organic functions lect 3
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
3 organic reaction types
substitution
additions
eliminations
whats heterolysis
when both the electrons pair of the covelent bond go to one of the fragments
what is a electrophile
when a carbocation is seeking an electron pair
whats a nucleophile
the ion or molecule with the electron pair that seeks out the positive charge of a carbocation
what are electron pair acceptors
acids
what are electron pair donors
bases
why are carbocations and carbanions very reactive
because of the structures they possess
why are free radicals important
as they are responsible for a number of disease states
whats the bronsted- lowry definition of an acid
a substance that donates a proton to another molecule
what is the bronsted-lowry definition of a base
a substance that accepts a proton from another molecule
What is the Ka
the equilibrum constant
what is the equilibrium constant
a calculation that gives the relative strength of acids
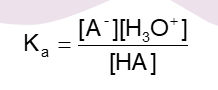
why is ethanoic acid stronget than ethanol
due to the nature of the anion formed after the H+ is formed
what does an electron withdrawing group do
stabilises carboxylate and strengthens acid
what is an electron donating group
destabilises carboxylate and weakens acid
key features of acidic functional groups
presence of a hydrogen atom which can dissociate from the group
delocalise the negative charge