INTG 0001: Neuroanatomy Terms I Must Know
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Neuron
The basic cell of the nervous system that processes and transmits information
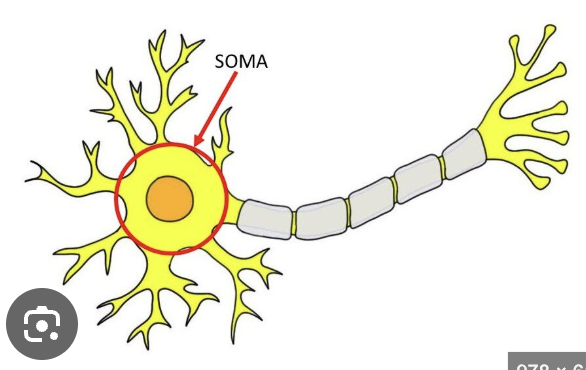
Soma
Cell body of a neuron, containing the nucleus and most organelles
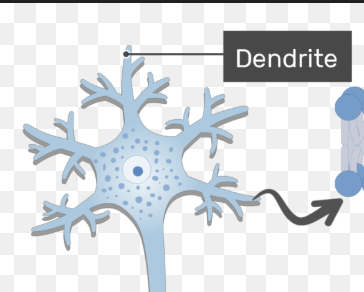
Dendrites
Branchlike extensions from the soma that receive signals from other neurons, transmitting them to the cell body aka soma
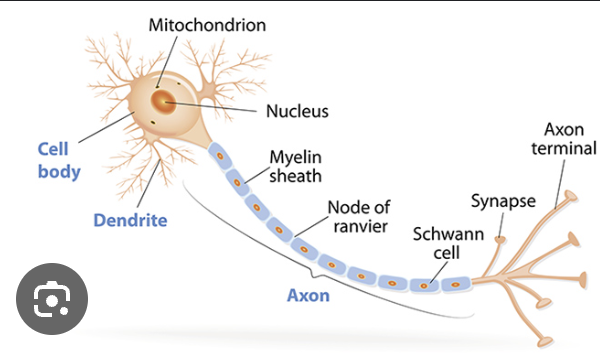
Axon
A long projection that carries electrical signals (action potentials) away from the soma to other cells
Action Potential
Rapid electrical pulse that travels along a neuron’s axon, allowing it to communicate with other cells.
Synapse
Tiny junction between two nerve cells (neurons) allowing them to communicate with each other, forming the basis of neural circuits in the brain and throughout the body.
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger neurons release to transmit signals across a synapse to other cells
Receptor
Specialized protein on neuron’s surface acting as a molecular docking station for chemical signals like neurotransmitters.
Anterior
towards the front
Posterior
towards the back
Rostral
towards the front, nose, head, similar to anterior
Caudal
towards the back, tail, similar to posterior
Superior
Anove
Inferior
Below
Dorsal
towards the back/top
Ventral
towards the belly/bottom
Medial
towards the middle to the brain/spinal cord, closer to the midline than lateral
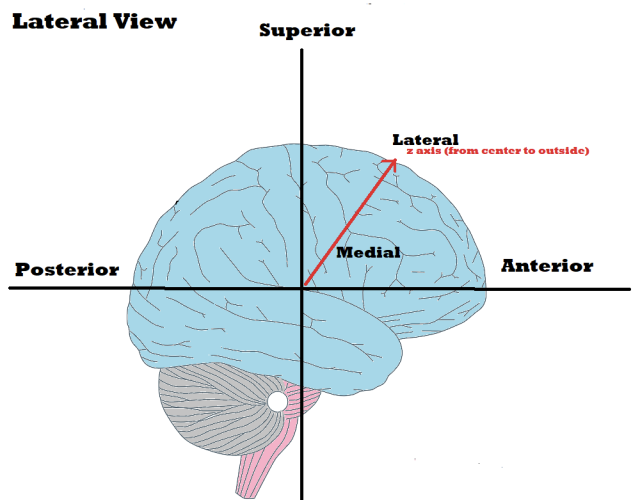
Lateral
Towards the side of the brain, away from the midline, left and right
Midline
Central, vertical line of the brain separating the left and right hemispheres
Contralateral
Idea that one side fo teh brain controls the opposite side fo teh body
Ipsilateral
Structures, functions, and pathways located on the same side of the brain/body
Axial Plane
Also known as the transverse or horizontal plane, divides brain into the upper (superior) and lower (inferior sections)
Coronal Plane
Vertical plane dividing the brain into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections
Sagittal Plane
Vertical plane dividing the brain into unequal or equal left and right halves
What are the lobes of the cerebral cortex?
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital (PIFT)
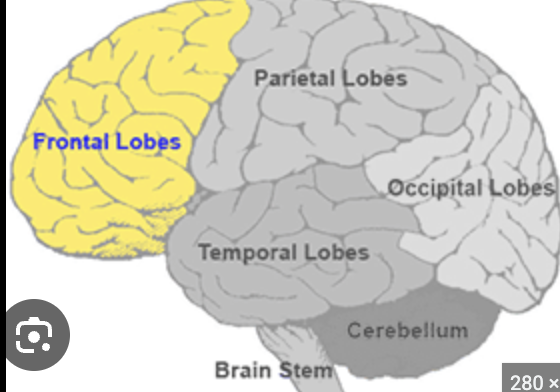
Frontal Lobe
Involved in decision-making, planning, voluntary movement, aspects of personality
Located in the anterior position of the brain, just behind the forehead
Parietal Lobe
Processes touch, spatial awareness, and sensory integration
Located in top/back portion of the brain
Temporal Lobe
Helps with hearing, language, and memory
Located
Occipital Lobe
Mainly utilized for vision