Bowel Elimination
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Components involved in bowel elimination
Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine, Rectum, Anus, and Defecation.
Factors that influence bowel elimination
Age, diet, fluid intake, physical activity, psychological factors, personal habits, position during defecation, pain, pregnancy, surgery and anesthesia, medication, and diagnostic tests.
Common bowel elimination problems
Constipation, Diarrhea, Incontinence, Flatulence, and Hemorrhoids.
What is a bowel diversion procedure that involves creating an opening from the intestine to the abdominal wall?
Ostomy.
What is ileoanal pouch anastomosis?
A surgical procedure that creates a pouch from the end of the small intestine to connect to the anus after the removal of the colon.
Critical thinking in bowel elimination involves integrating knowledge from various _____ to understand patient responses.
Disciplines.
Assessing bowel elimination should be based on the patient's ______.
Perspective.
Which abdominal region is located above the umbilicus and between the costal margins?
Epigastric.
Where are the Umbilical and Supra public locations located at?
Umbilical- Around the navel
Supra public- Above the symphysis pubis.
When performing a physical assessment for bowel movement what should the nurse inspect?
The mouth, the abdomen and the rectum.
What is the correct order of abdominal assessment?
Inspect, Auscultate, Percuss, Palpate.
Types of bowel sounds include normal, absent, hypoactive, and ______ sounds.
Hyperactive.
What do you inspection when looking the abdomen?
Symmetry, Shape, contour, umbilicus, skin, movement and pulsations.
Define Abdominal Girth
The measurement around the abdomen, typically taken at the level of the umbilicus, used to assess abdominal distention or obesity.
What is the order of ausculation?
Start in the lower right quadrant, then move to the upper right quadrant, the to the upper left quadrant and finally to the lower left quadrant.
Bowel Sounds
The normal bowel sound is high pitched gurgling nosies caused by air mixing with fluid during peristalsis.
Abnormal Bowel Sounds
Absent bowel sounds: lack of peristalsis (no sounds for 5 minutes in each quadrant.
Hypoactive- heard infrequently
Hyperactive- loud, growing sounds (borborygmic)
What should be reported immediately during auscultation?
Vascular abnormalities like bruits.
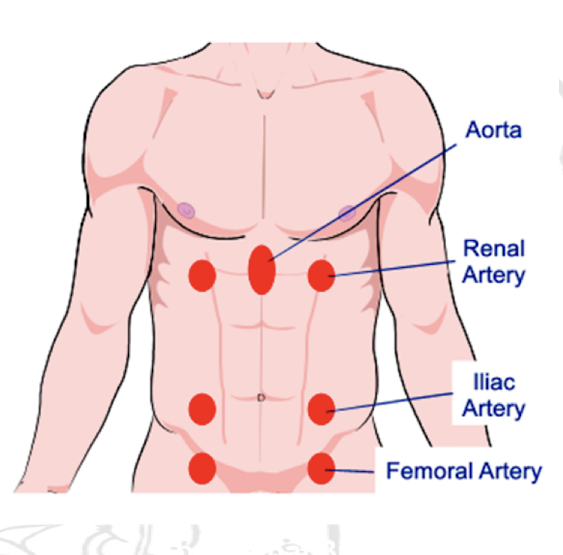
What should you listen to for percussion of the abdomen?
Listen for tympany and dullness, normally you will hear tympany because of the air in the underlying structure and dullness may indicate enlarged uterus, distended urinary bladder or ascitis.
How do you palpate the abdominal cavity?
Look for tenderness, distention or masses, only do light palpation (1/2 inch) and never palpate a pulsating abdominal mass. Rebound tenderness is a sign of appendicitis.
Characteristics to evaluate in stool findings include color, odor, ______, shape, and constituents.
Consistency.
Color variations in stool may indicate biliary issues. What color suggests this?
White or clay.
What does black or tarry stool indicate?
This may indicate blood is being lost somewhere early in the digestive tract, such as in the stomach or small intestine.
What does a noxious odor in stool suggest?
Absorption issues.
Red pale with fat translucent mucus of blood mucus Indicate ___
Infection, inflammation or cancer.
Narrow, pencil-shaped stool could indicate what type of condition?
Possible obstruction.
What are some laboratory tests that can be done?
Fecal Specimens: special collection containers, aseptic collection technique and is a culture.
Stool for ova and parasite: Specimen must be warn, must be sent to lab immediately.
Common nursing diagnoses related to bowel elimination include bowel incontinence, constipation, fecal impaction, and ______.
Diarrhea.
What are risk factors for constipation?
Laxative misuse, medications, lack of exercise, irregular bowel habits, chronic illness, low fiber diet, low fluid intake, anxiety, depression, cognitive impairment, immobility, developmental changes and neurological conditions.
What is impaction and how does it happen?
This is secondary to constipation and is a collection of hardened feces, clients are unable to expel, they are often comatose, confused and debilitated high risk. Oozing Diarrhea is a red flag.
Signs of fecal impaction may result from what two factors?
Constipation and immobility.
What are some common causes of diarrhea?
Antibiotic use, food intolerances, C. difficile infection, intestine the can’t absorb fluid fast.
Incontinence affects social interactions and ______.
Self-image.
What promotional technique is recommended for normal defecation?
Sitting position, good position on the bedpan, privacy, medications, laxative, antidiarrheal agents, digital removal of stool and colorectal cancer risk reduction.
What should be considered when positioning a patient on a bedpan?
Comfort and head elevation. To prevent muscle strain and discomfort be sure to elevate the head of the bed 30 to 45 degrees and always wear gloves when handling the bedpans.
Types of enemas include tap water, saline, soapsuds, and ______ solutions.
Hypertonic.
What are some important things to know about Edemas?
There are low volume and high volume edemas, low volume are about 120mL and high are between 500-1,000mL. These need to be warmed up to body temperature to prevent cramps for occurring.
What are key considerations for the care of patients with ostomies?
Irrigating and pouching ostomies, nutritional and psychological considerations, bowel training and promotion of regular exercise.
How should nursing skills evaluations be conducted?
Through the patient’s experience.
What position should patients be instructed to take for self-administered enemas?
Side-lying position.
Why is it important to check pulse for patients with cardiac concerns when administering enemas?
Due to vagus nerve stimulation risks.
What is a sign of fluid and electrolyte imbalance associated with diarrhea?
Skin integrity concerns.
What are the steps of abdominal assessment?
Inspection, Auscultation, Percussion, and Palpation.
What are normal bowel sounds per minute?
5-35 sounds/min.
What does tympany indicate during percussion?
Air or gas in the abdomen.
Name a contributing factor to alterations in bowel elimination: _____ habits.
Irregular.