IB SEHS OPTION B HL
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Personality
Relatively stable traits and enduring aspects of individuals. Making them unique but at the same time permit a comparison between individuals
Interactionist approach
Behaviour is a function of both personality and environment
Social learning theory
The theory proposes that people learn through observing demonstrations of others physical activity behaviours.
Motivation
The internal mechanism and external stimuli which arouse and direct our behaviour
Two types of motivation
Intrinsic motivation
Extrinsic motivation
Intrinsic motivation
Motivation from within one self
Pride etc.
Extrinsic motivation
Motivation from outside
Fame etc.
If you do a sports tournament with intrinsic motivation as a key motivation
Less pressure than people who participate with extrinsic motivation as a key motivation
If you do a sports tournament with extrinsic motivation as a key motivation
Increased anxiety and brings less joy
What is Intrinsic motivation driven by?
Personal goals, pride, achievements and self determination
What is Extrinsic motivation driven by?
Financial rewards, social rewards and trophies
Extrinsic rewards may
Reduce intrinsic motivation
Cognitive evaluation theory
Designed to explain the effects of external consequences on internal motivation
Self-determination theory
competence, autonomy, and relatedness are the three basic human needs, and the degree to which they are satisfied will go a long way to determining an individual's intrinsic motivation
Atkinson's model of Achievement Motivation
there is a need to achieve success in order to avoid failure.
How does Atkinson's model achieve success and avoid failure?
By setting a standard of excellence
Traits of high achievers
Risk takers, aim high
Traits of low achievers
Will avoid situations where they may be seen to fail
Goal Orientation
Why people are participating and what the meaning of succes and failure is
Task orientation, reasons for participation (Subset of goal orientation)
associated with intrinsic motivation, effort, persistence and enjoyment
Outcome orientation, reasons for participation (Subset of goal orientation)
judges success by how they compare to others
Task orientation, perception of succes and failure (Subset of goal orientation)
feel good about themselves and they have higher self-esteem because their perception of their ability is based on their own standards of reference or performance standards
Outcome orientation, perception of succes and failure (Subset of goal orientation)
you feel good when you win, but not so good about yourself when you lose
Weiner's attribution theory
based around self serving bias
Self serving bias
It was not our fault
(subset of self serving bias) Failure
Uncontrollable forces
-Weather
-Luck
(subset of self serving bias) Succes
Controllable factors
-Internal
-Personal
Why self serving bias?
To maintain athletes self-esteem and motivation
Locus (ponit or place)
Is a factor of
Casuality
-Internal
-External
Stability
-Stable
-Unstable
Control
-No control
-Have control
Arousal
Arousal is how physically ready, alert and/or prepared, and mentally motivated, interested and excited an athlete is prior to and throughout the performance
Theoretical approach to arousal
Drive reduction theory
Inverted U Hypothesis
Catastrophe Theory
Drive reduction theory
Humans will do the things that allow them to have their internal drive reduced
-When you are thirsty, you drink water.
Athletes possible emotions
Anxiety
Depression
Pleasure
Aroused athlete
Higher elevated heart rate and good cognitive engagement
Under aroused athlete
Not so good cognitive engagement
Anxiety
A negative emotional state which feelings of nervousness are associated with arousal of the body
Trait anxiety
An enduring personality trait
State anxiety
A temporary emotional condition
Measurement of anxiety
(SCAT - Sports Competition Anxiety test) Subjects respond to a questionnaire
Pros and cons of SCAT
Pro:
Easy to conduct
Cons:
Open to response bias
Physcological skill training (PST)
Systematic and consistent practice of mental or psychological skills
Goal of PST
Athletes to effectively function without needing direction from coach
If two athletes have same physical abilities who will win?
The athlete who has better mental skills
Three phases of PST
Education
Acquisition
Practice
Education PST
Increasing athlete awareness of the role of mental skills and how it can affect performance
Acquisition PST
Learning strategies and how to use PST
Practice PST
Automation of the skills
Goal setting
Enhancing self confidence and motivation
Three types of goals
Outcome
-Performing better than another team
Performance
-To throw a javelin 75 meters
Process
-Achieve specific targets and reduce anxiety
Mental imagery
Concentration enhancement
Two types of imagery
Internal
External
Internal imagery
The execution of a skill from your vantage point
External imagery
Viewing yourself from an outside, like a video
When can Mental imagery be performed
Before and after practice
Relaxation techniques
Arousal regulation and reducing anxiety
(Subset of relaxation techniques) Progressive muscular relaxation (PMR)
A technique used to manage stress, tension and anxiety
-Major muscle groups are tensed for a few seconds and then relaxed in sequence
(Subset of relaxation techniques) Breathing techniques
Mechanism for pre competition anxiety
-Just a breathing technique that makes you relax and decrease anxiety
(Subset of relaxation techniques) Bio feedback
Physically oriented technique
Electronic devices
Self talk
Mental preperation
Positive self talk
Positive self statements
-Enhance self esteem
-Performance etc.
Negative self talk
Negative self statements
-Decreases self esteem
-Perfomance etc.
thought stopping
Used to stop negative self talk and maybe even change it to positive self talk
Outline the term talent. (HL Only)
Talent is a multidimensional concept identified by
characteristics that are only partially genetically
determined. It involves psychological as well
as physiological, motor, sociological and
environmental factors.
Two areas of talent identification (HL Only)
Subjective Assessments
Objetive Assessments
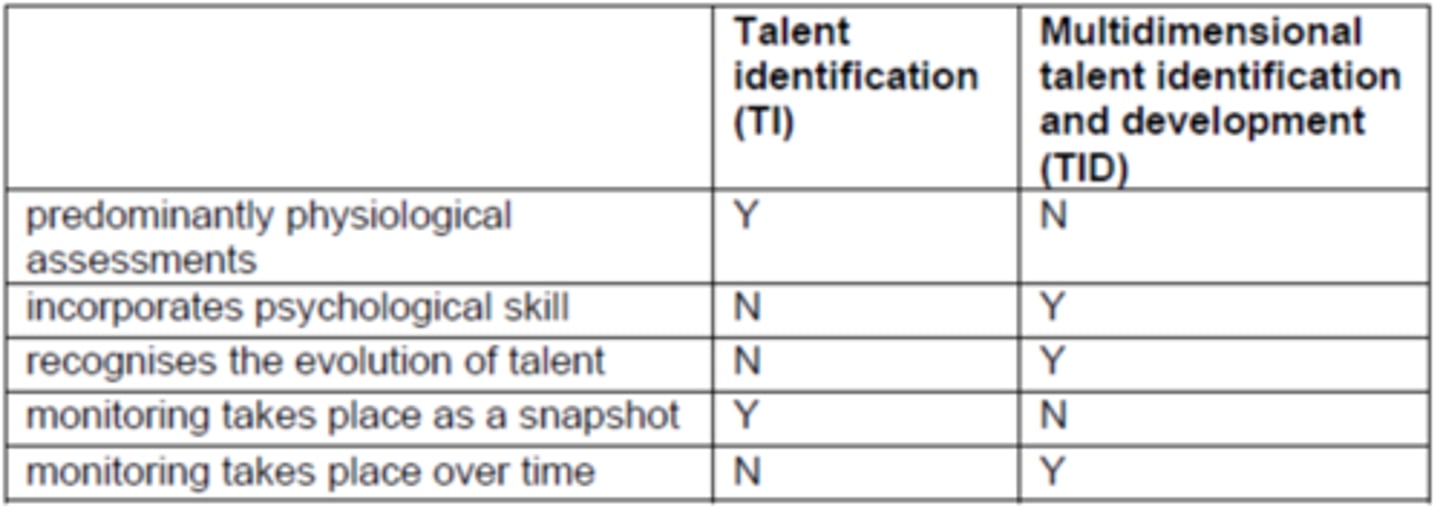
Multidimensional Talent Identification and Development (TID) (HL Only)
Need to monitor progress and behavior during a development program over time.
Balancing weaknesses in one area for strengths in another
Providing opportunities for athletes to develop psychological behaviors
Four stages of athlete development (HL Only)
Initiation
Development
Mastery
Maintenance
Four stages of athlete development (HL Only): Initiation
Characterized by high amounts of play and low levels of practice. Focused on multi-skills rather than specialization.
Four stages of athlete development (HL Only): Development
specialization of sporting skills will occur; a balance now between deliberate play and deliberate practice
Four stages of athlete development (HL Only): Mastery
involves low amounts of play and high levels of practice / focused on specific skills.
Four stages of athlete development (HL Only): Maintenance
the athlete is maintaining their high level of proficiency through high levels of practice.
Talent Transfer (HL Only)
is a reduction or cessation of participation in one sport in order to pursue another sport that involves similar skills or physiological requirements.
Reasons for an elite athlete to transfer to a second sport (HL Only)
an injury
plateau in performance / loss of motivation
desire to prolong an athlete's sporting career / geographical reasons
desire for a greater success than that in the first sport / financial reasons
Distinguish between talent identification and multidimensional talent identification and development.