CL)
sphingolipids
sphingomyelin (SM)
cholesterol
acts as fluidity buffer in lipid membranesho
homeoviscous adaptation
ability of cells to change their membrane lipid composition to control membrane fluidity
(introduction/ elimination of kinks/ unsaturated bonds, shorter/ longer acyl chains)
protein hierarchical structures
primary (linear sequence of AAs)
secondary (alpha helixes, beta sheets, held together w/ backbone h-bonds)
tertiary (3D protein shape)
quaternary (multiple tertiary structure peptides)
supramolecular complexes (multiple subunits associating w/ one another; 10s-100s)
Plant cell unique structures
Cell wall to maintain cell’s shape
Vacuole for water storage
Chloroplasts for photosynthesis
Plasmodesmata as cell junctions
Animal cell unique structures
Microvilli to increase SA for absorption of nutrients from surroundings
Single bilayer organelles
ER, ERGIC, golgi, TGN, PM, lysosomes, peroxisomes
Two bilayer organelles
Mitochondria/ chloroplasts, nucleusM
Monolayer organelles
Lipid droplets
How the first membranous organelles formed
Infolding of PM → nucleus + ER
Engulfing of another prokaryote → mitochondria + plastid (chloroplasts)
ER % membrane surface
Smooth: 10%, Rough: 50%
Combined 50-60%
ER % volume of cell
Smooth: 6%, Rough: 10%
(inner) Mitochondrial membrane % membrane surface
20-30%
Mitochondria % cell volume
20%
Cytosol % cell volume
50%
Rough ER morphology + function
sheet structure, enriched near nucleus/ golgi
secretory pathway for proteins, site of protein folding/ post-translational modifications, protein quality control, N-glycosylation
Smooth ER morphology + function
tubular structure evenly distributed through cytoplasm
steroid hormone synthesis, cellular detox center, calcium ion storage
ERGIC morphology + function
space between ER/ golgi; contains vesicles
sorts cargo for reconsumption by ER or consumption to golgi
Golgi morphology + function
stacked sacs (cisternae) with a cis face toward rough ER and trans face toward PM
flat centers w/ concentrated enzymes where reactions take place and fenestrated regions where transport takes place (COPI and COPII vesicles)
O-glycosylation, remodeling of N-glycans, stepwise modification of cargo, lipid synthesis/ transport, lipidation of proteins
TGN morphology + function
tubular system at the trans end of golgi apparatus
recieves cargo from endosomal system/ golgi, trasport of lysosomal enzymes to lysosomes/ endosomes, processing of proproteins, retrograde transport of golgi residents, calcium-dependent sorting (regulated/ constitutive secretion)
PM morphology + function
lipid bilayer with proteins throughout (fluid mosaic model)
physical barrier w/ selective permeabiilty, transport of solutes, endocytosis/ phagocytosis/ exocytosis, cell signaling
endo-lysosomal system morphology + function
network of interconnected vesicles/ tubules
endocytosis, phagocytosis, autophagy for digestion/ recycling using lysosomes
nucleus morphology + function
contains nuclear outer/ inner membranes, nucleolus, nuclear pores, continuous w/ ER
stores DNA, separates transcription from translation, selectively permeable
mitochondria morphology + function
outer/inner membrane with crystae for SA, filled with matrix/ matrix granules
ATP production, oxidation of fatty acids, citric acid cycle, DNA storage
lipid droplets morphology + function
organelles w/ a core of neutral lipids enclosed in phospholipid monolayer
energy storage to maintain homeostasis/ membrane homeostasis
peroxisomes morphology + function
lipid bilayer with crystalline core
generation/ scavenging of reactive oxygen species, breakdown of “difficult” molecules, biosynthesis of special membrane lipids
SDS-PAGE
technique by palade; uses gel as a sieve to separate proteins based on size
proteins are denatured + coated w/ ionic (negatively charged) detergent
pulse-change experiments
by palade; provides cells w/ a short pulse of radiolabeled AAs to observe where the newly synthesized proteins go over time
Blobel/ signal sequence hypothesis
proteins contain signal sequences that can direct them to the rough ER
Process: co-translational insertion of secretory proteins into the ER
ER signal sequence emerges from ribosome during protein synthesis
signal recognition particle binds the signal sequence/ pauses protein synthesis
the SS-SRP-ribosome complex binds to the SRP receptor which connects the complex to the translocon (sec61) using GTP
SRP dissociates and an additional GTP is used to line the protein up with the translocon channel
ribosome unpauses protein synthesis and continues building through translocon into ER lumen
SS sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase and is rapidly degraded
translation completes and protein is drawn the rest of the way into the lumen/ folded as the translocon closes
sec61
translocon
hourglass-shaped channel shaped by isoleucine (mimics hydrophobic membrane to interact with hydrophobic signal sequence)
lateral gate for transmembrane proteins to exit into the membrane
“plugged” gate
Process: membrane protein insertion to ER membrane
protein is connected into the translocon
hydrophobic stop-transfer anchor sequence enters the translocon channel during transcription
anchor sequence is transferred through lateral gate into membrane and translocon closes (positively charged is always in cytosol)
synthesis of the protein continues until the stop codon is reached
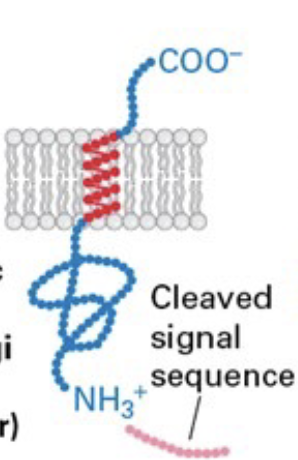
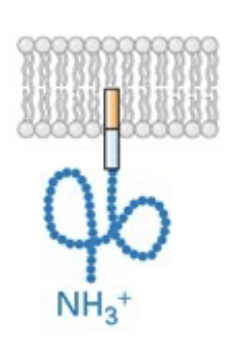
type I membrane protein
signal sequence at N-terminus, N-terminus in ER lumen and C-terminus in cytosol
type II membrane protein
C-terminus in ER lumen and N-terminus in cytosol
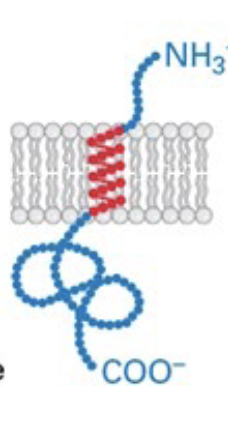
type III
N-terminus in ER lumen and C-terminus in cytosol
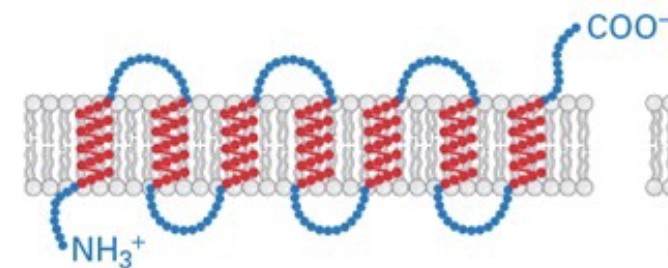
type IV
multiple anchoring regions in the membrane; weaving/ in out with N and C terminus on opposite sides of the membrane
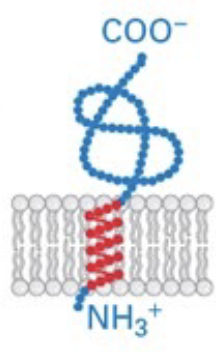
tail-anchored proteins
C-terminus is embedded in membrane, N-terminus in cytosol
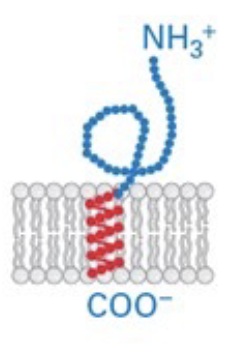
GPI-anchored proteins
tail anchored proteins are built with N-terminus in ER, then transferred off anchor region onto a GPI-molecule anchor
Process: N-glycosylation
occurs during protein synthesis through the translocon
N-glycan precursor (oligosaccharide) is made of 2 n-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), 9 mannose residues (Man), and 3 additional sugars (Glc) → (Glc)3(Man)9(GlcNAc)2
Oligosaccharides are added to asparagines in (Asn - x - Ser/Thr) regions on target proteins as they emerge through the translocon
Addition/ removal cycle of glucose residue plays a role in protein folding
Removal of one mannose residue
final product for cell export: (Man)8(GlcNAc)2
CNX/CRT
“chaperones” of correct protein folding in the ER that bind w/ the addition of glucose onto n-glycan regions and retain proteins in ER until properly folded
OS-9
if protein is continuing to be misfolded, mannose are trimmed and OS-9 exports misfolded protein for disposal
PDI
contains S-S disulfide bond that locates two “S” in the protein and transfers the disulfide bond to between them
as the protein continues to emerge, PDI transfers/ breaks bonds until the most thermodynamically stable
BiP
chaperone protein that binds to exposed regions of growing protein chain and stabilizes them until a protein is folded correctly
in influenza, activates Ire1 transmembrane proteins to dimerize and trigger other chaperones
Ts mutant genes
genes which at a permissive temp (lower), the protein forms normally, but at a restrictive temp (higher), the protein doesn’t fold
Necessary things for vesicular transport
machinery to attract a coating
coat proteins (w/ rigid form, deforms membrane to match, stabilizes the carrier)
uncoating of carrier (mechanism that takes coating away to allow for fusion)
machinery for fusion (specificity for the target membrane, ability to pull carrier/ target membrane together)
COPII vesicles
anteretrograde - from ER to golgi/ ERGICC
GAP, GTPase, GEF reationship
GAP makes GTPase more effective/ expidited
GEF exchanges GDP for GTP on GTPase to change from inactivated to activated
COPII vesicle biogenesis
Sar1-GDP (inactivated GTPase+GDP complex) interacts with Sec12 (GEF activity) on the ER membrane to activate Sar1
Sar1 integrates itself into the membrane on the cytosolic-facing side
Sar1-GTP recruits sec23/ sec 24 coat protein complex and sec 13/ sec 31 completes the coat assembly (double coating)
Coat curves and pinches off ER membrane region
Sec23 GAP activity stimulates Sar1-GTP hydrolysis, re-inactivating Sar1 and causing it to detach from the membrane along with the coating
** additional factors needed for bulkier cargo (animal cells)
COPI vesicles
retrograde - from golgi/ ERGIC to ER
COPI vesicles biogenesis
p24 attracts Arf1-GDP (inactivated GTPase + GDP complex) which interacts with GBF1 (GEF) in the cytosol to activate Arf1
Arf1-GTP recruits a coatomer that assembles on membrane and pinches off the vesicle
ArfGAP activity stimulates Arf1-GTP hydrolysis
Release of Arf-GDP from vesicle membrane causes disassembly of the coating
COPII/ COPI fusion mechanism
V-snares located on vesicles form coils with t-snares on target membrane 1 v-snare + 3 t-snares)
coiling of snares brings membranes close together for docking/ fusion
NSF ATPase separates the helix bundle after fusion occurs
COPII vesicle - cargo signals for proteins
transmembrane: Inner layer (sec23/ sec24) of COPII coat recognizes di-acidic + di-hydrophobic signals on cargo transmembrane proteins
other: ERGIC-53 binds high mannose n-glycans (Man8(GlcNAc)2) made in the ER to cluster them into COPII carriers; binding is pH-dependent and releases in acidic ERGIC environment
COPI vesicle - cargo signals for proteins
transmembrane: Coatomer of COPI recognizes basic signals on cargo transmembrane proteins
other: KDEL receptors bind to missorded ER-resident proteins in the ERGIC to incorporate them into COPI vesicle
Maturation model of intra-golgi transport
COPI vesicles move enzymes to former cisternae as they move forward and convert themselves from cis to trans; cargo stays stationary
Evidence: cis and trans golgi converted colors (cis protein color → trans protein color) over time in yeast cells
Stable cisternae/ vesicular transport model of intra-golgi trasport
Cisternae are stable compartments w/ a specific set of resident enzymes that stay put; cargo is transported between them w/ tubular or vesicular carriers
Evidence: In human cells over time, cis/ trans parts of the golgi were always cis/ trans
Process: Processing of N-glycans in Golgi
Cis golgi: mannosidases remove 3 man residues
Medial golgi: 1GlcNAc added, 2 more mannoses removed, 2 more GlcNAc added, 1 fucose added
Trans golgi: 3 gal (galactose) residues added
** some proteins selectively choose some steps and not other steps
O-glycosylation
occurs in the cis-golgi
O-glycan precursor binds to Ser/ Thr residues
Temperature-sensitive VSV G experiment
Golgi system was set up in vitro and injected w/ a temperature sensitive, radioactively labeled virus G protein
Misfolded protein under restrictive temps was retained in ER and properly folded protein under permissive temps moved through secretory pathway + could be observed
lipid composition throughout the cell
closer to PM: more rigid, more cholesterol/ sphingolipids
closer to interior: more fluid/ flexible, more phosphoacytylcholine
OSBP
feeds cholesterol from the ER where it’s produced into the trans-golgi PM
clathrin-coated vesicles (structure)
bud from TGN and PM for transport
3 heavy + 3 light chains = triskelions
36 triskelions = complete clathrin coating
5 types of cargo/ destinations for TGN to sort
retrograde transport of golgi enzymes to trans-golgi (GOLPH3)
lysosomal enzymes into lysosomes
lysosomal enzymes into late endosomes
constitutive secretory vesicles
regulated secretory vesicles
process: CCV biosynthesis
Arf1-GDP binds to cytosolic GEF and is activated
Arf1-GTP binds to TGN membrane, recruits cytosolic AP-1 (adapter protein) to the membrane
Arf1-GTP induces conformational change in AP-1 to open and attract cargo sorting motifs
Clathrin (coat proteins) are recruited by AP-1 and bind to form coating
Dynamin (GTPase) polymerizes and uses GTP to pinch off the membrane
Hsc70/ auxilin use more GTP to break down the clathrin coating on vesicle exterior and allow vesicles to be ready for fusion
TGN cargo signals for proteins (general proteins, golgi residents, lysosomal proteins)
general proteins:
u1 subunits: binds tyrosine+hydrophobic (YXX(hydrophobic)) regions on proteins
o1-y subunits: binds dileucine (LL) regions on proteins
golgi residents:
GOLPH3: recognizes golgi-resident protiens and confines them to COPI vesicles for retrograde transport back to the golgi
lysosomal proteins:
M6P receptor: binds to m6p on modified lysosomal enzymes and attracts clathrin coating
Process: TGN sorting lysosomal enzymes
Pre-TGN, in the cis-golgi:
GlcNAc phosphotransferase recognizes QS/HEY sequences in newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes + transfers phosphorylated GlcNAc to 1+ mannose residues
Phosphodiesterase removes GlcNAc group to leave a mannose 6 phosphate (M6P) on the lysosomal enzyme
TGN:
M6P receptor is active in the higher pH at the TGN membrane and recruits APs to create a clathrin coating
Clathrin coating is broken down w/ hsc70/ auxilin and can fuse with late endosome/ lysosomes (lower pH = M6P receptor releases enzyme)
M6P and vesicle can be recycled back to TGN and PM
Regulated exocytosis
requires a signal for exocytosis to occur; calcium dependent sorting
seen in synaptic vesicles and release of insulin by pancreatic beta cells
Constitutive secretory pathway
constantly secreting; calcium dependent sorting
TGN processing of proproteins
constitutive pathway:
Furin endoprotease cleaves peptide at c-terminal end of two consecutive AAs
regulated secretory pathway:
PC2 and PC3 endoproteases cleave central region of insulin
Carboxypeptidase cleaves two c-terminal basic AA residues