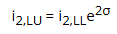Fixed Income
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Price (%of par) of a T-Period Zero-Coupon Bond
= 1 ÷ (1 + Sₜ)ᵗ
Return from bond credit migration

Forward Price (%of par) (at t = j) of a Zero-Coupon Bond Maturing at (j + k)
= 1 ÷ [1 + f(j,k)]ᵏ
Forward Pricing Model
The price of a forward is equal to the price of the bond at time j \cdot the forward rate
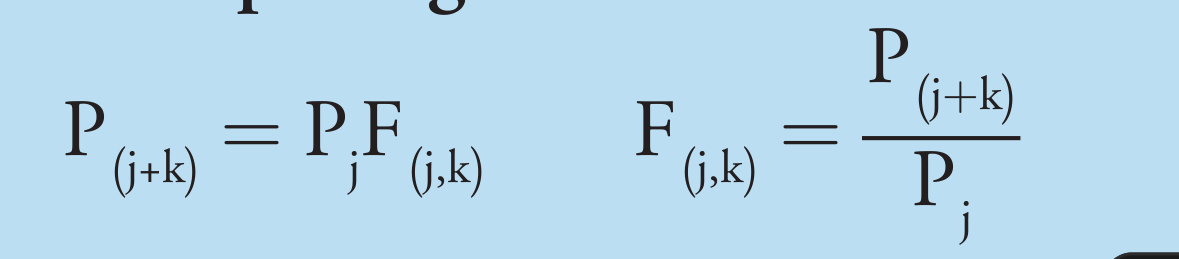
Forward Rate Model
How you derive a forward rate from spot rates. The spot rates at times j and j+k determine it
Swap Spread
= Swap Rateₜ − Treasury Yieldₜ
Represents derivative market credit and liquidity risk (swaps are traded and thus liquid is important)
TED Spread
= 3-Month MRR − 3-Month T-Bill Rate
Represents interbank credit risk only
MRR is unsecured interbank lending
MRR-OIS Spread
= MRR − Overnight Indexed Swap Rate
OIS is the expected Fed policy rate over term of swap
Measure of credit AND liquidity risk in the interbank market
Portfolio Value Change Due to Level, Steepness, and Curvature Movements
= −DᴸΔxᴸ − DˢΔxˢ − DᶜΔxᶜ
Callable Bond Value
= Vₛₜᵣₐᵢgₕₜ − Vcₐₗₗₐbₗₑ
Putable Bond Value
= Vstraight + Vput
Value of Put Option on Bond
= Vputable − Vstraight
Effective Duration
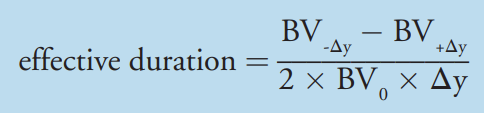
Effective Convexity
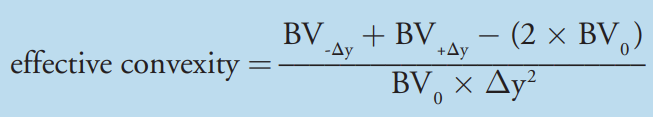
Minimum Value of Convertible Bond
= Greater of Conversion Value or Straight Value
Market Conversion Price of a Convertible Bond
= Market Price of Convertible Bond ÷ Conversion Ratio
Market Conversion Premium per Share
= Market Conversion Price − Stock’s Market Price
Market Conversion Premium Ratio
= Market Conversion Premium per Share ÷ Market Price of Common Stock
Premium Over Straight Value
= (Market Price of Convertible Bond ÷ Straight Value) − 1
Callable and Putable Convertible Bond Value
= Straight Value + Value of Call Option on Stock − Value of Call Option on Bond + Value of Put Option on Bond
Recovery Rate
= % of Money Received Upon Default
Loss Given Default (%)
= 100 − Recovery Rate
Expected Loss
= Probability of Default × Loss Given Default
=PoD x e(loss) per $ x Par
Present Value of Expected Loss
= Value of Risk-Free Bond − Value of Credit-Risky Bond
Upfront Premium % (CDS)
≈ (CDS Spread − CDS Coupon) × Duration
Price of CDS (per $100 Notional)
≈ $100 − Upfront Premium (%)
Profit for Protection Buyer
≈ Change in Spread × Duration × Notional Principal
Cox-Ingersoll-Ross model
o Equilibrium model
o Higher rates means higher rate volatility
o Interest rate movements are driven by people deciding whether to consume today or in the future
o Mean reverting

The Vasicek Model
o Equilibrium model
o Mean reverting
o Constant vol, doesn’t increase with rates
o Doesn’t force non-negative rates
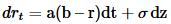
The Ho-Lee Model
o Arb Free Model
o Constant Vol,
o Used to price zero coupon bonds and thus the spot curve
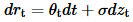
The Kalotay-Williams-Fabozzi (KWF) model
o Arb Free model
o no mean reversion, constant Vol
o ST rates are log normal
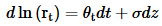
Gauss+ Model
o Central bank controls ST, MT rates revert to long term, and LT rates are also mean reverting and depend on macro
o Hump shaped volatility, most in the middle
Finding Nodal Rates