Ionic Compounds
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Ionic bonds form between
metals and nonmetals
ionic bonds form when electrons
transfer
monoatomic ions
single atom with a charge (+ or -)
cations are (+ or -)
positive
cations (gain/lose) electrons
lose
cations are (metals/nonmetals)
metals
anions are (+/-)
negative
anions (gain/lose) electrons
gain
anions are (metals/nonmetals)
nonmetals
have varying charges
transition metals
mixture of metals
alloy
binary compound
2 elements; metal and nonmetal
polyatomic ion
usual anion with more than one element; end in -ate or -ite
electrons found in the outer shell/highest energy level
valence electrons
How does an element achieve an octet?
has 8 valence electrons
Anions ______________ electrons to reach the octet
gain
Cations ______________ electrons to reach the octet
lose
What characteristics do ionic compounds have?
High melting point, high boiling point
Crystal lattice structure
Brittle, solid
Conduct electricity and heat in a molten or liquid state or aqueous (dissolved in water)
What is a metallic bond made up of?
Cations and delocalized electrons
How do metallic bonds work?
Cations are swarmed with delocalized electrons swimming around them
What are the properties of metals?
High melting point and boiling point
Malleable, durable, ductile, luster (SHINY)
What is this a picture of?
electron sea model
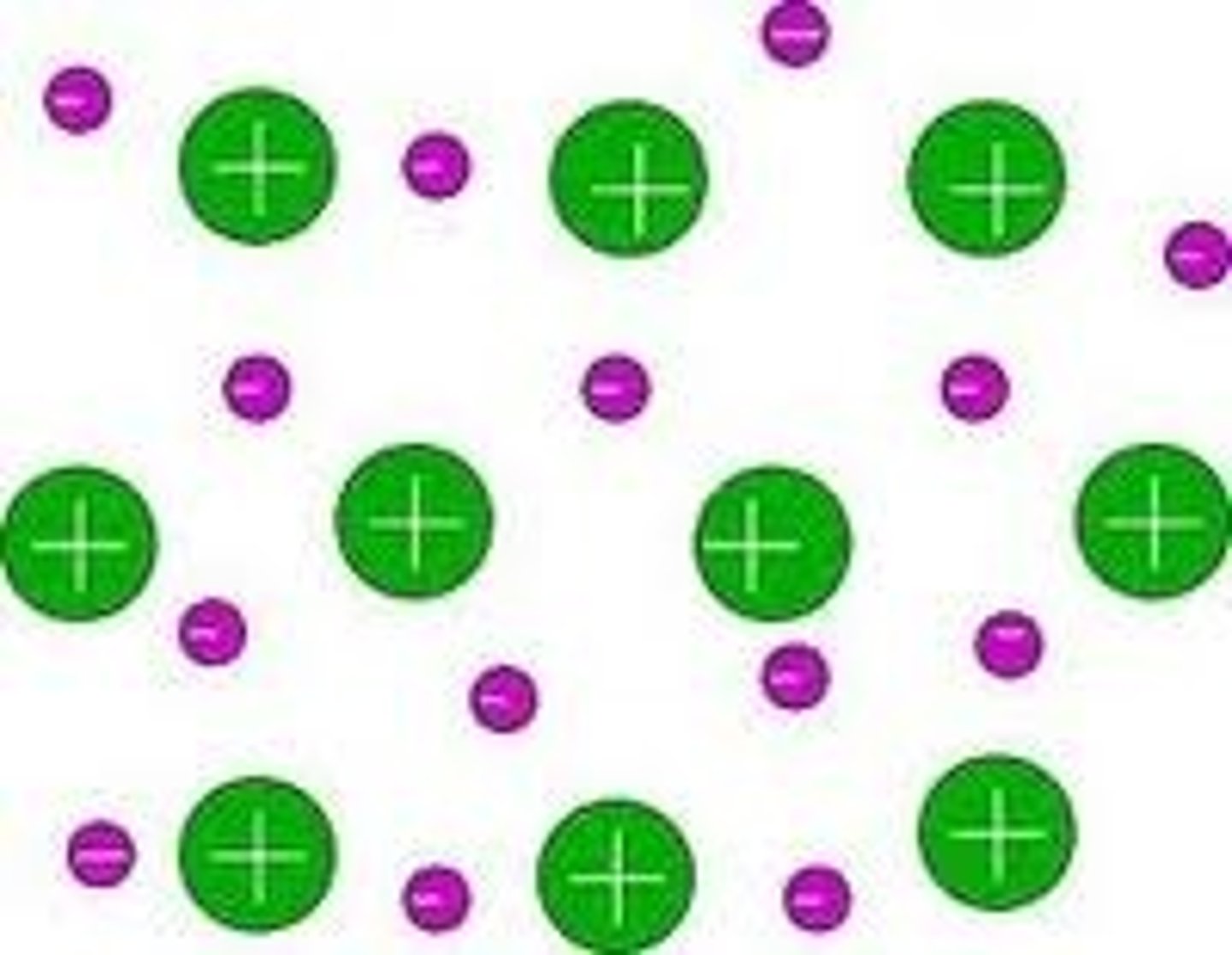
How does the electron sea model work?
cation don't move, valence electrons are swarming all over the place and not attached to a specific cation; allows for current to flow
How do you have a harder metal?
more delocalized electrons in the electron sea model
What is a chemical bond?
a force of attraction between two atoms
Are compounds neutral or charged?
neutral
Why do elements want to reach an octet?
stability
charge on group 1
+1
charge on group 2
+2
charge on group 13
+3
charge on group 3-12
varies - look at the back of the PT
charge on group 14
+/-4
charge on group 15
-3
charge on group 16
-2
charge on group 17
-1
charge on group 18
0
The number of electrons that a cation loses is (equal/less/more) than the number of electrons the anion gains?
equal
MgBr2 ratio of atoms
1 Mg: 2 Br
What is a formula unit?
chemical formula for any ionic compound
When do you use Roman Numerals?
for transition metals
binary anions ending changes to
-ide
If you have a polyatomic can you change the subscript on it to "reduce"
NO!!!!!, SO4 is SO4
How do you know if a polyatomic is present?
More than two capital letters (3 if it is a compound)
What groups can peroxides be made with?
groups 1 and 2
What is lattice energy?
the energy required to completely separate a mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions
How can you determine which compound has greater lattice energy?
size of the atom (smaller = stronger= greater lattice energy) or difference in charges (greater charge difference = stronger = greater lattice energy)
What is an electrolyte?
a liquid containing free-moving ions which conducts electricity
What kind of electrolytes can you have?
non, weak, and strong based on the substance present (ionic is strongest)
The hardness and strength of metals is based on the number of electrons the metal contributed to the sea - Do more or less electrons make it stronger?
more
What does it mean to be malleable?
The ability to be hammered or rolled into thin sheets, a property of metals.
What does it mean to be ductile?
the ability to be stretched into a wire