MCAT FL1 Missed
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the laws of thermodynamics?
-0th: two systems in equilibrium w/ third system are in thermal equilibrium
-1st: conservation of energy
-2nd: entropy of an isolated system always in increases
-3rd: entropy of a system approaches a constant as temp approaches abs zero
What is the equation for pressure and gauge pressure?
-in a fluid: Patm +pgh
-P=pgh
-gauge= Pabs - Patm
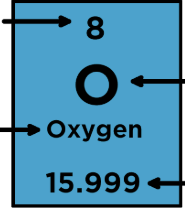
Name the element components
-8 = atomic number, # of protons
-O = abbreviation for element
-oxygen = name of element
-15.99 = atomic weight, weight of one mole of the substance
What is the principle of a photon?
-a photon is emitted if an electron moves from higher to lower energy level
-frequency proportional to energy is f= E/h
What is the equation of continuity?
A1V1 = A2V2
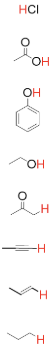
Name list of functional groups from weak acid → strong acid
-alkane, alkene, alkyne, ketone, alcohol, phenol, carboxylic acid, hydrochloric acid
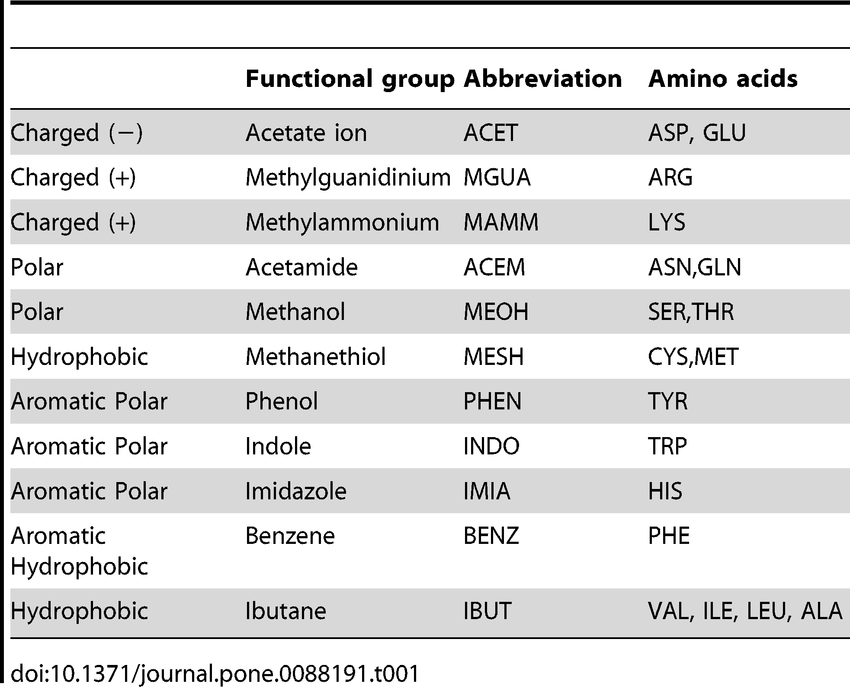
What are functional groups on AA?
What is the ideal gas law? Draw mnemonic to remember gas laws
-PV=nRT
-Can These Guys Possibly Be Victorious
Equations for capacitors
C = Q/V
U= ½ CV²
What is the equation for frequency in terms of wavelength and speed of light?
f= c/lambda
What are similarities that prokaryotes and eukaryotes have?
-contain DNA
-contain ribosomes
-have cell membrane
-have cytoplasm
What is the isoelectric point? What is the cation/anion ratio at pI?
-where an AA at the pH has no net charge (0)
-ratio is 1 at pI
What is an ionophore?
-class of compounds that form complexes with specific ions and facilitate their transport across cell membranes

Which cells secrete glucagon and insulin, respectively?
-alpha cells and beta cells, respetively
What are types of genetic info transfer in viruses/bacterial cells?
-transformation: genetic info from environment
-transduction: via a virus or viral vector
-conjugation: direct transfer from one bacterium to another
-transfection: only eukaryotes, foreign DNA through non-viral methods
Why are DNA motifs highly conserved?
-Because its essential to the organism’s survival
What is the change in intrathoracic pressure and action of the diaphragm during inhalation?
-decrease in pressure and diaphragm contracts
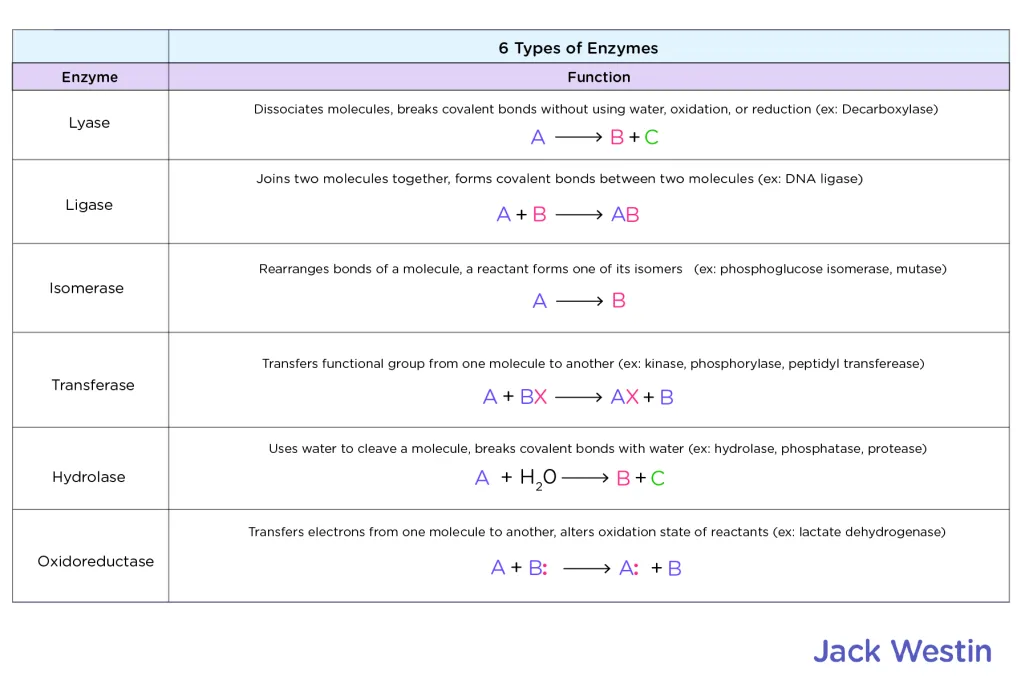
Types of enzymes
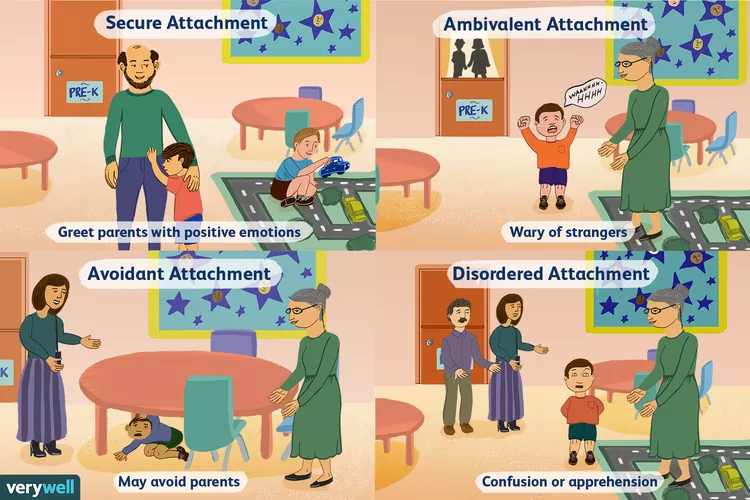
What are characteristics of the different attachment styles?
-secure: moderate distress, happy when CG back
-avoidant: apathy in both situations
-ambivalent: intense distress, apathy or not soothes with CG
-disorganized: disorientation, reject and/or approach CG

What are defense mechanisms
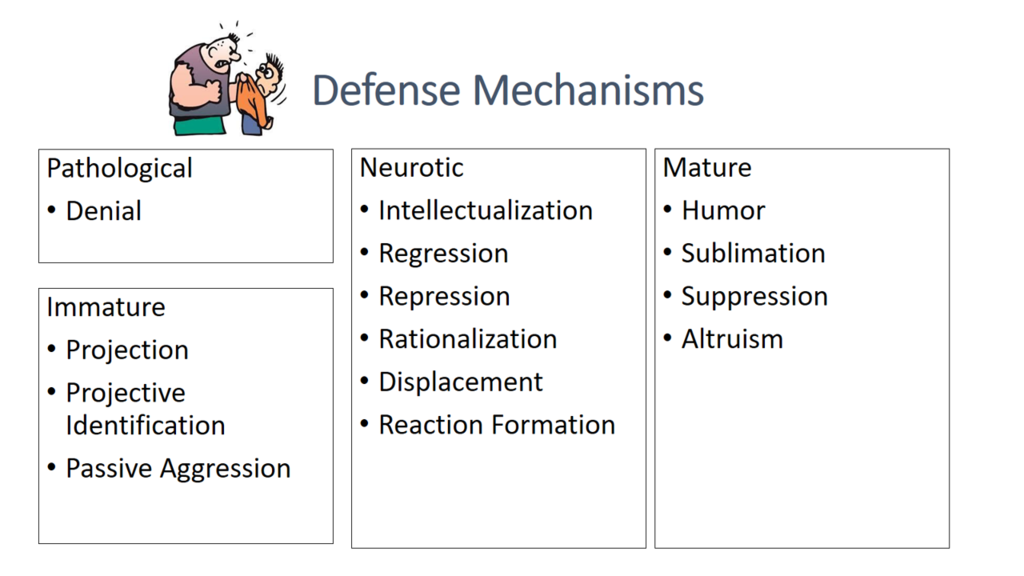
What are Erikson’s stages?
TAG in recess is so dope.
Trust vs mistrust
Autonomy vs shame
Guilt vs Initiative
Inferiority vs Industry
Role confusion vs Identity
Isolation vs Intimacy
Stagnation vs Generativity
Despair vs Integrity
What are the components of Psychodynamic theory?
-id: “pleasure” principle, instinct, unconscious
-superego: “moral” principle
-ego: “reality” principle, mediator between ID and superego
Race vs Ethnicity. What is racialization and racial formation?
-race is social construct
-ethnicity: harder to define but based on commonality
-racialization: assigning a behaviour or characteristics to a minority group by a majority group
-racial formation: theory that explores how racial groups identify form and changes over time due to different events
What is the fundamental attribution error?
-explains only the behavior/attributes of OTHER people
-When someone is successful, you attribute it to their environment
-When they fail, you blame it on their dispositional qualities
What is social facilitation?
-individual’s performance improves in the presence of others
What is weber’s law?
-the amount of change necessary to be noticed is related to the intensity of the original stimulus
What is the life course approach?
-aging viewed holistically in terms of social, biological, cultural, & psychological contexts
What is the differential association theory?
-criminal behaviour is learned when you associate with other people who indulge in criminal behaviour
How does response acquisition speed and likeliness of extinction differ between partial and continuous reinforcement?
-partial: slow to acquire but more resistant to extinction
-continuous: quick to acquire & less resistant to extinction
What is scapegoating?
-refers to erroneously assigning blame to an identifiable source, often when the real cause is abstract, such as globalization
What are the different types of memory
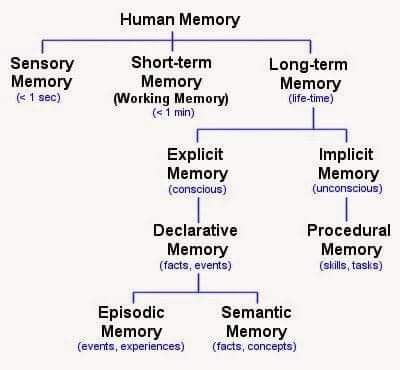
What is neural plasticity?
-refers to the ability of the nervous system to modify itself, functionally and structurally, in response to experience or injury
What is the Five Factor Model of Personality?
-OCEAN

What are hypothetical, conceptual, thematic, and operation definitions?
-hypothetical: a hypothesis
-conceptual: researcher describes social dynamics related to a concept
-thematic: a research theme refers to the larger area of research for a study (The WHAT)
-how n abstract concept as a variable is observed through different measurements (the HOW)
Difference between depolarization and hyperpolarization
-when membrane potential decreases from resting, its hyperpolarizes
-when membrane potential increasing from resting, it depolarizes