APP II- FINAL Review
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes Krysiak's Kahoot + cards based on her review ppt. + Canfield's stuff
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
95% CI of 0.45 to 1.25. You could expect the p value to be < 0.05 and the results to be statistically significant.
a. true
b. false
false
Which of the following assesses the methodological quality of clinical trials included in systematic review and meta analysis:
a. spearman correlation
b. chi-squared test
c. jaded score
d. ANOVA
c
The ARR in a study was calculated as 2.5%. The NNT is calculated to be:
a. 20
b. 30
c. 0.4
d. 40
d
Within a journal article, where can you find strengths/limitations of a study?
a. intro
b. results
c. discussion
d. methods
c
Patients that follow study procedures and are 100% compliant with medication are included in what type of analysis?
a. intention to treat
b. per protocol
c. subgroup
d. modified intention to treat
b
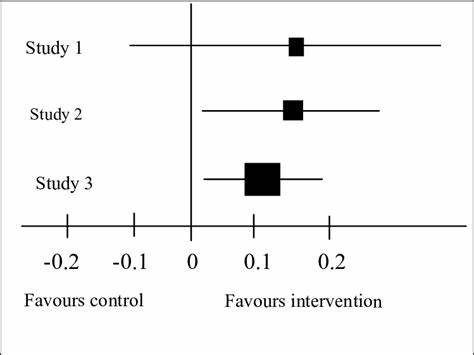
According to this image, which study has statistically significant results?
SATA:
a. study 1
b. study 2
c. study 3
(edit, I didn’t realize the picture I grabbed was a bad picture—> should say 1 instead of 0)
b, c
When you look at a forest plot, how can you tell if the study is statistically significant?
ANYTHING THAT CROSSES 1—> not significant
If it doesn’t cross 1—> significant
(omg bad picture yet again)
If Drug A has an NNT of 15 and Drug B has a NNT of 47. All other factors aside, which medication is preferred?
a. Drug A
b. Drug B
a
Which of the following is used most commonly to convey results of a meta-analysis?
a. forest plot
b. funnel plot
c. PRISMA diagram
d. evidence table
a
Effect size and power are used to determine:
a. sample size
b. surrogate endpoints
c. baseline measurement
d. process measurement
a
Guidelines are considered what type of resource??????????
a. primary
b. secondary
c. tertiary
c
I-squared statistic pertains to:
a. presence of publication bias
b. alpha error
c. association between continuous variables
d. heterogeneity among studies
d
A combination of 2 endpoints (ex: myocardial infarction or death to evaluate efficacy) are:
a. surrogate endpoints
b. clinical endpoints
c. safety endpoints
d. composite endpoints
d
Retrospective studies can tailor study measures to directly answer research questions.
a. true
b. false
b
One researcher in a study uses a different range when reporting lab values. This describes what type of bias?
a. researcher bias
b. historical bias
c. publication bias
d. information bias
d
Fixed effects model are/have: (select two)
a. due to random variation
b. different underlying effect for each study
c. narrower confidence interval
d. wider confidence interval
a,c
Inclusion of unpublished data minimizes this type of bias:
a. selection
b. publication
c. attrition
d. investigator
b
Using cholesterol level lab values to predict risk of having a heart attack is an example of:
a. surrogate endpoint
b. clinical endpoint
c. safety endpoint
d. composite endpoint
a
Balances subjects on baseline covariates, produces comparable groups regarding characteristics such as age, gender, etc.
a. block randomization
b. simple randomization
c. stratified randomization
d. adaptive randomization
c
Which of the following describes a study’s ability to be generalized in a clinical setting/to your patients:
a. internal validity
b. external validity
c. statistical significance
d. power
b
A relative risk of 1.52 means:
a. risk of disease is increased by 152%
b. risk of disease is increased by 52%
c. risk of exposure is increased by 152%
d. risk of exposure is increased by 52%
b
Drug A has a NNH of 15, and Drug B has a NNH of 47. All other factors aside, which medication is preferred?
a. Drug A
b. Drug B
b
What is the IMRaD format of an article? What does each letter stand for?
IMRaD stands for:
I- introduction
M- methods
R- results
D- discussion
in addition- abstract and references
What is the point of an abstract? Can it be used to make clinical decisions?
only used to decide whether or not the article is relevant
NEVER rely on for clinical decisions
What are the 5 types of research questions and the best study types to answer them?
diagnosis- prospective, blind comparison to the gold standard
therapy- meta-analysis of RCTs, systematic reviews of included RCTs, or RCT
prognosis- cohort>case control>case series
harm- RCT>cohort>case control>case series
prevention- RCT>cohort>case control>case series
Describe each kind of endpoint/outcome:
clinical endpoints
surrogate endpoints
composite endpoints
clinical endpoints
represent diseases/symptoms
DIRECT measure of how pts. feels, fxns, or survives
surrogate endpoints
used when outcome is too difficult to measure
indirect measures of clinical outcomes
composite endpoints
outcomes that captures pts. experiencing 1+ outcomes
you achieve outcome is ONE has been achieved
Are clinical and statistical significance the same thing? Describe each?
NOT THE SAME!!!!!
clinical- “REAL WORLD”—> efficacy or safety that is clinically meaningful in practice
statistical- indicated by p-value, evidence against the null hypothesis
What are some things to consider in preparation for a journal club?
make sure to collect…
review what?
make sure to collect background info—> provide recs on current guidelines, disease state, etc.
REVIEW SUPPLEMENTAL or APPENDICES when available
Bias are systematic errors in the way subjects are selected, measured, and analyzed.
Describe selection and measurement/information bias:
selection bias
error in the estimate of effect due to how subjects are SELECTED
occurs when subjects selected in the study AREN’T representative of the population or distribution of tx is related to the outcome
ex: only picking healthy 21-year olds for your study then trying to apply it to old ppl
measurement/information bias
occurs in data collection stage
when there are systematic differences btwn study groups regarding how exposures/outcomes are measured and reported
What is a confounding factor?
What is it associated with?
Is it a threat to internal/external validity?
basically is an outside variable that influences/associated with the TREATMENT AND OUTCOME!!!!!!!!!!
ex: if you were studying a new drug to see if it reduces heart attacks, a confounding variable could be # of smokers bc that could effect the treatment and outcome
threat to internal validity
What’s the difference between internal and external validity?
internal- Are the study results valid?
external- Will the results generalize to local practive?
What factors if conducted poorly, may lead to decreased internal and external validity?
internal- randomization, measurement/assessment of variables in the study, dropouts, attrition rate, overall methodology
external- recruitment and selection of participants, inclusion/exclusion criteria, sample size, setting
What is inclusion and exclusion criteria?
inclusion- what determines which pts. get included/enrolled in the study
exclusion- what determines which pts. are not included in the study
What’s the difference between open and closed cohort?
open—> participants enter/leave the study at different times. population may change over time
closed—> fixed group of participants followed over time, no new members are added
Risk Ratio is the ratio of the risk of an outcome in the exposed group to the risk in an unexposed group (exposed/unexposed= RR).
For example, If the risk of developing a disease is 10% in smokers and 2% in non-smokers, what is the relative risk and interpret it?
RR= 5, means that smokers are 5 TIMES more likely to develop the disease
What is risk difference?
difference in risk of an outcome between the exposed/unexposed groups
What’s the difference between a prospective and retrospective study?
prospective- “FUTURE”—> ppl are followed over time to observe outcomes
retrospective- “PAST”—> look back in time to analyze data/outcomes that have already occurred
Odds Ratio is the probability that an event will occur vs. the probability it won’t occur. Hazards Ratio is the rate an which an unfavorable event occurs within a period of time. Answer the following on how OR and HR are interpretated:
OR or HR =1 means what?
OR or HR> 1 means what?
OR or HR < 1 means what?
1= event rate equal in tx and control. No advantage to tx.
>1 = event rate in tx group is GREATER than control group
<1= event rate in tx group is LOWER than control group
What is a systematic review? What is a meta-analysis?
systematic review
QUALITATIVE process for identifying/summarizing EXISTING STUDIES that address a specific question
meta-analysis (also known as quantitative systematic review)
QUANTITATIVE synthesis of data from individual studies
GOAL: PRODUCE A SINGLE ESTIMATE OF TX effect
For each of the following say if it’s primary, secondary, or tertiary literature:
narrative review
qualitative systematic review
meta-analysis
narrative review- tertiary
qualitative systematic review- tertiary
meta-analysis- primary
What does PRISMA stand for? What is it?
preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
it is a guidance document that describes what info should be reported in systematic review
What is grey literature and why is it important to include in systematic reviews?
grey lit- data not formally published in standard sources (e.g. journals)
important to include to avoid publication bias
______________ is a graphical representation commonly used in meta-analyses to evaluate the results of multiple studies on the same topic.
forest plot
What does assessment of heterogeneity mean?
we are looking at how similar our studies are
(ex: if we are comparing 2 studies we want them to be similar and this measures that)
Do we want high or low heterogeneity?
low—> high heterogeneity would mean that there’s big differences btwn the studies
What are the 2 ways to assess heterogeneity?
Cochran’s Q test
I2 statistic
What’s the difference between a fixed effects model and a random effects model?
fixed—> assumes there is random variation, produces SMALLER CONFIDENCE INTERVAL
good for when there is low heterogeneity
random effects—> produces WIDER CONFIDENCE INTERVAL for the total overall effect, less accurate
used for when there is high heterogeneity
WHAT IS USED to assess publication bias?
FUNNEL PLOT!!!!!!!!!
others: statistical tests like Begg’s test and Egger’s test
What is PubMed?
______ database maintained by the _________________.
NOT a full _______________
DOES NOT provide ___________________________
free database maintained by the National Library of Medicine.
NOT a full text database
DOES NOT provide full text access to all articles
What are Boolean operators? What are 2 examples and their function?
boolean operators—> used to connect search terms when searching databases
use AND to connect key concept terms
use OR to add in additional terms that are similar to key concept terms
What is MeSH? Is it the only type of subject heading system?
“medical subject headings”—> subject headings that PubMed/Medline assigns to articles to help make them more findable
not the only subject heading system (other databases use dif ones) (FYI—> she said to remember this for the test)

What is automatic term mapping? Is it automatically applied to your search or do you have to add it?
automatic term mapping—> algorithm by PubMed to help expand your search
AUTOMATICALLY APPLIED anytime you do a simple search
How do you turn off automatic term mapping on PubMed?
use quotation marks (ex: “parkinson’s”)
use truncation (ex: parkinson*)
using another search filed other than all fields
Which of the following is true about search filters:
a. search filters are automatically applied to PubMed searches
b. search filters can be used to narrow your search to retrieve fewer articles
c. search filters include OR and AND
d. search filters can be used to broaden your search to retrieve more articles
b
A RCT trial compares medication X to a placebo. The study investigators determine that 1,000 pts. were necessary to have 80% power. The investigators included 1,250 pts. in their intention-to-treat analysis. Was power met?
yes
True or False: successful randomization leads to strong internal validity.
true
What’s the difference between block and stratified randomization?
stratified—> allows for balanced assignment to groups based on certain characteristics
blocked—> common form of restricted randomization to ensure similar sample sizes of tx groups
What’s the purpose of blinding in RCTs?
minimize investigator and detection bias
Define intention-to-treat:
pts. that are enrolled in the study and provide informed consent are analyzed
Define per-protocol:
only patients that comply with treatment protocol are included in the analysis
What is the only method of evaluating data that preserves randomization?
intention-to-treat analysis
Review:
How do you calculate NNT and NNH? What is the ROUNDING FOR EACH?
NNT and NNH = 1/ARR
NNT= ROUND UP
NNH= ROUND DOWN

More calculation review:
