9_3 Data representation flashcards
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is a bit?
1 bit is a unit of information, represented by the binary value 0 or 1.
How many bits in a byte?
8
How many bytes in a kB?
1000
How many kB in a MB?
1000
How many MB in a GB?
1000
How many GB in a TB?
1000
Convert 102 to binary:
01100110
Convert 00100100 to decimal:
68
What is 00110011 + 00110001?
01100100
What is 00010010 + 00010001 + 01100010?
10000101
Shift 11001100 TWO places right:
00110011
Shift 00000111 FOUR places left:
01110000
Why is hexadecimal used?
It represents every 4 bits as a single digit, which is easier for humans to remember and understand.
Convert 11011100 to hex:
DC
Convert 77 to hex:
4D
Convert E4 to binary:
11100100
Convert 17 into decimal:
23
What is ASCII?
American Standard Code for Information Interchange - a character set that uses 7 bits to represent characters
What is extended ASCII?
Same thing, but uses 8 bits, allowing more characters to be encoded.
What is Unicode?
Unicode was created to solve the issue that: ASCII still didn’t have enough characters to encode symbols or characters from other languages.
it uses 8 - 32 bits per character
the first 128 Unicode codes (0-127) are the same as ASCII so backwards compatible
What is colour depth?
Number of bits per pixel
What is the minimum colour depth for an image with 4 colours?
2 bits required - (convert the number of colours to a power of 2.)
e.g 4 = 22 so 2 bits needed
What happens if the colour depth is increased?
If colour depth is increased, more bits are used to represent each pixel, so overall file size will increase.
What is meant by ‘resolution’?
Number of pixels in a specific area
What is a pixel?
A square of colour represented by binary
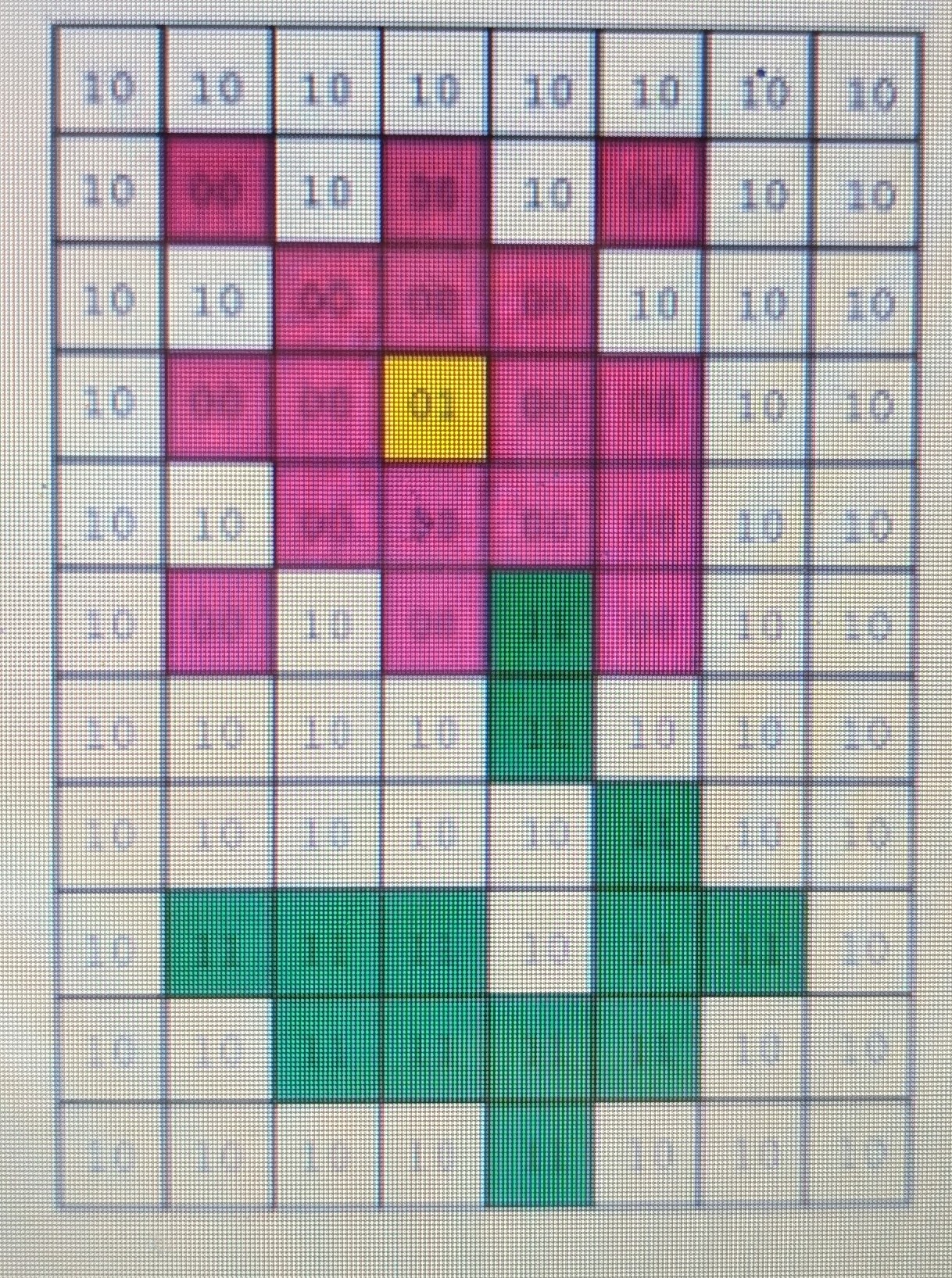
Make an image file for this bitmap image:
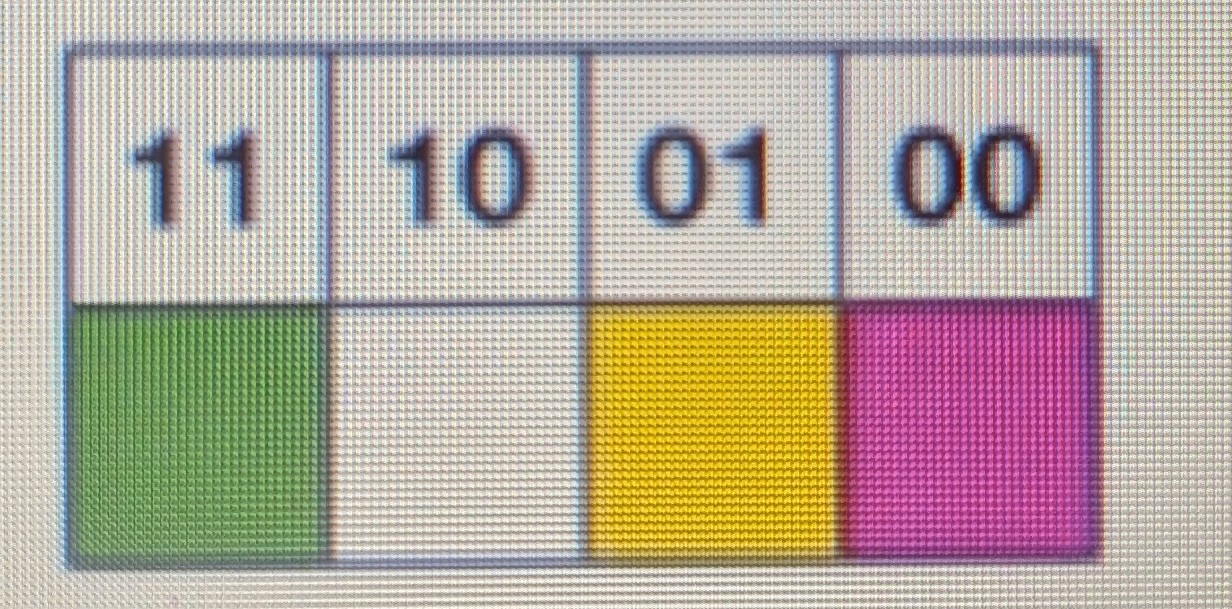
How do you calculate file size?
Size in bits = image width x image height x colour depth
How is sound stored on a computer?
Sound waves are analogue, so continuously changing.
To store on a computer, the waves need to be converted into a numerical representation, using an ADC (Analogue-to-Digital Converter).
Analogue sound is received by a microphone
This is converted into an electrical analogue signal
The signal amplitude (height of wave) is measured at regular intervals (sampled)
The values are rounded to a level (quantisation)
The values are stored as a series of binary numbers
What is a sample?
A sample is a measure of amplitude at a point in time
What is the sample resolution?
The sample resolution is the number of bits used to store each sample.
What is the sample rate?
The sample rate is the frequency with which you record the amplitude of the sound. i.e number of samples per second.
The more frequently the sound is sampled, the better the quality and smoother the playback will sound.
How does size/resolution affect the file size?
The greater size increases the file size, but the resolution does not affect the file size.
How do you calculate a sound file size, in bytes?
file size = sample rate (Hz) x sample resolution (bytes) x length of track (seconds)
What is the file size of a: 2 minute track with a sample rate of 10,000Hz, and a sample resolution of 16 bits?
120 × 10 000 × 2 = 2,400,000 bytes
Why would we compress data?
to make file size smaller
uses less storage space
quicker to send/email/download/upload
more usable
What are the 2 types of compression?
Lossy - original data cannot be recovered - cannot be reversed
Lossless - original data can be fully recovered - can be reversed
What is RLE (Run Length Encoding)?
RLE - simple form of lossless data compression, where runs of data are stored using frequency/data pairs.
however, is not so useful with files that don’t have many runs, and can increase the file size. It’s better on simple images, like icons, where many pixels are the same colour.
What is Huffman Coding?
Huffman Coding is a compression technique used to reduce the number of bits to represent each letter. The more frequently a letter appears in the text, the fewer bits are used to represent it in a text file.
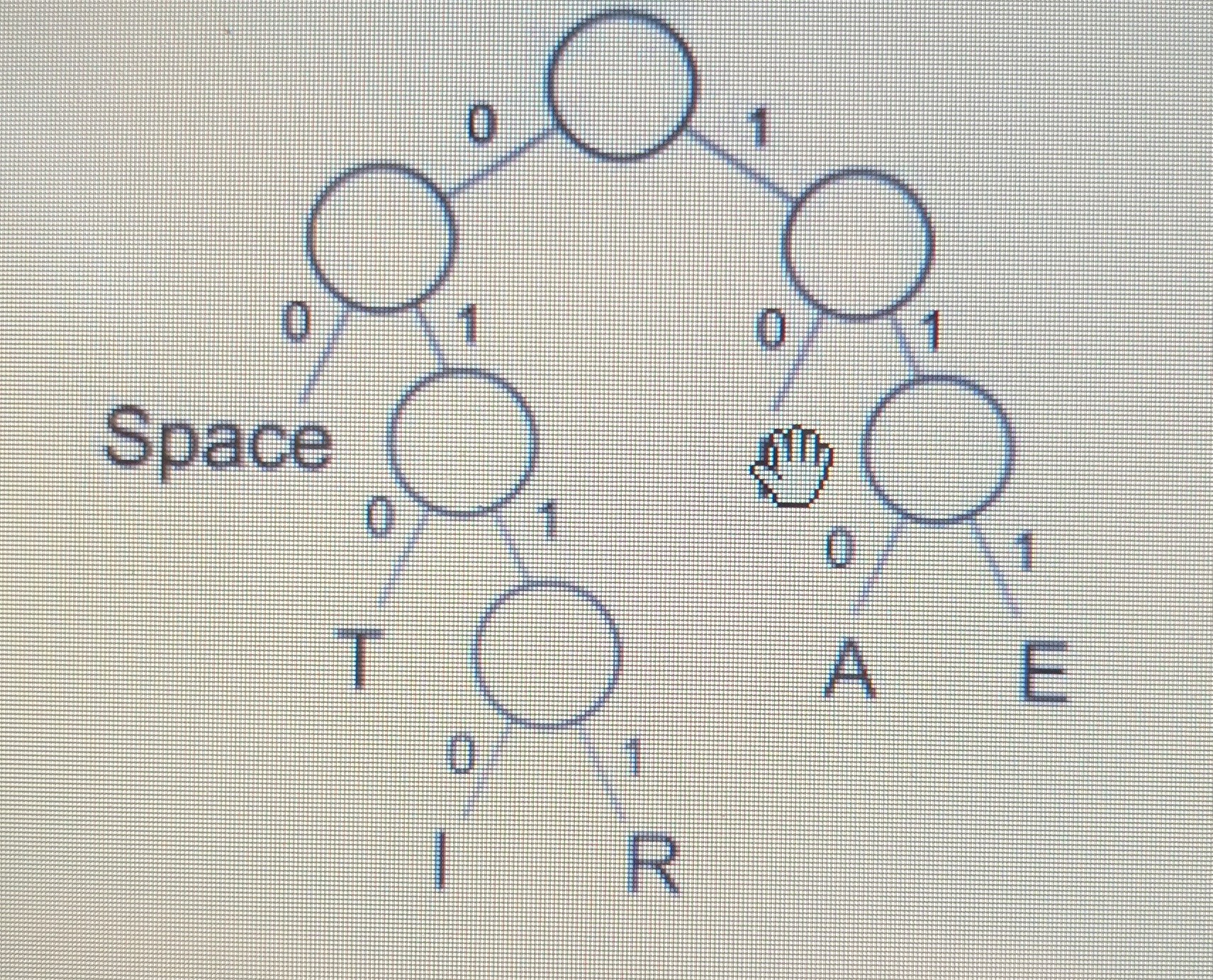
Using:
a) What would be the coding for the word PIT?
b) How many bits would these 3 letters take using the Huffman Code?
c) The sentence: PIPPA ATE A PEPPER uses 47 bits. How many bits would be needed if using ASCII?
d) How many bits are saved by compressing PIT with Huffman Coding?
a) 100110010
b) 9
c) 126
d) 12