Anatomy and Physiology Exam 2
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BOOOOONNNNNEEEEE?????????
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
what are the functions of the skeletal system
support, protection of internal organs, assist body movements with muscles, mineral homeostasis (store and release C and P), blood production (hemopoiesis), stores triglycerides in adipose cells of yellow marrow.
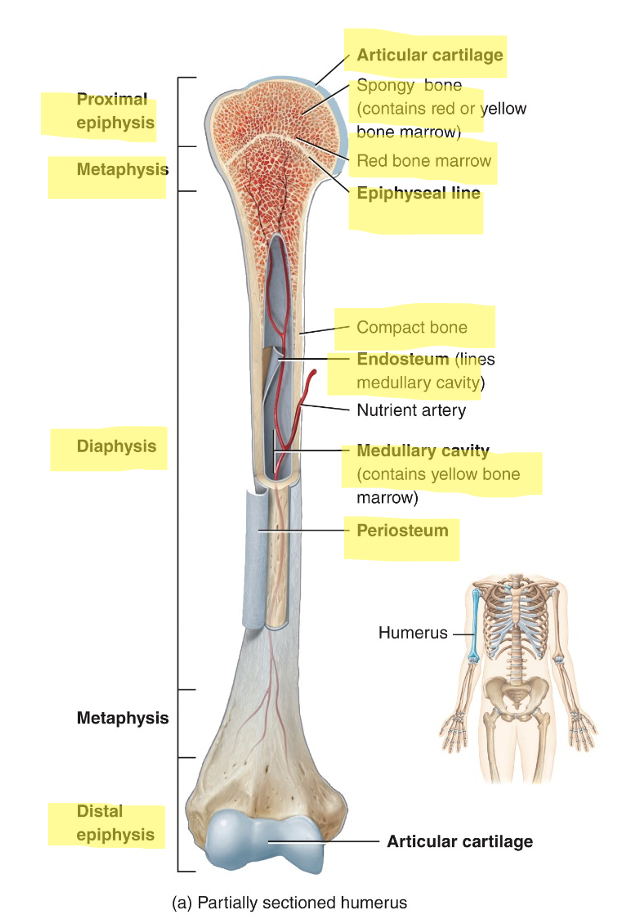
what are the parts of a long bone
diaphysis (bone shaft)
2 epiphyses (both ends of the bone at the joints)
2 metaphyses (region between diaphysis and epiphysis
articular cartilage covering both epiphyses
periosteum (connective tissue surrounding the diaphysis)
medullary cavity (hollow space within diaphysis)
endosteum (thin membrane lining the medullary cavity)
extracellular matrix composition
15% water, 30% collagen, 55% crystallized mineral salts(hydroxyapatite composed of calcium, phosphate, and calcium hydroxide)
what are the 4 types of bone cells
osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
osteoprogenitor cell
bone stem cells
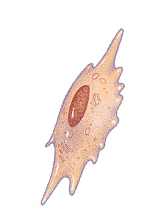
osteoblast
bone-building cells that secrete matrix and initiate calcification
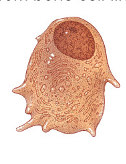
osteocyte
mature bone cell
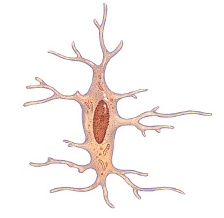
osteoclast
remodel bones, cause them to releasee calcium, bone resorption
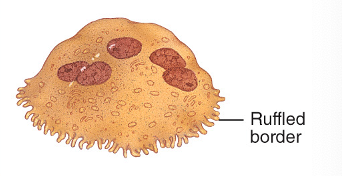
compact bone
protection and support, strongest
spongy bone
lightweight and provides tissue support.
how do periosteal arteries enter the diaphysis
through volkmann’s canals, accompanied by periosteal veins
how to do nutrient arteries enter the diaphysis
through the nutrient foramen, through which the nutrient veins exit.
ossification/osteogenesis
the process of bone formation
what are the 4 situations bones form
during embryological and fetal development
when bones grow before adulthood
when bones remodel
when fractures heal
endochondral ossification and where does it occur
replacement of cartilage with bone in the developing embryo and fetus; occurs in epiphyseal plates of long bones as they grow in length.
What factors affect bone growth and remodeling
minerals (C, P, Mg, F, Mn), vitamins (A, C, D, K, and B12), hormones (IGFs, T3, T4, sex hormones)
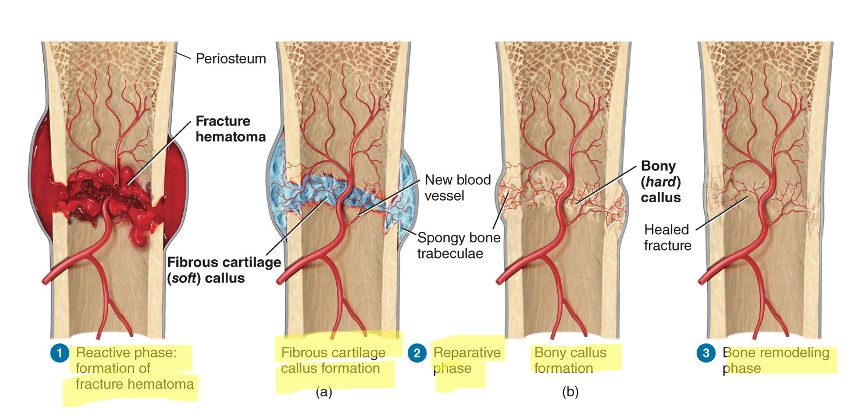
3 phases and 4 steps of a fracture
reactive phase (early inflammatory phase)
reparative phase (formation of fibrocartilaginous callus, then bony callus)
bony remodeling phase (bony callus is remodeled)
how does the parathyroid gland increase blood [Ca]
stimulates osteoclasts to increase bone resorption and release calcium
stimulates the production of calcitriol by the kidneys to increase calcium absorption in the intestines
how does aging affect bone tissue
older individuals, especially post-menopausal women, experience a decrease in bone mass when resorption by osteoclasts outpaces deposition by osteoblasts as the level of sex hormones diminishes starting during middle-aged adulthood. Decrease in bone mass and increased risk of osteoporosis.
bones need calcium and phosphorus to
make bone extracellular matrix hard
bones need manganese to
activate enzymes involved in the synthesis of bone extracellular matrix.
bones need vitamin c to
synthesize collagen, the main bone protein.
bones need growth hormone (GH) to
promote general growth of all tissues including bone. secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
bones need insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) to
promote normal bone growth by stimulating osteoblasts
Bones need thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) to
promote normal bone growth by stimulating osteoblasts; secreted by the thyroid gland
bones need sex hormones to
stimulate osteoblasts and promote the sudden “growth spurt” that occurs during adolescence; secreted by the ovaries in females and testes in males.
bones need parathyroid hormone (PTH) to
promote bone resorption by osteoclasts; secreted by the parathyroid glands
bones need calcitonin (CT) to
inhibit bone resorption by osteoclasts; secreted by the thyroid gland.
how does exercise affect bone growth?
weight-bearing activities stimulate osteoblasts, helping to build thicker and stronger bones and delay bone mass loss due to aging.
osteoporosis
bone resorption outpaces formation, 80% of those affected are women
rickets and osteomalacia
inadequate calcification of extracellular bone matrix. Rickets affect children and lead to bowed legs, skull, rib cage, or pelvis deformations. Osteomalacia affects adults and causes painful/tender bones and fractures with minor trauma.
osteoarthritis
degeneration of articular cartilage, leads to friction of bone against bone
osteomyelitis
infection of bone often caused by Staphylococcus aureus
osteopenia
reduced bone mass below normal
osteosarcoma
bone cancer that primarily affects osteoblasts
bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting what organs?
cranium surrounds brain, vertebrae surround spinal cord and ribs surround heart and lungs
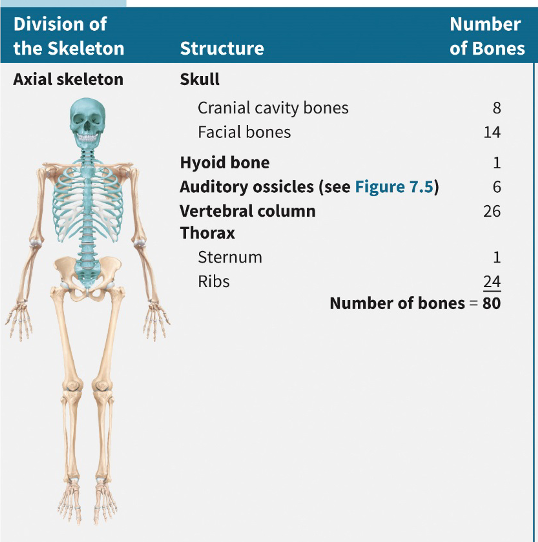
axial skeleton consists of
skull bones, auditory ossicles, hyoid bone, ribs, sternum, vertebrae and sacrum
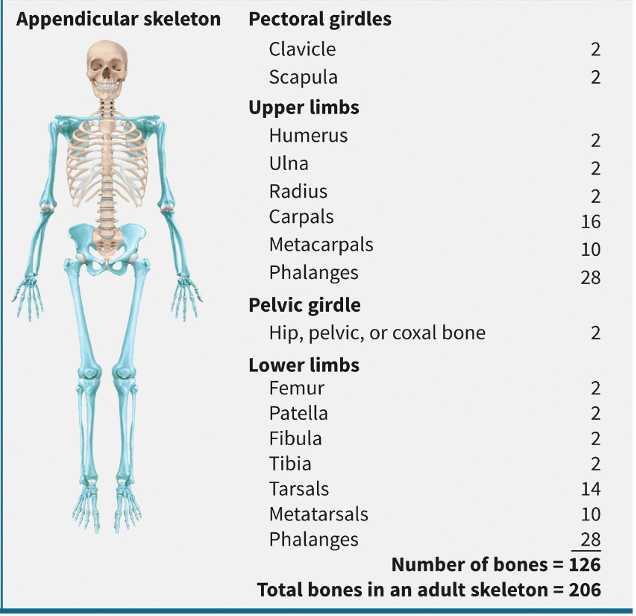
appendicular skeleton consists of
bones of the upper and lower extremities and the bones forming the girdles that connect the limbs to the axial skeleton
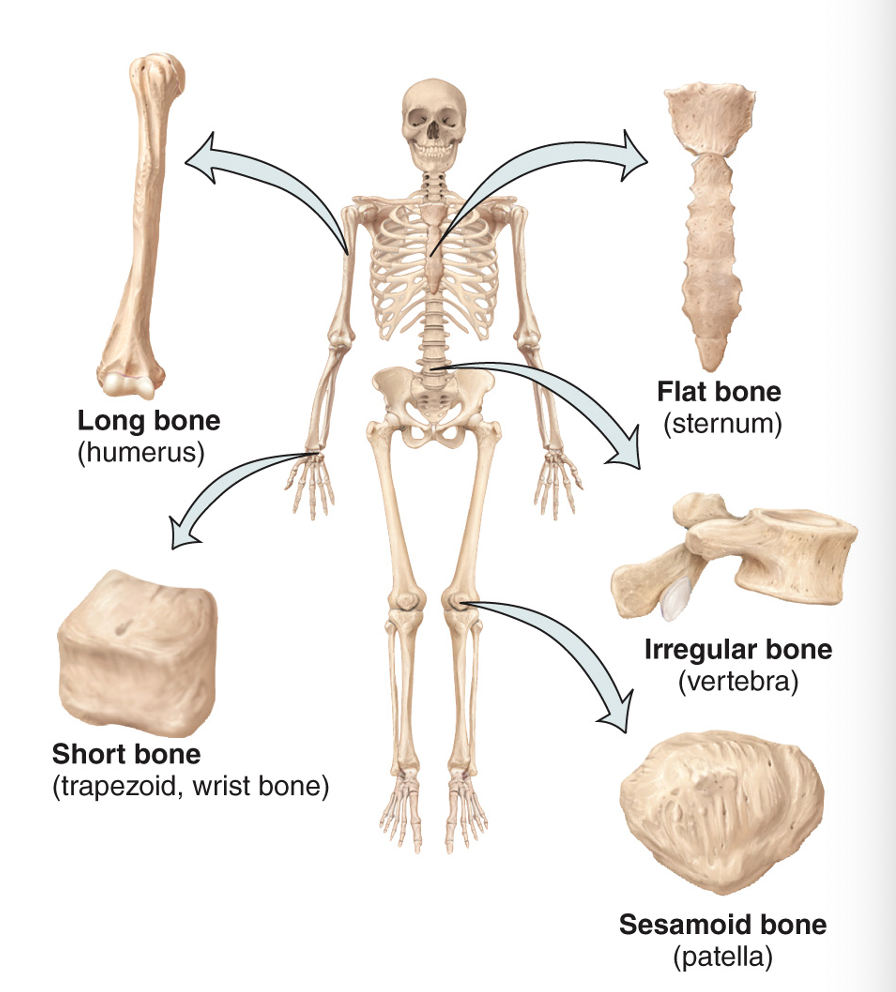
5 classifications of bones
long (greater length than width, i.e. humerus), short (cube-shaped, i.e. trapezoid, wrist bone), flat (thin layers of parallel plates, i.e. sternum ), irregular (complex shapes, i.e. vertebra), sesamoid (shaped like a sesame seed, i.e patella)
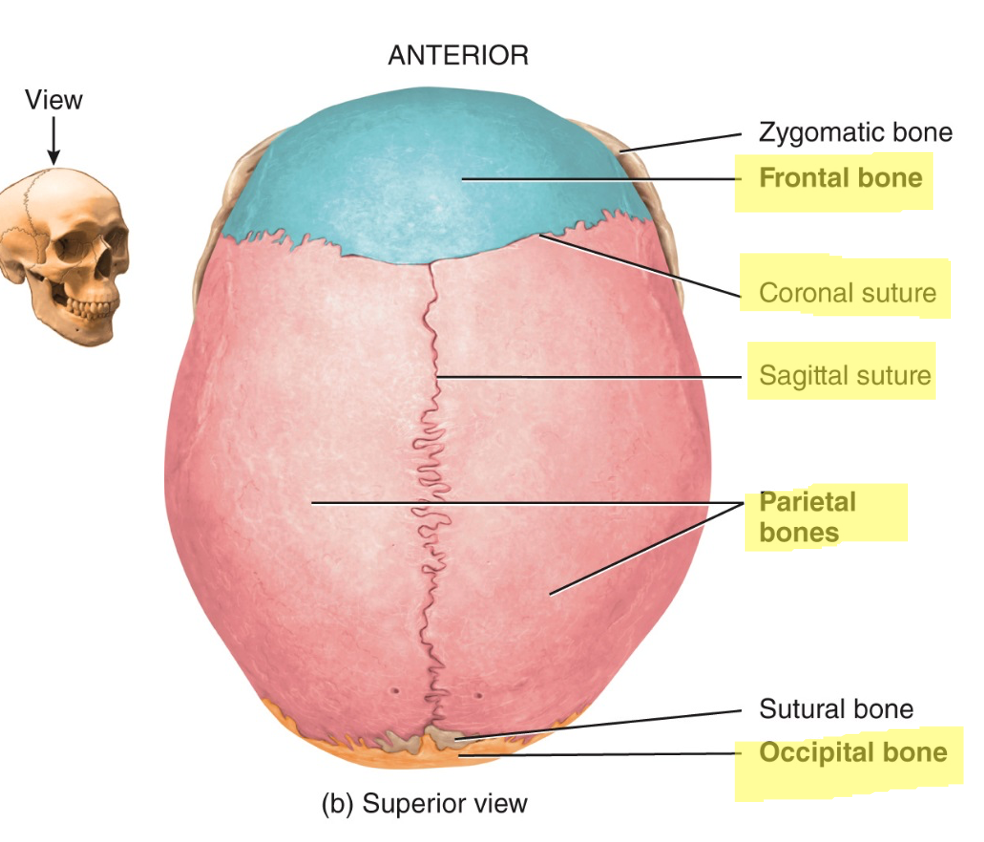
what are sutural bones and where are they found
small, extra bones plates located in the sutures (jointed areas where flat bones come together of cranial bones)
what are the 2 major types of surface markings
depressions and openings (foramen), and processes
what do depression and openings do
allow the passage of soft tissues and form joints
what are processes and what do they do
projections or outgrowths that form joints, and serve as attachment point for ligaments (attach bone to bone) and tendons (attach muscle to bone)
what is temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction
causes dull pain around the ear, tender jaw muscles, and clicking noise when opening/closing the mouth. caused by improperly aligned teeth, grinding of teeth, trauma to the head, arthritis, etc. treatment includes moist heat or ice, soft foods and pain relievers.
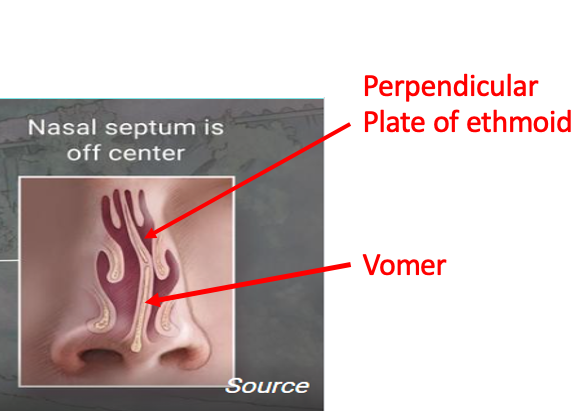
what is a deviated nasal septum
when the septum doesn’t run along the midline of the nasal cavity, caused by trauma to the nose or developmental abnormality. may lead to infection, inflammation, congestion, headaches, and nosebleeds and may require surgery to fix.
what is the mandible
lower jawbone; the largest and strongest facial bone. Only moveable skull bone other than the middle ear bones (auditory ossicles).
what passes through the carotid canal
internal carotid artery, sympathetic nerves for eyes.
what passes through the jugular
internal jugular vein
what passes through the magnum and where is it found
medulla oblongata and its membranes (meninges), accessory (XI) nerve, vertebral and spinal arteries. found in the occipital bone
what passes through the mental and where is it located
mental (chin) nerves and vessels, inferior to second premolar tooth in mandible.
what passes through the cribriform and where is it found
olfactory (I) nerve; cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
4 types of sutures in the skull
coronal, sagittal, lambdoid, and squamous
paranasal sinuses function and location
used as resonating chambers to enhance the voice, increase the SA of the nasal mucosa, and help to moisten it. If inflamed -- usually because of an allergic reaction or an infection -- they swell, make more mucus, and the channels that drain them can get blocked. The build-up of pressure in your sinuses causes pain that feels like a headache.
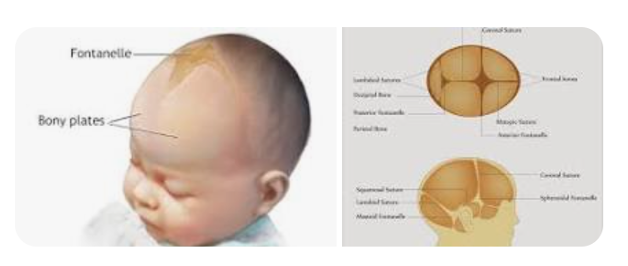
what are fontanels
two major soft spots on top of the head between the bones of the skull where bone formation isn’t complete
hyoid bone function
supports the tongue and provides an attachment site for some muscles in the neck and pharynx; does not articulate with any other bone
what is the vertebral column
also known as the spinal column, backbone, or spine, composed of 26 vertebrae divided into 5 regions, protects the spinal cord. each vertebrae have unique structures that help to identify which type they are in addition to common structures.
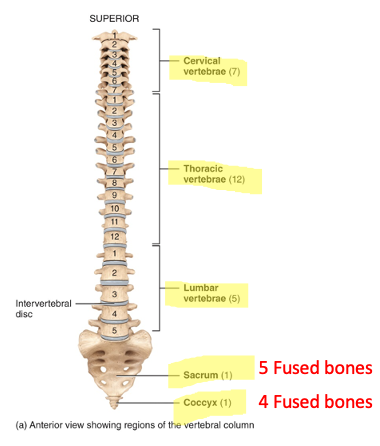
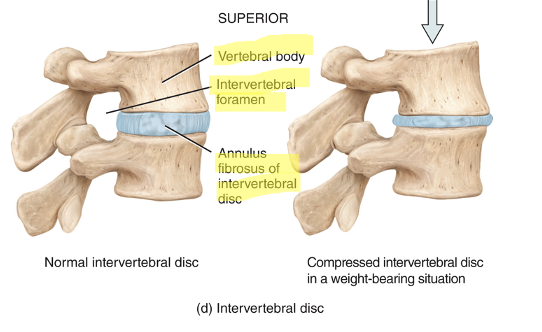
intervertebral discs location and function
between the bodies of the vertebrae from the second cervical to the sacrum; absorb shock and separate the vertebrae from one another
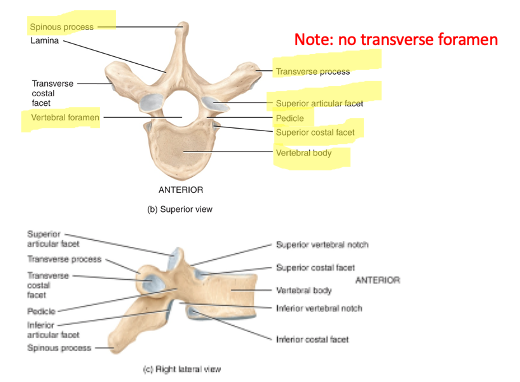
thoracic vertebrae function
Support the ribs and have special structures for rib head and tubercle attachment. no transverse foramen unlike cervical vertebrae
what is lumbar vertebrae
largest and strongest vertebrae, no special structures specifically associated with them
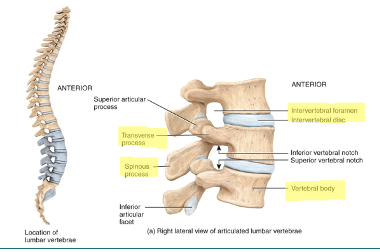
cervical vs thoracic vs lumbar vertebrae
cervical - small, one vertebral and two transverse, bifid spinous process
thoracic - larger, one vertebral, costal facets present for rib attachment
lumbar - largest, one vertebral
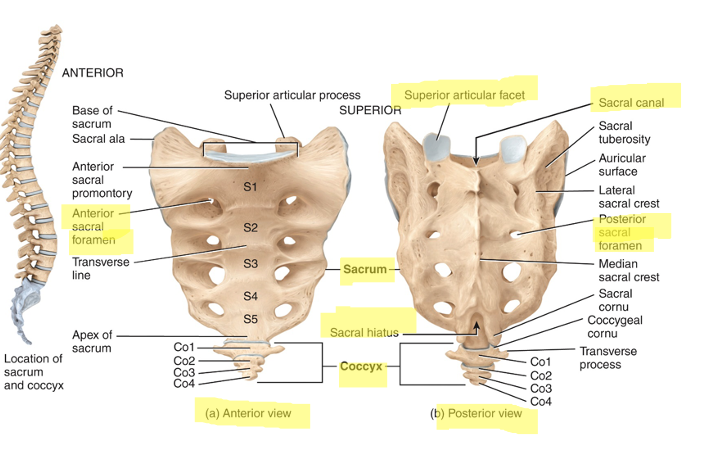
what are sacrum and coccyx
the sacrum is part of the pelvic girdle and is composed of 5 fused vertebrae
coccyx is smaller and composed of 4 fused vertebrae. both triangular shaped.
what is the thorax
entire chest region composed of sternum, ribs and costal cartilages
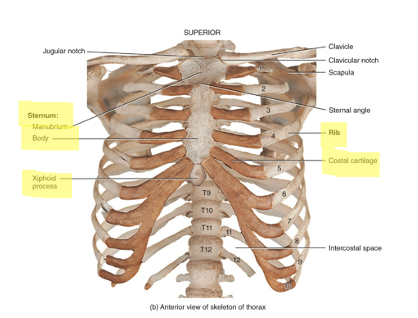
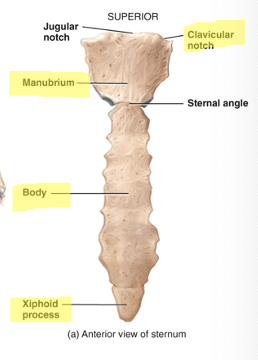
what is the sternum
articulates with the clavicles and the costal cartilages (attaches to ribs)
3 segments: the upper manubrium, the middle body, and the lower xiphoid process
ribs function
provide structural support to the thoracic cavity
12 pairs:
true (vertebosternal) ribs - first 7 pairs; their cartilage is directly connected to the sternum
false (vertebrochondral) ribs - next 5 pairs; cartilage is indirectly connected to the sternum
floating (vertebral) ribs - last 2 pairs; these are not connected to the sternum
disorders of the skeleton
herniated disc - may occur due to trauma or aging
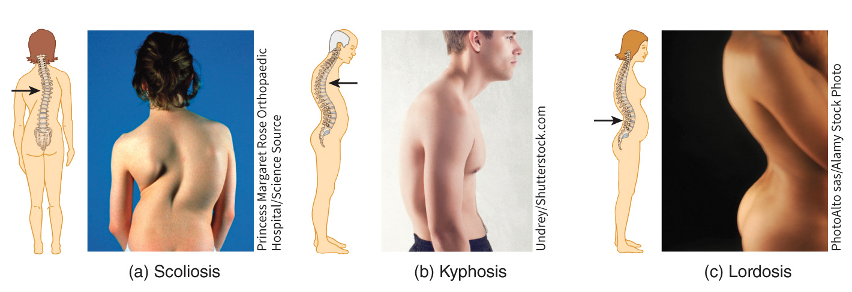
curve in the spinal column may become exaggerated
scoliosis (increased lateral curvature)
kyphosis (increased thoracic curve - bent forward)
lordosis (increased lumbar curve - bent backward)
Spina bifida
congenital defect of the vertebral column where the laminae do not develop normally. the degrees of this deformity vary from minor (spina bifida occulta) to severe (spina bifida with meningomyelocele).
When the neural tube [spine during early development] doesn't close all the way- vertebrae that protect the spinal cord do not form and close as they should.
vertebral column fractures are:
most commonly occur at C1, C2, C4-T, and T12-L2, and can result in spinal cord or nerve damage
purpose of appendicular skeleton
body movements; as “appendages” to the central skeleton and include the bones in the limbs and the girdles that attach them to the axial skeleton
pectoral (shoulder) girdle is
a clavicle (collar bone) and a scapula (shoulder blades)
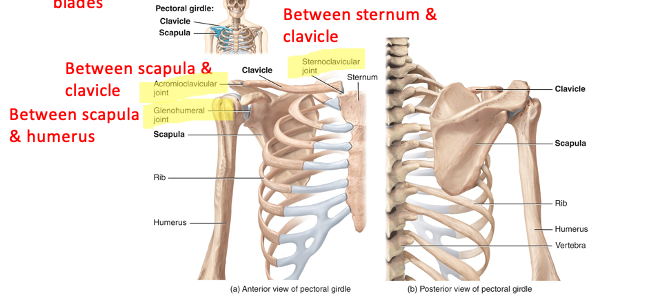
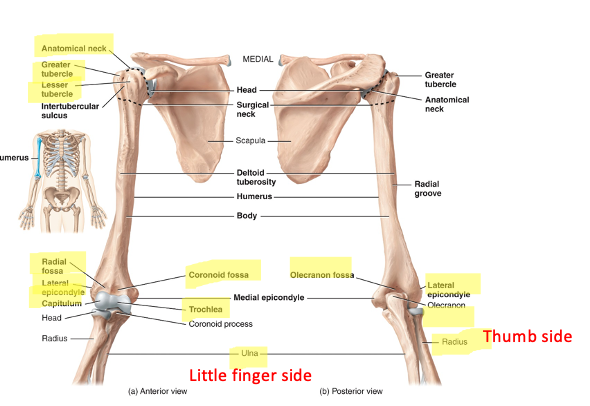
what does the humerus (arm bone) articulate with
articulates with the scapula proximally (its rounded head fits into the glenoid cavity) and with the radius and ulna distally (the trochlea articulates with the ulna and the capitulum with the radius)
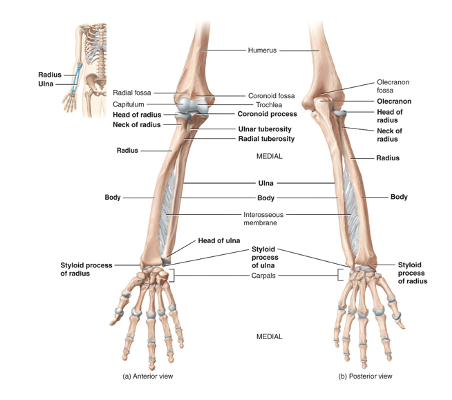
ulna and radius location
The olecranon and coronoid process at the proximal end of the ulna form the trochlear notch which wraps around the trochlea of the humerus making up the elbow joint. The radius is located on the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm. The articulation of its head with the capitulum of the humerus and with the ulna allows the forearm to rotate
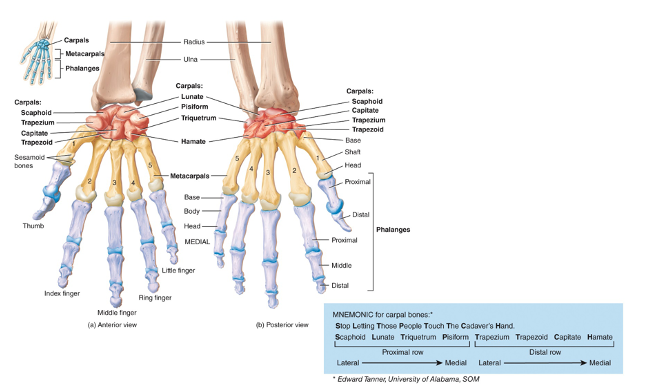
what are carpal bones
8 small bones connected to each other by ligaments; 2 rows
the proximal row (articulates with the distal radius and ulna)
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform
the distal row (articulates with the metacarpals)
trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
what are the five metacarpals
make up the palm and back of the hand, numbered I - V starting with the thumb. Bases articulate with the distal carpals while their heads articulate with the proximal phalanges
what are the phalanges
bones of the digits; 14 total (2 in the thumb, three in the other 4 fingers)
what is pelvic girdle made up of
of two hip bones (os coxa, coxal bones) that articulate with the sacrum posteriorly. Each hip bone is actually made up of three individual bones: ilium, ischium, pubis
The two bones articulate anteriorly at the pubic bones (pubic symphysis). There is a disc of fibrocartilage between the two bones
in the pelvic girdle, what does the femur articulate with
the acetabulum of the hip bone as a ball and socket joint, which is composed of parts of all three of the bones that make up the hip bone
what divides the pelvis into superior and inferior portions
pelvic brim, which is where the abdomen meets the pelvic cavity.
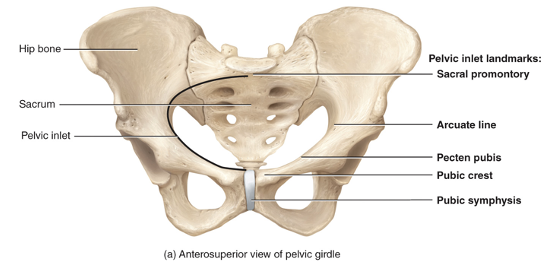
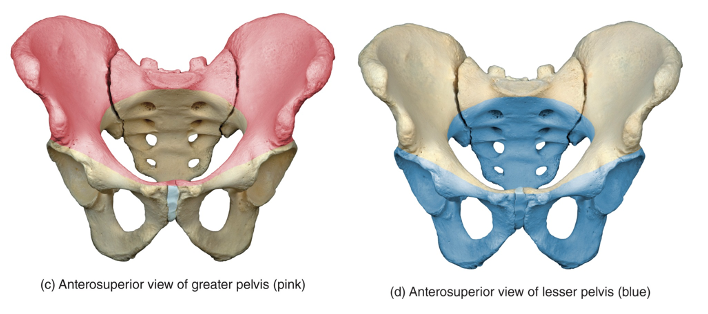
false (greater) pelvis is
The area of the bony pelvis superior to the pelvic brim
true (lesser) pelvis is
The area of the bony pelvis inferior to the pelvic brim
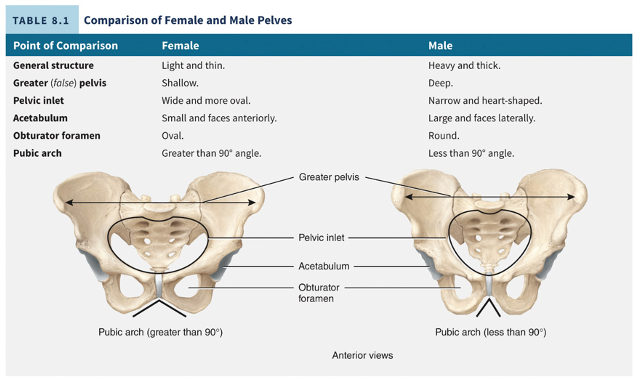
male vs female pelves
male bones are larger and heavier, female pelvis is wider and shallower to meet the requirements of pregnancy and childbirth
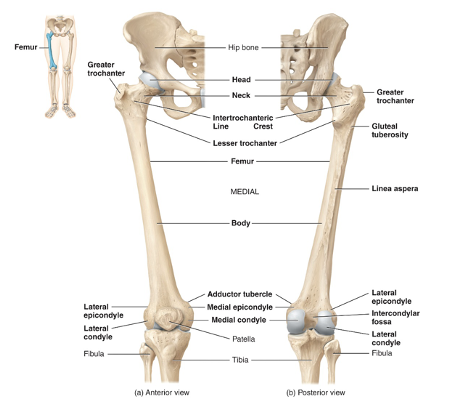
femur location
The proximal end (head) inserts into the acetabulum of the hip bone and the distal end articulates with the tibia and patella. longest, heaviest and strongest bone in the body
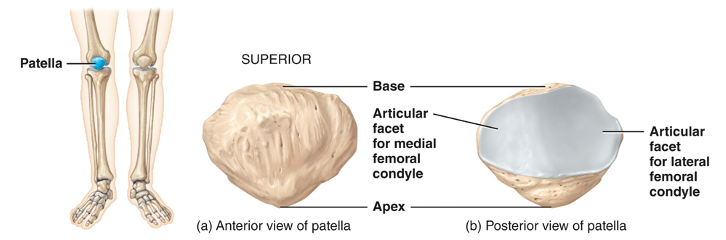
what is the patella
a triangular bone that develops in the quadriceps tendon. Its posterior surface articulates with the femur
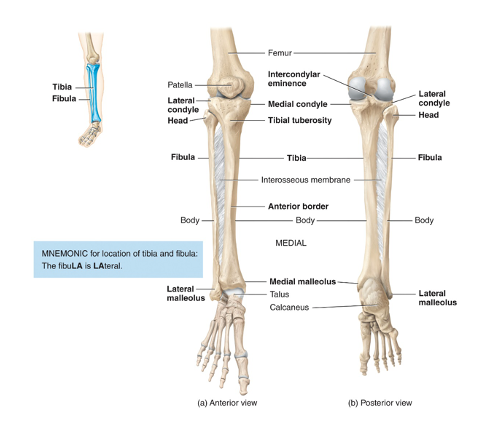
where is the tibia
lower leg, The tibia’s proximal end articulates with the femur
The tibia’s distal end articulates with the talus bone of the ankle
The tibial tuberosity on the anterior surface is the point of attachment for the patellar ligament
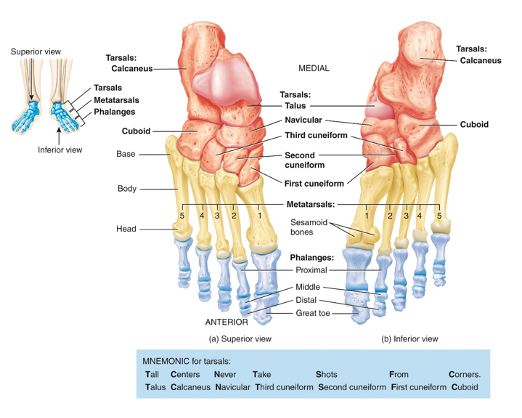
what is the tarsus composed of
7 tarsal bones: the talus, calcaneus, navicular, 3 cuneiforms and the cuboid
what is the metatarsus composed of
5 metatarsal bones and like the metacarpals, they are numbered I through V (1–5) starting with the big toe
make up the sole and dorsal surface of the foot
proximal ends articulate with the 3 cuneiform bones and the cuboid
distal ends articulate with the proximal phalanges
how are the phalanges in the lower limbs arranged
exactly like those of the hand
The big toe has a proximal and distal phalanx and the other toes have a proximal, middle and distal phalanx
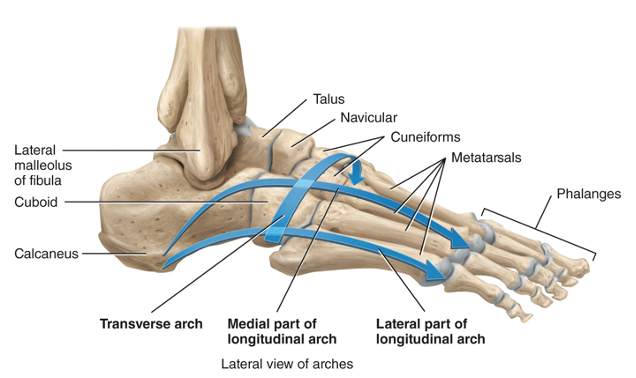
what are the two arches of the foot and what do they do
1) the longitudinal arch which is made up of a medial and a lateral portion and 2) the transverse arch. They allow the foot to support the weight of the body, provide leverage while walking, and distribute the body’s weight over the foot. They are supported by ligaments and tendons.
where does skeletal tissue arise from
mesoderm (the middle primary germ layer in embryos) but most of the skull arises from the ectoderm (the outer layer)
what are the 2 ways skull bones develop
The cartilaginous neurocranium (hyaline cartilage) undergoes endochondral ossification
The membranous neurocranium undergoes intramembranous ossification
where do face bones form
The cartilaginous viscerocranium comes from the cartilage of the pharyngeal arches and this forms the ear bones and hyoid bone
The membranous viscerocranium comes from the mesenchyme of the first pharyngeal arch, undergoes intramembranous ossification, and forms the facial bones
what is the skeleton of the limb girdles and limbs is derived from
the mesoderm
when does most of limb formation occur
week 4- week 8 after fertilization
what is a joint
point of contact between
two or more bones
cartilage and bone
teeth and bone
also called articulation or arthrosis
how are joints classified strructurally
3 classifications:
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
Fibrous joints are characterized by
a lack of synovial cavity
Articulating bones are held together with dense fibrous connective tissue
Permit little or no movement
2 types: Sutures (i.e. in skull) and syndesmoses (i.e. between tibia and fibula)
cartilaginous joints are characterized by
a lack of synovial cavity,
articulating bones held together with cartilage and connective tissue
permit little to no movement
2 types: synchondroses (i.e. between manubrium and first rib) and symphyses (i.e. pubic symphysis)
synovial joints are characterized by
a synovial cavity
Articulating bones are covered with articular cartilage, held together by ligaments, contain synovial fluid, have a nerve and blood supply, and are surrounded by an articular capsule
permit a large range of movement
what are bursae and tendon sheaths
Bursae – sac-like structures filled with synovial fluid that cushion movement of one body part over another
Tendon sheaths – tube-like bursae that wrap around tendons subject to a great deal of friction
found at many synovial joints
adduction vs abduction
moving towards the midline of the body vs moving away from midline of body
what are the 6 factors that affect contact and range of motion at synovial joints
Structure and shape of the articulating bones
Strength and tension of the joint ligaments
Arrangement and tension of the muscles
Contact of soft parts
Hormones
Disuse